Abstract
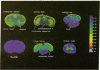
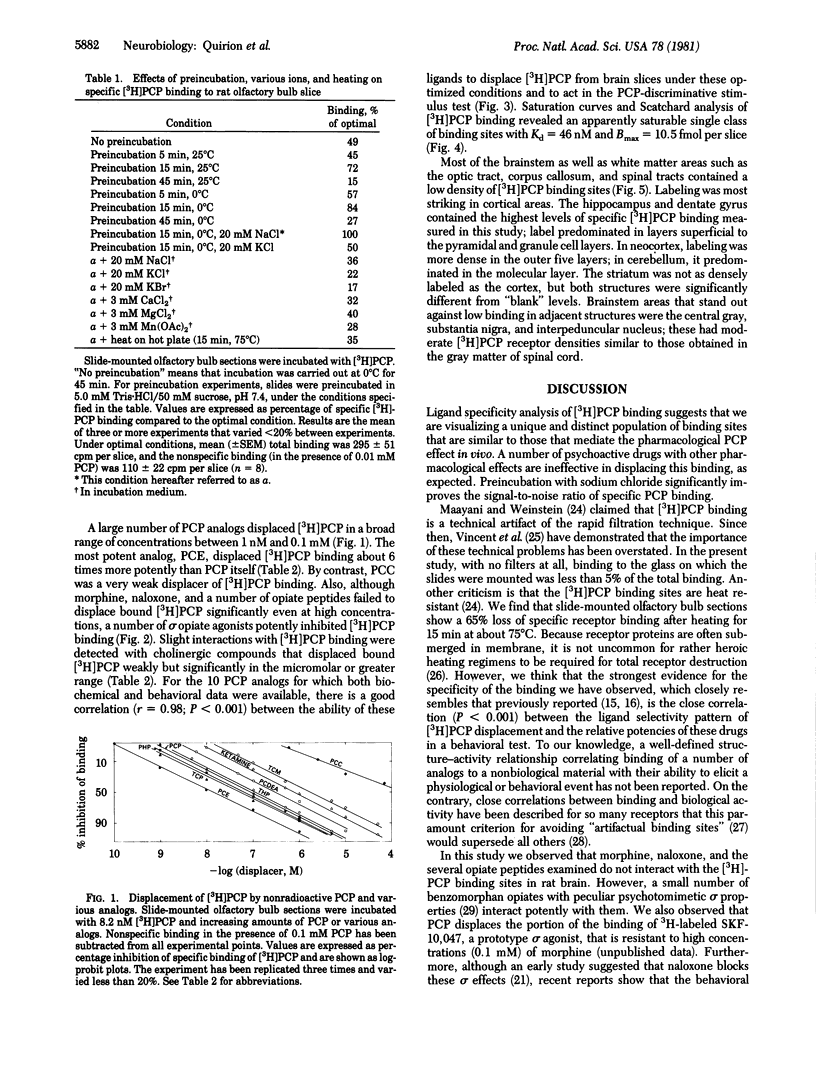
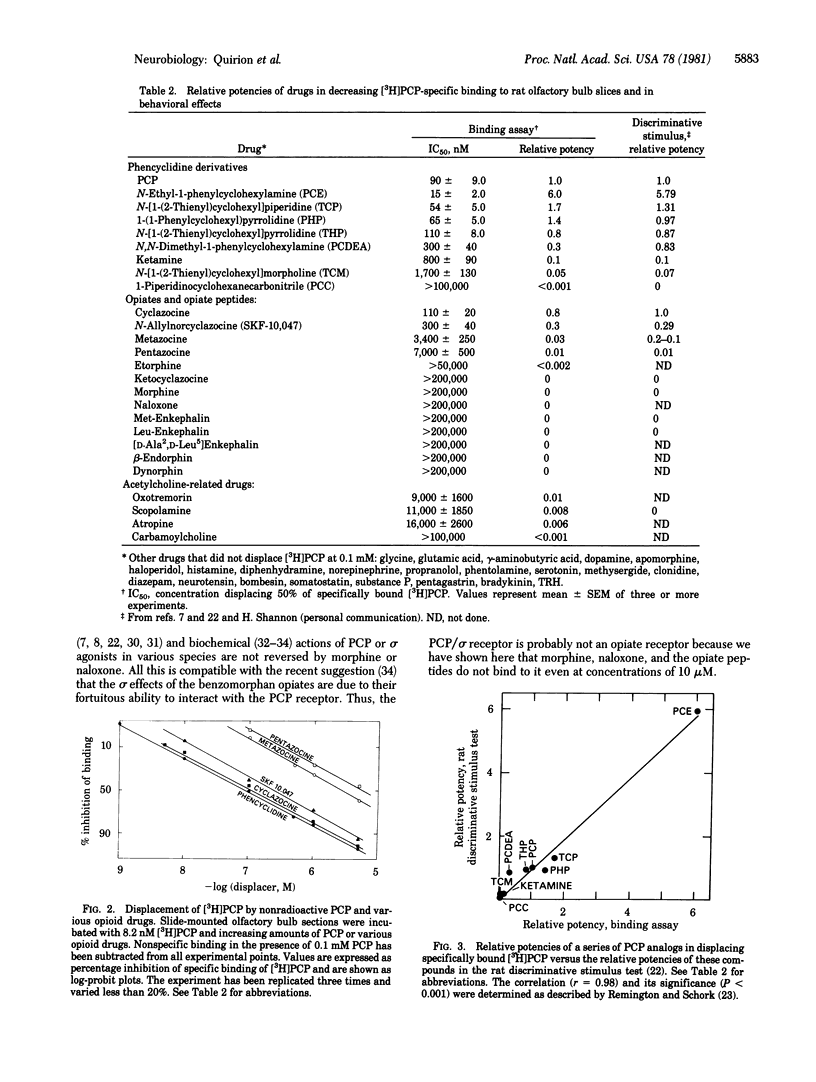
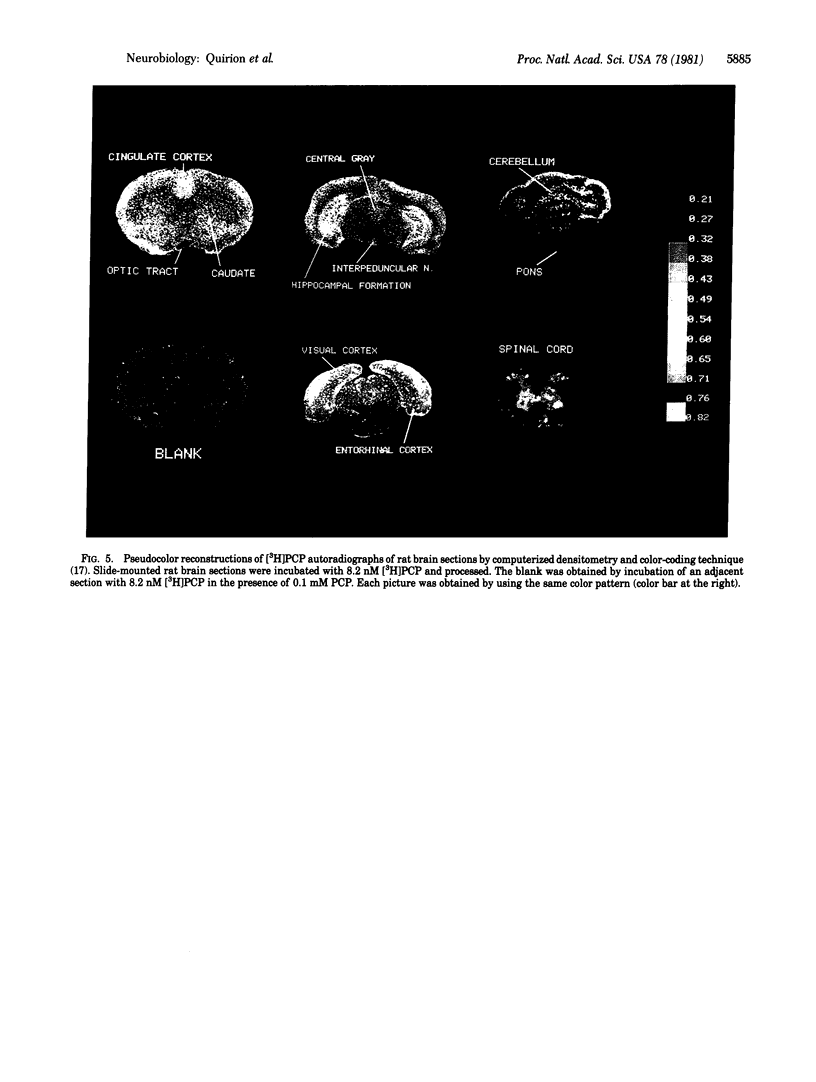
[3H]Phencyclidine ([3H]PCP) binds specifically to an apparently single class of binding sites on slide-mounted sections of rat olfactory bulb (Kd = 46 nM; Bmax = 10.5 fmol per slice). Bound [3H]PCP can be displaced by nonradioactive PCP and a series of its analogs with relative potencies that correlate closely (P less than 0.001) with values determined in a rat discrimination test that utilized PCP as a cue. Although morphine, naloxone, and opiate peptides do not displace bound [3H]PCP, psychotomimetic benzomorphans, classed as "sigma opiates," are quite potent displacers in vitro and have PCP-like behavioral properties in vivo. These results suggest that phencyclidine and the sigma opiates act at the same sites. [3H]PCP binding sites were visualized by using tritium-sensitive LKB film analyzed by computerized densitometry and color coding. The [3H]PCP binds most densely to cortical areas, diffusely in neocortex, and somewhat heterogeneously in the laminae of the hippocampal formation and dentate gyrus. Most of the brainstem and spinal cord show low specific [3H]PCP binding, with gray matter generally showing more binding than white.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albuquerque E. X., Tsai M. C., Aronstam R. S., Eldefrawi A. T., Eldefrawi M. E. Sites of action of phencyclidine. II. Interaction with the ionic channel of the nicotinic receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1980 Sep;18(2):167–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albuquerque E. X., Tsai M. C., Aronstam R. S., Witkop B., Eldefrawi A. T., Eldefrawi M. E. Phencyclidine interactions with the ionic channel of the acetylcholine receptor and electrogenic membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1224–1228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronstam R. S., Eldefrawi M. E., Eldefrawi A. T., Albuquerque E. X., Jim K. F., Triggle D. J. Sites of action of phencyclidine. III. Interactions with muscarinic receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1980 Sep;18(2):179–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayub Khan Yousufi M., Thomas J. W., Tallman J. F. Solubilization of benzodiazepine binding site from rat cortex. Life Sci. 1979 Jul 30;25(5):463–469. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90580-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen W. D., Gentleman S., Herkenham M., Pert C. B. Interconverting mu and delta forms of the opiate receptor in rat striatal patches. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4818–4822. