Abstract
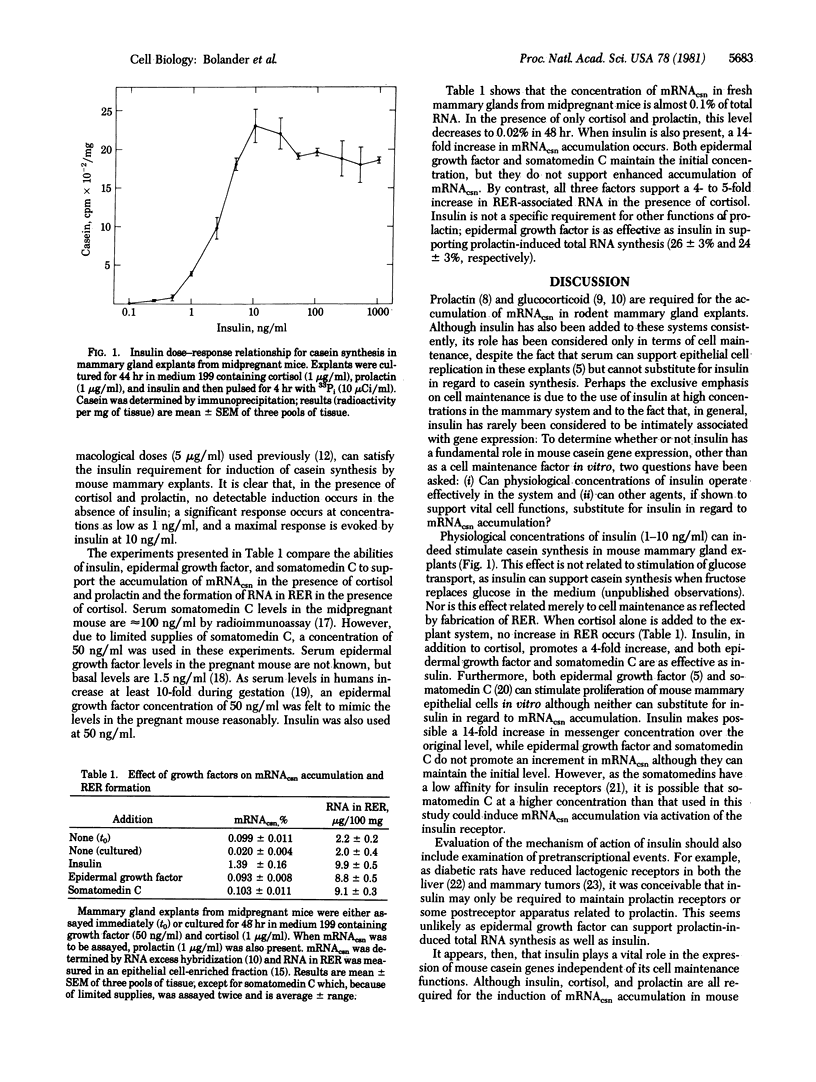
In the presence of cortisol and prolactin, insulin at concentrations as low as 1 ng/ml significantly stimulates casein synthesis in mammary explants from midpregnant mice; maximal synthesis occurs at 10 ng/ml. However, in the absence of insulin, no detectable immunoprecipitable casein is produced. Insulin also supports enhanced accumulation of casein mRNA in the presence of cortisol and prolactin; neither epidermal growth factor nor somatomedin C has this effect. These inductive actions of insulin are not secondary to a general maintenance effect on the mammary epithelial cell; insulin, epidermal growth factor, and somatomedin C can support the accumulation of RNA in rough endoplasmic reticulum equally well. In addition, these effects do not reflect a specific insulin requirement for prolactin sensitivity; epidermal growth factor can support prolactin-induced total RNA synthesis as well as insulin can. The results demonstrate that, although insulin, epidermal growth factor, and somatomedin C can all function as cell maintenance agents, only insulin, together with cortisol and prolactin, can induce casein mRNA accumulation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ances I. G. Serum concentrations of epidermal growth factor in human pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1973 Feb 1;115(3):357–362. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(73)90591-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C., Turtle J. R. Regulation of hepatic growth hormone receptors by insulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Sep 29;84(2):350–357. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90177-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Savage C. R., Jr Recent studies on the chemistry and biology of epidermal growth factor. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1974;30(0):551–574. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571130-2.50018-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ercole A. J., Underwood L. E. Ontogeny of somatomedin during development in the mouse. Serum concentrations, molecular forms, binding proteins, and tissue receptors. Dev Biol. 1980 Sep;79(1):33–45. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90071-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devinoy E., Houdebine L. M., Delouis C. Role of prolactin and glucocorticoids in the expression of casein genes in rabbit mammary gland organ culture. Quantification of casein mRNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 16;517(2):360–366. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(78)90202-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. I., Hager L. J., McKnight G. S. A somatomedin-like peptide hormone is required during the estrogen-mediated induction of ovalbumin gene transcription. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):187–193. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90243-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaffney E. V., Polanowski F. P., Blackburn S. E., Lambiase J. T., Burke R. E. Cultures of normal human mammary cells. Cell Differ. 1976 Jul;5(2):69–81. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(76)90001-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganguly R., Ganguly N., Mehta N. M., Banerjee M. R. Absolute requirement of glucocorticoid for expression of the casein gene in the presence of prolactin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6003–6006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Topper Y. J. Some effects of prolactin, insulin and hydrocortisone on RNA synthesis by mouse mammary gland, in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Apr 15;204(2):441–448. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90164-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. E., Lee K. L., Kenney F. T. Effects of insulin on messenger RNA activities in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1510–1513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juergens W. G., Stockdale F. E., Topper Y. J., Elias J. J. Hormone-dependent differentiation of mammary gland in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Aug;54(2):629–634. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.2.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G. L., Kahn C. R., Rechler M. M., Nissley S. P. Direct demonstration of separate receptors for growth and metabolic activities of insulin and multiplication-stimulating activity (an insulinlike growth factor) using antibodies to the insulin receptor. