Abstract
We have described previously a cell culture system in which the herpes simplex virus (HSV) type 2 (HSV-2) genome is maintained in a repressed form after treatment of infected cells with 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine and increase of incubation temperature from 37 degrees C to 39.5 degrees C. Infectious HSV-2 production was activated by altering incubation temperature or by superinfecting with human cytomegalovirus. We now report the establishment of an analogous system utilizing HSV type 1 (HSV-1). Human embryo lung cells were infected with HSV-1 and treated with 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine (25 micrograms/ml) for 7 days to minimize both synthesis of virus DNA and infectious virus while allowing expression of early virus genes. HSV-1 was maintained in an undetectable form for at least 72 days when the incubation temperature was raised from 37 degrees C to 40.5 degrees C after removal of the inhibitor. HSV-1 gene expression was then predictably turned on by superinfection with human cytomegalovirus or by reducing the incubation temperature. Virus replicated after activation was compared with the respective parental virus with regard to inhibition by the HSV-1-specific antiviral (E)-5-(2-bromovinyl)-2'-deoxyuridine and EcoRI, HindIII, and Xba I restriction endonuclease cleavage patterns. The results show activation of HSV gene expression in human cells by a human cytomegalovirus early gene function(s), followed by synthesis of parental-like HSV.
Full text
PDF
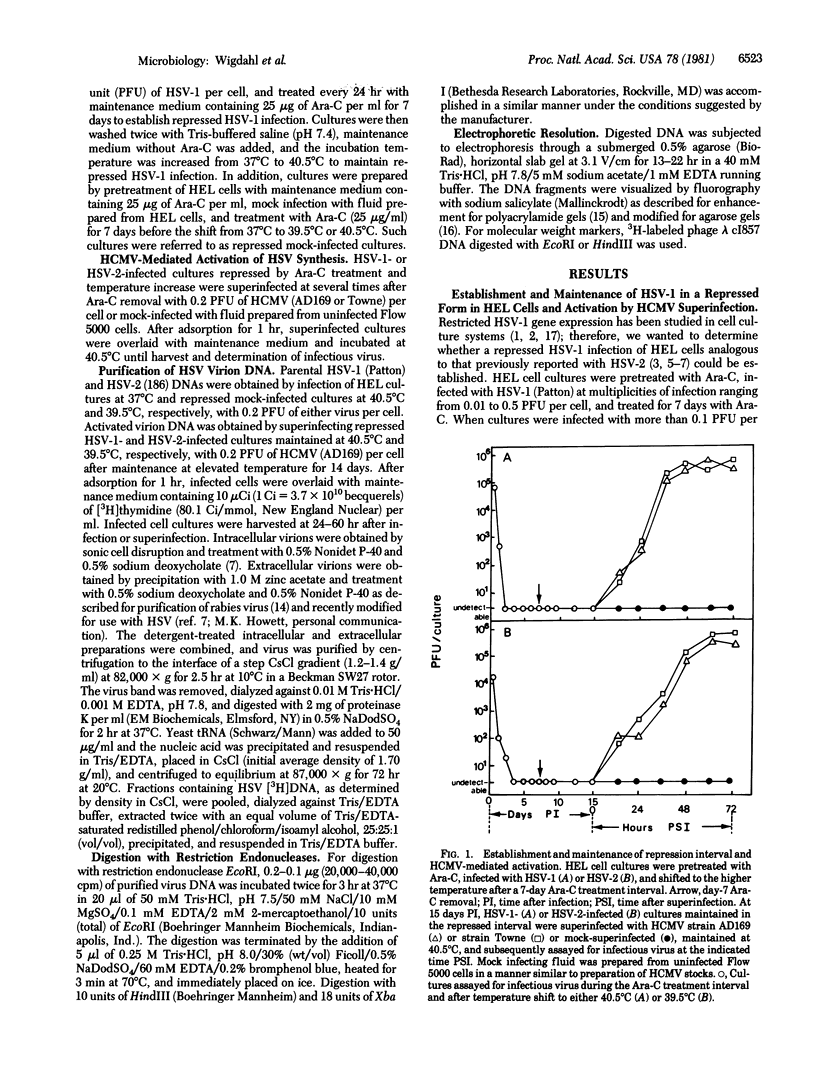
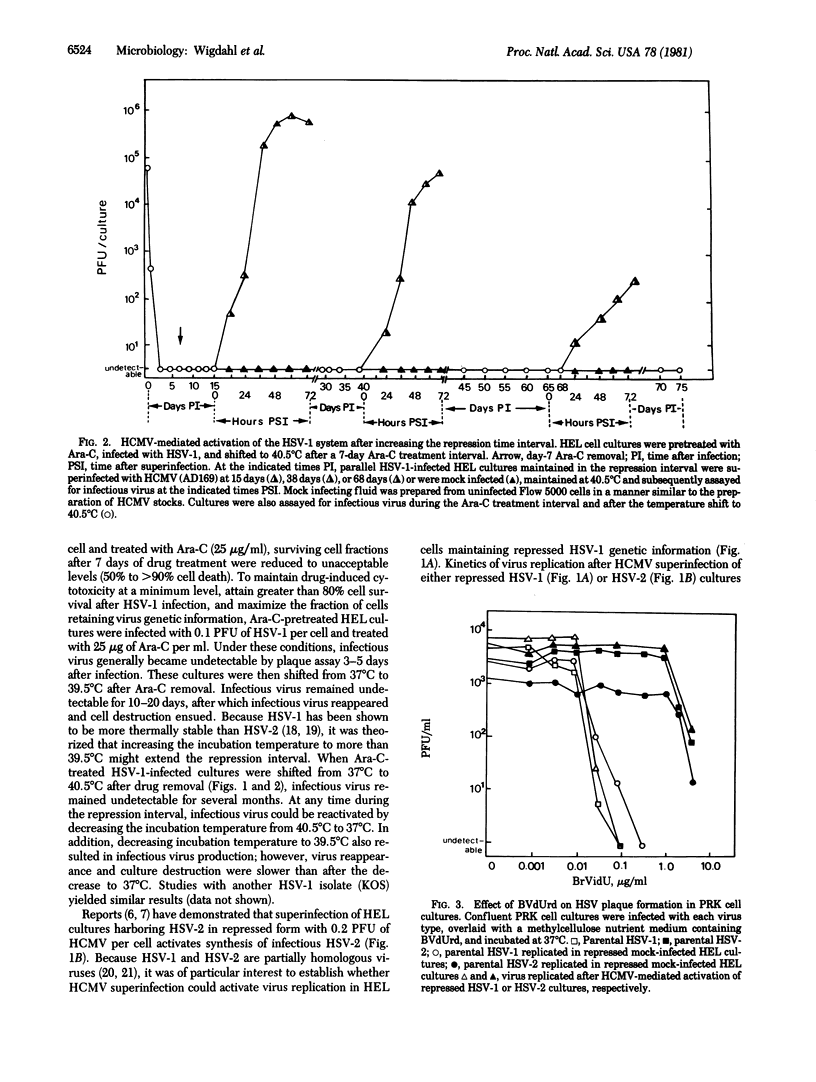
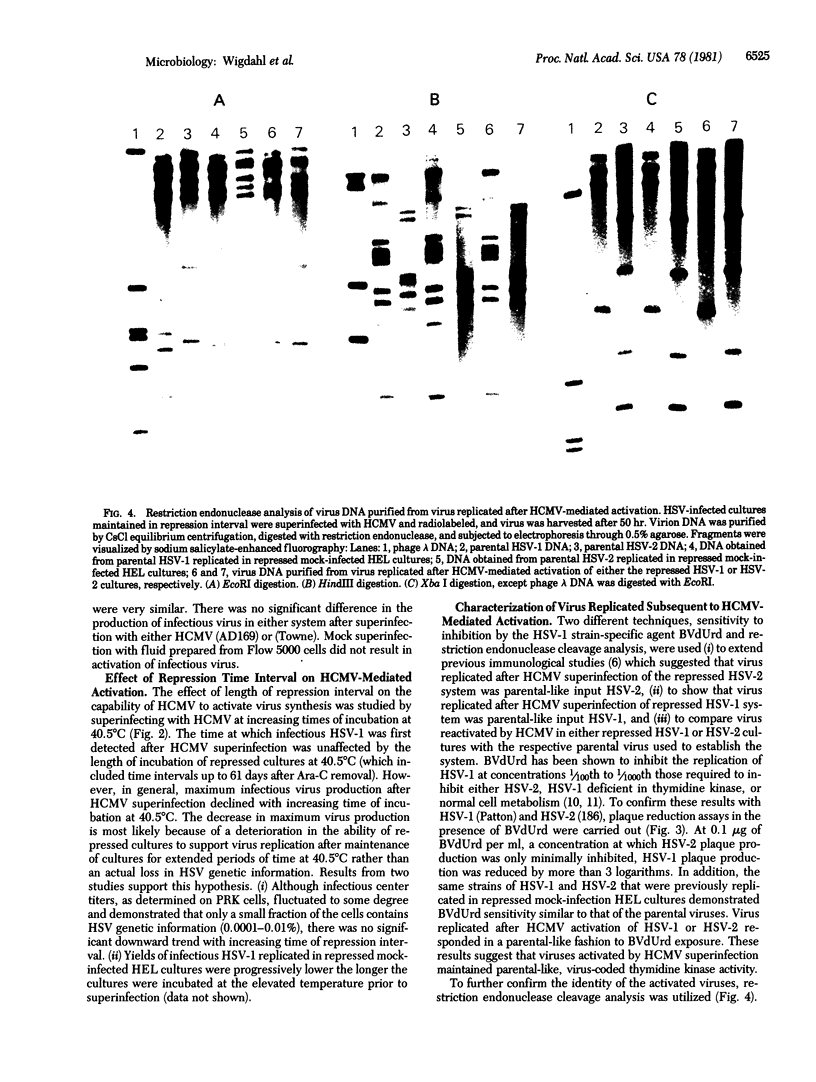

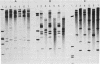
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler R., Glorioso J. C., Levine M. Infection by herpes simplex virus and cells of nervous system origin: characterization of a non-permissive interaction. J Gen Virol. 1978 Apr;39(1):9–20. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-39-1-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. P. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):132–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colberg-Poley A. M., Isom H. C., Rapp F. Involvement of an early human cytomegalovirus function in reactivation of quiescent herpes simplex virus type 2. J Virol. 1981 Mar;37(3):1051–1059. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.3.1051-1059.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colberg-Poley A. M., Isom H. C., Rapp F. Reactivation of herpes simplex virus type 2 from a quiescent state by human cytomegalovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5948–5951. