Abstract
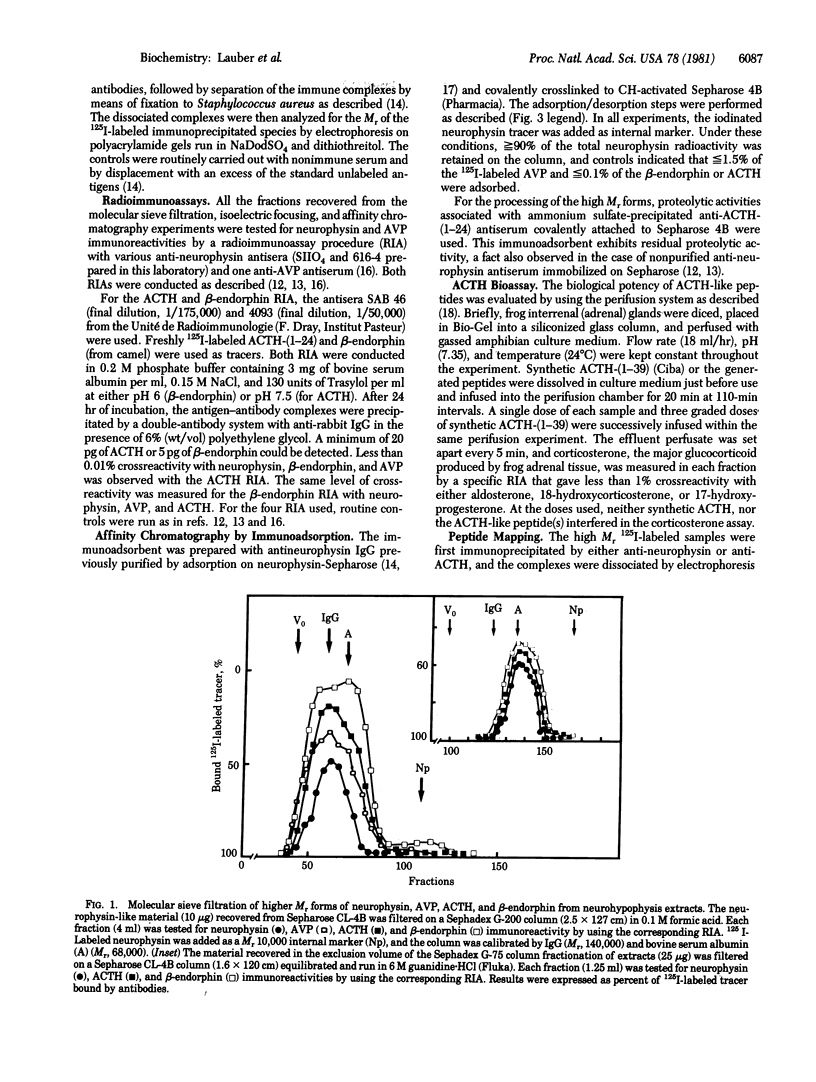
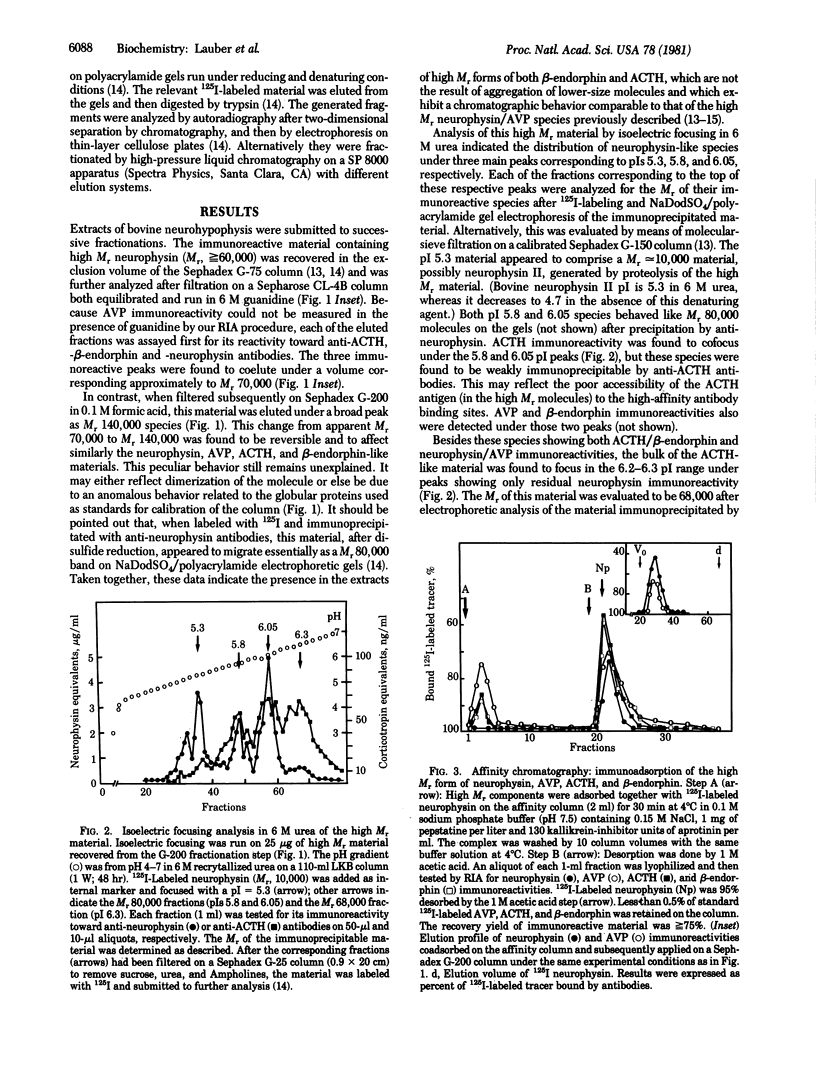
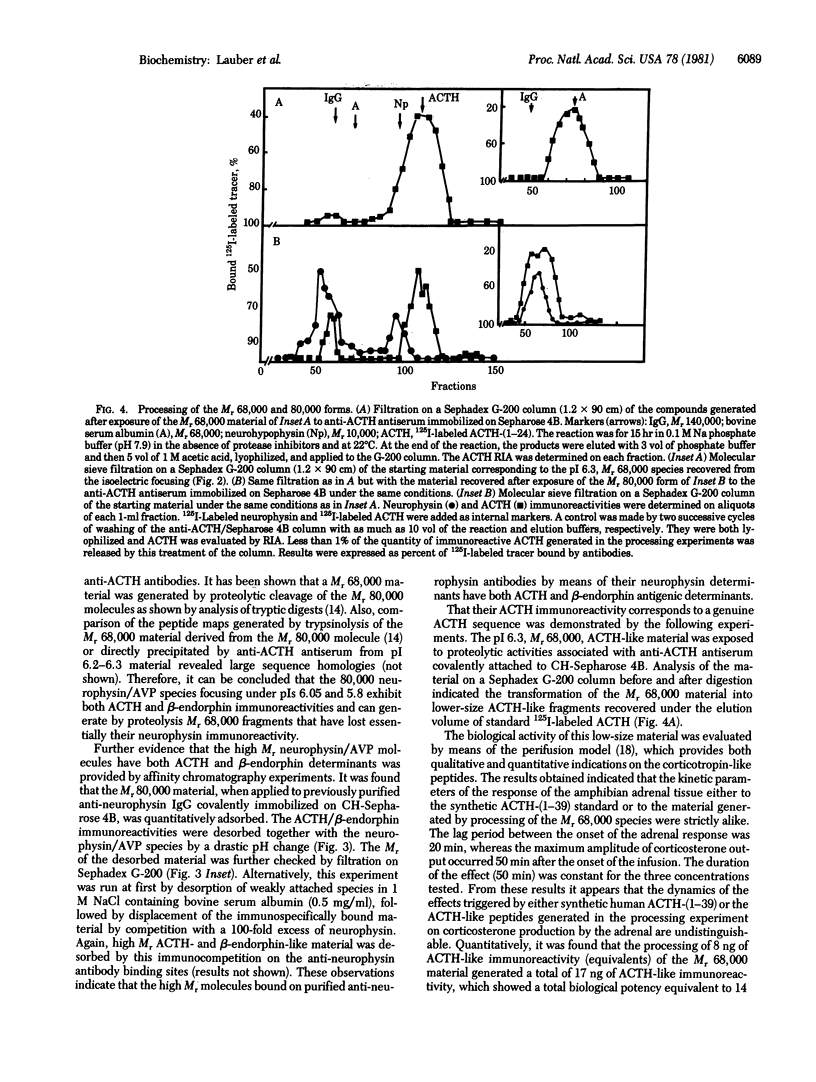
We have tested the hypothesis that the high Mr forms common to both neurophysin and vasopressin detected in bovine neurohypophysis extracts (Nicolas, P., Camier, M., Lauber, M., Masse, M.-J. O., Möhring, J. & Cohen, P. (1980) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77, 2587-2591) might also contain the sequences of other known neuropeptides. The following evidence indicates that corticotropin- and β-endorphin-like sequences are associated with similar high Mr forms and are included in these Mr 80,000 molecules. During the fractionation steps of high Mr material, both corticotropin and β-endorphin immunoreactive species were found to coelute with the neurophysin and vasopressin ones, either