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jul;66(1):130–140. doi: 10.1172/JCI109826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korc M., Owerbach D., Quinto C., Rutter W. J. Pancreatic islet-acinar cell interaction: amylase messenger RNA levels ar determined by insulin. Science. 1981 Jul 17;213(4505):351–353. doi: 10.1126/science.6166044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majumder G. C., Turkington R. W. Stimulation of mammary epithelial cell proliferation in vitro by protein factor(s) present in serum. Endocrinology. 1971 Jun;88(6):1506–1510. doi: 10.1210/endo-88-6-1506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markoff E., Talamantes F. The lactogenic response of mouse mammary explants to mose prolactin and growth hormone. Endocr Res Commun. 1980;7(4):269–278. doi: 10.3109/07435808009065978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matusik R. J., Rosen J. M. Prolactin induction of casein mRNA in organ culture. A model system for studying peptide hormone regulation of gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2343–2347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstone L. M., Piatigorsky J. delta-Crystallin gene expression in embryonic chick lens epithelia cultured in the presence of insulin. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Mar 1;105(1):9–14. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90147-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagaiah K., Bolander F. F., Jr, Nicholas K. R., Takemoto T., Topper Y. J. Prolactin-induced accumulation of casein mRNA in mouse mammary explants: a selective role of glucocorticoid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Jan 30;98(2):380–387. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90851-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka T., Topper Y. J. Hormone-dependent accumulation of rough endoplasmic reticulum in mouse mammary epithelial cells in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 25;246(24):7701–7707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono M., Oka T. The differential actions of cortisol on the accumulation of alpha-lactalbumin and casein in midpregnant mouse mammary gland in culture. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):473–480. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90522-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. D., Hilf R., Senior A. E. Prolactin binding to dissociated cells from rat mammary tumors and mammary gland. Cancer Biochem Biophys. 1979;3(3):117–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J., Klapper D. G., Fellows R. E., Grissom F. E., Schlueter R. J. Purification of somatomedin-C from human plasma: chemical and biological properties, partial sequence analysis, and relationship to other somatomedins. Biochemistry. 1980 Feb 19;19(4):790–797. doi: 10.1021/bi00545a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemoto T., Nagamatsu Y., Oka T. Casein and alpha-lactalbumin messenger RNAs during the development of mouse mammary gland. Isolation, partial purification, and translation in a cell-free system. Dev Biol. 1980 Aug;78(2):247–257. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90334-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomkins G. M., Thompson E. B., Hayashi S., Gelehrter T., Granner D., Peterkofsky B. Tyrosine transaminase induction in mammalian cells in tissue culture. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1966;31:349–360. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1966.031.01.045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turkington R. W. Induction of milk protein synthesis by placental lactogen and prolactin in vitro. Endocrinology. 1968 Mar;82(3):575–583. doi: 10.1210/endo-82-3-575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turkington R. W., Juergens W. G., Topper Y. J. Steroid structural requirements for mammary gland differentiation in vitro. Endocrinology. 1967 Jun;80(6):1139–1142. doi: 10.1210/endo-80-6-1139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turkington R. W. The role of epithelial growth factor in mammary gland development in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1969 Sep;57(1):79–85. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(69)90369-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D. Y., Hallowes R. C., Smith R. H., Amor V., Lewis D. J. A biochemical comparison of the lactogenic effect of prolactin and growth hormone on mouse mammary gland in organ culture. J Endocrinol. 1972 Feb;52(2):349–358. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0520349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


