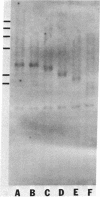
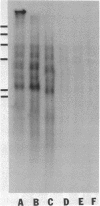
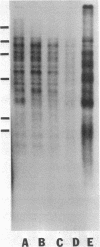
Abstract
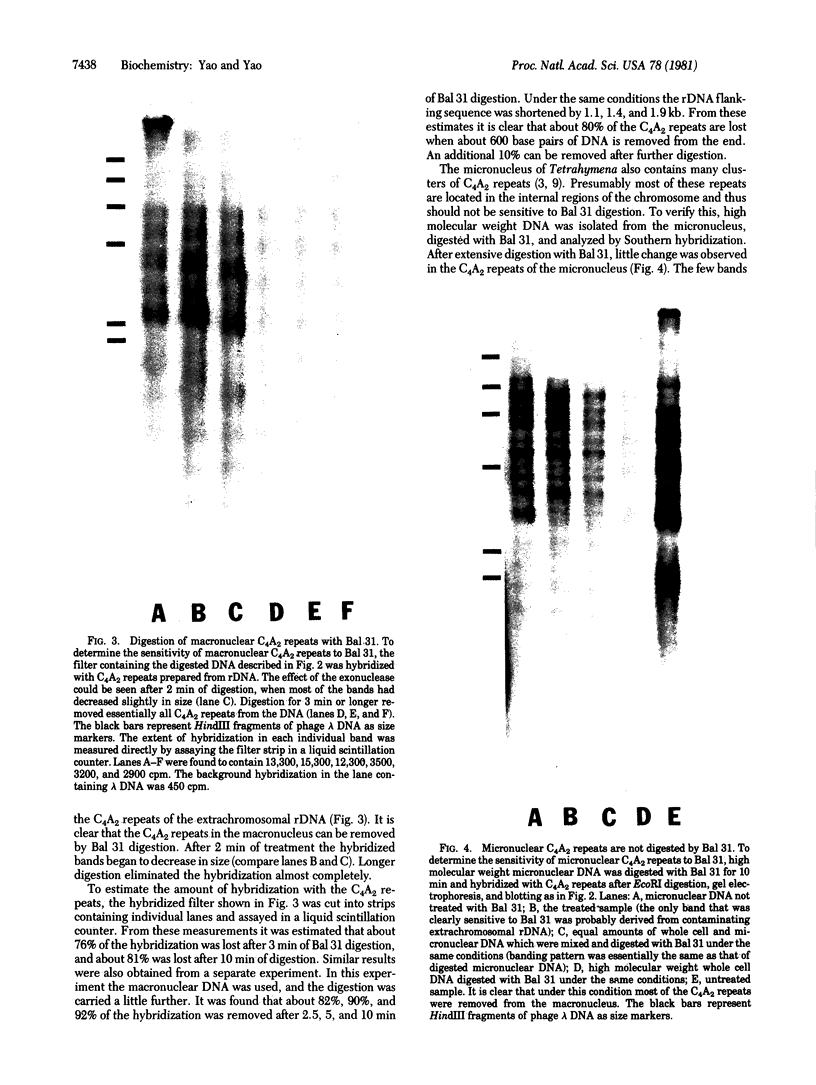
The tandemly repeated hexanucleotide C-C-C-C-A-A has previously been found near the termini of extrachromosomal gene coding for ribosomal RNA as well as in many other locations of the genome of Tetrahymena. Moreover, the organization of these clusters of repeats in the somatic macronucleus is different from that in the germinal micronucleus. In this study we used the exonuclease Bal 31 to show that the repeats are located near free ends of DNA in the macronucleus. When whole cell DNA or macronuclear DNA was digested with Bal 31 to remove approximately 600 base pairs from free ends, 80% of the C4A2 repeats were removed, as judged by hybridization. Because no particular cluster was resistant to exonuclease digestion, we believe that essentially all the C4A2 repeats are located near free ends of DNA. The C4A2 repeats in the micronucleus, on the other hand, were not digested by Bal 31.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackburn E. H., Gall J. G. A tandemly repeated sequence at the termini of the extrachromosomal ribosomal RNA genes in Tetrahymena. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):33–53. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90294-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engberg J., Andersson P., Leick V., Collins J. Free ribosomal DNA molecules from Tetrahymena pyriformis GL are giant palindromes. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jun 25;104(2):455–470. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90281-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorovsky M. A. Genome organization and reorganization in Tetrahymena. Annu Rev Genet. 1980;14:203–239. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.14.120180.001223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorovsky M. A., Yao M. C., Keevert J. B., Pleger G. L. Isolation of micro- and macronuclei of Tetrahymena pyriformis. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;9(0):311–327. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60080-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray H. B., Jr, Ostrander D. A., Hodnett J. L., Legerski R. J., Robberson D. L. Extracellular nucleases of Pseudomonas BAL 31. I. Characterization of single strand-specific deoxyriboendonuclease and double-strand deoxyriboexonuclease activities. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Sep;2(9):1459–1492. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.9.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karrer K. M., Gall J. G. The macronuclear ribosomal DNA of Tetrahymena pyriformis is a palindrome. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jun 25;104(2):421–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90280-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzen A. L., Cann G. M., Blackburn E. H. Sequence-specific fragmentation of macronuclear DNA in a holotrichous ciliate. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):313–320. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90321-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klobutcher L. A., Swanton M. T., Donini P., Prescott D. M. All gene-sized DNA molecules in four species of hypotrichs have the same terminal sequence and an unusual 3' terminus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3015–3019. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legerski R. J., Gray H. B., Jr, Robberson D. L. A sensitive endonuclease probe for lesions in deoxyribonucleic acid helix structure produced by carcinogenic or mutagenic agents. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8740–8746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka Y., Shiota S., Nakai S., Nishida Y., Okubo S. Inverted terminal repeat sequence in the macronuclear DNA of Stylonychia pustulata. Gene. 1980 Sep;10(4):301–306. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90150-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. B., Fleck E. W., Hellier L. E., Uhlenhopp E. Viscoelastic studies on Tetrahymena macronuclear DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5062–5065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao M. C., Blackburn E., Gall J. G. Amplification of the rRNA genes in Tetrahymena. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):1293–1296. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao M. C., Blackburn E., Gall J. Tandemly repeated C-C-C-C-A-A hexanucleotide of Tetrahymena rDNA is present elsewhere in the genome and may be related to the alteration of the somatic genome. J Cell Biol. 1981 Aug;90(2):515–520. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.2.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao M. C., Gorovsky M. A. Comparison of the sequences of macro- and micronuclear DNA of Tetrahymena pyriformis. Chromosoma. 1974;48(1):1–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00284863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao M. C. Ribosomal RNA gene amplification in Tetrahymena may be associated with chromosome breakage and DNA elimination. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):765–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90102-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]