under Mr 140,000 (in 0.1 M formic acid) or Mr 70,000-80,000 (in 6 M guanidine) elution volumes. Corticotropin immunoreactivity was found to cofocus at pIs 6.05 and 5.8 with the Mr 80,000 neurophysin-containing species. This material was submitted to affinity chromatography on purified anti-neurophysin antibodies covalently attached to Sepharose 4B. Both the corticotropin and β-endorphin immunoreactivities, together with the neurophysin and vasopressin immunoreactivities, were retained on the immunoadsorbent and codesorbed by either a drastic pH change or by selective displacement with an excess of neurophysin. Comparison of the tryptic-digest maps of either the Mr 68,000 fragment immunoprecipitated by anti-corticotropin antibodies or the Mr 68,000 fragment released after precipitation of the Mr 80,000 species by anti-neurophysin antibodies indicated large sequence homologies. Exposure of either the Mr 80,000 or 68,000 components to mild proteolytic activities resulted in the formation of lower-size fragments. The resulting corticotropin-like immunoreactive material, recovered under the elution volume of standard 125I-labeled corticotropin-(1-24), was tested for its ability to activate glucocorticoid biogenesis by the amphibian interrenal tissue (adrenal) in perifusion. It was found to exhibit a noticeable activity qualitatively undistinguishable from the one of the reference human corticotropin-(1-39). The name neurohypophyseal “coenophorin” (from the Greek word for common) is proposed for this class of Mr 80,000 polypeptides that might represent the common precursor store-house for a set of neuropeptides produced in the hypothalamo-neurohypophyseal tract.
