Abstract
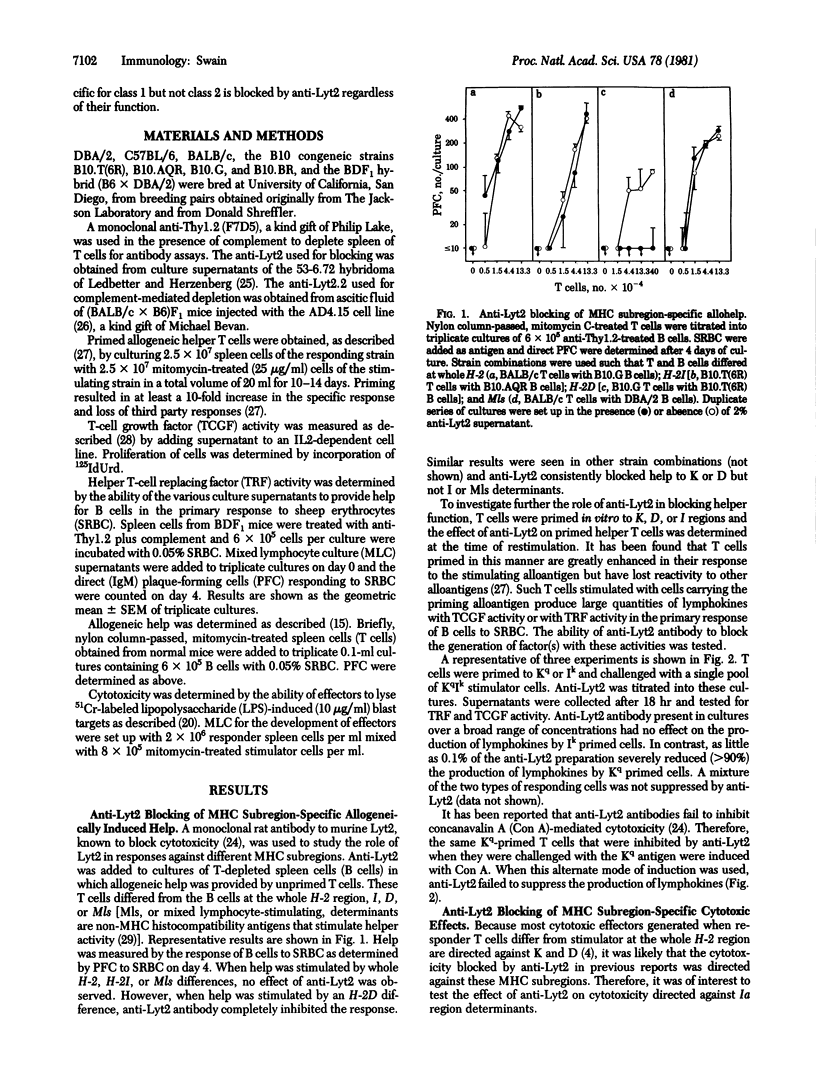
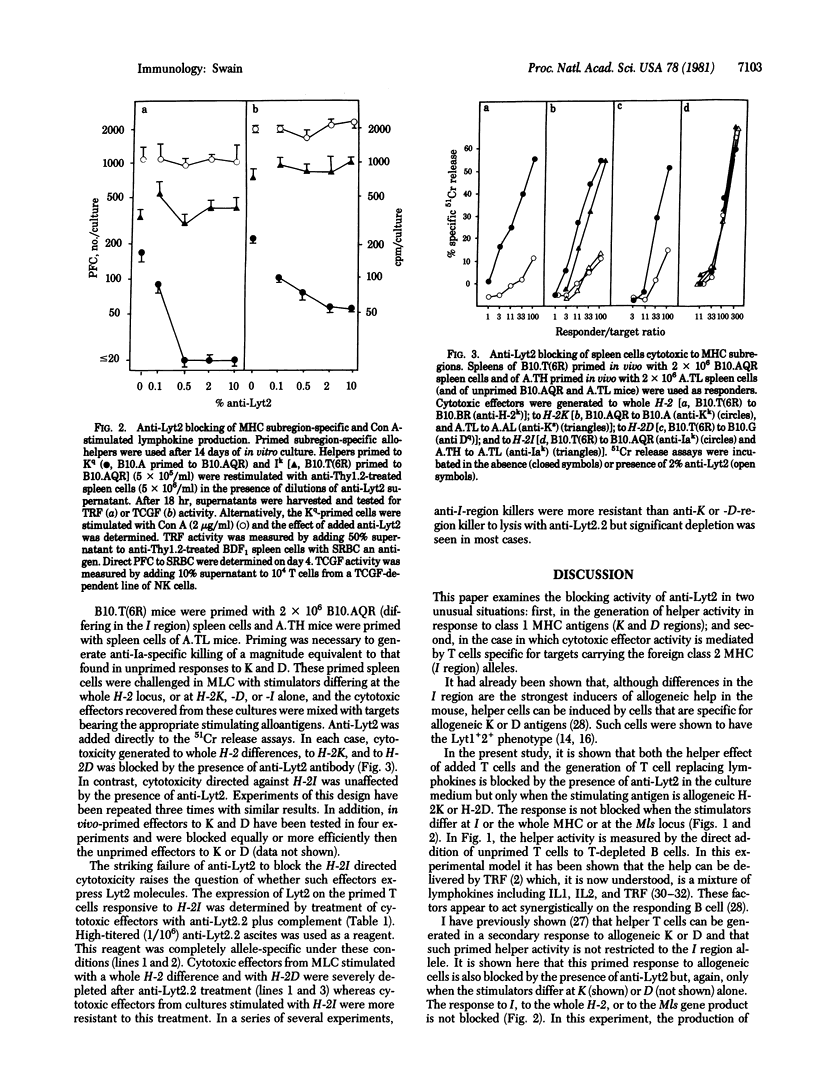
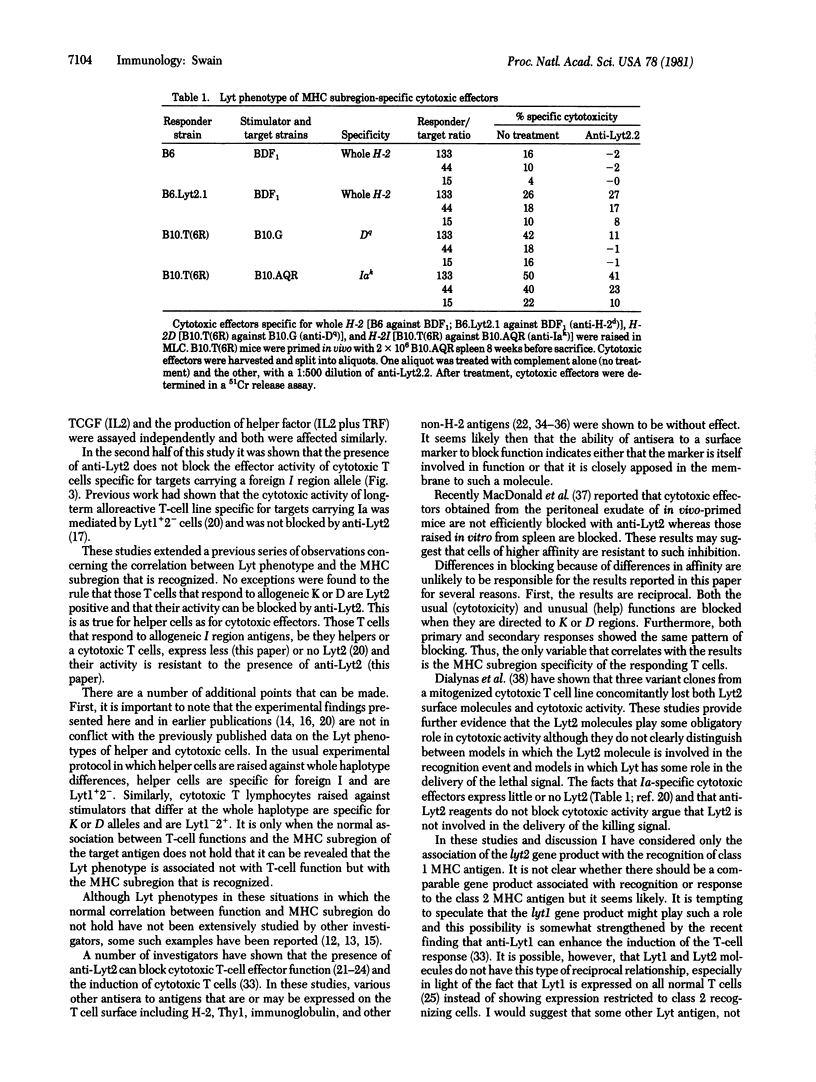
The effect of anti-Lyt2 on the generation of helper T-cell function and on cytotoxic effects specific for subregions of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) was determined. The addition of anti-Lyt2 without complement to in vitro cultures blocked the generation of allogeneic MHC-induced help and lymphokine production and cytotoxic effects when the response was directed against allogeneic class 1 MHC antigens (K and D gene products of the mouse H-2 complex) but had no effect when these responses were specific for class 2 MHC antigens (I region gene products). Anti-Lyt2 failed to block the response of help induced to allogeneic mixed lymphocyte-stimulating determinants or the production of lymphokines by T cells specific for class 1 MHC antigens when concanavalin A lectin was used to induce activity. These and earlier results indicate that the ability of anti-Lyt2 antisera to block function is correlated with T cell specificity for class 1 MHC antigens not with the functional activity of the cells.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bach F. H., Alter B. J. Alternative pathways of T lymphocyte activation. J Exp Med. 1978 Sep 1;148(3):829–834. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.3.829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach F. H., Bach M. L., Sondel P. M. Differential function of major histocompatibility complex antigens in T-lymphocyte activation. Nature. 1976 Jan 29;259(5541):273–281. doi: 10.1038/259273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach F. H., Widmer M. B., Bach M. L., Klein J. Serologically defined and lymphocyte-defined components of the major histocompatibility complex in the mouse. J Exp Med. 1972 Dec 1;136(6):1430–1444. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.6.1430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor H., Boyse E. A. Regulation of cellular and humoral immune responses by T-cell subclasses. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1977;41(Pt 1):23–32. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1977.041.01.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dialynas D. P., Loken M. R., Glasebrook A. L., Fitch F. W. Lyt-2-/Lyt 3- variants of a cloned cytolytic T cell line lack an antigen receptor functional in cytolysis. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):595–604. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty P. C., Blanden R. V., Zinkernagel R. M. Specificity of virus-immune effector T cells for H-2K or H-2D compatible interactions: implications for H-antigen diversity. Transplant Rev. 1976;29:89–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1976.tb00198.