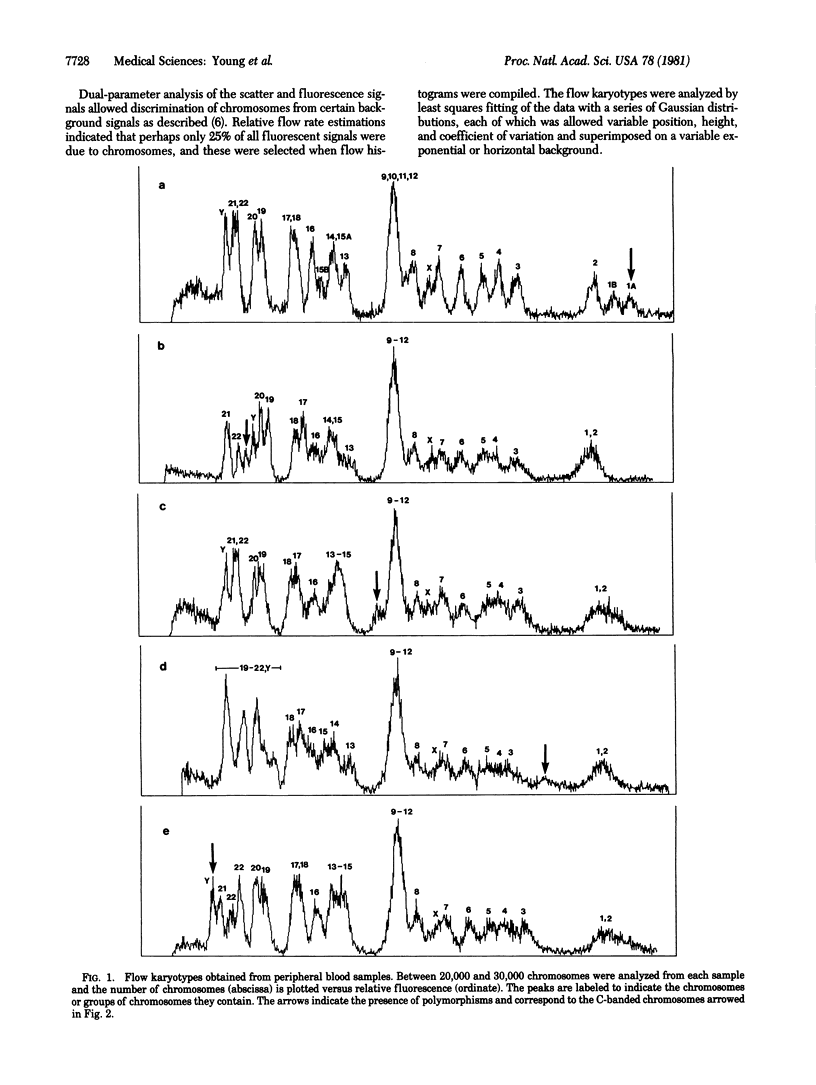
Abstract
A method for high-resolution analysis of the human karyotype by flow cytometry has been developed. Metaphase chromosomes are prepared from short-term peripheral blood cultures, stained with ethidium bromide, and analyzed on a standard fluorescence-activated cell sorter (FACS-II). Flow karyotypes with up to 20 peaks can be obtained with coefficients of variation in the range 1-2%. At this level of resolution the contribution of many of the human chromosomes can be evaluated separately. Significant and reproducible differences between normal individuals have been detected and have been correlated with differences in the centric heterochromatin of certain chromosomes as revealed in their C-banded karyotypes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carrano A. V., Gray J. W., Langlois R. G., Burkhart-Schultz K. J., Van Dilla M. A. Measurement and purification of human chromosomes by flow cytometry and sorting. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1382–1384. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cram L. S., Arndt-Jovin D. J., Grimwade B. G., Jovin T. M. Fluorescence polarization and pulse width analysis of chromosomes by a flow system. J Histochem Cytochem. 1979 Jan;27(1):445–453. doi: 10.1177/27.1.86570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray J. W., Carrano A. V., Steinmetz L. L., Van Dilla M. A., Moore D. H., 2nd, Mayall B. H., Mendelsohn M. L. Chromosome measurement and sorting by flow systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1231–1234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray J. W., Peters D., Merrill J. T., Martin R., Van Dilla M. A. Slit-scan flow cytometry of mammalian chromosomes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1979 Jan;27(1):441–444. doi: 10.1177/27.1.374608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. A., Tantravahi R., Dev V. G., Miller O. J. Frequency of satellite association of human chromosomes is correlated with amount of Ag-staining of the nucleolus organizer region. Am J Hum Genet. 1977 Sep;29(5):490–502. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillar R., Young B. D. A new method for the preparation of metaphase chromosomes for flow analysis. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Jan;29(1):74–78. doi: 10.1177/29.1.6162882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sörén L. Variability of the time at which PHA-stimulated lymphocytes initiate DNA synthesis. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Mar 30;78(1):201–208. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90055-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Stubblefield E. A new method for the rapid isolation of chromosomes, mitotic apparatus, or nuclei from mammalian fibroblasts at near neutral pH. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Mar;59(3):469–478. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90656-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]