Background: PKCδ signaling to mitochondria affects cellular apoptosis and metabolism.
Results: A structure-function study using FRET-based imaging reveals that PKCδ binds to and is active at mitochondria via multiple isozyme-specific determinants.
Conclusion: Determinants unique to PKCδ drive an interaction with mitochondria distinct from canonical PKC translocation to membranes.
Significance: Isozyme-specific interaction of PKCδ with mitochondria constitutes a novel recruitment mechanism and increases mitochondrial respiration.
Keywords: Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET), Mitochondria, Protein Domains, Protein Kinase C (PKC), Protein Phosphorylation, Protein Translocation, Signal Transduction
Abstract
PKCδ signaling to mitochondria has been implicated in both mitochondrial apoptosis and metabolism. However, the mechanism by which PKCδ interacts with mitochondria is not well understood. Using FRET-based imaging, we show that PKCδ interacts with mitochondria by a novel and isozyme-specific mechanism distinct from its canonical recruitment to other membranes such as the plasma membrane or Golgi. Specifically, we show that PKCδ interacts with mitochondria following stimulation with phorbol esters or, in L6 myocytes, with insulin via a mechanism that requires two steps. In the first step, PKCδ translocates acutely to mitochondria by a mechanism that requires its C1A and C1B domains and a Leu-Asn sequence in its turn motif. In the second step, PKCδ is retained at mitochondria by a mechanism that depends on its C2 domain, a unique Glu residue in its activation loop, intrinsic catalytic activity, and the mitochondrial membrane potential. In contrast, of these determinants, only the C1B domain is required for the phorbol ester-stimulated translocation of PKCδ to other membranes. PKCδ also basally localizes to mitochondria and increases mitochondrial respiration via many of the same determinants that promote its agonist-evoked interaction. PKCδ localized to mitochondria has robust activity, as revealed by a FRET reporter of PKCδ-specific activity (δCKAR). These data support a model in which multiple determinants unique to PKCδ drive a specific interaction with mitochondria that promotes mitochondrial respiration.
Introduction
PKC is a major family of serine/threonine kinases that plays crucial roles in cellular signal transduction, regulating diverse cellular behaviors such as survival, growth and proliferation, migration, and apoptosis (1–5). The ten full-length mammalian isozymes of the PKC family serve different biological roles and are regulated differently (1–5). These isozymes are classified as either conventional (α, the alternatively spliced βI and βII, and γ), novel (δ, ϵ, θ, η), or atypical (ζ, ι/λ) based on the nature of their N-terminal regulatory domains (1–5). Conventional and novel PKC isozymes possess tandem C1A and C1B regulatory modules that enable them to translocate to membranes in response to receptor-mediated generation of the lipid second messenger diacylglycerol (DAG)3 or in response to stimulation with phorbol esters, a class of tumor-promoting compounds that are potent functional DAG analogues. For conventional isozymes, translocation to membranes is also facilitated by a Ca2+-binding C2 regulatory module. The C2 domain of novel isozymes does not bind Ca2+ or directly enable translocation to membranes, but their C1B domain has a 100-fold higher affinity for DAG that compensates in membrane recruitment (6, 7). Additionally, the C2 domain of PKCδ serves as a phosphotyrosine protein-binding domain (8) and is itself tyrosine-phosphorylated at several key sites that drive nuclear localization of PKCδ (4, 9–11). Atypical isozymes are not regulated by either DAG or Ca2+ but do bind anionic phospholipids and bind other proteins via a PB1 domain. Constitutive phosphorylation at three conserved sites in the kinase domain of PKCs process them into a catalytically competent but inactive conformation (1–5, 12). These sites are the activation loop, phosphorylated by the upstream kinase phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1, and two C-terminal autophosphorylation sites: the turn motif and hydrophobic motif. The kinase complex mTORC2 promotes the priming phosphorylation of some PKC isozymes but not of PKCδ (13). The hallmark for PKC activation is its translocation to intracellular membranes, notably plasma membrane and Golgi, where second messenger- or phorbol ester-mediated engagement of its regulatory domains allosterically releases an autoinhibitory pseudosubstrate peptide sequence from its active site (1–5, 14).
PKCδ, a novel PKC isozyme ubiquitously expressed in mammalian tissues, has been implicated in both of the two main functions of mitochondria: mitochondrial apoptosis and metabolism. PKCδ knock-out mice exhibit various phenotypes, such as increased proliferation of B cells (15), exacerbated vein graft arteriosclerosis (16), and suppression of radiation-induced apoptosis in salivary parotid cells (17), that are consistent with a proapoptotic role for PKCδ. A large body of literature has addressed the role of PKCδ in apoptotic signaling to mitochondria, with cell fractionation and immunofluorescence experiments showing the activity-dependent translocation of PKCδ to mitochondria in a variety of cell lines upon induction of apoptosis (18–21). In particular, phorbol esters have been observed to induce the translocation of endogenous and exogenous PKCδ to mitochondria in multiple cell lines, with prolonged phorbol ester treatment leading to apoptosis (22, 23). PKCδ knock-out mice also exhibit cardiac phenotypes, which tend to show that PKCδ is cardioprotective (24, 25), and proteomic analysis of cardiac tissue from PKCδ knock-out mice shows changes in the levels of various metabolic proteins (24, 26). Importantly, PKCδ has been implicated in the regulation of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDHC), which controls the flux of fuel entering the citric acid cycle by converting pyruvate to acetyl CoA in the mitochondrial matrix, thereby regulating mitochondrial respiration. PKCδ does this either by activating the phosphatases that dephosphorylate and activate the PDHC in response to insulin in muscle and liver cells (27) or by indirectly inhibiting one of the kinases (PDH kinase 2) that phosphorylate and inactivate the PDHC in response to vitamin A in mouse embryonic fibroblasts (28–30). The precise mechanism by which PKCδ interacts with mitochondria remains to be established.
Here, we show that PKCδ binds to and is active at mitochondria by an isozyme-specific mechanism distinct from that driving the canonical PKC interaction with plasma membrane or Golgi. We examine signaling at mitochondria by visualizing and quantifying PKCδ translocation to, retention at, basal interactions with, and activity at mitochondria using FRET-based reporters in real time in live cells. We demonstrate that multiple determinants unique to PKCδ drive a highly specific interaction with mitochondria that promotes mitochondrial respiration.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Materials
Phorbol-12,13-dibutyrate (PDBu), Gö6976, Gö6983, bisindolylmaleimide (BisIV), and rottlerin were obtained from Calbiochem. 4-Amino-1-tert-butyl-3-(1′-naphthyl)-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine (NaPP1) was a generous gift from Dr. Kavita Shah. Insulin, oligomycin, carbonyl cyanide-4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenylhydrazone (FCCP), and Me2SO (as a solvent for drugs and as a vehicle control) were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich. The PKCδ phospho-activation loop, PKCδ/θ phospho-turn motif, and pan-PKC phospho-hydrophobic motif antibodies were purchased from Cell Signaling. The DsRed antibody, which recognizes the DsRed variant red fluorescent protein (RFP), and the GFP antibody, which recognizes the GFP variants cyan fluorescent protein (CFP) and yellow fluorescent protein (YFP), were obtained from Clontech.
Plasmids
All of the plasmids were constructed in the mammalian expression vector pcDNA3 (Invitrogen). Targeting of CFP and activity reporters to the outer membrane of mitochondria (Mito-CFP and Mito-δCKAR) was achieved by the addition of the sequence encoding the N-terminal 33 amino acids of TOM20 (translocase of the outer membrane 20) to the 5′ end of constructs (31–34). Targeting of CFP to Golgi (Golgi-CFP) was achieved by the addition of the sequence encoding the N-terminal 35 amino acids of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase to its 5′ end (31, 33). Targeting of CFP to the plasma membrane was achieved by the addition of the sequence encoding the N-terminal 7 amino acids of Lyn kinase to its 5′ end (31, 35). Full-length mouse PKCδ, rat PKCβII, and human PKCϵ and most of the PKCδ mutants were C-terminally YFP tagged (PKC-YFP) for the intermolecular FRET translocation assay. An N-terminally YFP-tagged mouse PKCδ (YFP-PKCδ) was also constructed and used to generate the PKCδE500G/D/Q and PKCδL636T/N637R kinase domain mutants. For PKCδΔC2, the first 126 residues were deleted. PKCδC2 consists of the first 88 residues of PKCδ. PKCδΔC1A, PKCδΔC1B, and PKCδΔC1AΔC1B were constructed by inserting KpnI restriction sites flanking the domain(s) of interest, digesting out the domain(s), and religating the plasmids. For PKCδΔC1A, residues His-159 to Cys-208 were deleted. For PKCδΔC1B, residues His-231 to Cys-280 were deleted. For PKCδΔC1AΔC1B, residues His-159 to Cys-280 were deleted. PKCδC1B consists of residues 225–281. PKCϵ(δC1B) consists of PKCϵ with its C1B domain (residues His-243 to Cys-292 on PKCϵ) replaced with the C1B domain of PKCδ (residues His-231 to Cys-280 on PKCδ). PKCδCF consists the C-terminal half of PKCδ beginning with residue Asn-328. PKCδRF/ϵCF consists of the N-terminal 327 residues of PKCδ fused directly to the C-terminal half of PKCϵ beginning with PKCϵ residue Ser-388. The PKCδE500G/D/Q, PKCδL636T/N637R, and PKCδM425A mutants were generated by site-directed mutagenesis following the QuikChange protocol (Stratagene). The C kinase activity reporter (CKAR) (31, 35, 36) and δCKAR (PKCδ-specific CKAR) (34) constructs have been described previously. The negative control Thr/Ala mutant of Mito-δCKAR (Mito-δCKART/A) was generated by site-directed mutagenesis following the QuikChange protocol. All of the constructs imaged in conjunction with the intramolecular FRET activity reporters were C-terminally RFP tagged.
Cell Culture and Transfection
COS-7 cells were cultured in DMEM (Cellgro) supplemented with 5% fetal bovine serum (HyClone or Invitrogen) and 1% penicillin/streptomycin (HyClone) at 37 °C in 5% CO2. COS-7 cells were transiently transfected using FuGENE 6 (Roche Applied Science) ∼24 h after the cells were plated. L6 myocytes were cultured in α-minimal essential medium (Invitrogen) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and 1% penicillin/streptomycin at 37 °C in 5% CO2. L6 myocytes were transiently transfected using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen) ∼24 h after the cells were plated.
Live Cell Fluorescence Imaging
The cells were plated onto sterilized glass coverslips in 35-mm imaging dishes and co-transfected with the indicated constructs to monitor either translocation via intermolecular FRET or activity via intramolecular FRET. Approximately 48 h post-transfection, the cells were washed twice with and subsequently imaged in Hanks' balanced salt solution (Cellgro) containing 1 mm CaCl2 in the dark at room temperature. For some experiments, the cells were pretreated with the specified drugs in Hanks' balanced salt solution for at least 20 min at 37 °C or as indicated. Otherwise, the indicated drugs were introduced during live cell imaging.
