Abstract
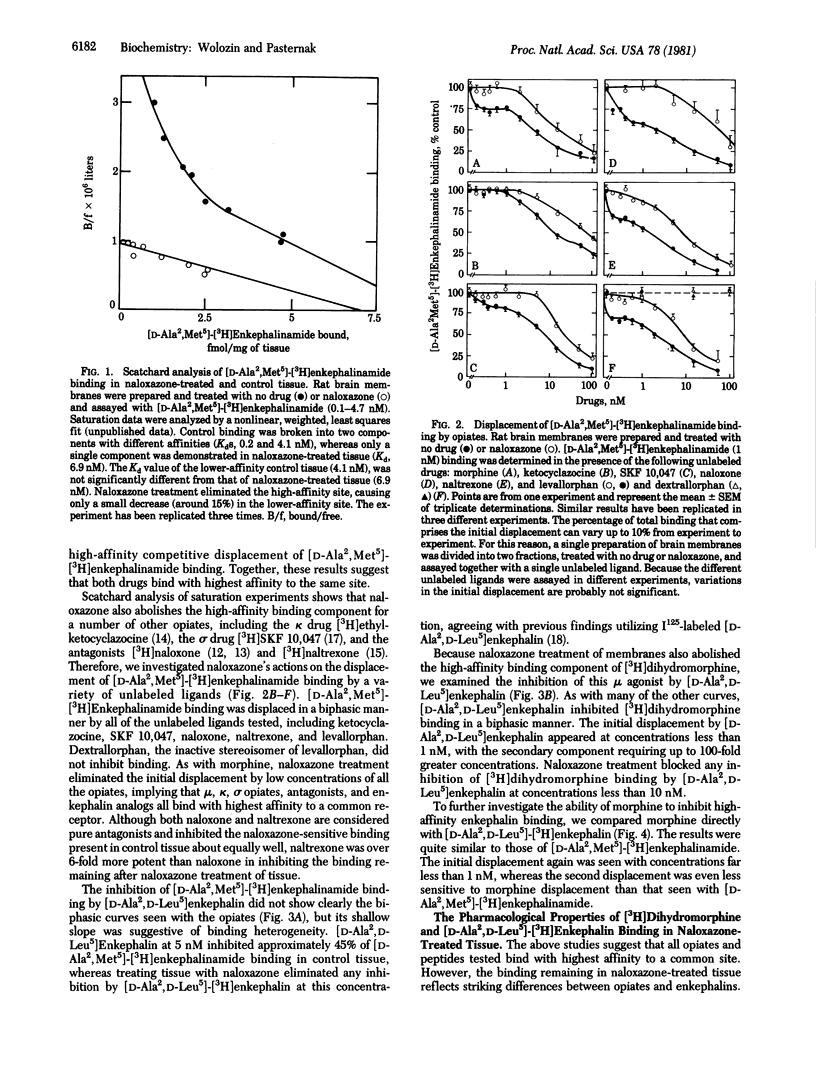
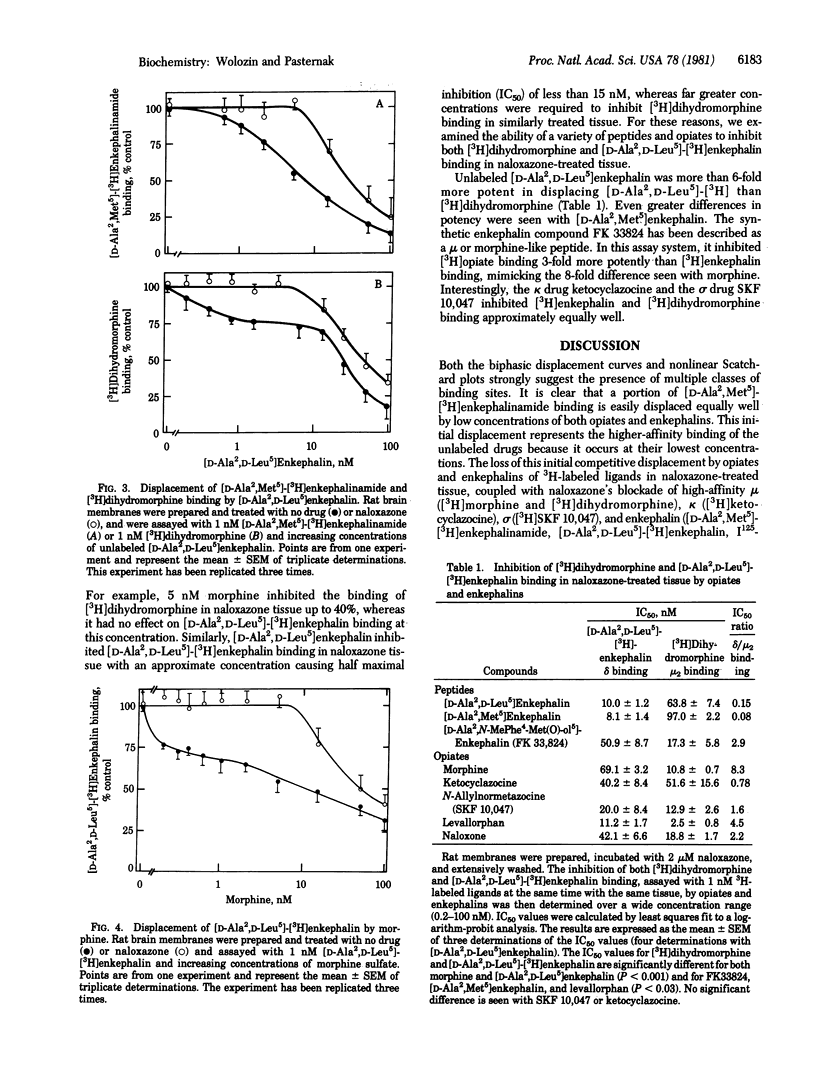
Detailed competitive displacement curves of 3H-labeled [D-Ala2,Met5]enkephalinamide, [D-Ala2,D-Leu5]enkephalin, and dihydromorphine by a series of opiates and enkephalins are biphasic, suggesting multiple sites. After treatment of tissue with naloxazone, the displacement of the three 3H-labeled ligands by all opiates and enkephalins tested becomes monophasic, losing the high-affinity displacement seen with low concentrations of both opiates and enkephalins. Coupled with Scatchard analysis of saturation experiments, these findings suggest a common site that binds both opiates and enkephalins equally well and with highest affinity (Kd values, less than 1 nM). Termed the mu 1 site, it corresponds to the previously described high-affinity site and appears to be the site responsible for analgesia under normal circumstances. The low-affinity binding of [3H]dihydromorphine (Kd, 3 nM) remaining after naloxazone treatment differs dramatically from low-affinity [D-Ala2,D-Leu5]-[3H]enkephalin binding (Kd, 5 nM). The mu 2 site, corresponding to the low-affinity [3H]dihydromorphine receptor sites, binds morphine (Ki, 10 nM) and dihydromorphine (Kd, 3 nM) far better than [D-Ala2,D-Leu5]enkephalin (Ki, 50 nM). Low-affinity [D-Ala2,D-Leu5]-[3H]enkephalin receptor sites bind [D-Ala2,D-Leu5]enkephalin (Ki, 5-8 nM) more potently than morphine (Ki, 71 nM) and correspond to the previously established delta receptor.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buatti M. C., Pasternak G. W. Multiple opiate receptors: phylogenetic differences. Brain Res. 1981 Aug 10;218(1-2):400–405. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)91319-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. J., Cooper B. R., Hazum E., Cuatrecasas P. Multiple opiate receptors: different regional distribution in the brain and differential binding of opiates and opioid peptides. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Jul;16(1):91–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. J., Cuatrecasas P. Multiple opiate receptors. Enkephalins and morphine bind to receptors of different specificity. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2610–2618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. J., Hazum E., Cuatrecasas P. Possible role of distinct morphine and enkephalin receptors in mediating actins of benzomorphan drugs (putative kappa and sigma agonists). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4469–4473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazum E., Chang K. J., Cuatrecasas P., Pasternak G. W. Naloxazone irreversibly inhibits the high affinity binding of [125I]D-ala2-D-leu5-enkephalin. Life Sci. 1981 Jun 29;28(26):2973–2979. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90274-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. Isolation of an endogenous compound from the brain with pharmacological properties similar to morphine. Brain Res. 1975 May 2;88(2):295–308. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90391-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J., Smith T. W., Kosterlitz H. W., Fothergill L. A., Morgan B. A., Morris H. R. Identification of two related pentapeptides from the brain with potent opiate agonist activity. Nature. 1975 Dec 18;258(5536):577–580. doi: 10.1038/258577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord J. A., Waterfield A. A., Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W. Endogenous opioid peptides: multiple agonists and receptors. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):495–499. doi: 10.1038/267495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak G. W., Childers S. R., Snyder S. H. Naloxazone, a long-acting opiate antagonist: effects on analgesia in intact animals and on opiate receptor binding in vitro. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Sep;214(3):455–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak G. W., Childers S. R., Snyder S. H. Opiate analgesia: evidence for mediation by a subpopulation of opiate receptors. Science. 1980 May 2;208(4443):514–516. doi: 10.1126/science.6245448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak G. W., Goodman R., Snyder S. H. An endogenous morphine-like factor in mammalian brain. Life Sci. 1975 Jun 15;16(12):1765–1769. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90270-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak G. W., Hahn E. F. Long-acting opiate agonists and antagonists: 14-hydroxydihydromorphinone hydrazones. J Med Chem. 1980 Jun;23(6):674–676. doi: 10.1021/jm00180a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak G. W. Multiple opiate receptors: [3H]ethylketocyclazocine receptor binding and ketocyclazocine analgesia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3691–3694. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak G. W., Snyder S. H. Identification of novel high affinity opiate receptor binding in rat brain. Nature. 