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton R. W. Further studies of the stimulation of DNA synthesis in cultures of spleen cell suspensions by homologous cells in inbred strains of mice and rats. J Exp Med. 1965 Oct 1;122(4):759–770. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.4.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollander N., Pillemer E., Weissman I. L. Blocking effect of lyt-2 antibodies on T cell functions. J Exp Med. 1980 Sep 1;152(3):674–687. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.3.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollander N., Pillemer E., Weissman I. L. Effects of Lyt antibodies on T-cell functions: augmentation by anti-Lyt-1 as opposed to inhibition by anti-Lyt-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1148–1151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappler J. W., Marrack P. C. Helper T cells recognise antigen and macrophage surface components simultaneously. Nature. 1976 Aug 26;262(5571):797–799. doi: 10.1038/262797a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D. H., Hamaoka T., Dorf M. E., Benacerraf B. Cell interactions between histoincompatible T and B lymphocytes. The H-2 gene complex determines successful physiologic lymphocyte interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Sep;70(9):2624–2628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.9.2624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D. H., Paul W. E., Goidl E. A., Benacerraf B. Carrier function in anti-hapten antibody responses. 3. Stimulation of antibody synthesis and facilitation of hapten-specific secondary antibody responses by graft-versus-host reactions. J Exp Med. 1971 Feb 1;133(2):169–186. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.2.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A. K., Wigzell H. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte membrane components: an analysis of structures related to function. Contemp Top Mol Immunol. 1977;6:209–244. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-2841-4_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J., Chiang C. L., Hauptfeld V. Histocompatibility antigens controlled by the I region of the murine H-2 complex. II. K/D region compatibility is not required for I-region cell-mediated lymphocytotoxicity. J Exp Med. 1977 Feb 1;145(2):450–454. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.2.450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Herzenberg L. A. Xenogeneic monoclonal antibodies to mouse lymphoid differentiation antigens. Immunol Rev. 1979;47:63–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald H. R., Thiernesse N., Cerottini J. C. Inhibition of T cell-mediated cytolysis by monoclonal antibodies directed against Lyt-2: heterogeneity of inhibition at the clonal level. