Abstract
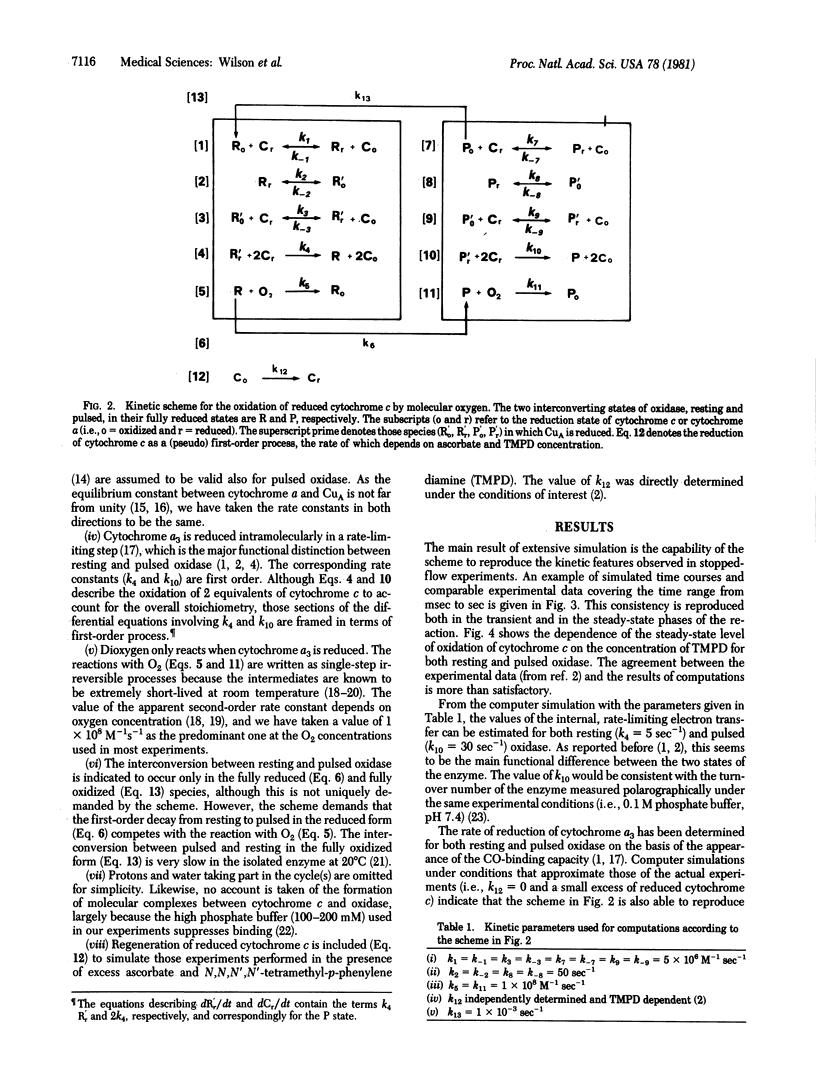
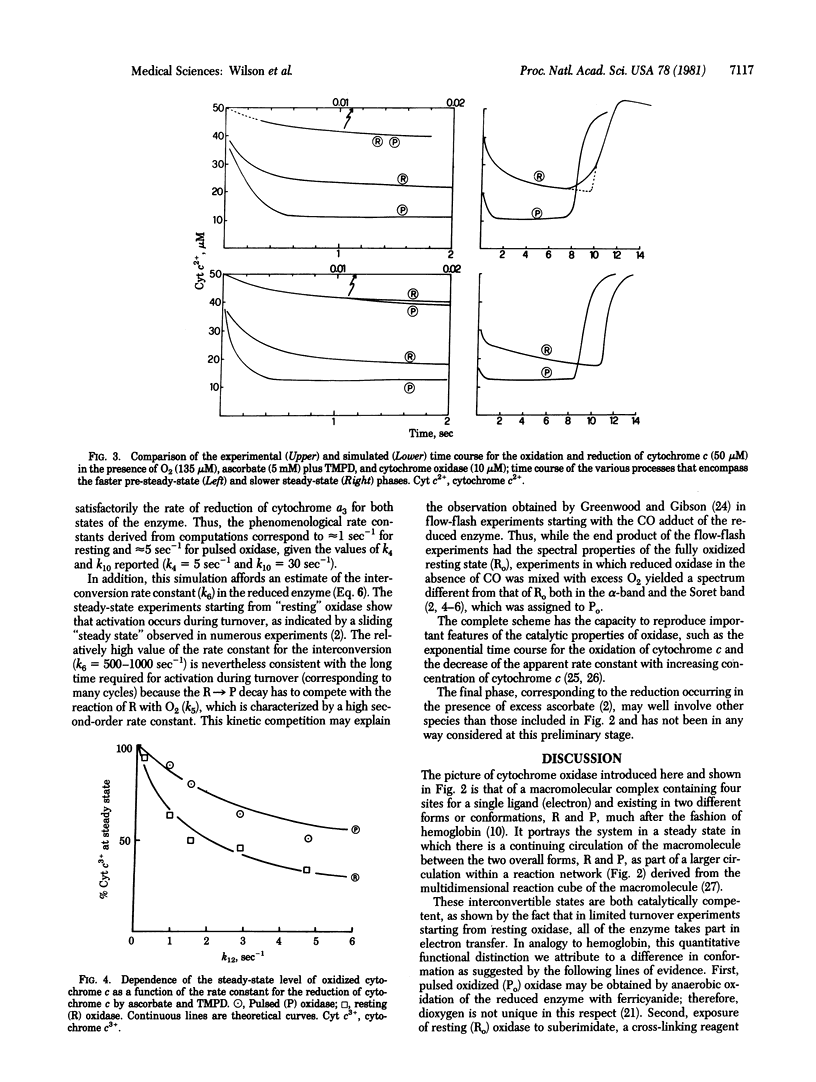
The catalytic properties of pulsed and resting cytochrome c oxidase (ferrocytochrome c: oxygen oxidoreductase, EC 1.9.3.1), expressed in terms of a minimal kinetic scheme and simulated by numerical computations, were successfully described. A two-state model, in which the relative amounts of the enzyme present in each conformation are regulated by the rates of electron flux and O2 binding on one side and the interconversion rates on the other, accounts for the activation of cytochrome c oxidase during turnover.