Keywords: prohormones, precursors, hypothalamus, radioimmunoassay, affinity chromatography
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnea A., Cho G., Pilotte N. S., Porter J. C. Regional differences in the molecular weight profiles of corticotropin and alpha-melanotropin the hypothalamus. Endocrinology. 1981 Jan;108(1):150–156. doi: 10.1210/endo-108-1-150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaumont A., Fuentes J. A., Hughes H., Metters K. M. Opioid peptide precursors in striatum. FEBS Lett. 1980 Dec 15;122(1):135–137. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80420-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownstein M. J., Gainer H. Neurophysin biosynthesis in normal rats and in rats with hereditary diabetes insipidus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):4046–4049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.4046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camier M., Lauber M., Möhring J., Cohen P. Evidence for higher molecular weight immunoreactive forms of vasopressin in the mouse hypothalamus. Relationships with putative proneurophysins. FEBS Lett. 1979 Dec 15;108(2):369–373. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80566-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrétien M., Benjannet S., Gossard F., Gianoulakis C., Crine P., Lis M., Seidah N. G. From beta-lipotropin to beta-endorphin and 'pro-opio-melanocortin'. Can J Biochem. 1979 Sep;57(9):1111–1121. doi: 10.1139/o79-143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gainer H., Sarne Y., Brownstein M. J. Neurophysin biosynthesis: conversion of a putative precursor during axonal transport. Science. 1977 Mar 25;195(4284):1354–1356. doi: 10.1126/science.65791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giudice L. C., Chaiken I. M. Immunological and chemical identification of a neurophysin-containing protein coded by messenger RNA from bovine hypothalamus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3800–3804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieger D. T., Liotta A., Suda T., Palkovits M., Brownstein M. J. Presence of immunoassayable beta-lipotropin in bovine brain and spinal cord: lack of concordance with ACTH concentrations. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jun 6;76(3):930–936. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91591-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauber M., Camier M., Cohen P. Immunological and biochemical characterization of distinct high molecular weight forms of neurophysin and somatostatin in mouse hypothalamus extracts. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jan 15;97(2):343–347. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80118-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leboulenger F., Delarue C., Tonon M. C., Jegou S., Vaudry H. In vitro study of frog (Rana radibunda Pallas) interrenal function by use of a simplified perifusion system. I. Influence of adrenocorticotropin upon corticosterone release. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1978 Nov;36(3):327–338. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(78)90114-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C., Joseph-Bravo P., Sherman T., Chan L., McKelvy J. F. Cell-free synthesis of putative neurophysin precursors from rat and mouse hypothalamic poly (A)-RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Aug 13;89(3):943–950. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91869-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mains R. E., Eipper B. A., Ling N. Common precursor to corticotropins and endorphins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):3014–3018. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.3014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R., Voigt K. H. Enkephalins co-exist with oxytocin and vasopressin in nerve terminals of rat neurohypophysis. Nature. 1981 Feb 5;289(5797):502–504. doi: 10.1038/289502a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moldow R., Yalow R. S. Extrahypophysial distribution of corticotropin as a function of brain size. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):994–998. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möhring B., Möhring J. Plasma ADH in normal Long-Evans rats and in Long-Evans rats heterozygous and homozygous for hypothalamic diabetes insipidus. Life Sci. 1975 Oct 15;17(8):1307–1314. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90143-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi S., Inoue A., Kita T., Nakamura M., Chang A. C., Cohen S. N., Numa S. Nucleotide sequence of cloned cDNA for bovine corticotropin-beta-lipotropin precursor. Nature. 1979 Mar 29;278(5703):423–427. doi: 10.1038/278423a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolas P., Camier M., Lauber M., Masse M. J., Möhring J., Cohen P. Immunological identification of high molecular weight forms common to bovine neurophysin and vasopressin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2587–2591. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pradelles P., Morgat J. L., Fromageot P., Camier M., Bonne D., Cohen P., Bockaert J., Jard S. Tritium labelling of 8-lysine vasopressin and its purification by affinity chromatography on sepharose bound neurophysins. FEBS Lett. 1972 Oct 1;26(1):189–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80570-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. L., Herbert E. Characterization of a common precursor to corticotropin and beta-lipotropin: identification of beta-lipotropin peptides and their arrangement relative to corticotropin in the precursor synthesized in a cell-free system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5300–5304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmale H., Richter D. Immunological identification of a common precursor to arginine vasopressin and neurophysin II synthesized by in vitro translation of bovine hypothalamic mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):766–769. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



