Abstract
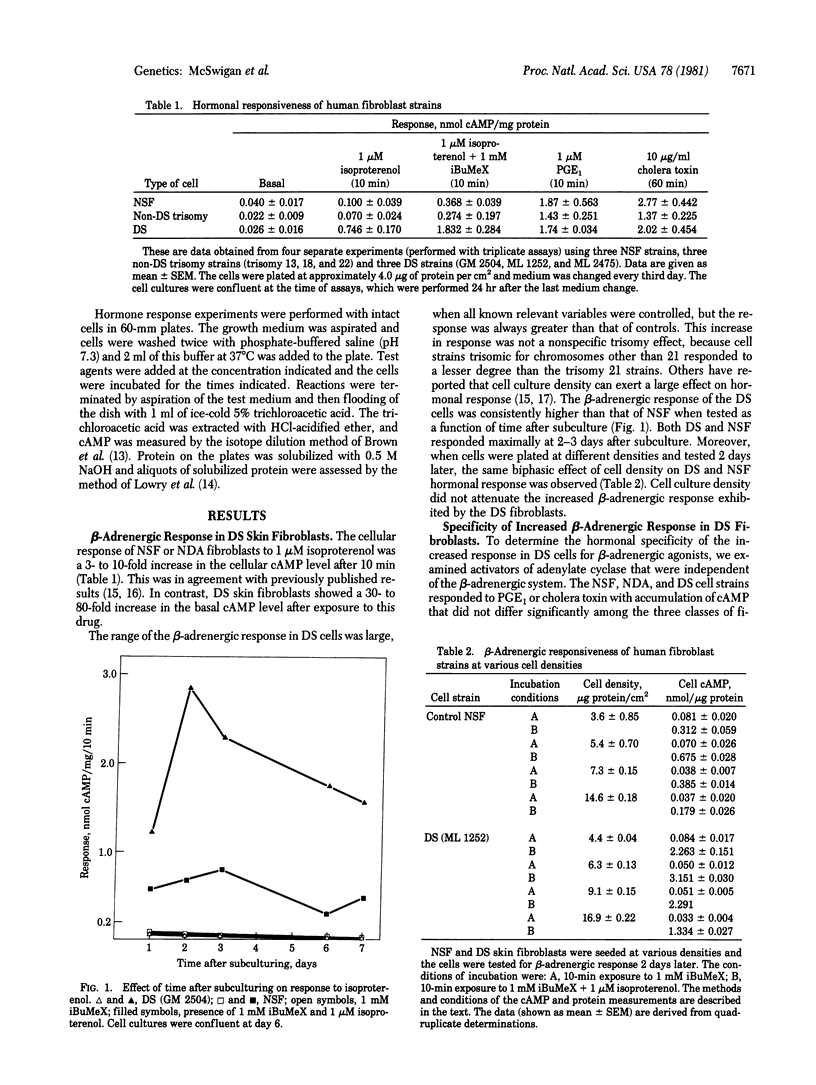
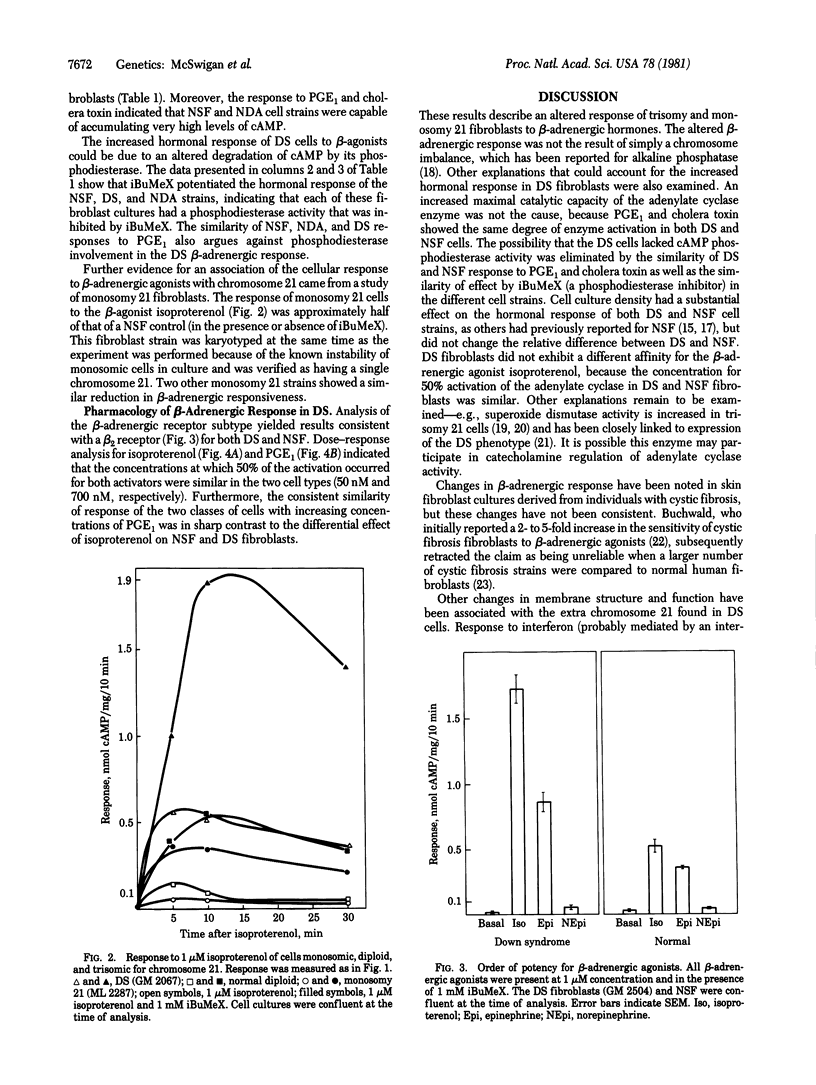
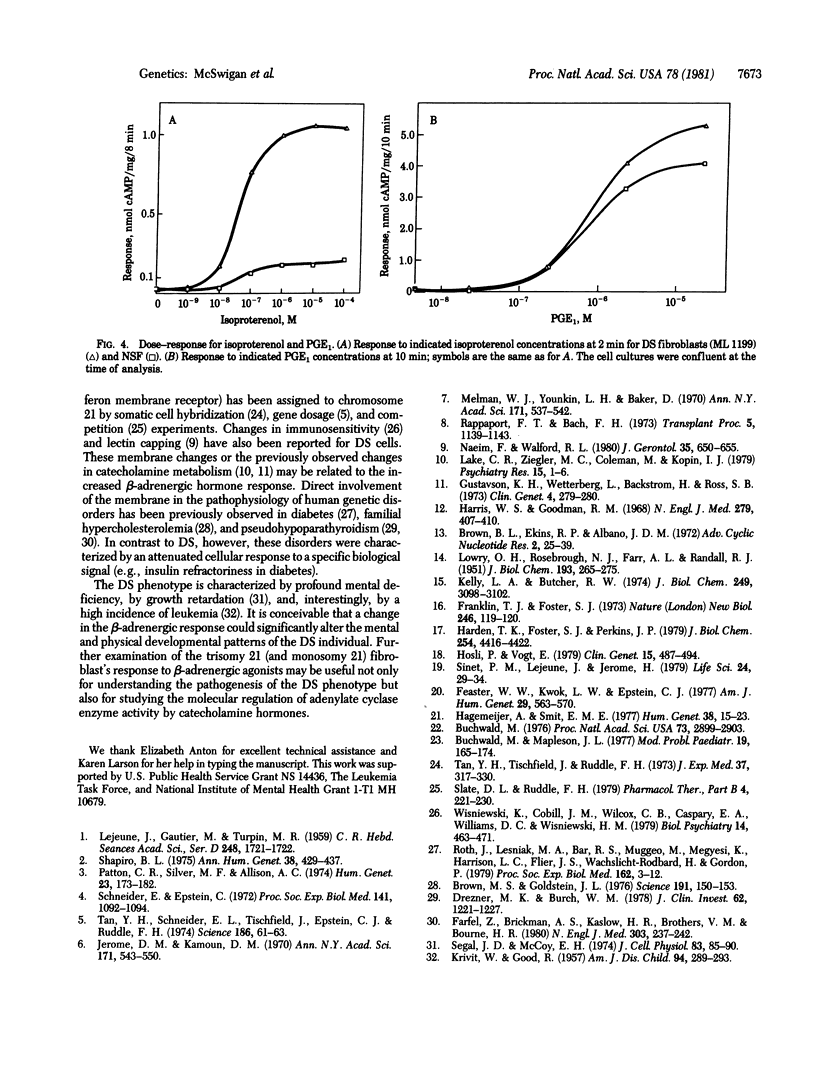
The hormonal response to human skin fibroblasts after exposure to beta-adrenergic agonists, prostaglandin E1 (PGE1), and cholera toxin was monitored by intracellular cyclic AMP accumulation. Down syndrome (DS; trisomy 21) cells had an approximately 10-fold greater response to beta-adrenergic agonists than did either normal diploid skin fibroblasts or other aneusomic fibroblast strains (trisomy 13, 18, and 22). The altered response in DS fibroblasts was specific for beta-adrenergic agonists, because treatment of DS or control cells with PGE1 or cholera toxin resulted in the same degree of cyclic AMP accumulation. Experiments with 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine, a cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase inhibitor, indicated that the increased response of DS fibroblasts was not primarily a function of altered cyclic AMP degradation. Monosomy 21 cells responded less than normal diploid fibroblasts to stimulation by the beta-adrenergic agonist isoproterenol. These findings suggest that genetic information on chromosome 21 participates in regulating the beta-adrenergic response of human fibroblasts.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown B. L., Ekins R. P., Albano J. D. Saturation assay for cyclic AMP using endogenous binding protein. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1972;2:25–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Receptor-mediated control of cholesterol metabolism. Science. 1976 Jan 16;191(4223):150–154. doi: 10.1126/science.174194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchwald M. Abnormal levels of 3':5'-cyclic AMP in isoproterenol-stimulated fibroblasts from patients with cystic fibrosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2899–2903. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchwald M., Mapleson J. L. Adenosine 3':5'-cyclic AMP in fibroblasts from patients with cystic fibrosis and its relationship to secretion. Mod Probl Paediatr. 