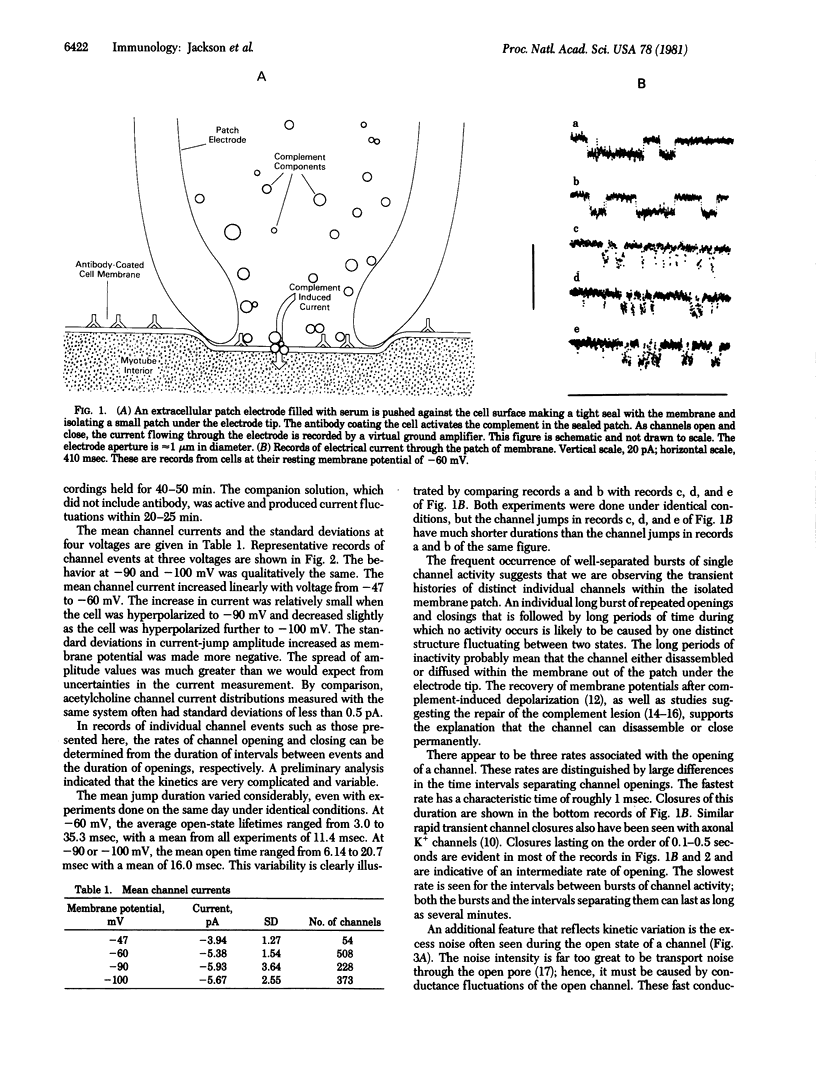
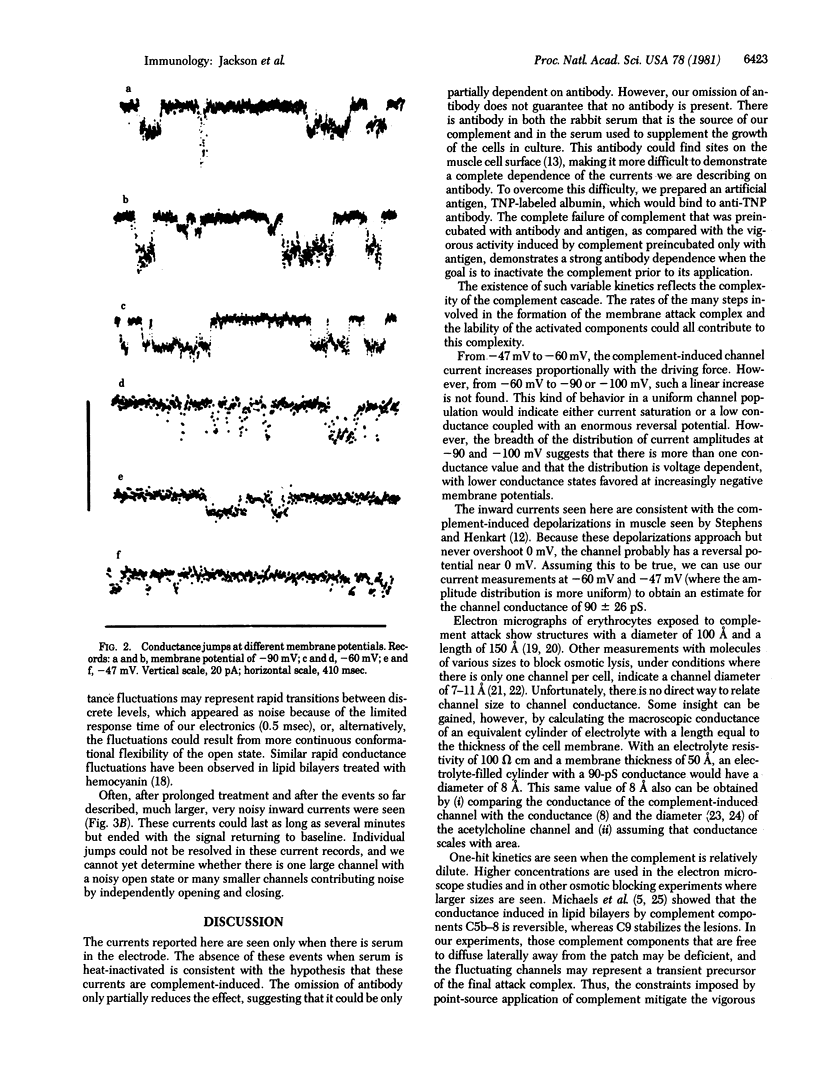
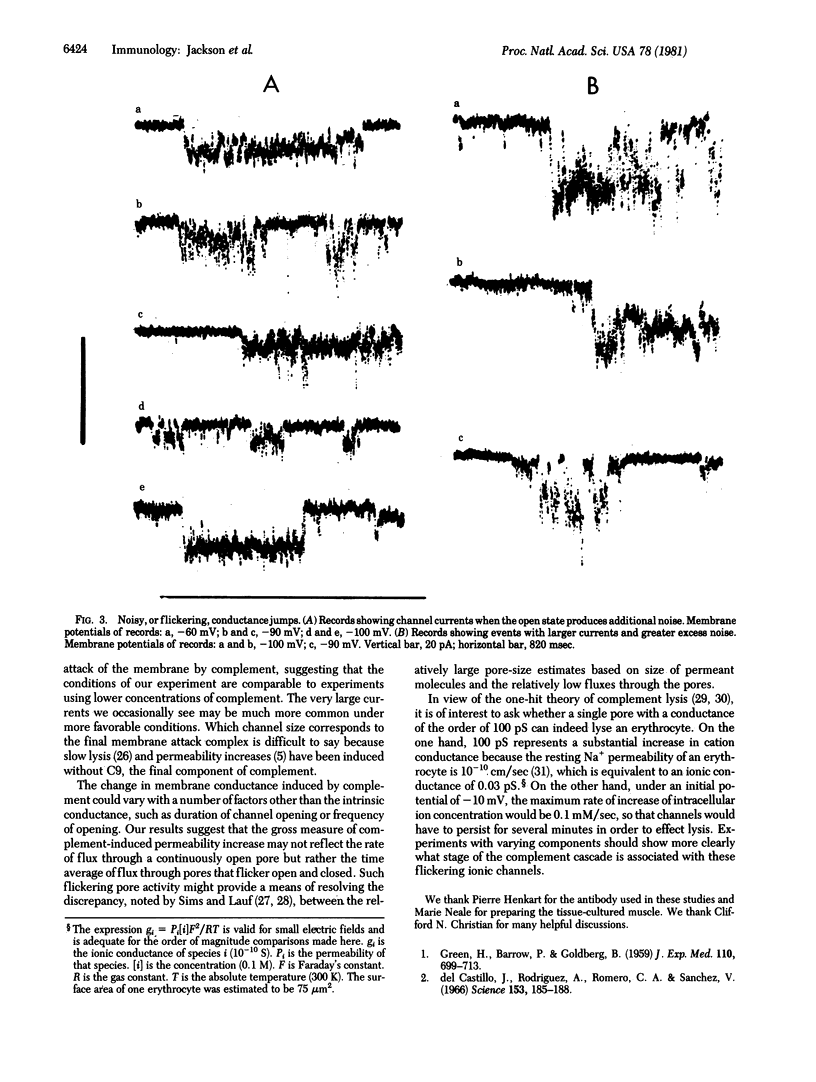
Abstract
An extracellular patch electrode was used to record ionic currents from individual complement-induced channels in the membranes of antibody-coated skeletal muscle. The amplitude of the single-channel currents leads to an estimate of 90 pS for the unit conductance. The kinetics of channel opening and closing show marked variability and complexity. Channels flicker open and closed repeatedly, indicating that once these lesions form, they undergo rapid structural transitions between discrete conducting and nonconducting states.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barfort P., Arquilla E. R., Vogelhut P. O. Resistance changes in lipid bilayers: immunological applications. Science. 1968 Jun 7;160(3832):1119–1121. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3832.1119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Molecular nature of the complement lesion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5655–5659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle M. D., Borsos T. The terminal stages of immune hemolysis--a brief review. Mol Immunol. 1980 Mar;17(3):425–432. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(80)90064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle M. D., Gee A. P., Borsos T. Studies on the terminal stages of immune hemolysis. VI. Osmotic blockers of differing Stokes' radii detect complement-induced transmembrane channels of differing size. J Immunol. 1979 Jul;123(1):77–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle M. D., Ohanian S. H., Borsos T. Lysis of tumor cells by antibody and complement. VII. Complement-dependent 86Rb release--a nonlethal event? J Immunol. 1976 Oct;117(4):1346–1350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burakoff S. J., Martz E., Benacerraf B. Is the primary complement lesion insufficient for lysis? Failure of cells damaged under osmotic protection to lyse in EDTA or at low temperature after removal of osmotic protection. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1975 May;4(1):108–126. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(75)90045-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti F., Neher E. Single channel recordings of K+ currents in squid axons. Nature. 