Full text
PDF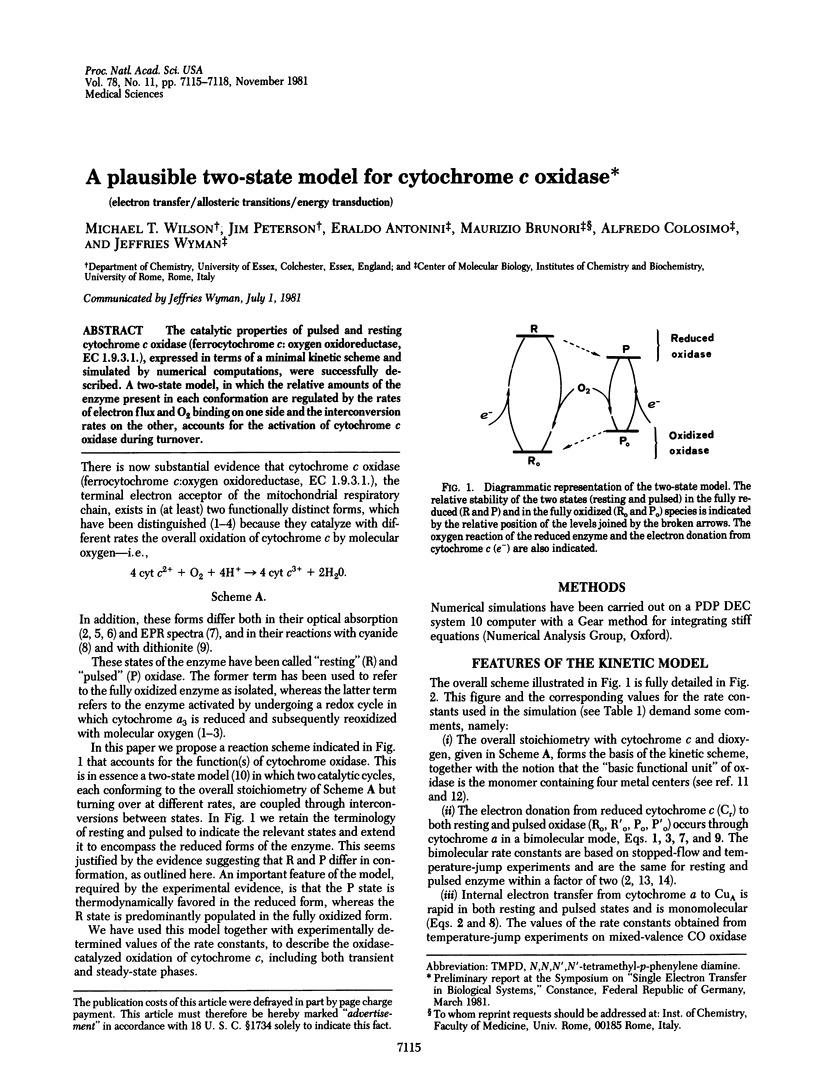

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonini E., Brunori M., Colosimo A., Greenwood C., Wilson M. T. Oxygen "pulsed" cytochrome c oxidase: functional properties and catalytic relevance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3128–3132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonaventura C., Bonaventura J., Brunori M., Wilson M. Functional studies on crosslinked bovine cytochrome c oxidase. FEBS Lett. 1978 Jan 1;85(1):30–34. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)81241-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brittain T., Greenwood C. Kinetic studies on the binding of cyanide to oxygenated cytochrome c oxidase. Biochem J. 1976 May 1;155(2):453–455. doi: 10.1042/bj1550453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunori M., Colosimo A., Rainoni G., Wilson M. T., Antonini E. Functional intermediates of cytochrome oxidase. Role of "pulsed" oxidase in the pre-steady state and steady state reactions of the beef enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):10769–10775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunori M., Colosimo A., Sarti P., Antonini E., Wilson M. T. 'Pulsed' cytochrome oxidase may be produced without the advent of dioxygen. FEBS Lett. 1981 Apr 20;126(2):195–198. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80240-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chance B., Saronio C., Leigh J. S., Jr Functional intermediates in the reaction of membrane-bound cytochrome oxidase with oxygen. J Biol Chem. 1975 Dec 25;250(24):9226–9237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errede B., Kamen M. D. Comparative kinetic studies of cytochromes c in reactions with mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase and reductase. Biochemistry. 1978 Mar 21;17(6):1015–1027. doi: 10.1021/bi00599a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson-Miller S., Brautigan D. L., Margoliash E. Definition of cytochrome c binding domains by chemical modification. III. Kinetics of reaction of carboxydinitrophenyl cytochromes c with cytochrome c oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 10;253(1):149–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBSON Q. H., GREENWOOD C. THE REACTION OF CYTOCHROME OXIDASE WITH CYTOCHROME C. J Biol Chem. 1965 Feb;240:888–894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood C., Brittain T. Studies on partially reduced mammalian cytochrome oxidase reactions with ferrocytochrome c. Biochem J. 1976 Sep 1;157(3):591–598. doi: 10.1042/bj1570591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood C., Gibson Q. H. The reaction of reduced cytochrome C oxidase with oxygen. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 25;242(8):1782–1787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood C., Gibson Q. H. The reaction of reduced cytochrome C oxidase with oxygen. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 25;242(8):1782–1787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood C., Wilson M. T., Brunori M. Studies on partially reduced mammalian cytochrome oxidase. Reactions with carbon monoxide and oxygen. Biochem J. 1974 Feb;137(2):205–215. doi: 10.1042/bj1370205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leigh J. S., Jr, Wilson D. F., Owen C. S., King T. E. Heme-heme interaction in cytochrome c oxidase: the cooperativity of the hemes of cytochrome c oxidase as evidenced in the reaction with CO. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Feb;160(2):476–486. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90424-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONOD J., WYMAN J., CHANGEUX J. P. ON THE NATURE OF ALLOSTERIC TRANSITIONS: A PLAUSIBLE MODEL. J Mol Biol. 1965 May;12:88–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80285-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyle J., Mitchell P. Cytochrome c oxidase is not a proton pump. FEBS Lett. 1978 Apr 15;88(2):268–272. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80190-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muijsers A. O., Tiesjema R. H., Henderson R. W., Van Gelder B. F. Biochemical and biophysical studies on cytochrome aa 3 . VII. The effect of cytochrome c on the oxidation-reduction potential of isolated cytochrome aa 3 . Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Apr 20;267(1):216–221. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90154-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myer Y. P. Conformation of cytochromes. V. Cytochrome c oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1241–1248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orii Y., King T. E. On the nature of the three intermediate species formed after reaction of reduced cytochrome oxidase with oxygen. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 10;251(23):7487–7493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen L. C., Cox R. P. Reduction of oxygen-pulsed cytochrome c oxidase by cytochrome c and other electron donors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Mar 7;590(1):128–137. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(80)90152-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosén S., Brändén R., Vänngård T., Malmström B. G. EPR evidence for an active form of cytochrome c oxidase different from the resting enzyme. FEBS Lett. 1977 Feb 15;74(1):25–30. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80744-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroedl N. A., Hartzell C. R. Oxidative titrations of reduced cytochrome aa3: correlation of midpoint potentials and extinction coefficients observed at three major absorption bands. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 15;16(23):4961–4965. doi: 10.1021/bi00642a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw R. W., Hansen R. E., Beinert H. The oxygen reactions of reduced cytochrome c oxidase. Position of a form with an unusual EPR signal in the sequence of early intermediates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Nov 8;548(2):386–396. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(79)90143-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikström M., Krab K. Proton-pumping cytochrome c oxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Aug 17;549(2):177–122. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(79)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. T., Greenwood C., Brunori M., Antonini E. Kinetic studies on the reaction between cytochrome c oxidase and ferrocytochrome c. Biochem J. 1975 Apr;147(1):145–153. doi: 10.1042/bj1470145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyman J. The turning wheel: a study in steady states. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3983–3987. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YONETANI T., RAY G. S. STUDIES ON CYTOCHROME OXIDASE. VI. KINETICS OF THE AEROBIC OXIDATION OF FERROCYTOCHROME C BY CYTOCHROME OXIDASE. J Biol Chem. 1965 Aug;240:3392–3398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