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):1671–1675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama E., Shiku H., Stockert E., Oettgen H. F., Old L. J. Cytotoxic T cells: Lyt phenotype and blocking of killing activity by Lyt antisera. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1977–1981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada M., Henney C. S. The differentiation of cytotoxic T cells in vitro. II. Amplifying factor(s) produced in primary mixed lymphocyte cultures against K/D stimuli require the presence of Lyt 2+ cells but not Lyt 1+ cells. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):300–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panfili P. R., Dutton R. W. Alloantigen-induced T helper activity. I. Minimal genetic differences necessary to induce a positive allogeneic effect. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):1897–1901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raulet D. H., Gottlieb P. D., Bevan M. J. Fractionation of lymphocyte populations with monoclonal antibodies specific for LYT-2.2 and LYT-3.1. J Immunol. 1980 Sep;125(3):1136–1143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs D. H., Winn H. J., Russell P. S. The immunologic response to xenografts. Recognition of mouse H-2 histocompatibility antigens by the rat. J Immunol. 1971 Aug;107(2):481–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiku H., Kisielow P., Bean M. A., Takahashi T., Boyse E. A., Oettgen H. F., Old L. J. Expression of T-cell differentiation antigens on effector cells in cell-mediated cytotoxicity in vitro. Evidence for functional heterogeneity related to the surface phenotype of T cells. J Exp Med. 1975 Jan 1;141(1):227–241. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.1.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara N., Hämmerling U., Sachs D. H. Mouse alloantibodies capable of blocking cytotoxic T cell function. II. Further study on the relationship between the blocking antibodies and the products of the Lyt-2 locus. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Aug;10(8):589–594. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara N., Sachs D. H. Mouse alloantibodies capable of blocking cytotoxic T-cell function. I. Relationship between the antigen reactive with blocking antibodies and the Lyt-2 locus. J Exp Med. 1979 Sep 19;150(3):432–444. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.3.432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A. T-cell growth factor. Immunol Rev. 1980;51:337–357. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb00327.