1976 Oct 24;19:165–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drezner M. K., Burch W. M., Jr Altered activity of the nucleotide regulatory site in the parathyroid hormone-sensitive adenylate cyclase from the renal cortex of a patient with pseudohypoparathyroidism. J Clin Invest. 1978 Dec;62(6):1222–1227. doi: 10.1172/JCI109242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farfel Z., Brickman A. S., Kaslow H. R., Brothers V. M., Bourne H. R. Defect of receptor-cyclase coupling protein in psudohypoparathyroidism. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jul 31;303(5):237–242. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198007313030501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feaster W. W., Kwok L. W., Epstein C. J. Dosage effects for superoxide dismutase-1 in nucleated cells aneuploid for chromosome 21. Am J Hum Genet. 1977 Nov;29(6):563–570. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin T. J., Foster S. J. Leakage of cyclic AMP from human diploid fibroblasts in tissue culture. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 28;246(152):119–120. doi: 10.1038/newbio246119a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustavson K. H., Wetterberg L., Bäckström M., Ross S. B. Catechol-O-methyltransferase activity in erythrocytes in Down's syndrome. Clin Genet. 1973;4(3):279–280. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1973.tb01156.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagemeijer A., Smit E. M. Partial trisomy 21. Further evidence that trisomy of band 21q22 is essential for Down's phenotype. Hum Genet. 1977 Aug 31;38(1):15–23. doi: 10.1007/BF00295803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harden T. K., Foster S. J., Perkins J. P. Differential expression of components of the adenylate cyclase system during growth of astrocytoma cells in culture. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4416–4422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris W. S., Goodman R. M. Hyper-reactivity to atropine in Down's syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1968 Aug 22;279(8):407–410. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196808222790805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hösli P., Vogt E. High alkaline phosphatase activity in isoproterenol stimulated fibroblast cultures from patients with numerically unbalanced chromosomal aberrations. Clin Genet. 