Abstract
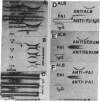
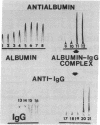
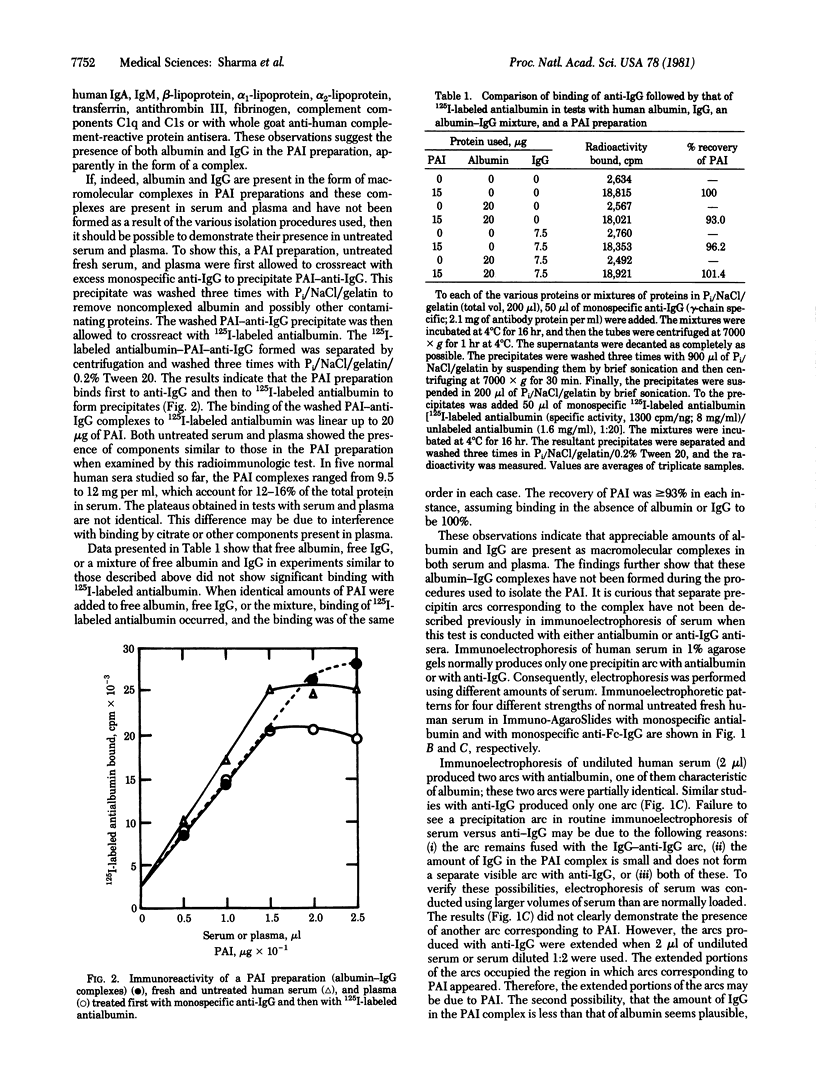
Macromolecular albumin-IgG complexes have been isolated from human serum and characterized immunologically. These complexes are shown to be present in plasma also and appear to be normal constituents of blood. The complexes can be demonstrated in normal serum and plasma by immunoelectrophoresis and rocket immunoelectrophoresis, as well as by use of a two-step radioimmunologic binding test. The albumin-IgG complexes inhibit adhesion of human platelets to glass and account for 12-16% of the total protein in serum.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cazenave J. P., Dejana E., Kinlough-Rathbone R. L., Richardson M., Packham M. A., Mustard J. F. Prostaglandins I2 and E1 reduce rabbit and human platelet adherence without inhibiting serotonin release from adherent platelets. Thromb Res. 1979;15(1-2):273–279. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90073-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George J. N. Direct assessment of platelet adhesion to glass: a study of the forces of interaction and the effects of plasma and serum factors, platelet function, and modification of the glass surface. Blood. 1972 Dec;40(6):862–874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartree E. F. Determination of protein: a modification of the Lowry method that gives a linear photometric response. Anal Biochem. 1972 Aug;48(2):422–427. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. C., Taylor R. G., Rudel L. L. Low density lipoprotein inhibition of avian thrombocyte adhesion to glass. Thromb Res. 1978 Sep;13(3):543–549. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(78)90140-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. G., Mohammad S. F., Chuang H. Y., Richardson P. D. The adhesion of platelets to subendothelium, collagen and artifilial surfaces. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1976 Oct;3(2):98–116. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1086132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad S. F., Hardison M. D., Chuang H. Y., Mason R. G. Adhesion of human blood platelets to glass polymer surfaces. II. Demonstration of the presence of a natural platelet adhesion inhibitor in plasma and serum. Haemostasis. 1976;5(2):96–114. doi: 10.1159/000214123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad S. F., Hardison M. D., Glenn C. H., Morton B. D., Bolan J. C., Mason R. G. Adhesion of human blood platelets to glass and polymer surfaces. I. Studies with platelets in plasma. Haemostasis. 1974;3(5-6):257–270. doi: 10.1159/000214064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tangen O., Berman H. J., Marfey P. Gel filtration. A new technique for separation of blood platelets from plasma. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1971 Jun 30;25(2):268–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollefsen D. M., Feagler J. R., Majerus P. W. The binding of thrombin to the surface of human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 25;249(8):2646–2651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston M. J., Woods H. F., Turney J. H. Antiplatelet agents and extracorporeal circulation. Int J Artif Organs. 1980 May;3(3):129–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]