The images were acquired via a 100× objective on a Zeiss Axiovert microscope (Carl Zeiss Microimaging, Inc.) using a MicroMax digital camera (Roper-Princeton Instruments) controlled by MetaFluor software version 3.0 (Universal Imaging Corp.). Optical filters were obtained from Chroma Technologies. Time lapse images of CFP, FRET, YFP, and RFP were collected every 15 s through either a 10% or a 25% neutral density filter. CFP and FRET images were obtained through a 420/20-nm excitation filter, a 450-nm dichroic mirror, and either a 475/40-nm emission filter (CFP), or a 535/25-nm emission filter (FRET). YFP images monitored as a control for photobleaching were obtained through a 495/10-nm excitation filter, a 505-nm dichroic mirror, and a 535/25-nm emission filter. RFP images were obtained through a 560/25-nm excitation filter, a 593-nm dichroic mirror, and a 629/53-nm emission filter. Excitation and emission filters were switched in the filter wheel (Lambda 10-2; Sutter). Integration times were 200 ms for CFP and FRET and 100 ms for YFP and RFP.
For each cell imaged, a region encompassing the cellular organelle of interest was manually selected on the CFP image, and MetaFluor calculated a FRET ratio consisting of the average FRET/CFP emission ratio (for intermolecular FRET translocation reporters) or CFP/FRET emission ratio (for intramolecular FRET activity reporters) for this region. Base-line FRET ratios were acquired for 5 min before introduction of drugs, and the trace for each cell was slope-adjusted for any base-line drift (31) and normalized to the average base-line value. Throughout this paper, normalized FRET ratios are plotted as the means ± S.E. of data from the specified n number of cells (typically 10 cells/group) imaged over at least three and more typically five independent experiments.
The cells were stained with MitoTracker Deep Red (Invitrogen Molecular Probes) by being incubated with a 167 nm working solution of MitoTracker in prewarmed culture medium for 15 min at 37 °C and 15 min at room temperature before being washed and imaged in Hanks' balanced salt solution. The images were pseudocolored and overlaid to visualize co-localization using ImageJ.
Immunoblotting
COS-7 cells grown in 6-well dishes were collected for immunoblotting ∼24 h after transfection, when cells had grown to confluency. The cells were washed with ice-cold PBS; then lysed on ice in a buffer containing 1% Triton X-100, 50 mm Tris (pH 7.5), 10 mm Na4P2O7, 50 mm NaF, 100 mm NaCl, 5 mm EDTA, 2 mm benzamidine, 50 μg/ml leupeptin, 1 mm PMSF, and 1 mm sodium vanadate; and then cleared by centrifugation at 16,000 × g for 2.5 min. Detergent-solubilized lysates were separated on SDS-PAGE gels, transferred onto PVDF membranes, and probed using the indicated antibodies. The blots were visualized via chemiluminescence on a FluorChem imaging system (Alpha Innotech).
Analysis of Mitochondrial Respiration
COS-7 cells transfected with each of the indicated constructs were plated in quintuplicate at 40,000 cells/well in growth medium in an XF-96-well plate (Seahorse Bioscience) for each experiment. Approximately 24 h later, the medium was changed to unbuffered DMEM containing 10 mm glucose, 10 mm pyruvate, and 2 mm GlutaMAX (Invitrogen), and a Seahorse Extracellular Flux Analyzer XF96 (Seahorse Bioscience) was used to measure the oxygen consumption rate (OCR). Rates of basal, State 4 (in the presence of 2 μm oligomycin), and uncoupler-stimulated (in the presence of a titrated concentration of FCCP) respiration were assessed. The cumulative data over multiple experiments are presented as the means ± S.E. relative to the vector control group. The same cells were plated in parallel in 6-well dishes to monitor the rates of cell growth and collected for immunoblotting to confirm expression of the constructs.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using Prism 6 (GraphPad Software).
RESULTS
Intermolecular FRET Demonstrates that PKCδ Interacts with Mitochondria via an Isozyme-specific Mechanism
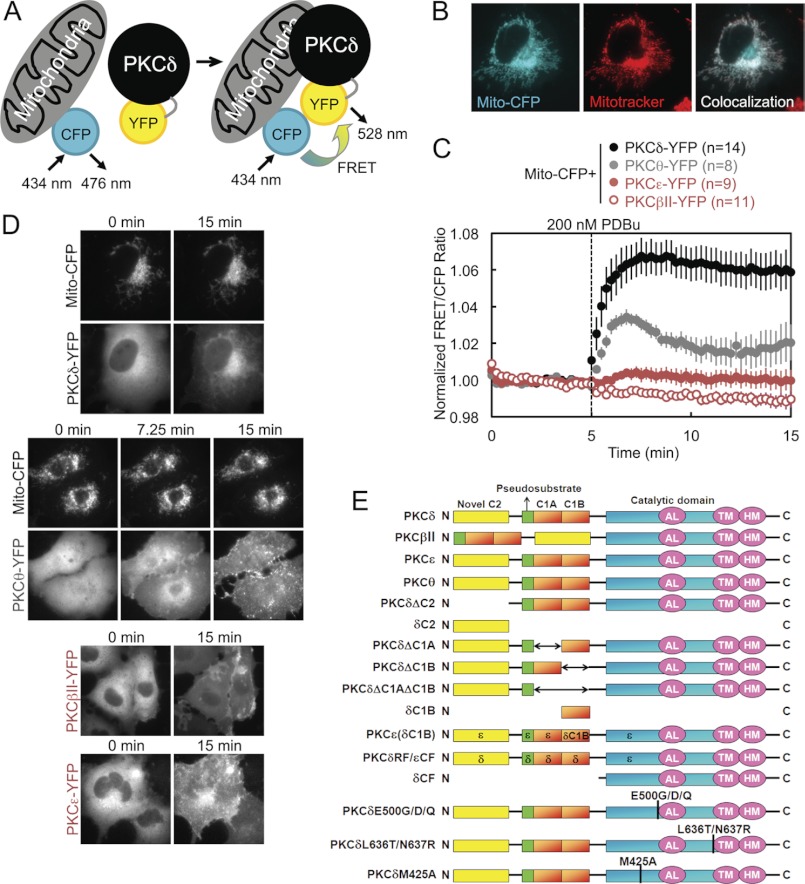
To investigate the possibility that PKC signals at and interacts directly with mitochondria, we employed an intermolecular FRET reporter assay to monitor in real time and in live cells the interactions between an energy donor CFP targeted to the outer membrane of mitochondria using a mitochondrial localization sequence (31–34) and a co-transfected energy acceptor YFP fused to PKC (Fig. 1A). An increase in the FRET signal upon stimulation indicated translocation by a particular PKC isozyme to mitochondria. Proper localization of CFP to mitochondria in COS-7 cells was confirmed by the strandlike appearance of CFP consistent with the appearance of mitochondria in healthy cells and by its co-localization with MitoTracker Deep Red (Fig. 1B). YFP-tagged PKC isozymes tended to be excluded from the nucleus but were otherwise basally localized diffusely throughout the cytoplasm, with a basal concentration of PKCδ in particular at Golgi (Fig. 1D). Acute activation of PKCs by stimulation with 200 nm of the phorbol ester PDBu induced all the PKCs to translocate rapidly to various intracellular membranes (Fig. 1D), but only PKCδ translocated to and was retained at mitochondria (Fig. 1, C, black, and D). This was both quantified by a robust real time increase in the FRET signal aggregated over many cells and multiple experiments (Fig. 1C) and corroborated in time lapse YFP images (Fig. 1D). Despite phorbol esters being potent PKC agonists that activate all conventional and novel PKC isozymes, this translocation by PKCδ to mitochondria proved to be an isozyme-specific phenomenon. PDBu did not induce a similar FRET response in either the conventional PKC isozyme PKCβII or the novel PKC isozyme PKCϵ (Fig. 1C, red), despite the fact that both these isozymes clearly responded to PDBu by translocating to other cellular membranes (Fig. 1D). The only other PKC isozyme that was observed to translocate to mitochondria was PKCθ, the PKC isozyme most closely related to PKCδ (37) but whose expression is much more limited (primarily to hematopoietic cells (38) and skeletal muscle (39)), which translocated to mitochondria at the same initial rate as PKCδ but was retained to a lesser degree (Fig. 1C, gray). These data reveal that PKCδ interacts with mitochondria via a unique mechanism distinct from the canonical C1-mediated binding to DAG or phorbol esters in the membrane.
FIGURE 1.
Intermolecular FRET demonstrates that PKCδ interacts with mitochondria via an isozyme-specific mechanism. A, diagram of intermolecular FRET translocation reporter, in which an increase in the FRET signal between mitochondrially targeted CFP and YFP-tagged PKC constructs indicates PKC translocation to mitochondria. B, pseudocolored images of a COS-7 cell transfected with mitochondrially targeted CFP (Mito-CFP) and stained using MitoTracker for mitochondria. Co-localization of CFP and MitoTracker is indicated in white. C, COS-7 cells co-transfected with Mito-CFP and the indicated YFP-tagged PKC isozyme were stimulated with 200 nm PDBu during FRET imaging, which induced a rapid and sustained increase in the FRET/CFP ratio from PKCδ, a transient increase from PKCθ, and no significant change from either PKCβII or PKCϵ. Throughout this paper, FRET ratios are plotted as the means ± S.E. of data from the specified n number of cells imaged over at least three independent experiments. D, representative CFP and YFP channel time lapse images of COS-7 cells co-transfected with Mito-CFP and the indicated YFP-labeled PKC constructs and monitored for FRET ratio changes in response to PDBu stimulation. The specified times correspond to time points on the FRET ratio plots in C and indicate images captured at the beginning (0 min), the end (15 min), and, for PKCθ, the FRET ratio high point (7.25 min). The images for PKCδ and PKCθ visually show their translocation to mitochondria after PDBu stimulation. The images for PKCβII and PKCϵ show their PDBu-responsive translocation to other intracellular membranes, despite their lack of FRET responses at mitochondria. E, schematic of the PKC isozymes and PKCδ constructs used throughout the paper.
