Abstract
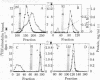
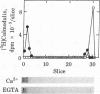
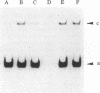
A calmodulin-binding protein called "caldesmon" was purified from chicken gizzard muscle as the major calmodulin-binding protein in this tissue. Its molecular weight estimated by sodium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis was 150,000, and two of these polypeptides constituted the native molecule. Caldesmon is an actin-binding protein also, binding F-actin reversibly in the presence or absence of Ca2+. The interaction of caldesmon with F-actin was abolished by the binding of calmodulin with the caldesmon. Because the interaction between caldesmon and calmodulin was Ca2+-dependent but the interaction between caldesmon and F-actin was not, Ca2+ acts as a flip-flop switch between the formations of two complexes, caldesmon.calmodulin and caldesmon.F-actin: increasing the formation of the former complex at increased Ca2+ level and the formation of the latter complex at decreased Ca2+ level. The equilibrium of the formations of both complexes was achieved at a Ca2+ concentration near 1 microM.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cheung W. Y. Cyclic 3',5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Demonstration of an activator. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Feb 6;38(3):533–538. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90747-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedman J. R., Welsh M. J., Means A. R. Ca2+-dependent regulator. Production and characterization of a monospecific antibody. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7515–7521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Bretscher A., Weber K. Calcium control of the intestinal microvillus cytoskeleton: its implications for the regulation of microfilament organizations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6458–6462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Weber K. Calmodulin-binding proteins of the microfilaments present in isolated brush borders and microvilli of intestinal epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10551–10554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grand R. J., Perry S. V. Calmodulin-binding proteins from brain and other tissues. Biochem J. 1979 Nov 1;183(2):285–295. doi: 10.1042/bj1830285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grand R. J., Perry S. V. The binding of calmodulin to myelin basic protein and histone H2B. Biochem J. 1980 Aug 1;189(2):227–240. doi: 10.1042/bj1890227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa T., Takahashi S., Hayashi H., Hatano S. Fragmin: a calcium ion sensitive regulatory factor on the formation of actin filaments. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 10;19(12):2677–2683. doi: 10.1021/bi00553a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe C. L., Mooseker M. S., Graves T. A. Brush-border calmodulin. A major component of the isolated microvillus core. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):916–923. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itano T., Itano R., Penniston J. T. Interactions of basic polypeptides and proteins with calmodulin. Biochem J. 1980 Sep 1;189(3):455–459. doi: 10.1042/bj1890455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakiuchi S., Sobue K., Yamazaki R., Nagao S., Umeki S., Nozawa Y., Yazawa M., Yagi K. Ca2+-dependent modulator proteins from Tetrahymena pyriformis, sea anemone, and scallop and guanylate cyclase activation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):19–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakiuchi S., Yamazaki R. Calcium dependent phosphodiesterase activity and its activating factor (PAF) from brain studies on cyclic 3',5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase (3). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Dec 9;41(5):1104–1110. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90199-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B., Crouch T. H., Krinks M. H. Calcineurin: a calcium- and calmodulin-binding protein of the nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6270–6273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B., Krinks M. H. Purification of cyclic 3',5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase inhibitory protein by affinity chromatography on activator protein coupled to Sepharose. Biochemistry. 1978 Jan 10;17(1):120–126. doi: 10.1021/bi00594a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. T., Burgess D. R. Identification and organization of the components in the isolated microvillus cytoskeleton. J Cell Biol. 1979 Dec;83(3):667–673. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.3.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maékawa S., Abe T. Isolation of a new calmodulin-binding protein from rat brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Nov 28;97(2):621–627. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90309-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Means A. R., Dedman J. R. Calmodulin--an intracellular calcium receptor. Nature. 1980 May 8;285(5760):73–77. doi: 10.1038/285073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mimura N., Asano A. Ca2+-sensitive gelation of actin filaments by a new protein factor. Nature. 1979 Nov 1;282(5734):44–48. doi: 10.1038/282044a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma R. K., Desai R., Thompson T. R., Wang J. H. Purification of the heat-stable inhibitor protein of the Ca2+-activated cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase by affinity chromatography. Can J Biochem. 1978 Jun;56(6):598–604. doi: 10.1139/o78-090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma R. K., Desai R., Waisman D. M., Wang J. H. Purification and subunit structure of bovine brain modulator binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):4276–4282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobue K., Muramoto Y., Yamazaki R., Kakiuchi S. Distribution in rat tissues of modulator-binding protein of particulate nature. Studies with 3H-modulator protein. FEBS Lett. 1979 Sep 1;105(1):105–109. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80896-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Watt S. The regulation of rabbit skeletal muscle contraction. I. Biochemical studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin and the proteolytic fragments of myosin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4866–4871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teo T. S., Wang J. H. Mechanism of activation of a cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate phosphodiesterase from bovine heart by calcium ions. Identification of the protein activator as a Ca2+ binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 10;248(17):5950–5955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watterson D. M., Sharief F., Vanaman T. C. The complete amino acid sequence of the Ca2+-dependent modulator protein (calmodulin) of bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):962–975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi K., Yazawa M., Kakiuchi S., Ohshima M., Uenishi K. Identification of an activator protein for myosin light chain kinase as the Ca2+-dependent modulator protein. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 10;253(5):1338–1340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin H. L., Stossel T. P. Control of cytoplasmic actin gel-sol transformation by gelsolin, a calcium-dependent regulatory protein. Nature. 1979 Oct 18;281(5732):583–586. doi: 10.1038/281583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]