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L. Association of Ly phenotypes, T cell function and MHC recognition. Fed Proc. 1980 Nov;39(13):3110–3113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L., Dennert G., Warner J. F., Dutton R. W. Culture supernatants of a stimulated T-cell line have helper activity that acts synergistically with interleukin 2 in the response of B cells to antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2517–2521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L., Dennert G., Wormsley S., Dutton R. W. The Lyt phenotype of a long-term allospecific T cell line. Both helper and killer activities to IA are mediated by Ly-1 cells. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Mar;11(3):175–180. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L., Panfili P. R. Helper cells activated by allogeneic H-2K or H-2D differences have a Ly phenotype distinct from those responsive to I differences. J Immunol. 1979 Feb;122(2):383–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L., Panfili P. R. Helper cells activated by allogeneic H-2K or H-2D differences have a Ly phenotype distinct from those responsive to I differences. J Immunol. 1979 Feb;122(2):383–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L. Significance of class 1 and class 2 major histocompatibility complex antigens: help to allogeneic K and D antigens does not involve I recognition. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2307–2309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner H., Götze D., Ptschelinzew L., Röllinghoff M. Induction of cytotoxic T lymphocytes against I-region-coded determinants: in vitro evidence for a third histocompatibility locus in the mouse. J Exp Med. 1975 Dec 1;142(6):1477–1487. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.6.1477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J., Gillis S., Marbrook J., Mochizuki D., Smith K. A. Biochemical and biological characterization of lymphocyte regulatory molecules. I. Purification of a class of murine lymphokines. J Exp Med. 1979 Oct 1;150(4):849–861. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.4.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wettstein P. J., Bailey D. W., Mobraaten L. E., Klein J., Frelinger J. A. T-lymphocyte response to H-2 mutants. I. Proliferation is dependent on Ly 1+2+ cells. J Exp Med. 1978 May 1;147(5):1395–1404. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.5.1395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. H-2 compatability requirement for T-cell-mediated lysis of target cells infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Different cytotoxic T-cell specificities are associated with structures coded for in H-2K or H-2D;. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1427–1436. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