1975 Feb 13;253(5492):563–565. doi: 10.1038/253563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak G. W., Snyder S. H. Opiate receptor binding: effects of enzymatic treatments. Mol Pharmacol. 1974 Mar;10(2):183–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak G. W., Wilson H. A., Snyder S. H. Differential effects of protein-modifying reagents on receptor binding of opiate agonists and antagonists. Mol Pharmacol. 1975 May;11(3):340–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak G. W., Zhang A., Tecott L. Developmental differences between high and low affinity opiate binding sites: their relationship to analgesia and respiratory depression. Life Sci. 1980 Sep 29;27(13):1185–1190. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90470-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simantov R., Snyder S. H. Morphine-like peptides in mammalian brain: isolation, structure elucidation, and interactions with the opiate receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2515–2519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teschemacher H., Opheim K. E., Cox B. M., Goldstein A. A peptide-like substance from pituitary that acts like morphine. I. Isolation. Life Sci. 1975 Jun 15;16(12):1771–1775. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90271-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang A. Z., Chang J. K., Pasternak G. W. The actions of naloxazone on the binding and analgesic properties of morphiceptin (NH2Tyr-Pro-Phe-Pro-CONH2), a selective mu-receptor ligand. Life Sci. 1981 Jun 22;28(25):2829–2836. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90098-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang A. Z., Pasternak G. W. Ontogeny of opioid pharmacology and receptors: high and low affinity site differences. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jul 17;73(1):29–40. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90142-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang A. Z., Pasternak G. W. Opiates and enkephalins: a common binding site mediates their analgesic actions in rats. Life Sci. 1981 Aug 24;29(8):843–851. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90041-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang A. Z., Pasternak G. W. mu- and delta-opiate receptors: correlation with high and low affinity opiate binding sites. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Oct 17;67(2-3):323–324. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90518-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



