Abstract
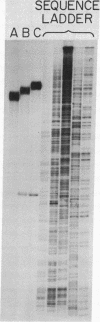
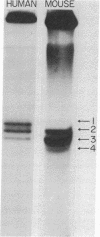
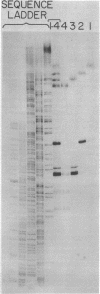
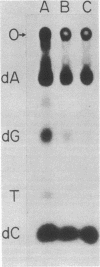
Animal mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) maintains a displacement loop (D loop) at the heavy strand origin of replication. These D loops represent sharply limited synthesis of heavy strands and provide a unique opportunity to examine the termination of DNA synthesis. Direct sizing at the nucleotide level indicates that the 3' ends of D-loop strands of human and mouse mtDNA are discrete and map within three to five nucleotides on the complementary template strand. In the case of human mtDNA, there is a single trinucleotide stop point 51-53 nucleotides downstream from a 15-nucleotide template sequence (3'T-A-A-C-C-C-A-A-A-A-A-T-A-C-A 5') which is repeated four times in the mouse mtDNA D-loop region 3'(T-A-A-Py-Py-A-A-A-T-T-A-C-A 5'). The stop points of the five major mouse D-loop strands are 24-63 nucleotides downstream from the four repeated template sequences. These results suggest that the arrest of D-loop strand elongation is an event determined by template sequence.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S., Bankier A. T., Barrell B. G., de Bruijn M. H., Coulson A. R., Drouin J., Eperon I. C., Nierlich D. P., Roe B. A., Sanger F. Sequence and organization of the human mitochondrial genome. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):457–465. doi: 10.1038/290457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battey J., Clayton D. A. The transcription map of human mitochondrial DNA implicates transfer RNA excision as a major processing event. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11599–11606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Clayton D. A. Mechanism of mitochondrial DNA replication in mouse L-cells: asynchronous replication of strands, segregation of circular daughter molecules, aspects of topology and turnover of an initiation sequence. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jul 15;86(4):801–824. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90355-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D., Clayton D. A. Mechanism of mitochondrial DNA replication in mouse L-cells: kinetics of synthesis and turnover of the initiation sequence. J Mol Biol. 1978 Feb 15;119(1):49–68. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90269-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D., Clayton D. A. The number of mitochondrial deoxyribonucleic acid genomes in mouse L and human HeLa cells. Quantitative isolation of mitochondrial deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 25;249(24):7991–7995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. M., Shine J., Goodman H. M. Human mitochondrial DNA: analysis of 7S DNA from the origin of replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):735–739. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichler D. C., Wang T. S., Clayton D. A., Korn D. In vitro replication of mitochondrial DNA. Elongation of the endogenous primer sequence in D loop mitochondrial DNA by human DNA polymerase beta. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7888–7893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillum A. M., Clayton D. A. Displacement-loop replication initiation sequence in animal mitochondrial DNA exists as a family of discrete lengths. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):677–681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillum A. M., Clayton D. A. Mechanism of mitochondrial DNA replication in mouse L-cells: RNA priming during the initiation of heavy-strand synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1979 Dec 5;135(2):353–368. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90441-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasamatsu H., Robberson D. L., Vinograd J. A novel closed-circular mitochondrial DNA with properties of a replicating intermediate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2252–2257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapper D. P., Clayton D. A. Mechanism of replication of human mitochondrial DNA. Localization of the 5' ends of nascent daughter strands. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):5109–5115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tu C. P., Cohen S. N. 3'-end labeling of DNA with [alpha-32P]cordycepin-5'-triphosphate. Gene. 1980 Jul;10(2):177–183. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90135-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Etten R. A., Walberg M. W., Clayton D. A. Precise localization and nucleotide sequence of the two mouse mitochondrial rRNA genes and three immediately adjacent novel tRNA genes. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):157–170. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90164-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]