Regulatory Domains of PKCδ Are Necessary but Not Sufficient for PDBu-induced Translocation to and Retention at Mitochondria
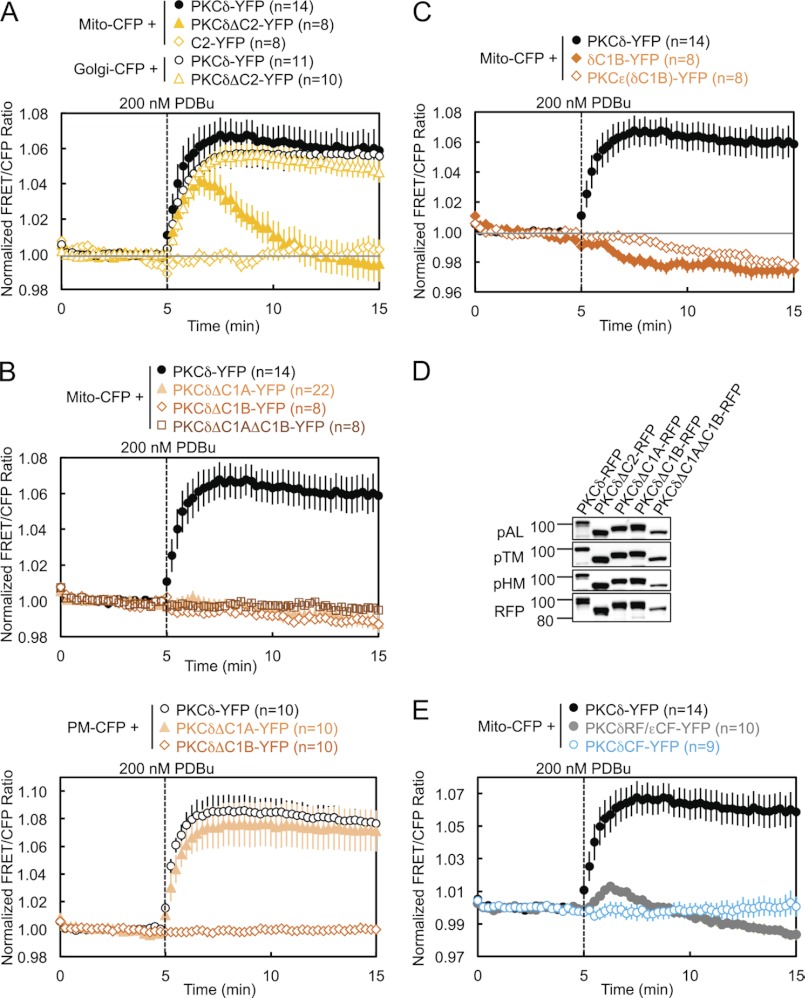
To address the isozyme-specific mechanism by which PKCδ binds mitochondria, we investigated the determinants necessary for the interaction (Fig. 1E). Deletion of the C2 domain of PKCδ resulted in a transient association of PKCδ with mitochondria: the half-time for mitochondrial translocation (∼30 s) was similar to that for wild-type enzyme, but the construct was released from the membrane with a half-time of ∼2 min (Fig. 2A, closed symbols, and supplemental Fig. S1). Thus, the C2 domain of PKCδ, although not required for its initial translocation to mitochondria, is necessary for its retention there. In contrast, deletion of the C2 domain had no effect on PKCδ translocation to and retention at the Golgi (Fig. 2A, open circles and triangles). The isolated δC2 domain did not translocate to mitochondria (Fig. 2A, diamonds), indicating that the role of the δC2 domain in retaining PKCδ at mitochondria is not sufficient to bring it to mitochondria. These data reveal that the C2 domain of PKCδ contributes to the retention of PKCδ at mitochondria.
FIGURE 2.
Regulatory domains of PKCδ are necessary but not sufficient for PDBu-induced translocation to and retention at mitochondria. A–C and E, COS-7 cells co-transfected with the indicated CFP and YFP constructs were monitored for their FRET ratio responses to stimulation with 200 nm PDBu. D, COS-7 cells transfected with the indicated PKCδ-RFP constructs were lysed and immunoblotted with phospho-specific antibodies against the activation loop (pAL), turn motif (pTM), and hydrophobic motif (pHM) of PKC and with the DsRed antibody for expression of the RFP-tagged constructs.
Deletion of the C1A domain, the C1B domain, or both C1 domains abolished the translocation of PKCδ to mitochondria (Fig. 2B, upper panel, and supplemental Fig. S1), indicating that both C1 domains of PKCδ are necessary for its translocation to mitochondria. In contrast, only the C1B domain is required for the translocation of PKCδ to plasma membrane: deletion of the C1A domain alone had no effect on the interaction of PKCδ with plasma membrane (Fig. 2B, lower panel). Neither the isolated δC1B domain nor a chimera of PKCϵ with its ϵC1B domain substituted with the δC1B translocated to mitochondria (Fig. 2C and supplemental Fig. S1), indicating that the δC1B domain, despite being the primary phorbol ester-binding domain of PKCδ (40), is not sufficient to promote PKCδ PDBu-induced interaction with mitochondria. All of these regulatory domain deletion mutants of PKCδ were properly primed by phosphorylation at the activation loop, turn motif, and hydrophobic motif (Fig. 2D). Finally, neither the regulatory fragment (RF) of PKCδ (fused with the catalytic fragment of PKCϵ to form a properly folded and phorbol ester-sensitive full-length PKCδ/ϵ chimera) nor its catalytic fragment (CF) alone were capable of translocating to mitochondria (Fig. 2E and supplemental Fig. S1), indicating that at least one determinant outside the RF is necessary for the interaction of PKCδ with mitochondria.
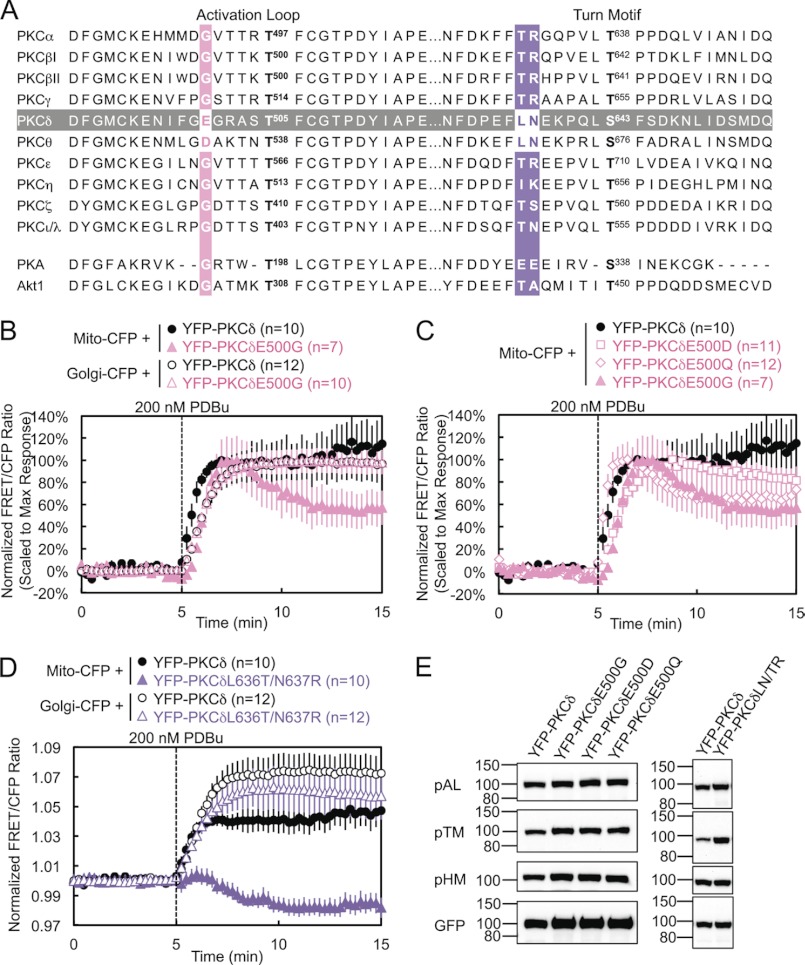
Critical Residues in the Activation Loop and Turn Motif
PKCδ and PKCθ have a unique acidic residue (E and D, respectively) five amino acids N-terminal of the activation loop phosphorylation site, where all the other PKC isozymes as well as PKA and Akt possess a glycine (Fig. 3A). Mutation of this glutamate to glycine in PKCδ (E500G) modestly delayed its translocation to mitochondria by 30 s but significantly decreased its retention at mitochondria to ∼60% by 10 min after PDBu stimulation (Fig. 3B, solid symbols, and supplemental Fig. S1). In contrast, E500G had no effect on the interaction of PKCδ with other membranes such as Golgi (Fig. 3B, open symbols).
FIGURE 3.
Critical residues in the activation loop and turn motif. A, amino acid sequence alignment of the activation loop and turn motif of all PKC isozymes, as well as of Akt and PKA. (PKCγ and δ, PKA, and Akt1 sequences are mouse; PKCϵ, θ, and ζ sequences are human; PKCα, βI, βII, η, and ι/λ sequences are the same between human and mouse and are shown with human numbering.) The sequence of PKCδ is highlighted in gray, and the alignments for the PKCδ residues mutated in the activation loop and turn motif are highlighted in pink and purple, respectively. B–D, COS-7 cells co-transfected with the indicated CFP and YFP constructs were monitored for their FRET ratio responses to stimulation with 200 nm PDBu. E, COS-7 cells transfected with the indicated YFP-PKCδ constructs were lysed and immunoblotted with phospho-specific antibodies against the activation loop (pAL), turn motif (pTM), and hydrophobic motif (pHM) of PKC and with the GFP antibody for expression of the YFP-tagged constructs.
To determine whether the charge or the size of this Glu plays the most critical role in PKCδ interactions with mitochondria, we also mutated this residue to either an aspartate (E500D) or a glutamine (E500Q). The E500D mutation, which retains the negative charge of Glu but slightly decreases the size of the residue, caused little loss of retention at mitochondria, although, like E500G, it also translocated after a 30-s delay (Fig. 3C, squares). Thus, the smaller but negatively charged Asp can mostly compensate for the role of Glu-500 in retention. This is consistent with the ability of PKCθ, which possesses an Asp at this position, to interact somewhat with mitochondria (Fig. 1C). Also, mutation of the Asp on PKCθ to a Glu did not improve its retention at mitochondria (data not shown). The E500Q mutation, which retains the size of Glu but loses the charge at this residue, caused a loss of retention similar to that of E500G, without delaying translocation to mitochondria (Fig. 3C, diamonds). Thus, the negative charge of Glu-500 is responsible for its role in retention of PKCδ at mitochondria, whereas the bulk of Glu-500 contributes slightly to the initial affinity of PKCδ for mitochondria. When both the negative charge and bulk of Glu-500 were lost in E500G, PKCδ both translocated with a slight delay and partially lost retention at mitochondria (Fig. 3C, triangles).
PKCδ and PKCθ also possess a unique Leu-Asn sequence near the turn motif, where most of the other PKC isozymes possess a Thr-Arg sequence (Fig. 3A). Mutation of these two residues (denoted L636T/N637R or LN/TR) resulted in a complete loss of PDBu-induced interaction by PKCδ with mitochondria (Fig. 3D, closed symbols, and supplemental Fig. S1), highlighting the importance of these two residues in the isozyme-specific interaction of PKCδ with mitochondria upon activation. Indeed, FRET between mitochondria and the LN/TR mutant actually decreased upon stimulation, indicating the translocation of PKCδLN/TR away from mitochondria in preference for other PDBu-containing membranes and therefore implying the basal localization of PKCδLN/TR to mitochondria. In contrast, the LN/TR mutation did not affect the interaction of PKCδ with Golgi (Fig. 3D, open symbols). PKCδ and PKCθ also possess a Ser-Phe sequence at the turn motif phosphorylation site, where most of the other PKC isozymes possess a Thr-Pro sequence. In contrast to the nearby LN/TR mutation, neither PKCδS643T nor PKCδS643T/F644P behaved significantly differently from wild-type PKCδ in their interactions with mitochondria (data not shown). Thus, the unique LN turn motif sequence of PKCδ and PKCθ contributes to their unique mitochondrial recognition.
Despite the proximity of these mutations to conserved phosphorylation sites, these activation loop and turn motif mutants were fully phosphorylated at the activation loop, turn motif, and hydrophobic motif (Fig. 3E). Thus, their loss of interactions with mitochondria cannot be attributed to the loss of processing phosphorylations.
