Abstract
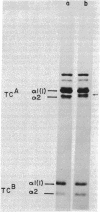
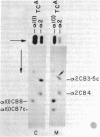
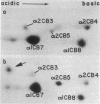
Cells in culture from a woman with a variety of the Marfan syndrome produce two species of the alpha 2 chains of type I collagen. One alpha 2 chain appears normal; the abnormal chain has a higher apparent molecular weight than normal and migrates more slowly during electrophoresis in sodium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gels. A similar change in electrophoretic behavior is seen in the prepro alpha 2 chain and the pN alpha 2 chain (which contains the amino-terminal extension). Asymmetric cleavage of the pepsin-treated procollagens with a fibroblast collagenase locates the abnormal segment amino terminal to the cleavage site, and analysis of cyanogen bromide peptides of collagenase cleavage peptides and of whole collagens indicates that the abnormal segment is in either the alpha 2CB3 peptide or the short segment of alpha 2CB5 amino terminal to the collagenase site of the altered alpha 2 chain. The higher apparent molecular weight is consistent with the insertion of a small peptide fragment of approximately 20 amino acids. This alteration in chain size has marked effects on crosslinking because collagen from the patient's skin was 5-10 times more extractable in nondenaturing solvents than that from control skins. Although the abnormal chain was not found in several other individuals with the Marfan syndrome, these findings suggest that the phenotype may be the expression of a variety of primary structure alterations in the chains of type I collagen that interfere with normal crosslink formation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appel A., Horwitz A. L., Dorfman A. Cell-free synthesis of hyaluronic acid in Marfan syndrome. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 10;254(23):12199–12203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barsh G. S., Byers P. H. Reduced secretion of structurally abnormal type I procollagen in a form of osteogenesis imperfecta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5142–5146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benya P. D. Two-dimensional CNBr peptide patterns of collagen types I, II and III. Coll Relat Res. 1981;1(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(80)80004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P., Sage H. Structurally distinct collagen types. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:957–1003. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.004521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd C. D., Tolstoshev P., Schafer M. P., Trapnell B. C., Coon H. C., Kretschmer P. J., Nienhuis A. W., Crystal R. G. Isolation and characterization of a 15-kilobase genomic sequence coding for part of the Pro alpha 2 chain of sheep type I collagen. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):3212–3220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers P. H., Siegel R. C., Holbrook K. A., Narayanan A. S., Bornstein P., Hall J. G. X-linked cutis laxa: defective cross-link formation in collagen due to decreased lysyl oxidase activity. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jul 10;303(2):61–65. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198007103030201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fietzek P. P., Kühn K. The primary structure of collagen. Int Rev Connect Tissue Res. 1976;7:1–60. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-363707-9.50007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg T., Müller P. K. The marfan's syndrome. In vitro study of collagen metabolism in tissue specimens of the aorta. Exp Cell Biol. 1977;45(3-4):207–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laitinen O., Uitto J., Iivanainen M., Hannuksela M., Kivirikko K. I. Collagen metabolism of the skin in Marfan's syndrome. Clin Chim Acta. 1968 Sep;21(3):321–326. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(68)90062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamberg S. I., Dorfman A. Synthesis and degradation of hyaluronic acid in the cultured fibroblasts of Marfan's disease. J Clin Invest. 1973 Oct;52(10):2428–2433. doi: 10.1172/JCI107433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layman D. L., McGoodwin E. B., Martin G. R. The nature of the collagen synthesized by cultured human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):454–458. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layman D. L., Narayanan A. S., Martin G. R. The production of lysyl oxidase by human fibroblasts in culture. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Mar;149(1):97–101. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90302-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macek M., Hurych J., Chvapil M., Kadlecová V. Study of fibroblasts in Marfan's syndrome. Humangenetik. 