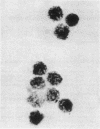
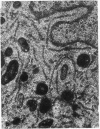
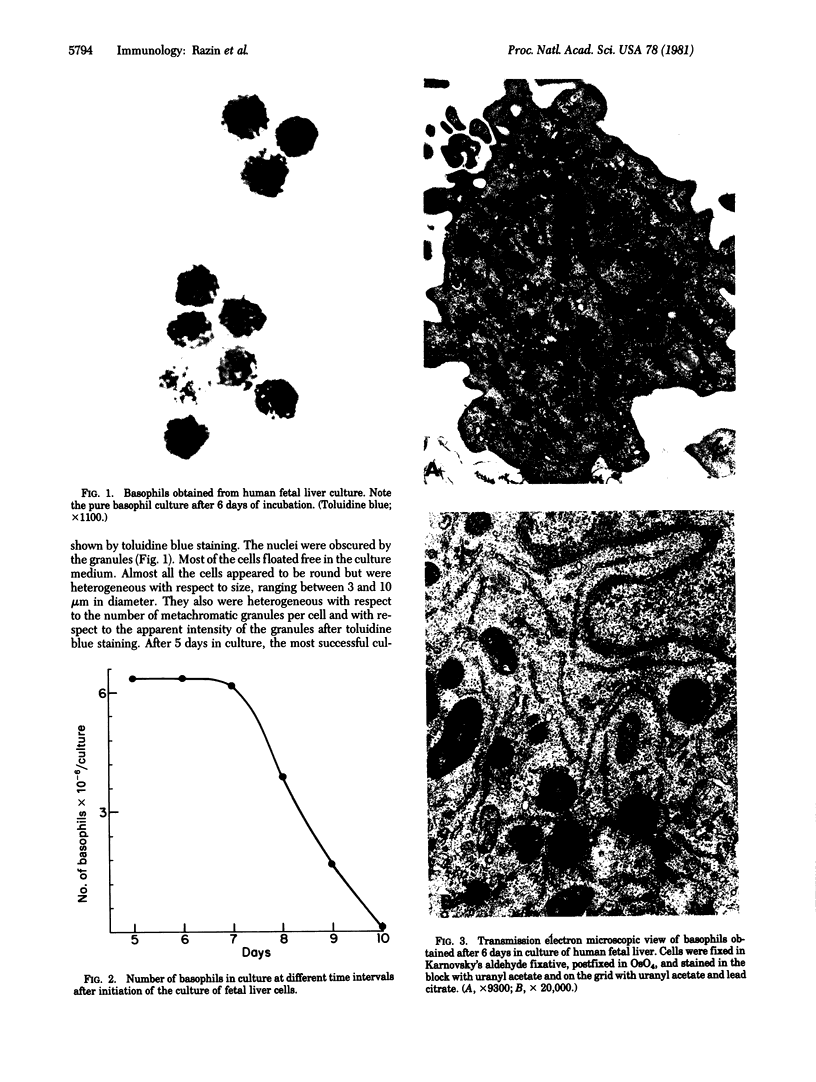
Abstract
An initially homogeneous population of basophilic polymorphonuclear leukocytes was derived from human fetal liver cells grown in culture for 5-7 days. The cells were characterized as basophils by their morphology, histologic staining characteristics, and histamine content, and by the presence of IgE receptors on their surface. In this culture system the basophils were viable for up to 10 days.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anton A. H., Sayre D. F. A modified fluorometric procedure for tissue histamine and its distribution in various animals. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1969 Apr;166(2):285–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breton-Gorius J., Reyes F. Ultrastructure of human bone marrow cell maturation. Int Rev Cytol. 1976;46:251–321. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60993-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka K., Ishizaka T. Identification of gamma-E-antibodies as a carrier of reaginic activity. J Immunol. 1967 Dec;99(6):1187–1198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Adachi T., Chang T-H, Ishizaka K. Development of mast cells in vitro. II. Biologic function of cultured mast cells. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):211–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Tomioka H., Ishizaka K. Degranulation of human basophil leukocytes by anti-gamma E antibody. J Immunol. 1971 Mar;106(3):705–710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura Y., Hatanaka K., Murakami M., Shibata H. Presence of mast cell precursors in peripheral blood of mice demonstrated by parabiosis. Blood. 1979 Jun;53(6):1085–1088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin E., Cordon-Cardo C., Good R. A. Growth of a pure population of mouse mast cells in vitro with conditioned medium derived from concanavalin A-stimulated splenocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2559–2561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrader J. W., Lewis S. J., Clark-Lewis I., Culvenor J. G. The persisting (P) cell: histamine content, regulation by a T cell-derived factor, origin from a bone marrow precursor, and relationship to mast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):323–327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker-Franklin D. Ultrastructural evidence for the common origin of human mast cells and basophils. Blood. 1980 Sep;56(3):534–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]