1980 May 15;285(5761):140–143. doi: 10.1038/285140a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Castillo J., Rodriguez A., Romero C. A., Sanchez V. Lipid films as transducers for detection of antigen-antibody and enzyme-substrate reactions. Science. 1966 Jul 8;153(3732):185–188. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3732.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN H., BARROW P., GOLDBERG B. Effect of antibody and complement on permeability control in ascites tumor cells and erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1959 Nov 1;110:699–713. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.5.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L. Y., Catterall W. A., Ehrenstein G. Selectivity of cations and nonelectrolytes for acetylcholine-activated channels in cultured muscle cells. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Apr;71(4):397–410. doi: 10.1085/jgp.71.4.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey J. H., Dourmashkin R. R. The lesions in cell membranes caused by complement. Adv Immunol. 1969;11:75–115. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60478-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. B., Lecar H. Single postsynaptic channel currents in tissue cultured muscle. Nature. 1979 Dec 20;282(5741):863–864. doi: 10.1038/282863a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre R., Alvarez O., Ehrenstein G., Espinoza M., Reyes J. The nature of the voltage-dependent conductance of the hemocyanin channel. J Membr Biol. 1975 Dec 4;25(1-2):163–181. doi: 10.1007/BF01868573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Läuger P. Shot noise in ion channels. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Nov 17;413(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90053-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeno T., Edwards C., Anraku M. Permeability of the endplate membrane activated by acetylcholine to some organic cations. J Neurobiol. 1977 Mar;8(2):173–184. doi: 10.1002/neu.480080208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaels D. W., Abramovitz A. S., Hammer C. H., Mayer M. M. Increased ion permeability of planar lipid bilayer membranes after treatment with the C5b-9 cytolytic attack mechanism of complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2852–2856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Sakmann B. Single-channel currents recorded from membrane of denervated frog muscle fibres. Nature. 