1966;3(2):87–97. doi: 10.1007/BF00291289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matalon R., Dorfman A. The accumulation of hyaluronic acid in cultured fibroblasts of the Marfan syndrome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Jul 26;32(2):150–154. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90361-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PONSETI I. V., BAIRD W. A. Scoliosis and dissecting aneurysm of the aorta in rats fed with Lathyrus odoratus seeds. Am J Pathol. 1952 Nov-Dec;28(6):1059–1077. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Davidson J. M., Gagnon J., Rowe D. W., Bornstein P. NH2-terminal sequence of the chick proalpha1(I) chain synthesized in the reticulocyte lysate system. Evidence for a transient hydrophobic leader sequence. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 10;254(5):1433–1436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinnell S. R., Krane S. M., Kenzora J. E., Glimcher M. J. A heritable disorder of connective tissue. Hydroxylysine-deficient collagen disease. N Engl J Med. 1972 May 11;286(19):1013–1020. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197205112861901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priest R. E., Moinuddin J. F., Priest J. H. Letter: Collagen of Marfan syndrome is abnormally soluble. Nature. 1973 Oct 5;245(5423):264–266. doi: 10.1038/245264a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prockop D. J., Kivirikko K. I., Tuderman L., Guzman N. A. The biosynthesis of collagen and its disorders (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1979 Jul 12;301(2):77–85. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197907123010204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyeritz R. E., McKusick V. A. The Marfan syndrome: diagnosis and management. N Engl J Med. 1979 Apr 5;300(14):772–777. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197904053001406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. W., McGoodwin E. B., Martin G. R., Grahn D. Decreased lysyl oxidase activity in the aneurysm-prone, mottled mouse. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):939–942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. W., McGoodwin E. B., Martin G. R., Sussman M. D., Grahn D., Faris B., Franzblau C. A sex-linked defect in the cross-linking of collagen and elastin associated with the mottled locus in mice. J Exp Med. 1974 Jan 1;139(1):180–192. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.1.180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. W., Moen R. C., Davidson J. M., Byers P. H., Bornstein P., Palmiter R. D. Correlation of procollagen mRNA levels in normal and transformed chick embryo fibroblasts with different rates of procollagen synthesis. Biochemistry. 1978 May 2;17(9):1581–1590. doi: 10.1021/bi00602a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheck M., Siegel R. C., Parker J., Chang Y. H., Fu J. C. Aortic aneurysm in Marfan's syndrome: changes in the ultrastructure and composition of collagen. J Anat. 1979 Oct;129(Pt 3):645–657. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel R. C. Lysyl oxidase. Int Rev Connect Tissue Res. 1979;8:73–118. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-363708-6.50009-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmann B., Tuderman L., Peltonen L., Martin G. R., McKusick V. A., Prockop D. J. Evidence for a structural mutation of procollagen type I in a patient with the Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type VII. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8887–8893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stricklin G. P., Bauer E. A., Jeffrey J. J., Eisen A. Z. Human skin collagenase: isolation of precursor and active forms from both fibroblast and organ cultures. Biochemistry. 1977 Apr 19;16(8):1607–1615. doi: 10.1021/bi00627a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stricklin G. P., Eisen A. Z., Bauer E. A., Jeffrey J. J. Human skin fibroblast collagenase: chemical properties of precursor and active forms. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 13;17(12):2331–2337. doi: 10.1021/bi00605a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel A., Holbrook K. A., Steinmann B., Gitzelmann R., Byers P. H. Abnormal collagen fibril structure in the gravis form (type I) of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Lab Invest. 1979 Feb;40(2):201–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogeli G., Avvedimento E. V., Sullivan M., Maizel J. V., Jr, Lozano G., Adams S. L., Pastan I., de Crombrugghe B. Isolation and characterization of genomic DNA coding for alpha 2 type I collagen. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Apr 25;8(8):1823–1837. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.8.1823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozney J., Hanahan D., Morimoto R., Boedtker H., Doty P. Fine structural analysis of the chicken pro alpha 2 collagen gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):712–716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]