Abstract
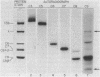
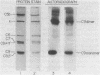
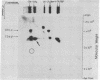
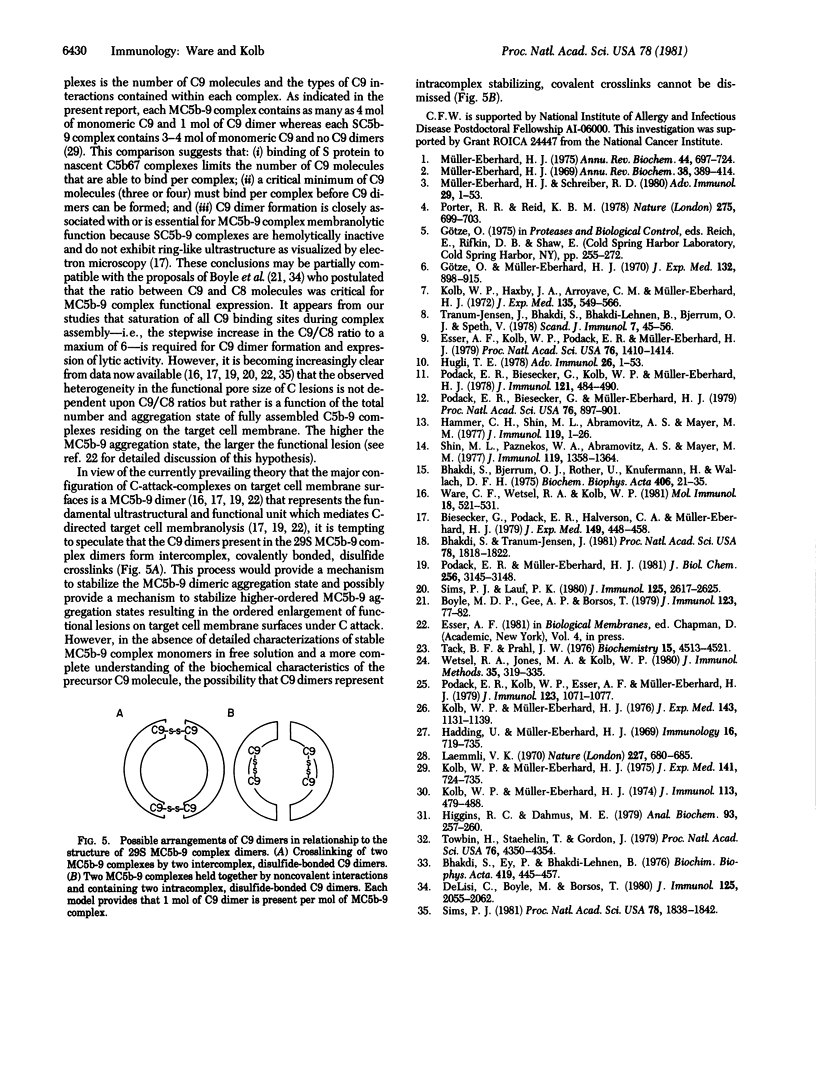
The 158,000 Mr protein, previously designated C5c, present in fully assembled complement (C) membrane attack complexes (MC5b-9) has been identified as a disulfide-bonded dimer of C9. This conclusion was based on the observations that: (i) a portion of the 125I-radiolabeled precursor C9 incorporated into MC5b-9 complexes comigrated with the 158,000 Mr protein band in NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide slab gels; (ii) monospecific antisera produced against native C9 and the 158,000 Mr protein immunologically crossreacted with monomeric native C9 by double immunodiffusion and with monomeric C9 and the 158,000 Mr protein on immunoreplication procedures; and (iii) two-dimensional NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide slab gel electrophoresis, in which the second dimension was conducted under reducing conditions, revealed that the 158,000 Mr protein contained two identical 71,000 Mr subunits which comigrated with monomeric C9. Molar ratio estimates indicated that 1 mol of C5b, C9 dimer, C6, C7, and C8 and 3-4 mol of C9 monomer were present per MC5b-9 complex. Each fully assembled membrane-bound MC5b-9 complex would therefore have a calculated Mr of 982,000. The presence of C9 dimers in the hemolytically active 29S dimeric form of the MC5b-9 complex and the absence of C9 dimers in the hemolytically inactive 23S monomeric form of the fluid phase SC5b-9 complex strongly suggest an important role for C9 dimer formation in MC5b-9 complex structure and function. The most probable function of C9 dimers would be the formation of intercomplex disulfide crosslinks which would provide a mechanism to stabilize the assembly of MC5b-9 into aggregates of increasing size on the target membrane surface which would thus be responsible for the observed pore size heterogeneity of functional C lesions.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhakdi S., Bjerrum O. J., Rother U., Knüfermann H., Wallach D. F. Immunochemical analyses of membrane-bound complement. Detection of the terminal complement complex and its similarity to "intrinsic" erythrocyte membrane proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Sep 16;406(1):21–35. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90039-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Ey P., Bhakdi-Lehnen B. Isolation of the terminal complement complex from target sheep erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Feb 6;419(3):445–457. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90258-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Molecular weight of the membrane C5b-9 complex of human complement: characterization of the terminal complex as a C5b-9 monomer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1818–1822. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biesecker G., Podack E. R., Halverson C. A., Müller-Eberhard H. J. C5b-9 dimer: isolation from complement lysed cells and ultrastructural identification with complement-dependent membrane lesions. J Exp Med. 1979 Feb 1;149(2):448–458. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.2.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle M. D., Gee A. P., Borsos T. Studies on the terminal stages of immune hemolysis. VI. Osmotic blockers of differing Stokes' radii detect complement-induced transmembrane channels of differing size. J Immunol. 1979 Jul;123(1):77–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLisi C., Boyle M., Borsos T. Analysis of the colloid osmotic step of complement-mediated immune hemolysis. J Immunol. 1980 Nov;125(5):2055–2062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esser A. F., Kolb W. P., Podack E. R., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Molecular reorganization of lipid bilayers by complement: a possible mechanism for membranolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1410–1414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Götze O., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Lysis of erythrocytes by complement in the absence of antibody. J Exp Med. 1970 Nov;132(5):898–915. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.5.898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadding U., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The ninth component of human complement: isolation, description and mode of action. Immunology. 1969 Jun;16(6):719–735. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer C. H., Shin M. L., Abramovitz A. S., Mayer M. M. On the mechanism of cell membrane damage by complement: evidence on insertion of polypeptide chains from C8 and C9 into the lipid bilayer of erythrocytes. J Immunol. 1977 Jul;119(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins R. C., Dahmus M. E. Rapid visualization of protein bands in preparative SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1979 Mar;93(2):257–260. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(79)80148-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugli T. E., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Anaphylatoxins: C3a and C5a. Adv Immunol. 