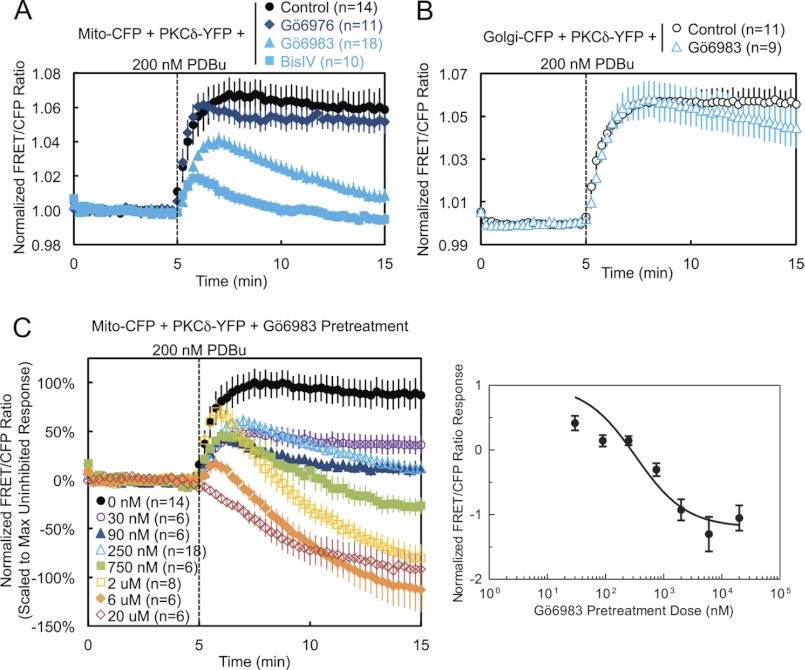
Pharmacological Inhibition Demonstrates That PKCδ Interaction with Mitochondria Is Dependent on Novel PKC Activity
We next addressed whether the catalytic activity of PKCδ is necessary for its interaction with mitochondria. Pretreatment of cells with either the active site inhibitor Gö6983 or the substrate-uncompetitive inhibitor BisIV (41), both general PKC inhibitors that inhibit conventional and novel PKC isozymes, including PKCδ, caused both a dramatic reduction in the PDBu-induced translocation of PKCδ to mitochondria and a loss of retention reminiscent of deletion of the C2 domain (Fig. 4A, light blue symbols, and supplemental Fig. S1, Gö6983). In contrast, pretreatment with the conventional PKC isozyme-specific inhibitor Gö6976, which does not inhibit PKCδ, had no effect on mitochondrial translocation (Fig. 4A, dark blue). In contrast to its effects on mitochondrial translocation, pharmacological inhibition with Gö6983 did not affect the interaction of PKCδ with Golgi membranes (Fig. 4B). Pretreatment of cells with increasing concentrations of Gö6983 unveiled a dose-responsive inhibition of the phorbol ester-stimulated interaction of PKCδ with mitochondria, with concentrations above 750 nm inhibitor revealing the displacement of basally bound PKCδ from mitochondria, presumably to other phorbol ester-enriched membranes (Fig. 4C, left panel). Analysis of the scaled FRET ratio 10 min following phorbol ester treatment revealed a classic dose-response curve (Fig. 4C, right panel). Thus, pharmacological inhibition shows that the activity of novel PKCs is necessary for the interaction of PKCδ with mitochondria.
FIGURE 4.
Pharmacological inhibition demonstrates that PKCδ interaction with mitochondria is dependent on novel PKC activity. A, COS-7 cells co-transfected with Mito-CFP and PKCδ-YFP were pretreated with either 500 nm of the conventional PKC inhibitor Gö6976, 250 nm of the general PKC active site inhibitor Gö6983, or 2.5 μm of the general PKC substrate-uncompetitive inhibitor BisIV for at least 20 min at 37 °C and compared with unpretreated cells in their FRET ratio responses to 200 nm PDBu stimulation. B, COS-7 cells co-transfected with Golgi-CFP and PKCδ-YFP were pretreated with 250 nm Gö6983 for at least 20 min at 37 °C and compared with unpretreated cells in their FRET ratio responses to 200 nm PDBu stimulation. C, COS-7 cells co-transfected with Mito-CFP and PKCδ-YFP were pretreated with the indicated concentrations of Gö6983 for at least 20 min at 37 °C and compared with unpretreated cells in their FRET ratio responses to 200 nm PDBu stimulation (left panel). The means ± S.E. of the normalized FRET ratios at 15 min (after 10 min of PDBu stimulation) were plotted as a function of the log of the inhibitor concentration to generate a Gö6983 dose-response curve (right panel).
Specific Inhibition of PKCδ Activity Prevents Its Retention at Mitochondria
To determine whether the intrinsic catalytic activity of PKCδ, rather than the activity of another inhibitor-sensitive novel PKC isoform, is necessary for its interaction with mitochondria, we took advantage of chemical genetics (42–44). We generated a PKCδ gatekeeper mutant by mutating a conserved bulky methionine residue in the ATP-binding pocket of PKCδ to a smaller alanine residue (PKCδM425A) (42, 43). This enlarges the active site to accommodate the small molecule inhibitor NaPP1, which cannot bind wild-type kinases (44). We then used CKAR, a genetically encoded, FRET-based general PKC activity reporter (35, 36), and δCKAR, a similar reporter specific for PKCδ activity (34), to monitor the activity of endogenous and overexpressed PKC(δ) in real time in live cells. As measured using either CKAR (Fig. 5A) or δCKAR (Fig. 5B), wild-type and gatekeeper mutant PKCδ were activated by PDBu stimulation, but only the activity of the gatekeeper mutant of PKCδ was specifically sensitive to subsequent inhibition by NaPP1. Additionally, as measured using δCKAR, pretreatment with NaPP1 completely blocked the PDBu-stimulated activity of the gatekeeper mutant of PKCδ, without preventing the activation of exogenous wild-type PKCδ (Fig. 5C). Having ascertained the specificity of our approach, we then used the gatekeeper mutant of PKCδ in our intermolecular FRET translocation assay. Specific inhibition of PKCδ gatekeeper mutant activity by pretreatment of cells with NaPP1 prevented its retention at mitochondria (Fig. 5D) without affecting its interaction with the plasma membrane (Fig. 5E).
FIGURE 5.
Specific inhibition of PKCδ activity prevents its retention at mitochondria. A, COS-7 cells transfected with CKAR alone or together with wild-type PKCδ-RFP or with the gatekeeper mutant PKCδM425A-RFP were stimulated with 200 nm PDBu and then inhibited with 1 μm NaPP1 during FRET imaging. B and C, COS-7 cells co-transfected with δCKAR and either RFP, PKCδ-RFP, or PKCδM425A-RFP were either stimulated with 200 nm PDBu and then inhibited with 1 μm NaPP1 (B) or first inhibited with 1 μm NaPP1 and then stimulated with 200 nm PDBu (C). D, COS-7 cells co-transfected with Mito-CFP and either PKCδ-YFP or PKCδM425A-RFP were either left unpretreated/pretreated with Me2SO vehicle control or pretreated with 1 μm NaPP1 for 30 min at 37 °C before 200 nm PDBu stimulation during FRET imaging. E, COS-7 cells co-transfected with CFP-targeted to the plasma membrane (PM-CFP) and either PKCδ-YFP or PKCδM425A-RFP were either left unpretreated/pretreated with Me2SO vehicle control or pretreated with 1 μm NaPP1 for 30 min at 37 °C before 200 nm PDBu stimulation during FRET imaging. F, COS-7 cells co-transfected with δCKAR and PKCδ-RFP were pretreated with either Me2SO vehicle control, 10 μm rottlerin, or 750 nm Gö6983 for 30 min at 37 °C before PDBu stimulation during FRET imaging.
We chose to use this chemical genetics approach to specifically inhibit PKCδ activity because of the lack of reliable PKCδ-specific inhibitors. Rottlerin has been used commonly in the literature as a PKCδ-specific inhibitor, but this has been refuted, and the effects of rottlerin have been attributed to its role as a mitochondrial uncoupler rather than as a PKCδ inhibitor (45, 46). Here, we provide further evidence using δCKAR that, in contrast to Gö6983, a bona fide PKC inhibitor capable of inhibiting PKCδ, pretreatment with rottlerin does not inhibit phorbol ester-stimulated PKCδ activity in cells (Fig. 5F).
Mitochondrially Targeted δCKAR Reveals That PKCδ Is Active at Mitochondria
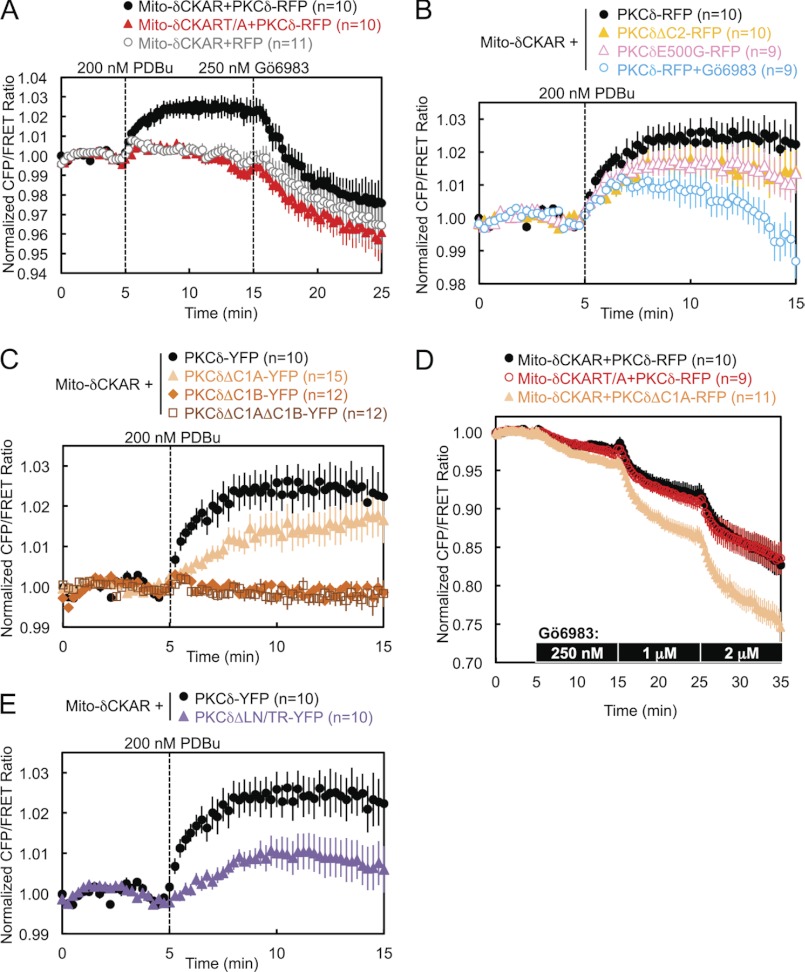
We next asked whether the PKCδ bound to mitochondria is catalytically active. We specifically monitored PKCδ activity at mitochondria by targeting δCKAR to the outer membrane of mitochondria using the same mitochondrial localization sequence as Mito-CFP. The FRET responses of Mito-δCKAR indicated that PDBu stimulation, which had induced PKCδ to translocate to mitochondria, also induced PKCδ activity there; this stimulated activity was completely reversed by Gö6983 (Fig. 6A, black circles). The PDBu-stimulated FRET response from Mito-δCKAR was specifically caused by phosphorylation of the phospho-acceptor threonine in the substrate of the reporter peptide by exogenous PKCδ, because the negative control Thr to Ala (denoted T/A) version of the reporter did not respond significantly to phorbol ester treatment (Fig. 6A, red triangles) and because the reporter could not detect any significant endogenous PKCδ activity (Figs. 6A, gray circles, and 5, B and C). The portion of the Gö6983-induced reversal in FRET ratio that drops below base line must be attributed to the reddish-yellow color of this inhibitor, which produces an artifactual FRET response observed even with the negative control reporter Mito-δCKART/A (Fig. 6A, red triangles).