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEN G., ENSOR C. R., RUSSELL D., BOHNER B. The pharmacology of 1-(1-phenylcyclohexyl) piperidine-HCl. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1959 Nov;127:241–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. J., Hazum E., Cuatrecasas P. Possible role of distinct morphine and enkephalin receptors in mediating actins of benzomorphan drugs (putative kappa and sigma agonists). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4469–4473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty J. D., Simonovic M., So R., Meltzer H. Y. The effect of phencyclidine on dopamine synthesis and metabolic in rat striatum. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Jul 25;65(2-3):139–149. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90386-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goochee C., Rasband W., Sokoloff L. Computerized densitometry and color coding of [14C] deoxyglucose autoradiographs. Ann Neurol. 1980 Apr;7(4):359–370. doi: 10.1002/ana.410070414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtzman S. G. Phencyclidine-like discriminative effects of opioids in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Sep;214(3):614–619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSTONE M., EVANS V., BAIGEL S. Sernyl (CI-395) in clinical anaesthesia. Br J Anaesth. 1959 Oct;31:433–439. doi: 10.1093/bja/31.10.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maayani S., Weinstein H. "Specific binding" of 3H-phencyclidine: artifacts of the rapid filtration method. Life Sci. 1980 Jun 9;26(23):2011–2022. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90634-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maayani S., Weinstein H., Ben-Zvi N., Cohen S., Sokolovsky M. Psychotomimetics as anticholinergic agents. I. 1-Cyclohexylpiperidine derivatives: anticholinesterase activity and antagonistic activity to acetylcholine. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 Apr 15;23(8):1263–1281. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90330-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. R., Berman M. H., Krewsun I., Small S. F. Phencyclidine-induced stereotyped behavior and serotonergic syndrome in rat. Life Sci. 1979 Apr 30;24(18):1699–1703. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90255-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. R., Eades C. G., Thompson J. A., Huppler R. E., Gilbert P. E. The effects of morphine- and nalorphine- like drugs in the nondependent and morphine-dependent chronic spinal dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Jun;197(3):517–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marwaha J., Palmer M. R., Woodward D. J., Hoffer B. J., Freedman R. Electrophysiological evidence for presynaptic actions of phencyclidine on noradrenergic transmission in rat cerebellum. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Dec;215(3):606–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearlson G. D. Psychiatric and medical syndromes associated with phencyclidine (PCP) abuse. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1981 Jan;148(1):25–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rainey J. M., Jr, Crowder M. K. Letter: Ketamine or phencyclidine. JAMA. 1974 Nov 11;230(6):824–824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon H. E. Evaluation of phencyclidine analogs on the basis of their discriminative stimulus properties in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Mar;216(3):543–551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H. Phencyclidine. Nature. 1980 Jun 5;285(5764):355–356. doi: 10.1038/285355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai M. C., Albuquerque E. X., Aronstam R. S., Eldefrawi A. T., Eldefrawi M. E., Triggle D. J. Sites of action of phencyclidine. I. Effects on the electrical excitability and chemosensitive properties of the neuromuscular junction of skeletal muscle. Mol Pharmacol. 1980 Sep;18(2):159–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent J. P., Cavey D., Kamenka J. M., Geneste P., Lazdunski M. Interaction of phencyclidines with the muscarinic and opiate receptors in the central nervous system. Brain Res. 1978 Aug 18;152(1):176–182. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90145-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent J. P., Kartalovski B., Geneste P., Kamenka J. M., Lazdunski M. Interaction of phencyclidine ("angel dust") with a specific receptor in rat brain membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4678–4682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent J. P., Vignon J., Kartalovski B., Lazdunski M. Binding of phencyclidine to rat brain membranes: technical aspect. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Nov 7;68(1):73–77. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90064-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood P. L., Stotland M., Richard J. W., Rackham A. Actions of mu, kappa, sigma, delta and agonist/antagonist opiates on striatal dopaminergic function. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Dec;215(3):697–703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zukin S. R., Zukin R. S. Specific [3H]phencyclidine binding in rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5372–5376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]