Abstract
From Anthopleura elegantissima and from Hydra attenuata, a morphogenetic peptide—the head activator—was isolated in pure form. The sequence of the head activator was established by enzymatic and by chemical degradation of the whole peptide or fragments thereof and subsequent analysis of the amino acids by micromethods. The head activator from both sources was identical and has the sequence:
<pGlu-Pro-Pro-Gly-Gly-Ser-Lys-Val-Ile-Leu-Phe.
Keywords: hydra head activator, neuropeptide, high-pressure liquid chromatography, sequence microdetermination
Full text
PDF
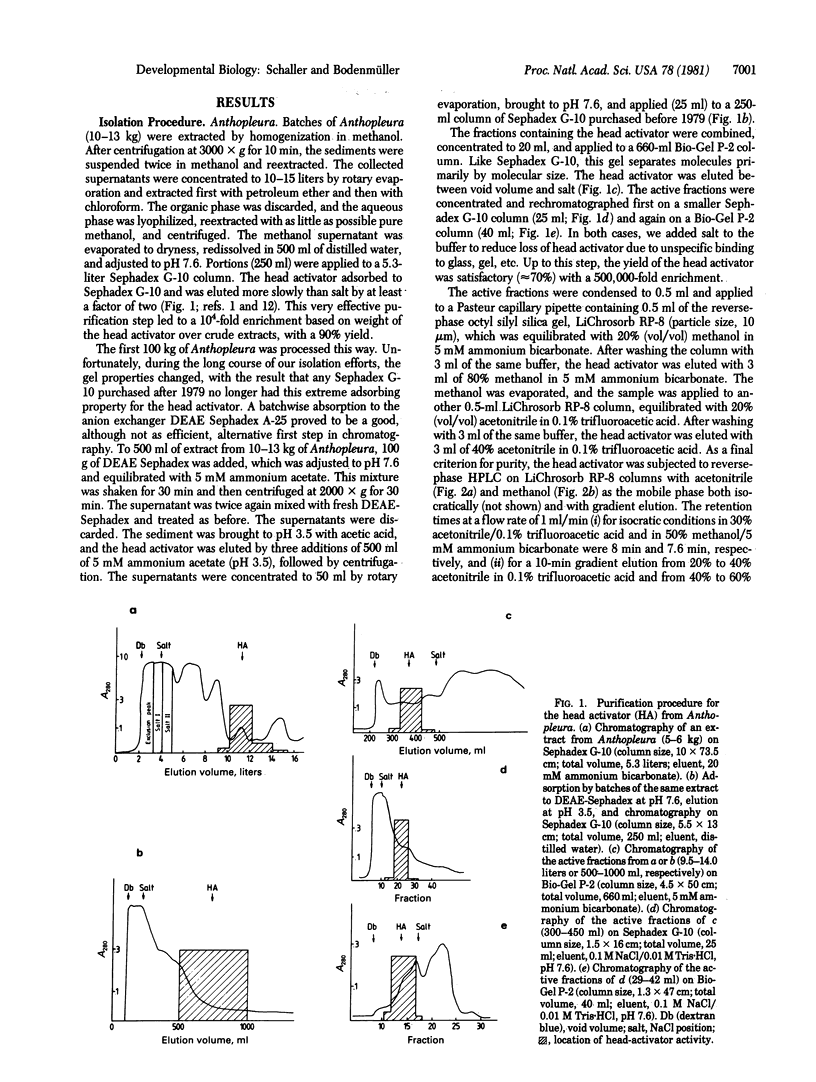
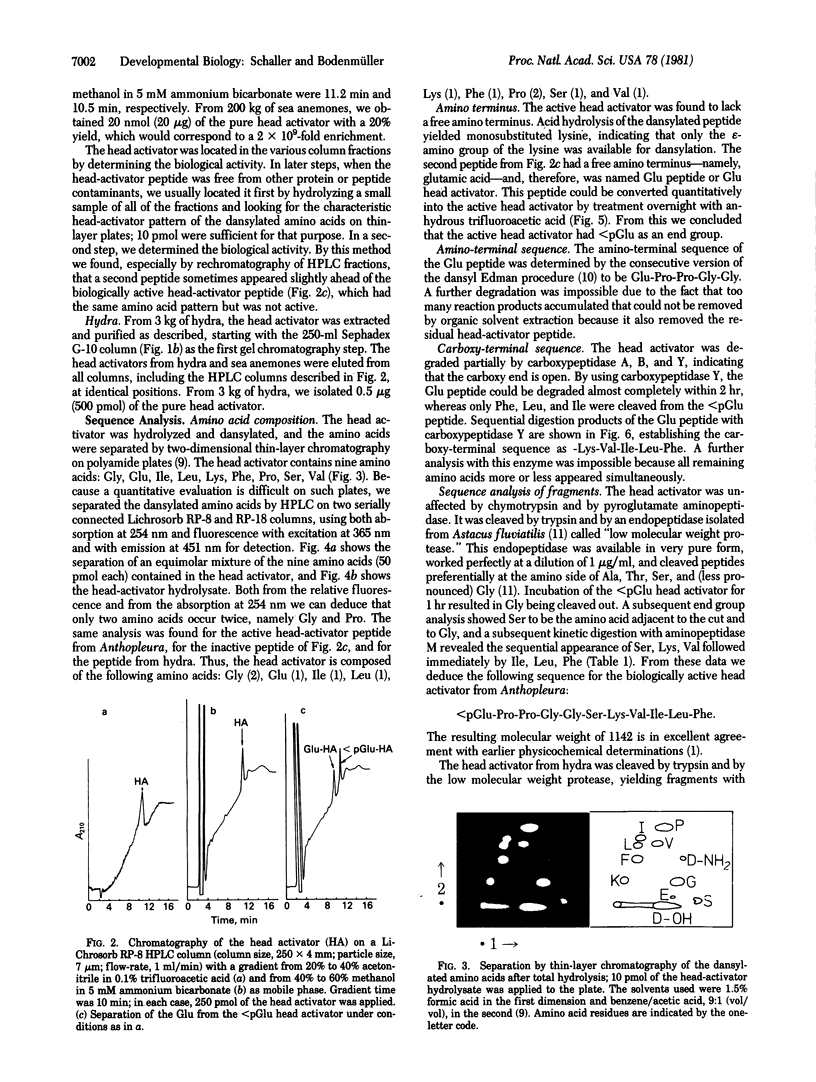
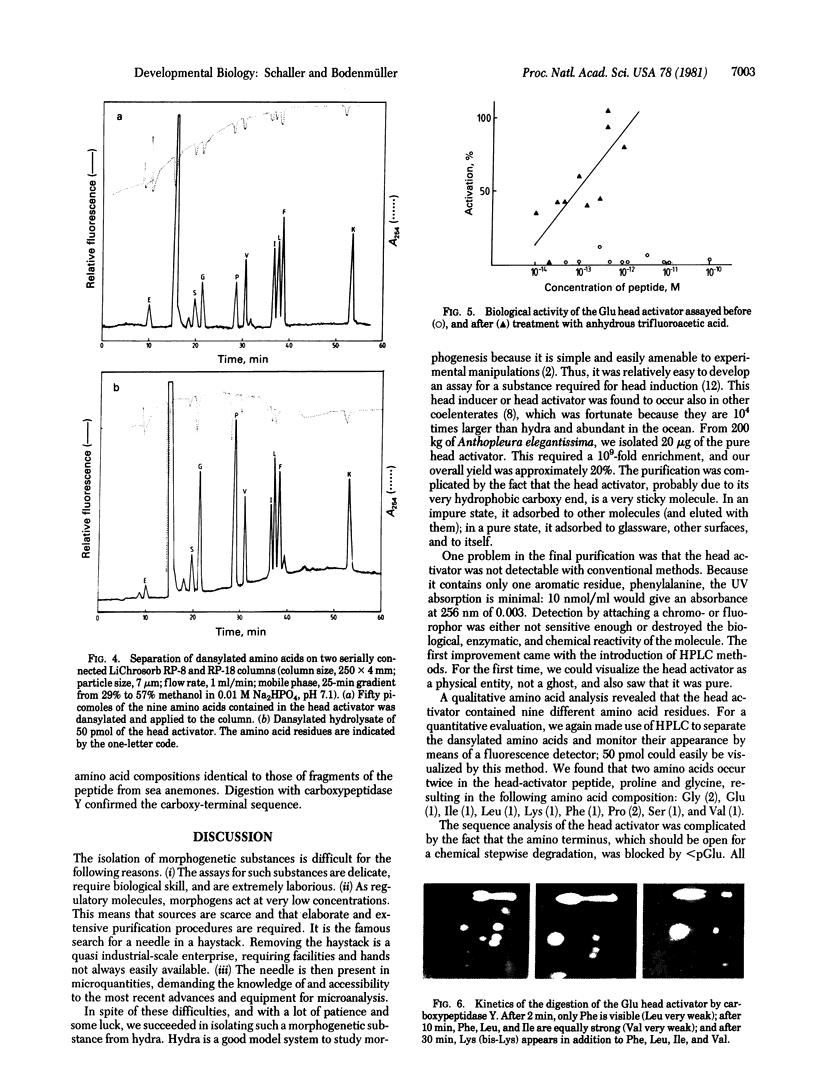

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birr C., Zachmann B., Bodenmüller H., Schaller H. C. Synthesis of a new neuropeptide, the head activator from hydra. FEBS Lett. 1981 Aug 31;131(2):317–321. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80394-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodenmüller H., Schaller H. C., Darai G. Human hypothalamus and intestine contain a hydra-neuropeptide. Neurosci Lett. 1980 Jan;16(1):71–74. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(80)90103-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray W. R., Smith J. F. Rapid sequence analysis of small peptides. Anal Biochem. 1970 Jan;33(1):36–42. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90436-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller H. C. A neurohormone from hydra is also present in the rat brain. J Neurochem. 1975 Aug;25(2):187–188. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1975.tb12249.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller H. C. Action of the head activator as a growth hormone in hydra. Cell Differ. 1976 Apr;5(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(76)90009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller H. C. Action of the head activator on the determination of interstitial cells in hydra. Cell Differ. 1976 Apr;5(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(76)90010-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller H. C. Isolation and characterization of a low-molecular-weight substance activating head and bud formation in hydra. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1973 Feb;29(1):27–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller H., Gierer A. Distribution of the head-activating substance in hydra and its localization in membranous particles in nerve cells. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1973 Feb;29(1):39–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart J. M., Channabasavaiah K. Evolutionary aspects of some neuropeptides. Fed Proc. 1979 Aug;38(9):2302–2308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwilling R., Dörsam H., Torff H. J., Rödl J. Low molecular mass protease: evidence for a new family of proteolytic enzymes. FEBS Lett. 1981 May 5;127(1):75–78. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80344-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