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colberg-Poley A. M., Isom H., Rapp F. Experimental HSV latency using phosphonoacetic acid. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1979 Oct;162(1):235–237. doi: 10.3181/00379727-162-40655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq E., Descamps J., De Somer P., Barr P. J., Jones A. S., Walker R. T. (E)-5-(2-Bromovinyl)-2'-deoxyuridine: a potent and selective anti-herpes agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2947–2951. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq E., Descamps J., Verhelst G., Walker R. T., Jones A. S., Torrence P. F., Shugar D. Comparative efficacy of antiherpes drugs against different strains of herpes simplex virus. J Infect Dis. 1980 May;141(5):563–574. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.5.563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ecker J. R., Hyman R. W. Analysis of interruptions in the phosphodiester backbone of herpes simplex virus DNA. Virology. 1981 Apr 15;110(1):213–216. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90024-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esparza J., Purifoy D. J., Schaffer P. A., Benyesh-Melnick M. Isolation, complementation and preliminary phenotypic characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus type 2. Virology. 1974 Feb;57(2):554–565. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90194-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdes J. C., Marsden H. S., Cook M. L., Stevens J. G. Acute infection of differentiated neuroblastoma cells by latency-positive and latency-negative herpes simplex virus ts mutants. Virology. 1979 Apr 30;94(2):430–441. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90473-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. I. Cascade regulation of the synthesis of three groups of viral proteins. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):8–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.8-19.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieff E., Hoyer B., Bachenheimer S., Roizman B. Genetic relatedness of type 1 and type 2 herpes simplex viruses. J Virol. 1972 May;9(5):738–745. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.5.738-745.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipe D. M., Batterson W., Nosal C., Roizman B., Buchan A. Molecular genetics of herpes simplex virus. VI. Characterization of a temperature-sensitive mutant defective in the expression of all early viral gene products. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):539–547. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.539-547.