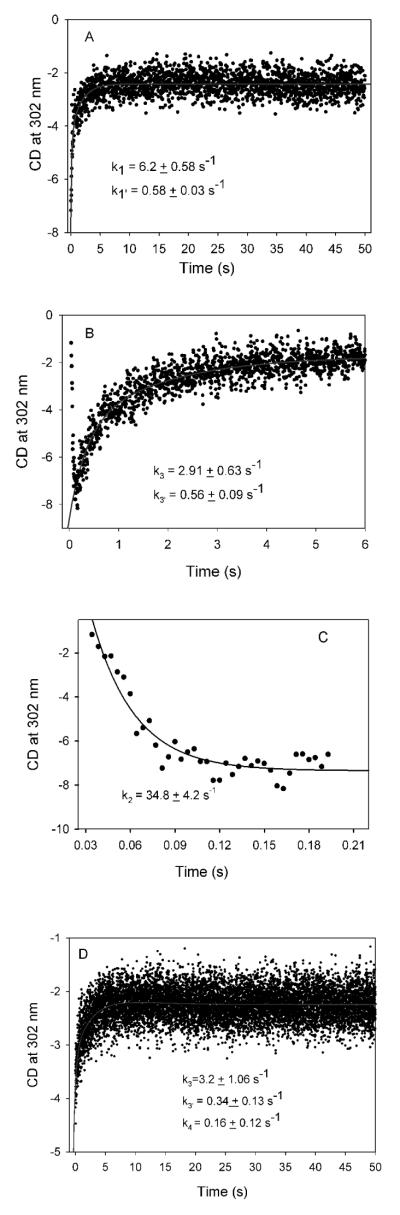
Figure 6.
ime course of the reaction of V51D GCL with glyoxylate monitored by stopped-flow CD. (A) Formation of 1′,4′-iminoglycolylThDP at pH 7.6 and 6 °C. V51D GCL (3.6 mg/mL, concentration of active centers = 55.6 μM) in 0.1 M KH2PO4 (pH 7.6) containing 0.5 mM ThDP, 2.5 mM MgCl2, 1.0 mM DTT and 10 μM FAD in one syringe was mixed with an equal volume of 2.0 mM glyoxylate in the same buffer in the second syringe. Data were fitted to a double exponential equation (eq 4). (B) The decarboxylation of 1′,4′-iminoglycolyl-ThDP and the formation of TSA-ThDP complex at pH 7.6 and 15 °C. V51D GCL (2.3 mg/mL, concentration of active centers = 35.5 μM) in one syringe was mixed with 2.0 mM glyoxylate in the second syringe at 15 °C. (C) Time-dependent decarboxylation of 1′,4′-iminoglycolylThDP with data from Figure 5 (B) expanded. Data were fitted to a single exponential (eq 5). (D) The formation of TSA-ThDP complex and TSA release by V51D GCL at pH 7.6. The V51D GCL (1.7 mg/mL, concentration of active centers = 26 μM) was pre-incubated with 0.5 mM glyoxylate for 15 min in one syringe, and was then mixed at 6 °C with 16 mM glyoxylate in the second syringe. The data were fitted to a triple exponential (eq 6).