1976 Apr 29;260(5554):799–802. doi: 10.1038/260799a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Sakmann B., Steinbach J. H. The extracellular patch clamp: a method for resolving currents through individual open channels in biological membranes. Pflugers Arch. 1978 Jul 18;375(2):219–228. doi: 10.1007/BF00584247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. J., Sachs F. Single ionic channels observed in tissue-cultured muscle. Nature. 1979 Dec 20;282(5741):861–863. doi: 10.1038/282861a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramm L. E., Mayer M. M. Life-span and size of the trans-membrane channel formed by large doses of complement. J Immunol. 1980 May;124(5):2281–2287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommel F. A., Mayer M. M. Studies of guinea pig complement component C9: reaction kinetics and evidence that lysis of EAC1-8 results from a single membrane lesion caused by one molecule of C9. J Immunol. 1973 Mar;110(3):637–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigworth F. J., Neher E. Single Na+ channel currents observed in cultured rat muscle cells. Nature. 1980 Oct 2;287(5781):447–449. doi: 10.1038/287447a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims P. J., Lauf P. K. Analysis of solute diffusion across the C5b-9 membrane lesion of complement: evidence that individual C5b-9 complexes do not function as discrete, uniform pores. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2617–2625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims P. J. Permeability characteristics of complement-damaged membranes: evaluation of the membrane leak generated by the complement proteins C5b-9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1838–1842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens C. L., Henkart P. A. Electrical measurements of complement-mediated membrane damage in cultured nerve and muscle cells. J Immunol. 1979 Feb;122(2):455–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolfi R. L. Immune lytic transformation: a state of irreversible damage generated as a result of the reaction of the eighth component in the guinea pig complement system. J Immunol. 1968 Jan;100(1):46–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wobschall D., McKeon C. Step conductance increases in bilayer membranes induced by antibody-antigen-complement action. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Dec 1;413(2):317–321. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90117-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]