FIGURE 6.
Mitochondrially targeted δCKAR reveals that PKCδ is active at mitochondria. A, COS-7 cells co-transfected with either Mito-δCKAR or the negative control reporter Mito-δCKART/A and either PKCδ-RFP or RFP were monitored for their FRET ratio responses to stimulation with 200 nm PDBu and inhibition with 250 nm Gö6983. B, C, and E, COS-7 cells co-transfected with Mito-δCKAR and the indicated RFP-tagged PKCδ constructs were monitored for their FRET ratio responses to stimulation with 200 nm PDBu. D, COS-7 cells co-transfected with either Mito-δCKAR or Mito-δCKART/A and either PKCδ-RFP or PKCδΔC1A-RFP were titrated with the indicated increasing net concentrations of Gö6983.
Perturbations that had caused a loss of retention by PKCδ at mitochondria, such as deletion of the C2 domain, the mutation E500G, or inhibition of PKC activity by Gö6983, resulted in overall lower levels of PDBu-stimulated activity at mitochondria (Fig. 6B) and, in the case of Gö6983 pretreatment, a loss of sustained activity there (Fig. 6B, open blue circles). Deletion of either the C1B domain alone or both C1 domains, which had abolished PDBu-stimulated translocation by PKCδ to mitochondria, similarly abolished PDBu-stimulated PKCδ activity at mitochondria (Fig. 6C, orange diamonds and dark orange squares). PKCδ with the C1A domain alone deleted, however, unexpectedly retained some activity at mitochondria (Fig. 6C, light orange triangles), despite its lack of translocation there. This activity can be attributed to a higher basal localization by PKCδΔC1A to mitochondria, which was revealed by directly using Gö6983 to inhibit basal levels of PKCδ activity during FRET imaging. As previously noted, the addition of the reddish-yellow Gö6983 during imaging produces an artifactual below base-line drop in the FRET ratio, and increasing concentrations of Gö6983 produced the same magnitude of artifactual drops in FRET ratio in both Mito-δCKAR and Mito-δCKART/A in the presence of wild-type PKCδ-RFP (Fig. 6D, black and red circles). Nonetheless, the significantly greater inhibitor-induced drops in FRET ratio in the presence of PKCδΔC1A (Fig. 6D, light orange triangles) compared with wild-type PKCδ indicate that deletion of the C1A domain increases the basal activity of PKCδ at mitochondria, which is also corroborated by the greater basal localization of PKCδΔC1A at mitochondria evident in images of the fluorescently labeled construct (supplemental Fig. S1). Similarly, the LN/TR mutant of PKCδ, which had failed to translocate to mitochondria, exhibited some activity at mitochondria (Fig. 6E), which can also be attributed to its basal localization at mitochondria, as evidenced from its translocation away from mitochondria in preference for other membranes in response to PDBu stimulation (Fig. 3D).
Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Modulates the Retention of PKCδ at Mitochondria
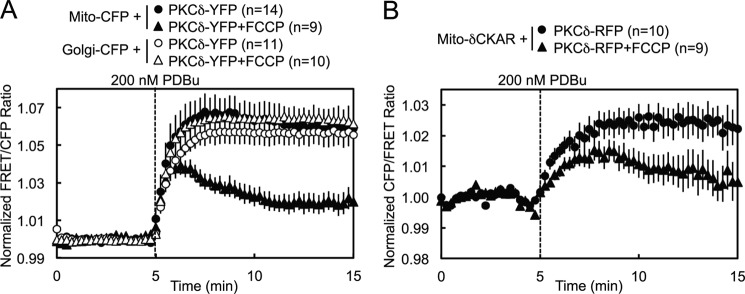
Pretreatment of cells with 500 nm FCCP, a mitochondrial uncoupler that dissipates the mitochondrial membrane potential by acting as a protonophore, resulted in a partial loss of retention by PKCδ at mitochondria following PDBu-stimulated translocation (Fig. 7A, closed symbols, and supplemental Fig. S1), whereas it had no effect on the retention of PKCδ at Golgi (Fig. 7A, open symbols). Similarly, FCCP pretreatment caused PDBu-stimulated activity by PKCδ at mitochondria to be lower and less sustained (Fig. 7B). These data are consistent with the mitochondrial membrane potential contributing to PKCδ retention at mitochondria.
FIGURE 7.
Mitochondrial membrane potential modulates the retention of PKCδ at mitochondria. A, COS-7 cells co-transfected with either Mito-CFP or Golgi-CFP and PKCδ-YFP were pretreated with 500 nm of the mitochondrial uncoupler FCCP for 15 min at room temperature and compared with unpretreated controls in their FRET ratio responses to 200 nm PDBu stimulation. B, COS-7 cells co-transfected with Mito-δCKAR and PKCδ-RFP were pretreated with 500 nm FCCP for 30 min at 37 °C and compared with the unpretreated control in their FRET ratio responses to 200 nm PDBu stimulation.
Independent versus Coincident Mechanisms of PKCδ Interaction with Mitochondria
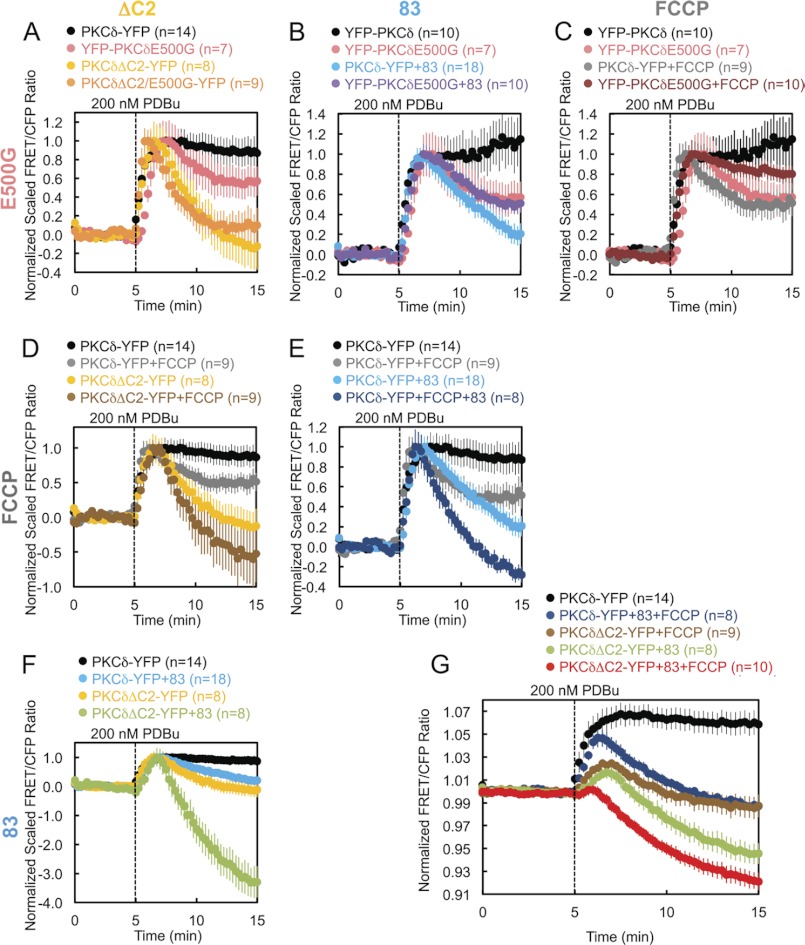
The foregoing results identified four perturbations that affect the retention of PKCδ at mitochondria: deletion of the C2 domain (PKCδΔC2), Gö6983 pretreatment, FCCP pretreatment, or removal of the negative charge at Glu-500 (PKCδE500G). To resolve whether these perturbations affect the same mechanism for retaining PKCδ at mitochondria or whether they affect independent mechanisms, we tested every one of the six possible perturbation pairings to determine whether the combined effect of each pair produced either an additive/synergistic or nonadditive effect on the retention of PKCδ at mitochondria. An additive or synergistic effect of two perturbations would suggest simultaneous disruption of two independent determinants driving the interaction of PKCδ with mitochondria. A lack of additivity or synergism would indicate that the two perturbations had coincided in affecting a single determinant driving the interaction of PKCδ with mitochondria. Using this type of analysis, we determined that the mechanism of retention regulated by Glu-500 is part of the same mechanism regulated by the C2 domain (Fig. 8A), PKCδ activity (Fig. 8B), or the mitochondrial membrane potential (Fig. 8C). In contrast, the mechanisms of retention regulated by the C2 domain, PKCδ activity, and the mitochondrial membrane potential are all independent mechanisms (Fig. 8, D–F). By combining the latter three independent mechanisms of retention, we completely abolished the PDBu-stimulated interaction of PKCδ with mitochondria, actually causing PKCδ basally localized to mitochondria to translocate away from mitochondria in preference for other membranes (Fig. 8G, red circles).
FIGURE 8.
Independent versus coincident mechanisms of PKCδ interaction with mitochondria. A–G, COS-7 cells co-transfected with Mito-CFP and the indicated YFP-tagged PKCδ constructs were monitored for their FRET ratio responses to stimulation with 200 nm PDBu. Some dishes were pretreated with 250 nm Gö6983 (83) and/or 500 nm FCCP, as indicated, for 30 min at 37 °C. A–F, each graph presents the separate and combined effects of two of the four perturbations that affect the retention of PKCδ at mitochondria, with the pairings of perturbations indicated by the column and row headers. The data were scaled to the maximal PDBu-stimulated response for each experiment after normalization to average base-line values. G, the three perturbations found to independently disrupt PKCδ interactions with mitochondria were combined, and the result was juxtaposed to those of unperturbed PKCδ and each of the three possible pairings of the independent perturbations.
Functional Effects of PKCδ Interaction with Mitochondria
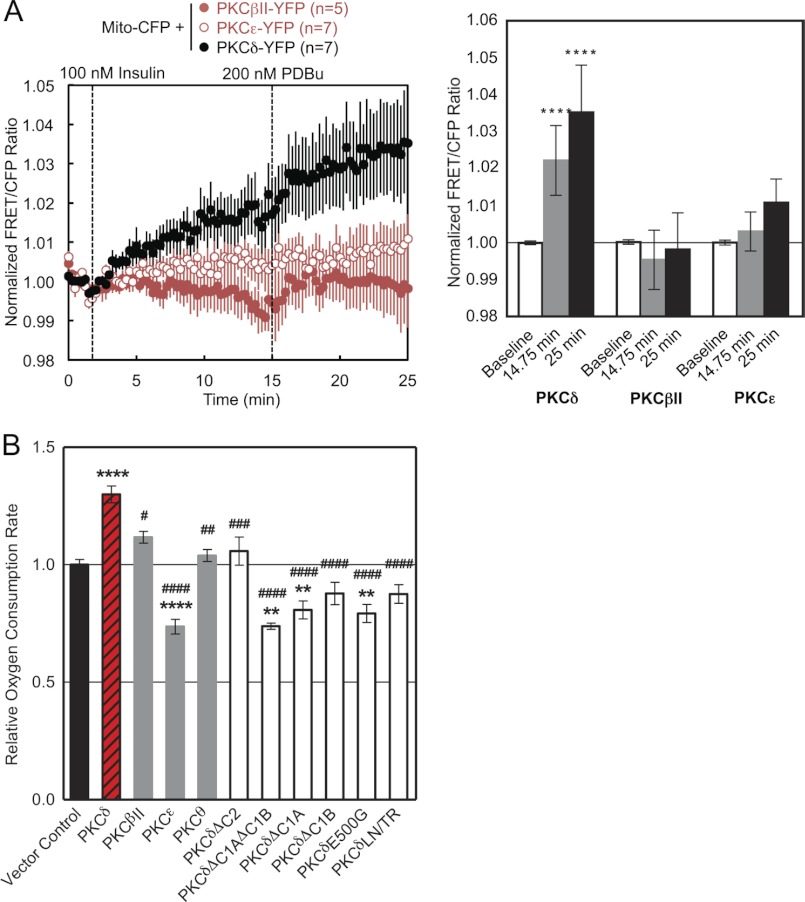
We next examined whether the translocation of PKCδ to mitochondria is triggered by a natural agonist. Stimulation of L6 skeletal muscle cells with 100 nm insulin resulted in the translocation of PKCδ, but not PKCϵ or PKCβII, to mitochondria; this translocation was further increased following phorbol ester stimulation, but again only for PKCδ (Fig. 9A). These data reveal that a natural agonist also causes the isozyme-specific recruitment of PKCδ to mitochondria.
