Abstract
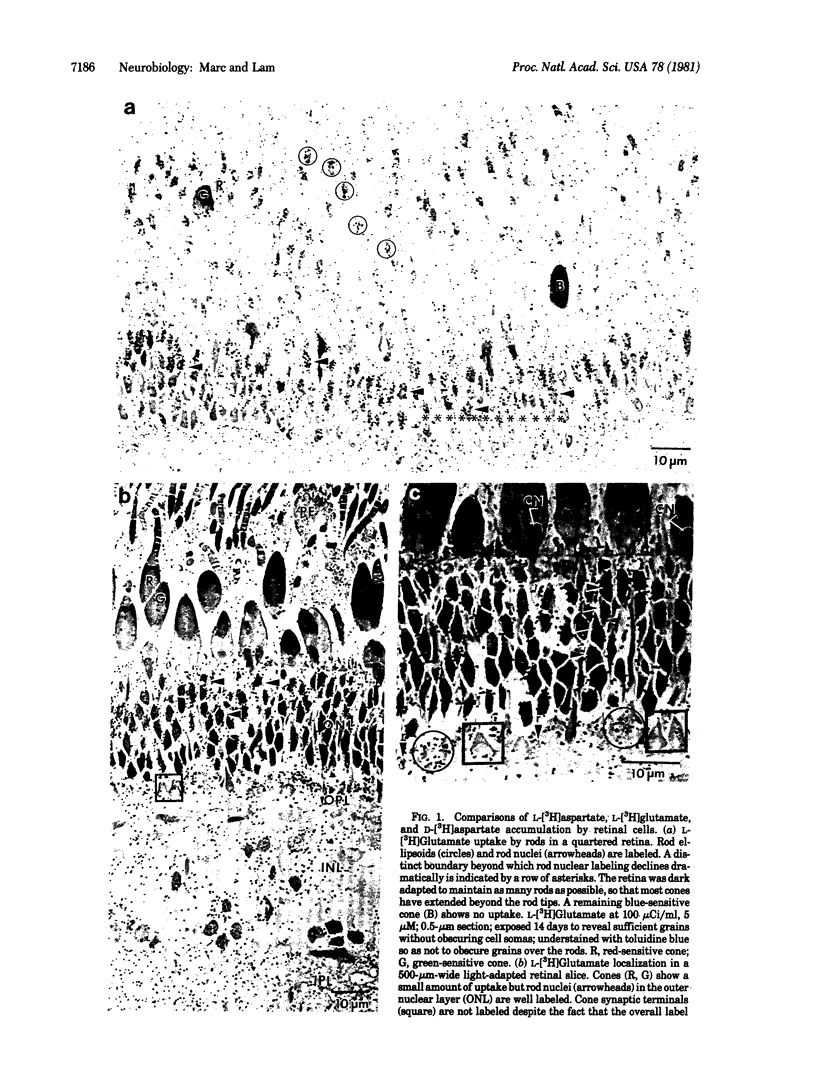
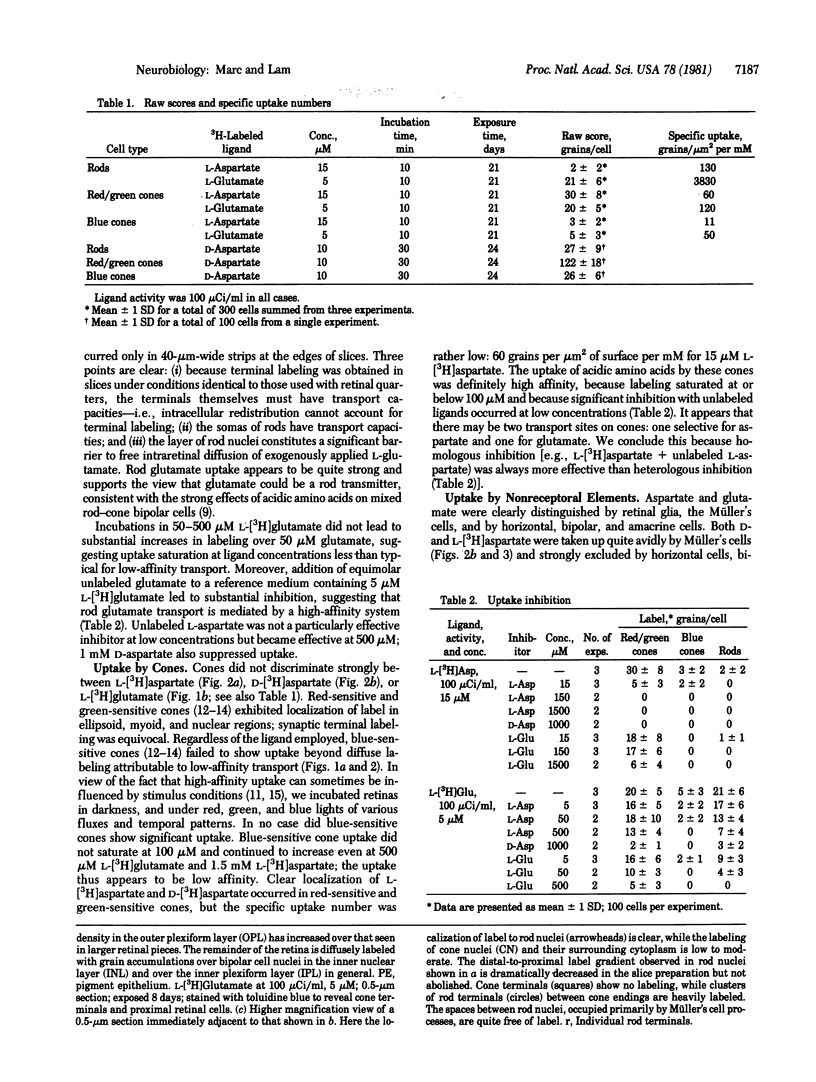
The uptake of acidic amino acids by goldfish photoreceptors was investigated by light microscope autoradiography. Isolated retinas were incubated in media containing micromolar amounts of L-[3H]aspartate, L-[3H]glutamate, and D-[3H]aspartate. We have four major observations. (i) Rods accumulate L-[3H]glutamate with a high-affinity transport system; they exhibit a glutamate-to-aspartate selectivity ratio of 30:1. When incubated in 1-10 microM L-[3H]glutamate, rods label more densely than cones. A unit area of rod membrane transports glutamate 30 times better than a unit area of cone membrane. (ii) Red-sensitive and green-sensitive cones show accumulation of L-[3H]aspartate, D-[3H]aspartate, and L-[3H]glutamate, apparently with high affinity, but with little selectivity. Because rods have poor aspartate uptake, red-sensitive and green-sensitive cones may be preferentially labeled with L-[3H]aspartate or D-[3H]aspartate, (iii) Blue-sensitive cones show no uptake of L-[3H]aspartate, D-[3H]aspartate, or L-[3H]glutamate other than that attributable to low-affinity transport. (iv) Various cell types in the goldfish retina can clearly discriminate between glutamate and aspartate, unlike acidic amino acid transport systems described in mammalian brain.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balcar V. J., Johnston G. A. The structural specificity of the high affinity uptake of L-glutamate and L-aspartate by rat brain slices. J Neurochem. 1972 Nov;19(11):2657–2666. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01325.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cervetto L., MacNichol E. F., Jr Inactivation of horizontal cells in turtle retina by glutamate and aspartate. Science. 1972 Nov 17;178(4062):767–768. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4062.767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies L. P., Johnston G. A. Uptake and release of D- and L-aspartate by rat brain slices. J Neurochem. 1976 May;26(5):1007–1014. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb06485.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling J. E., Ripps H. Adaptation in skate photoreceptors. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Dec;60(6):698–719. doi: 10.1085/jgp.60.6.698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURUKAWA T., HANAWA I. Effects of some common cations on electroretinogram of the toad. Jpn J Physiol. 1955 Dec 15;5(4):289–300. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.5.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida A. T., Fain G. L. D-aspartate potentiates the effects of L-glutamate on horizontal cells in goldfish retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5890–5894. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan W. J., Snyder S. H. High affinity uptake systems for glycine, glutamic and aspaspartic acids in synaptosomes of rat central nervous tissues. Brain Res. 1972 Jul 20;42(2):413–431. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90540-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marc R. E., Lam D. M. Glycinergic pathways in the goldfish retina. J Neurosci. 1981 Feb;1(2):152–165. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.01-02-00152.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marc R. E., Sperling H. G. Color receptor identities of goldfish cones. Science. 1976 Feb 6;191(4226):487–489. doi: 10.1126/science.1246634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marc R. E., Sperling H. G. The chromatic organization of the goldfish cone mosaic. Vision Res. 1976;16(11):1211–1224. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(76)90044-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marc R. E., Stell W. K., Bok D., Lam D. M. GABA-ergic pathways in the goldfish retina. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Nov 15;182(2):221–244. doi: 10.1002/cne.901820204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami M., Otsu K., Otsuka T. Effects of chemicals on receptors and horizontal cells in the retina. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(3):899–913. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami M., Otsuka T., Shimazaki H. Effects of aspartate and glutamate on the bipolar cells in the carp retina. Vision Res. 1975 Mar;15(3):456–458. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(75)90101-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negishi K., Drujan B. D. Effects of some amino acids on horizontal cells in the fish retina. J Neurosci Res. 1979;4(5-6):351–363. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490040504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stell W. K., Hárosi F. I. Cone structure and visual pigment content in the retina of the goldfish. Vision Res. 1976;16(6):647–657. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(76)90013-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storm-Mathisen J. Glutamic acid and excitatory nerve endings: reduction of glutamic acid uptake after axotomy. Brain Res. 1977 Jan 21;120(2):379–386. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90918-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugawara K., Negishi K. Effects of some amino acids on the horizontal cell membrane potential in the isolated carp retina. Vision Res. 1973 May;13(5):977–981. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(73)90076-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkovsky P., Nelson J., Ripps H. Action spectra and adaptation properties of carp photoreceptors. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Apr;61(4):401–423. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.4.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu S. M., Dowling J. E. L-aspartate: evidence for a role in cone photoreceptor synaptic transmission in the carp retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5205–5209. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]