1978;26:1–53. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60228-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klob W. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The membrane attack mechanism of complement: the three polypeptide chain structure of the eigth component (C8). J Exp Med. 1976 May 1;143(5):1131–1139. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.5.1131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb W. P., Haxby J. A., Arroyave C. M., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Molecular analysis of the membrane attack mechanism of complement. J Exp Med. 1972 Mar 1;135(3):549–566. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.3.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb W. P., Muller-Eberhard H. J. The membrane attack mechanism of complement. Isolation and subunit composition of the C5b-9 complex. J Exp Med. 1975 Apr 1;141(4):724–735. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb W. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Mode of action of human C9: adsorption of multiple C9 molecules to cell-bound C8. J Immunol. 1974 Aug;113(2):479–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J. Complement. Annu Rev Biochem. 1969;38:389–414. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.38.070169.002133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J. Complement. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:697–724. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.003405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J., Schreiber R. D. Molecular biology and chemistry of the alternative pathway of complement. Adv Immunol. 1980;29:1–53. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60042-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Biesecker G., Kolb W. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The C5b-6 complex: reaction with C7, C8, C9. J Immunol. 1978 Aug;121(2):484–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Biesecker G., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Membrane attack complex of complement: generation of high-affinity phospholipid binding sites by fusion of five hydrophilic plasma proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):897–901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Kolb W. P., Esser A. F., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Structural similarities between C6 and C7 of human complement. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1071–1077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Membrane attack complex of complement. Evidence for its dimeric structure based on hybrid formation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3145–3148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter R. R., Reid K. B. The biochemistry of complement. Nature. 1978 Oct 26;275(5682):699–704. doi: 10.1038/275699a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin M. L., Paznekas W. A., Abramovitz A. S., Mayer M. M. On the mechanism of membrane damage by C: exposure of hydrophobic sites on activated C proteins. J Immunol. 1977 Oct;119(4):1358–1364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims P. J., Lauf P. K. Analysis of solute diffusion across the C5b-9 membrane lesion of complement: evidence that individual C5b-9 complexes do not function as discrete, uniform pores. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2617–2625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims P. J. Permeability characteristics of complement-damaged membranes: evaluation of the membrane leak generated by the complement proteins C5b-9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1838–1842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tack B. D., Prahl J. W. Third component of human complement: purification from plasma and physicochemical characterization. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 5;15(20):4513–4521. doi: 10.1021/bi00665a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tranum-Jensen J., Bhakdi S., Bhakdi-Lehnen B., Bjerrum O. J., Speth V. Complement lysis: the ultrastructure and orientation of the C5b-9 complex on target sheep erythrocyte membranes. Scand J Immunol. 1978;7(1):45–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00425.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware C. F., Wetsel R. A., Kolb W. P. Physicochemical characterization of fluid phase (SC5b-9) and membrane derived (MC5b-9) attack complexes of human complement purified by immunoadsorbent affinity chromatography or selective detergent extraction. Mol Immunol. 1981 Jun;18(6):521–531. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(81)90130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetsel R. A., Jones M. A., Kolb W. P. Immunoadsorbent affinity purification of the fifth component (C5) of human complement and development of a highly sensitive hemolytic assay. J Immunol Methods. 1980;35(3-4):319–335. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90258-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]