FIGURE 9.
Functional effects of PKCδ interaction with mitochondria. A, L6 myocytes co-transfected with Mito-CFP and YFP-tagged PKCδ, PKCβII, or PKCϵ were monitored for their FRET ratio responses to stimulation with 100 nm insulin followed by 200 nm PDBu (left panel). The bar graph shows the mean FRET ratios before the addition of agonists (Baseline), after 13 min of insulin stimulation (14.75 min), and after an additional 10 min of PDBu stimulation (25 min) (right panel). The level of statistically significant differences is indicated as follows: ****, p < 0.0001 compared with PKCδ base line by Šídák's multiple comparison post hoc test following one-way analysis of variance. B, the maximal oxygen consumption rates of COS-7 cells transfected with the indicated constructs were measured after treatment with 2 μm oligomycin and 750 nm FCCP using a Seahorse Extracellular Flux Analyzer XF96. For each experiment, the data were gathered in quintuplicate and normalized to the vector control group. The data plotted reflect the cumulative means ± S.E. of six (vector control), five (PKCδ), three (PKCδΔC1B), two (PKCβII, PKCϵ, PKCδΔC2, PKCδΔC1A, PKCδE500G, PKCδLN/TR), or one (PKCθ, PKCδΔC1AΔC1B) independent experiments. The levels of statistically significant differences are indicated as follows: **, p < 0.01 and ****, p < 0.0001 compared with vector control and #, p < 0.05; ##, p < 0.01; ###, p < 0.001; ####, p < 0.0001 compared with PKCδ by both Bonferroni's and Šídák's multiple comparison post hoc tests following one-way analysis of variance.
To investigate the physiological relevance of the PKCδ-specific interaction with mitochondria, we measured the effect of PKCδ overexpression on the OCR of intact COS-7 cells. Overexpression of PKCδ but not of PKCβII, PKCϵ, or PKCθ resulted in a significant increase in the OCR and thus the mitochondrial respiration of these cells relative to a vector control (Fig. 9B). In contrast, PKCϵ overexpression significantly decreased the cellular OCR (Fig. 9B). Differences in OCR between groups were observed regardless of whether the basal (data not shown), State 4 (data not shown), or uncoupler-stimulated rates (Fig. 9B) were measured, but differences were most pronounced in the uncoupler-stimulated rates.
Structural alterations that had perturbed the interaction of PKCδ with mitochondria all resulted in a loss of the increase in OCR produced by overexpression of wild-type PKCδ (Fig. 9B). Mitochondrial respiration upon overexpression of PKCδΔC2 was no different from that of vector control (Fig. 9B). Overexpression of PKCδΔC1AΔC1B, PKCδΔC1A, or PKCδE500G actually had the dominant negative effect of reducing mitochondrial respiration below vector control levels (Fig. 9B). Overexpression of PKCδΔC1B or PKCδLN/TR also tended to reduce mitochondrial respiration below that of vector control but did not reach statistical significance (Fig. 9B). All of the constructs were successfully overexpressed in these cells, as determined by Western blotting (data not shown). Differences in mitochondrial respiration did not result from differences in cellular proliferation, because the same cells plated in triplicate in parallel with the OCR measurements did not exhibit significant differences in proliferation, as determined by cell counts (data not shown). Thus, the isozyme-specific structural ability of PKCδ to interact with mitochondria has the functional consequence of increasing mitochondrial respiration.
DISCUSSION
Using an intermolecular FRET translocation reporter and an intramolecular FRET PKCδ activity reporter to monitor PKC translocation to and PKCδ activity at mitochondria in real time in live cells, we show that PKCδ translocates rapidly to and is active at the outer membrane of mitochondria upon activation with phorbol esters or, in L6 myocytes, with insulin. The mechanism of this translocation is distinct from that of the canonical C1 domain-mediated recognition of DAG or phorbol esters that drives conventional and novel PKC isozymes to the plasma membrane and Golgi. First, the interaction of PKCδ with mitochondria is isozyme-specific and therefore not simply phorbol ester-mediated (Fig. 1, C and D). Second, structure-function analysis reveals that the mechanism of the phorbol ester-stimulated interaction of PKCδ with mitochondria depends on multiple unique determinants in both the regulatory and catalytic moieties of PKCδ that do not affect canonical PKCδ membrane translocation (Figs. 2 and 3). Third, the interaction depends on its intrinsic catalytic activity, in contrast to canonical translocation (Figs. 4 and 5). Fourth, the interaction depends on the mitochondrial membrane potential, which is unnecessary for canonical membrane translocation (Fig. 7A). These data support a novel mechanism that drives PKCδ and, to a lesser extent, PKCθ, to mitochondria.
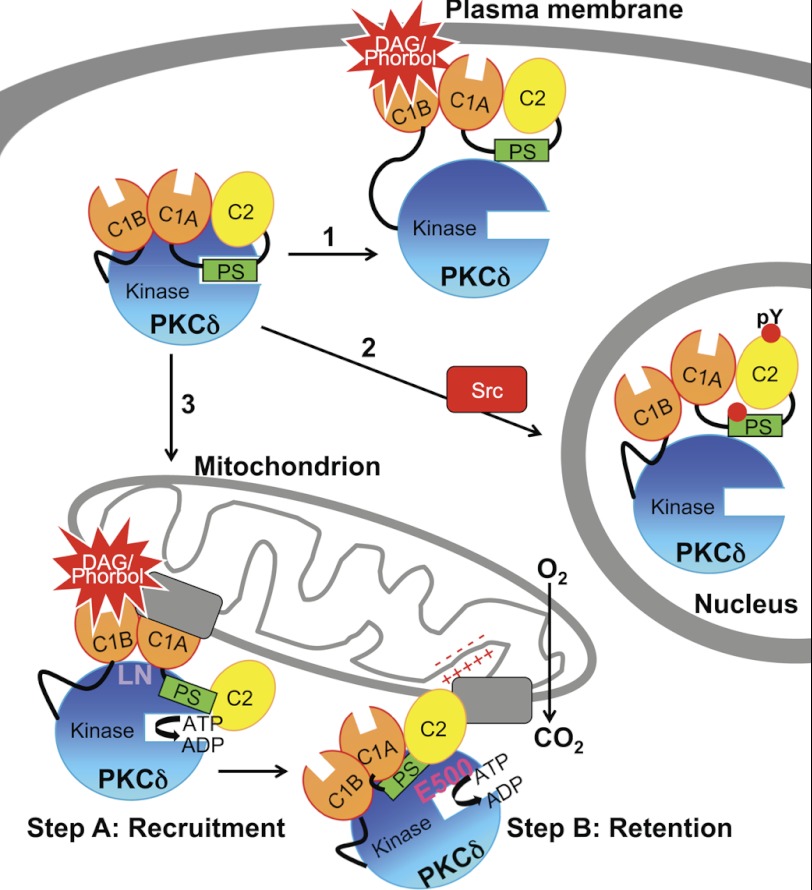
PKCδ stands out among the PKC isozymes in two ways. First, it is structurally different: it has a unique activation loop containing a phosphomimetic Glu five residues N-terminal to the phosphorylated Thr that may partly account for its ability to be activated without phosphorylation by phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1 (47, 48) and whose phosphorylation is agonist-dependent as well as constitutive (49, 50), and it has a unique turn motif that may account for its lack of regulation by mTORC2 (13). These structural features are shared by only one other isozyme, PKCθ. Second, it translocates and is activated by two mechanisms: the canonical lipid-dependent activation at intracellular membranes (Fig. 10, arrow 1) and a novel tyrosine kinase-dependent (and phorbol ester-independent) activation (50–53) that causes translocation into the nucleus (4, 9–11, 34) and plays a role in apoptosis (4, 9–11, 52) (Fig. 10, arrow 2). Here, we unveil a third unique property of PKCδ: this isozyme uniquely interacts with and is activated at mitochondria, where it promotes mitochondrial respiration (Fig. 10, arrow 3).
FIGURE 10.
Model showing three mechanisms for the agonist-evoked redistribution of cytosolic PKCδ to intracellular compartments and summarizing the determinants involved in its interaction with mitochondria. Arrow 1, canonical binding of PKCδ to DAG-containing membranes such as the plasma membrane (shown) and Golgi is mediated by the C1B domain. Arrow 2, Src-dependent translocation of PKCδ to the nucleus depends on Tyr phosphorylation (indicated by red circles) of PKCδ. Arrow 3, the novel, isozyme-specific interaction of PKCδ with mitochondria occurs via two steps: step A, an initial recruitment step that depends on the C1A and C1B domains and on Leu-Asn (LN) in the turn motif, and step B, a retention step that depends on four elements: the C2 domain, an acidic residue in the activation loop (Glu-500, E500), intrinsic catalytic activity (represented by ATP→ADP), and the mitochondrial membrane potential (represented by plus and minus signs). One or more protein scaffolds (gray rectangles) at mitochondria are hypothesized to mediate this interaction, which promotes mitochondrial respiration.
The phorbol ester-stimulated interaction of PKCδ with mitochondria occurs in two steps and depends on multiple parameters (Fig. 10). First, both C1 domains and a unique LN sequence in the turn motif are required for the initial recruitment of PKCδ to mitochondria (Fig. 10, Step A). Fluorescently tagged phorbol esters have been visualized to distribute to mitochondria (54), and we speculate that the interaction between the C1B domain of PKCδ and phorbol esters distributing to mitochondria helps to bring other determinants on PKCδ into contact with mitochondria. Alternatively, PKCδ is capable of binding PDBu in the absence of membrane lipids, albeit with lower affinity (55), and this interaction may directly drive the interaction of PKCδ with nonmembrane targets at mitochondria; there is precedent for phorbol ester-mediated binding by other PKC isozymes to nonmembrane structures (56) and for C1 domains to mediate protein, as well as lipid, interactions (57). Second, the C2 domain, its intrinsic catalytic activity, and the mitochondrial membrane potential independently regulate the sustained interaction of PKCδ at mitochondria, whereas the charge of Glu-500 on PKCδ cooperates with all of the latter three mechanisms to retain PKCδ at mitochondria (Fig. 10, Step B). Interestingly, phorbol esters have been shown to alter the mitochondrial membrane potential in PKCδ-overexpressing keratinocytes (23) and to potentiate and accelerate the effect of a mitochondrial ATP-dependent K+ channel opener (58). In contrast, only the C1B domain among all of these is required for the phorbol ester-stimulated translocation of PKCδ to other intracellular membranes such as the plasma membrane and Golgi (this paper and Ref. 40).
