Abstract
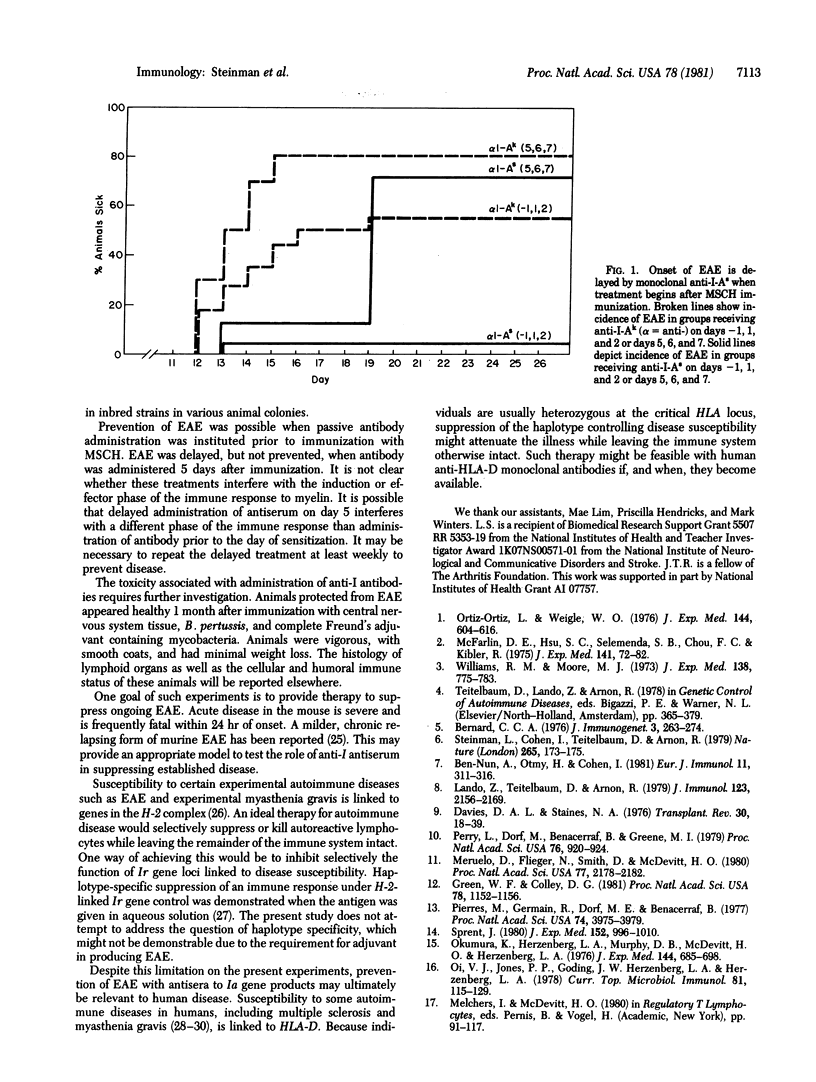
Prevention of experimental allergic encephalitis in SJL/J [H-2s] mice was achieved with in vivo administration of antibody reactive with I-As gene products prior to immunization with spinal cord antigen. No protection was evident in animals that received antisera specific for I-Js gene products. Administration of antibody to I-As beginning 5 days after immunization with spinal cord antigen delayed, but did not prevent, the onset of experimental allergic encephalitis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnett L. B., McFarlin D. E. Genetic control of antibody production to myelin basic protein in mice. J Neuroimmunol. 1981 Mar;1(1):53–59. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(81)90007-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Nun A., Otmy H., Cohen I. R. Genetic control of autoimmune encephalomyelitis and recognition of the critical nonapeptide moiety of myelin basic protein in guinea pigs are exerted through interaction of lymphocytes and macrophages. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Apr;11(4):311–316. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman P. W., Patrick J. Linkage between the frequency of muscular weakness and loci that regulate immune responsiveness in murine experimental myasthenia gravis. J Exp Med. 1980 Sep 1;152(3):507–520. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.3.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard C. C., Carnegie P. R. Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice: immunologic response to mouse spinal cord and myelin basic proteins. J Immunol. 1975 May;114(5):1537–1540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard C. C. Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice: genetic control of susceptibility. J Immunogenet. 1976 Aug;3(4):263–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-313x.1976.tb00583.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D. A., Staines N. A. A cardinal role for I-region antigens (Ia) in immunological enhancement, and the clinical implications. Transplant Rev. 1976;30:18–39. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1976.tb00213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green W. F., Colley D. G. Modulation of Schistosoma mansoni egg-induced granuloma formation: I-J restriction of T cell-mediated suppression in a chronic parasitic infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1152–1156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habu S., Yamauchi K., Gershon R. K., Murphy D. B. A non-T:non-B cell bears I-A, I-E, I-J, and Tla (Qa-1?) determinants. Immunogenetics. 1981;13(3):215–225. doi: 10.1007/BF00350788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lando Z., Teitelbaum D., Arnon R. Effect of cyclophosphamide on suppressor cell activity in mice unresponsive to EAE. J Immunol. 1979 Nov;123(5):2156–2160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lublin F. D., Maurer P. H., Berry R. G., Tippett D. Delayed, relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in mice. J Immunol. 1981 Mar;126(3):819–822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt H. O. Regulation of the immune response by the major histocompatibility system. N Engl J Med. 1980 Dec 25;303(26):1514–1517. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198012253032606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarlin D. E., Hsu S. C., Slemenda S. B., Chou F. C., Kibler R. F. The immune response against myelin basic protein in two strains of rat with different genetic capacity to develop experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Exp Med. 1975 Jan 1;141(1):72–81. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.1.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meruelo D., Flieger N., Smith D., McDevitt H. O. In vivo or in vitro treatments with anti-I-J alloantisera abolish immunity to AKR leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2178–2182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D. B., Herzenberg L. A., Okumura K., Herzenberg L. A., McDevitt H. O. A new I subregion (I-J) marked by a locus (Ia-4) controlling surface determinants on suppressor T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1976 Sep 1;144(3):699–712. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.3.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oi V. T., Jones P. P., Goding J. W., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A. Properties of monoclonal antibodies to mouse Ig allotypes, H-2, and Ia antigens. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;81:115–120. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67448-8_18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okumura K., Herzenberg L. A., Murphy D. B., McDevitt H. O., Herzenberg L. A. Selective expression of H-2 (i-region) loci controlling determinants on helper and suppressor T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1976 Sep 1;144(3):685–698. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.3.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz-Ortiz L., Weigle W. O. Cellular events in the induction of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in rats. J Exp Med. 1976 Sep 1;144(3):604–616. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.3.604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry L. L., Dorf M. E., Benacerraf B., Greene M. I. Regulation of immune response to tumor antigen: interference with syngeneic tumor immunity by anti-IA alloantisera. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):920–924. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierres M., Germain R. N., Dorf M. E., Benacerraf B. Potentiation of a primary in vivo antibody response by alloantisera against gene products of the I region of the H-2 complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3975–3979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raine C. S., Barnett L. B., Brown A., Behar T., McFarlin D. E. Neuropathology of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in inbred strains of mice. Lab Invest. 1980 Aug;43(2):150–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprent J. Effects of blocking helper T cell induction in vivo with anti-Ia antibodies. Possible role of I-A/E hybrid molecules as restriction elements. J Exp Med. 1980 Oct 1;152(4):996–1010. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.4.996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman L., Cohen I. R., Teitelbaum D., Arnon R. Regulation of autosensitisation to encephalitogenic myelin basic protein by macrophage-association and soluble antigen. Nature. 1977 Jan 13;265(5590):173–175. doi: 10.1038/265173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Säfwenberg J., Hammarström L., Lindblom J. B., Matell G., Möller E., Osterman P. O., Smith C. I. HLA-A, -B, -C and -D antigens in male patients with myasthenia gravis. Tissue Antigens. 1978 Aug;12(2):136–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1978.tb01309.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. M., Moore M. J. Linkage of susceptibility to experimental allergic encephalomyelitis to the major histocompatibility locus in the rat. J Exp Med. 1973 Oct 1;138(4):775–783. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.4.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