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M., Goldin A. L., Glorioso J. C. Persistence of herpes simplex virus genes in cells of neuronal origin. J Virol. 1980 Jul;35(1):203–210. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.1.203-210.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig H. O., Biswal N., Benyesh-Melnick M. Studies on the relatedness of herpesviruses through DNA-DNA hybridization. Virology. 1972 Jul;49(1):95–101. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(72)80010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill F. J., Goldberg R. J., Rapp F. Herpes simplex virus latency in cultured human cells following treatment with cytosine arabinoside. J Gen Virol. 1972 Feb;14(2):189–197. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-14-2-189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill F. J. Prolongation of herpes simplex virus latency in cultured human cells by temperature elevation. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):41–46. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.41-46.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPP F. VARIANTS OF HERPES SIMPLEX VIRUS: ISOLATION, CHARACTERIZATION, AND FACTORS INFLUENCING PLAQUE FORMATION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Nov;86:985–991. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.5.985-991.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffer P. A., Aron G. M., Biswal N., Benyesh-Melnick M. Temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1: isolation, complementation and partial characterization. Virology. 1973 Mar;52(1):57–71. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90398-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokol F., Kuwert E., Wiktor T. J., Hummeler K., Koprowski H. Purification of rabies virus grown in tissue culture. J Virol. 1968 Aug;2(8):836–849. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.8.836-849.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wentworth B. B., French L. Plaque assay of cytomegalovirus strains of human origin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Nov;135(2):253–258. doi: 10.3181/00379727-135-35031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanishi K., Rapp F. Induction of host DNA synthesis and DNA polymerase by DNA-negative temperature-sensitive mutants of human cytomegalovirus. Virology. 1979 Apr 15;94(1):237–241. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90457-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanishi K., Rapp F. Temperature-sensitive mutants of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):416–418. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.416-418.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]