Stimulation with phorbol esters or with insulin in L6 myocytes enables us to observe an interaction between PKCδ and mitochondria because it produces an acute change in the FRET ratio. However, our data also support a model in which a significant amount of PKCδ associates basally with mitochondria via many of the same determinants. First, the C1B domain of PKCδ is basally localized to mitochondria, because FRET between Mito-CFP and δC1B-YFP decreases upon phorbol ester stimulation (Fig. 2C), reflecting translocation of the isolated domain basally localized to mitochondria away to other membranes. Second, full-length PKCδ also appears to be basally localized to mitochondria, because pretreatment with greater than 750 nm Gö6983 (Fig. 4C) or combining multiple perturbations that disturb the retention of PKCδ at mitochondria (Fig. 8) not only bring its phorbol ester-stimulated FRET ratio with Mito-CFP back down to base line but further below base line, indicating disturbance of its basal interaction with mitochondria. In contrast, the C1A domain of PKCδ may block its basal interaction with mitochondria, because deletion of the C1A domain increases the extent of basal PKCδ activity at mitochondria, as revealed by titration with inhibitor (Fig. 6D) and by the low level of activity induced by phorbol esters (Fig. 6C) despite the lack of PKCδΔC1A translocation (Fig. 2B). By comparison, deletion of the C1B domain alone or in combination with C1A results in no translocation to (Fig. 2B) and no basal phorbol ester-induced activity at mitochondria (Fig. 6C). The C1A domain may basally recruit PKCδ to other membranes or mask the basal interactions of the neighboring C1B domain with mitochondria. In a manner similar to PKCδΔC1A, the turn motif mutant PKCδLN/TR also appears to be basally localized to mitochondria, translocating in net away from mitochondria upon PDBu stimulation (Fig. 3D) yet still exhibiting some activity at mitochondria from the basally localized pool (Fig. 6E). Thus, the C1B and C2 domains, its intrinsic catalytic activity, as well as the mitochondrial membrane potential may contribute to the basal interaction of PKCδ with mitochondria, whereas the C1A domain and the LN motif may interfere with it.
Consistent with PKCδ localizing basally to mitochondria, we found that unstimulated PKCδ overexpression increases mitochondrial respiration (Fig. 9B). This is consistent with reports that PKCδ activates the PDHC, which converts pyruvate to acetyl CoA, thereby increasing mitochondrial respiration. Caruso et al. (27) showed that insulin stimulation of L6 skeletal muscle cells and immortalized hepatocytes induces PKCδ to translocate to mitochondria and to phosphorylate PDH phosphatases 1 and 2, which then dephosphorylate and activate the PDHC, increasing mitochondrial respiration. The work of Hammerling and co-workers (28, 29) demonstrated in mouse embryonic fibroblasts that retinol, or vitamin A, induces a PKCδ signalosome composed of retinol, PKCδ, cytochrome c, and the adapter protein p66Shc to dephosphorylate and inhibit PDH kinase 2, which usually phosphorylates and inactivates the PDHC, thereby leading also to the activation of the PDHC and increased mitochondrial respiration. In addition, we found that overexpression of PKCϵ, which has been shown to oppose both the apoptotic (2) and metabolic (30) effects of PKCδ, actively decreases mitochondrial respiration relative to vector control (Fig. 9B), consistent with its proposed role of inhibiting the PDHC (30). Finally, none of the PKCδ mutant constructs that had been defective in phorbol ester-induced interaction with mitochondria produced the same increase in oxygen consumption rate as wild-type PKCδ (Fig. 9B), indicating that the structural elements important for the interaction of PKCδ with mitochondria are also important for its effect on mitochondrial respiration. Indeed, PKCδΔC1AΔC1B, PKCδΔC1A, and PKCδE500G actually significantly reduced mitochondrial respiration below vector control levels in a manner similar to PKCϵ (Fig. 9B). One possibility is that these constructs that interact imperfectly with mitochondria produce dominant negative effects by mislocalizing or displacing endogenous PKCδ from mitochondria.
It remains to be determined whether PKCδ produces its effect on mitochondrial respiration by remaining on the cytoplasmic surface of the mitochondrial outer membrane and simply transducing signals to substrates on the surface of mitochondria (e.g., by phosphorylating intermediate phosphatases that are then translocated into the mitochondrial matrix, where they regulate the PDHC) or whether PKCδ is itself subsequently translocated into the mitochondria, possibly by protein partners that mediate the retention step of its interaction with mitochondria. In addition to the kinase and phosphatases that regulate the PDHC, other potentially relevant metabolic substrates of PKCδ that have been noted in the literature include the d subunit of ATP synthase in the inner membrane of mitochondria (in neonatal cardiac myocytes exposed to hypoxia or phorbol ester (59)) and the M2 splice isoform of pyruvate kinase (in MCF-7 cells (60)), which plays an important role in the metabolic switch from the use of glucose in oxidative phosphorylation to its use in aerobic glycolysis in tumors (61). These latter two mechanisms would not likely be at play in the increased rates of uncoupler-stimulated respiration that we observed.
Past studies of PKCδ signaling to mitochondria have used kinase-dead constructs of PKCδ and pharmacological inhibition with rottlerin to attempt to establish the need for catalytic activity. Some studies have even used Gö6976 as a PKCδ inhibitor (28, 29), whereas Gö6976 is actually a conventional-selective PKC inhibitor that does not inhibit novel PKCs even at micromolar concentrations (62). Our data and others in the literature show rottlerin not to be a PKCδ-specific inhibitor, with its effects being attributable to its role as a mitochondrial uncoupler (45, 46). We have also found that kinase-dead constructs of PKCδ, especially the K376R mutant used predominantly in the literature, are not fully primed by phosphorylations (data not shown) and therefore may not be properly folded and competent for activation. This study uses the more reliable pharmacological tools of Gö6983 and BisIV as general PKC inhibitors (Fig. 4) and the chemical genetics approach of a gatekeeper mutant of PKCδ shown by our data to be specifically inhibited by NaPP1 (Fig. 5). Furthermore, live cell FRET imaging is a more sensitive and informative technique for evaluating molecular interactions than biochemical techniques such as pulldowns, fractionations, and immunofluorescence because it can detect and quantify transient, low affinity, dynamic interactions in real time and in a more physiological cellular context and can be used to determine the kinetics of an interaction.
Although this study was performed in a simplified system that employed overexpression of PKCδ and primarily phorbol ester stimulation, the mechanisms revealed by this study should be generalizable to more physiological systems. First, PKCδ overexpression was ∼4-fold that of endogenous PKCδ levels in transfected COS-7 cells by Western blot analysis (data not shown). Second, PKCδ is basally localized to mitochondria via many of the same determinants that drive its phorbol ester-stimulated translocation. Third, unstimulated PKCδ overexpression increases mitochondrial respiration, and mutation of any of the structural elements that play a role in the phorbol ester-induced interaction of PKCδ with mitochondria abolishes this basal effect, with some mutations even further reducing respiration. Fourth, stimulation of myocytes with insulin, a physiological agonist, produces the same isozyme-specific interaction of PKCδ with mitochondria.
Our data support a model in which multiple determinants unique to PKCδ, involving its C2, C1A, and C1B domains, critical residues in its activation loop and turn motif, its kinase activity, and the mitochondrial membrane potential, contribute to a specific interaction with the outer membrane of mitochondria, where PKCδ is active, thereby regulating mitochondrial respiration (Fig. 10). Given the noncanonical nature of the interaction between PKCδ and the mitochondrial outer membrane and the participation of multiple determinants unique to PKCδ, we speculate that one or more protein scaffolds at the mitochondria mediate this isoform-specific interaction.
Supplementary Material
This work was supported, in whole or in part, by National Institutes of Health Grants GM43154 (to A. C. N.) and P01 DK054441 (to A. C. N. and A. N. M.).

This article contains supplemental Fig. S1.
- DAG
- diacylglycerol
- CKAR
- C kinase activity reporter
- δCKAR
- PKCδ-specific CKAR
- PDHC
- pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
- PDBu
- phorbol-12,13-dibutyrate
- BisIV
- bisindolylmaleimide IV
- NaPP1
- 4-amino-1-tert-butyl-3-(1′-naphthyl)-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine
- FCCP
- carbonyl cyanide-4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenylhydrazone
- RFP
- red fluorescent protein
- CFP
- cyan fluorescent protein
- YFP
- yellow fluorescent protein
- TOM20
- translocase of the outer membrane 20
- Mito-
- mitochondrially targeted
- PM
- plasma membrane
- OCR
- oxygen consumption rate
- RF
- regulatory fragment
- CF
- catalytic fragment.