1979 Jun;15(6):487–494. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1979.tb00830.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRIVIT W., GOOD R. A. Simultaneous occurrence of mongolism and leukemia; report of a nationwide survey. AMA J Dis Child. 1957 Sep;94(3):289–293. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1957.04030040075012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly L. A., Butcher R. W. The effects of epinephrine and prostaglandin E-1 on cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate levels in WI-38 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 25;249(10):3098–3102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEJEUNE J., GAUTIER M., TURPIN R. Etude des chromosomes somatiques de neuf enfants mongoliens. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1959 Mar 16;248(11):1721–1722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake C. R., Ziegler M. G., Coleman M., Kopin I. J. Evaluation of the sympathetic nervous system in trisomy-21 (Down's syndrome). J Psychiatr Res. 1979;15(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0022-3956(79)90002-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naeim F., Walford R. L. Disturbance of redistribution of surface membrane receptors on peripheral mononuclear cells of patients with Down's syndrome and of aged individuals. J Gerontol. 1980 Sep;35(5):650–655. doi: 10.1093/geronj/35.5.650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton G. R., Silver M. F., Allison A. C. Comparison of cell cycle time in normal and trisomic cells. Humangenetik. 1974;23(3):173–182. doi: 10.1007/BF00285103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapaport F. T., Bach F. H. Genetic studies of cell-surface determinants in human developmental anomalies--a preliminary report. Transplant Proc. 1973 Jun;5(2):1139–1143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Lesniak M. A., Bar R. S., Muggeo M., Megyesi K., Harrison L. C., Flier J. S., Wachslicht-Rodbard H., Gorden P. An introduction to receptors and receptor disorders. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1979 Oct;162(1):3–12. doi: 10.3181/00379727-162-40608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider E. L., Epstein C. J. Replication rate and lifespan of cultured fibroblasts in Down's syndrome. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Dec;141(3):1092–1094. doi: 10.3181/00379727-141-36940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal D. J., McCoy E. E. Studies on Down's syndrome in tissue culture. I. Growth rates and protein contents of fibroblast cultures. J Cell Physiol. 1974 Feb;83(1):85–90. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040830112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro B. L. Amplified developmental instability in Down's syndrome. Ann Hum Genet. 1975 May;38(4):429–437. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1975.tb00632.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinet P. M., Lejeune J., Jerome H. Trisomy 21 (Down's syndrome). Glutathione peroxidase, hexose monophoshate shunt and I.Q. Life Sci. 1979 Jan 1;24(1):29–33. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90276-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slate D. L., Ruddle F. H. Genetics of the interferon system. Pharmacol Ther. 1979;4(1):221–230. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(79)90020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan Y. H., Schneider E. L., Tischfield J., Epstein C. J., Ruddle F. H. Human chromosome 21 dosage: effect on the expression of the interferon induced antiviral state. Science. 1974 Oct 4;186(4158):61–63. doi: 10.1126/science.186.4158.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan Y. H., Tischfield J., Ruddle F. H. The linkage of genes for the human interferon-induced antiviral protein and indophenol oxidase-B traits to chromosome G-21. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):317–330. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski K., Cobill J. M., Wilcox C. B., Caspary E. A., Williams D. G., Wisniewski H. M. T lymphocytes in patients with Down's syndrome. Biol Psychiatry. 1979 Jun;14(3):463–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