REFERENCES
- 1. Newton A. C. (2010) Protein kinase C. Poised to signal. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol Metab. 298, E395–E402 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Griner E. M., Kazanietz M. G. (2007) Protein kinase C and other diacylglycerol effectors in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 7, 281–294 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Steinberg S. F. (2008) Structural basis of protein kinase C isoform function. Physiol. Rev. 88, 1341–1378 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Reyland M. E. (2009) Protein kinase C isoforms. Multi-functional regulators of cell life and death. Front. Biosci. 14, 2386–2399 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Rosse C., Linch M., Kermorgant S., Cameron A. J., Boeckeler K., Parker P. J. (2010) PKC and the control of localized signal dynamics. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 11, 103–112 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Giorgione J. R., Lin J. H., McCammon J. A., Newton A. C. (2006) Increased membrane affinity of the C1 domain of protein kinase Cδ compensates for the lack of involvement of its C2 domain in membrane recruitment. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 1660–1669 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Dries D. R., Gallegos L. L., Newton A. C. (2007) A single residue in the C1 domain sensitizes novel protein kinase C isoforms to cellular diacylglycerol production. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 826–830 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Benes C. H., Wu N., Elia A. E., Dharia T., Cantley L. C., Soltoff S. P. (2005) The C2 domain of PKCδ is a phosphotyrosine binding domain. Cell 121, 271–280 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Adwan T. S., Ohm A. M., Jones D. N., Humphries M. J., Reyland M. E. (2011) Regulated binding of importin-α to protein kinase Cδ in response to apoptotic signals facilitates nuclear import. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 35716–35724 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Blass M., Kronfeld I., Kazimirsky G., Blumberg P. M., Brodie C. (2002) Tyrosine phosphorylation of protein kinase Cδ is essential for its apoptotic effect in response to etoposide. Mol. Cell. Biol. 22, 182–195 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Humphries M. J., Ohm A. M., Schaack J., Adwan T. S., Reyland M. E. (2008) Tyrosine phosphorylation regulates nuclear translocation of PKCδ. Oncogene 27, 3045–3053 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Cameron A. J., De Rycker M., Calleja V., Alcor D., Kjaer S., Kostelecky B., Saurin A., Faisal A., Laguerre M., Hemmings B. A., McDonald N., Larijani B., Parker P. J. (2007) Protein kinases, from B to C. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 35, 1013–1017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Ikenoue T., Inoki K., Yang Q., Zhou X., Guan K. L. (2008) Essential function of TORC2 in PKC and Akt turn motif phosphorylation, maturation and signalling. EMBO J. 27, 1919–1931 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Gallegos L. L., Newton A. C. (2008) Spatiotemporal dynamics of lipid signaling. Protein kinase C as a paradigm. IUBMB Life 60, 782–789 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Miyamoto A., Nakayama K., Imaki H., Hirose S., Jiang Y., Abe M., Tsukiyama T., Nagahama H., Ohno S., Hatakeyama S., Nakayama K. I. (2002) Increased proliferation of B cells and auto-immunity in mice lacking protein kinase Cδ. Nature 416, 865–869 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Leitges M., Mayr M., Braun U., Mayr U., Li C., Pfister G., Ghaffari-Tabrizi N., Baier G., Hu Y., Xu Q. (2001) Exacerbated vein graft arteriosclerosis in protein kinase Cδ-null mice. J. Clin. Invest. 108, 1505–1512 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Humphries M. J., Limesand K. H., Schneider J. C., Nakayama K. I., Anderson S. M., Reyland M. E. (2006) Suppression of apoptosis in the protein kinase Cδ null mouse in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 9728–9737 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Basu A., Woolard M. D., Johnson C. L. (2001) Involvement of protein kinase C-δ in DNA damage-induced apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 8, 899–908 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Denning M. F., Wang Y., Tibudan S., Alkan S., Nickoloff B. J., Qin J. Z. (2002) Caspase activation and disruption of mitochondrial membrane potential during UV radiation-induced apoptosis of human keratinocytes requires activation of protein kinase C. Cell Death Differ. 9, 40–52 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Basu A. (2003) Involvement of protein kinase C-δ in DNA damage-induced apoptosis. J. Cell Mol. Med. 7, 341–350 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Matassa A. A., Carpenter L., Biden T. J., Humphries M. J., Reyland M. E. (2001) PKCδ is required for mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis in salivary epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 29719–29728 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Majumder P. K., Pandey P., Sun X., Cheng K., Datta R., Saxena S., Kharbanda S., Kufe D. (2000) Mitochondrial translocation of protein kinase C δ in phorbol ester-induced cytochrome c release and apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 21793–21796 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Li L., Lorenzo P. S., Bogi K., Blumberg P. M., Yuspa S. H. (1999) Protein kinase Cδ targets mitochondria, alters mitochondrial membrane potential, and induces apoptosis in normal and neoplastic keratinocytes when overexpressed by an adenoviral vector. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19, 8547–8558 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Mayr M., Chung Y. L., Mayr U., McGregor E., Troy H., Baier G., Leitges M., Dunn M. J., Griffiths J. R., Xu Q. (2004) Loss of PKC-δ alters cardiac metabolism. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 287, H937–H945 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Mayr M., Metzler B., Chung Y. L., McGregor E., Mayr U., Troy H., Hu Y., Leitges M., Pachinger O., Griffiths J. R., Dunn M. J., Xu Q. (2004) Ischemic preconditioning exaggerates cardiac damage in PKC-δ null mice. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 287, H946–H956 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Mayr M., Siow R., Chung Y. L., Mayr U., Griffiths J. R., Xu Q. (2004) Proteomic and metabolomic analysis of vascular smooth muscle cells. Role of PKCδ. Circ. Res. 94, e87–e96 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Caruso M., Maitan M. A., Bifulco G., Miele C., Vigliotta G., Oriente F., Formisano P., Beguinot F. (2001) Activation and mitochondrial translocation of protein kinase Cδ are necessary for insulin stimulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex activity in muscle and liver cells. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 45088–45097 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Acin-Perez R., Hoyos B., Gong J., Vinogradov V., Fischman D. A., Leitges M., Borhan B., Starkov A., Manfredi G., Hammerling U. (2010) Regulation of intermediary metabolism by the PKCδ signalosome in mitochondria. FASEB J. 24, 5033–5042 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Acin-Perez R., Hoyos B., Zhao F., Vinogradov V., Fischman D. A., Harris R. A., Leitges M., Wongsiriroj N., Blaner W. S., Manfredi G., Hammerling U. (2010) Control of oxidative phosphorylation by vitamin A illuminates a fundamental role in mitochondrial energy homoeostasis. FASEB J. 24, 627–636 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Gong J., Hoyos B., Acin-Perez R., Vinogradov V., Shabrova E., Zhao F., Leitges M., Fischman D., Manfredi G., Hammerling U. (2012) Two protein kinase C isoforms, δ and ϵ, regulate energy homeostasis in mitochondria by transmitting opposing signals to the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. FASEB J. 26, 3537–3549 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Gallegos L. L., Kunkel M. T., Newton A. C. (2006) Targeting protein kinase C activity reporter to discrete intracellular regions reveals spatiotemporal differences in agonist-dependent signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 30947–30956 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Kanaji S., Iwahashi J., Kida Y., Sakaguchi M., Mihara K. (2000) Characterization of the signal that directs Tom20 to the mitochondrial outer membrane. J. Cell Biol. 151, 277–288 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Sasaki K., Sato M., Umezawa Y. (2003) Fluorescent indicators for Akt/protein kinase B and dynamics of Akt activity visualized in living cells. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 30945–30951 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Kajimoto T., Sawamura S., Tohyama Y., Mori Y., Newton A. C. (2010) Protein kinase Cδ-specific activity reporter reveals agonist-evoked nuclear activity controlled by Src family of kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 41896–41910 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Violin J. D., Zhang J., Tsien R. Y., Newton A. C. (2003) A genetically encoded fluorescent reporter reveals oscillatory phosphorylation by protein kinase C. J. Cell Biol. 161, 899–909 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Violin J. D., Newton A. C. (2003) Pathway illuminated. Visualizing protein kinase C signaling. IUBMB Life 55, 653–660 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Sossin W. S. (2007) Isoform specificity of protein kinase Cs in synaptic plasticity. Learn Mem. 14, 236–246 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Baier G., Telford D., Giampa L., Coggeshall K. M., Baier-Bitterlich G., Isakov N., Altman A. (1993) Molecular cloning and characterization of PKC theta, a novel member of the protein kinase C (PKC) gene family expressed predominantly in hematopoietic cells. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 4997–5004 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Osada S., Mizuno K., Saido T. C., Suzuki K., Kuroki T., Ohno S. (1992) A new member of the protein kinase C family, nPKC theta, predominantly expressed in skeletal muscle. Mol. Cell. Biol. 12, 3930–3938 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Pu Y., Garfield S. H., Kedei N., Blumberg P. M. (2009) Characterization of the differential roles of the twin C1a and C1b domains of protein kinase C-δ. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 1302–1312 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Hoshi N., Langeberg L. K., Gould C. M., Newton A. C., Scott J. D. (2010) Interaction with AKAP79 modifies the cellular pharmacology of PKC. Mol. Cell 37, 541–550 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Shah K., Liu Y., Deirmengian C., Shokat K. M. (1997) Engineering unnatural nucleotide specificity for Rous sarcoma virus tyrosine kinase to uniquely label its direct substrates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 94, 3565–3570 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Liu Y., Shah K., Yang F., Witucki L., Shokat K. M. (1998) Engineering Src family protein kinases with unnatural nucleotide specificity. Chem Biol. 5, 91–101 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Bishop A. C., Shah K., Liu Y., Witucki L., Kung C., Shokat K. M. (1998) Design of allele-specific inhibitors to probe protein kinase signaling. Curr. Biol. 8, 257–266 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Soltoff S. P. (2001) Rottlerin is a mitochondrial uncoupler that decreases cellular ATP levels and indirectly blocks protein kinase Cδ tyrosine phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 37986–37992 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Soltoff S. P. (2007) Rottlerin. An inappropriate and ineffective inhibitor of PKCδ. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 28, 453–458 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Stempka L., Schnölzer M., Radke S., Rincke G., Marks F., Gschwendt M. (1999) Requirements of protein kinase Cδ for catalytic function. Role of glutamic acid 500 and autophosphorylation on serine 643. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 8886–8892 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Liu Y., Belkina N. V., Graham C., Shaw S. (2006) Independence of protein kinase C-δ activity from activation loop phosphorylation. Structural basis and altered functions in cells. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 12102–12111 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Le Good J. A., Ziegler W. H., Parekh D. B., Alessi D. R., Cohen P., Parker P. J. (1998) Protein kinase C isotypes controlled by phosphoinositide 3-kinase through the protein kinase PDK1. Science 281, 2042–2045 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Rybin V. O., Guo J., Gertsberg Z., Elouardighi H., Steinberg S. F. (2007) Protein kinase Cepsilon (PKCϵ) and Src control PKCδ activation loop phosphorylation in cardiomyocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 23631–23638 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Konishi H., Yamauchi E., Taniguchi H., Yamamoto T., Matsuzaki H., Takemura Y., Ohmae K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. (2001) Phosphorylation sites of protein kinase C δ in H2O2-treated cells and its activation by tyrosine kinase in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 98, 6587–6592 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Kaul S., Anantharam V., Yang Y., Choi C. J., Kanthasamy A., Kanthasamy A. G. (2005) Tyrosine phosphorylation regulates the proteolytic activation of protein kinase Cδ in dopaminergic neuronal cells. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 28721–28730 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Rybin V. O., Guo J., Sabri A., Elouardighi H., Schaefer E., Steinberg S. F. (2004) Stimulus-specific differences in protein kinase C δ localization and activation mechanisms in cardiomyocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 19350–19361 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Tran P. L., Deugnier M. A. (1985) Intracellular localization of 12-O-3-N-dansylamino TPA in C3H/10T1/2 mouse cell line. Carcinogenesis 6, 433–439 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Kazanietz M. G., Barchi J. J., Jr., Omichinski J. G., Blumberg P. M. (1995) Low affinity binding of phorbol esters to protein kinase C and its recombinant cysteine-rich region in the absence of phospholipids. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 14679–14684 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Slater S. J., Ho C., Stubbs C. D. (2002) The use of fluorescent phorbol esters in studies of protein kinase C-membrane interactions. Chem Phys Lipids 116, 75–91 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Colón-González F., Kazanietz M. G. (2006) C1 domains exposed. From diacylglycerol binding to protein-protein interactions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1761, 827–837 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Sato T., O'Rourke B., Marbán E. (1998) Modulation of mitochondrial ATP-dependent K+ channels by protein kinase C. Circ. Res. 83, 110–114 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Nguyen T., Ogbi M., Johnson J. A. (2008) δ protein kinase C interacts with the D subunit of the F1F0 ATPase in neonatal cardiac myocytes exposed to hypoxia or phorbol ester. Implications for F1F0 ATPase regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 29831–29840 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Siwko S., Mochly-Rosen D. (2007) Use of a novel method to find substrates of protein kinase C δ identifies M2 pyruvate kinase. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 39, 978–987 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Christofk H. R., Vander Heiden M. G., Harris M. H., Ramanathan A., Gerszten R. E., Wei R., Fleming M. D., Schreiber S. L., Cantley L. C. (2008) The M2 splice isoform of pyruvate kinase is important for cancer metabolism and tumour growth. Nature 452, 230–233 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Martiny-Baron G., Kazanietz M. G., Mischak H., Blumberg P. M., Kochs G., Hug H., Marmé D., Schächtele C. (1993) Selective inhibition of protein kinase C isozymes by the indolocarbazole Gö 6976. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 9194–9197 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.