Background: XRCC1 interacts with multiple DNA repair proteins.
Results: Identification of mutant versions of XRCC1 that are defective in binding with a different single partner.
Conclusion: Interaction between XRCC1 and polynucleotide kinase 3′-phosphatase is critical for the retention of XRCC1 at DNA damage sites and DNA damage repair.
Significance: Insights into function of one of three DNA end processing factors that bind to the same region of XRCC1.
Keywords: Base Excision Repair, Confocal Microscopy, DNA Damage, DNA Repair, Protein-Protein Interactions, PNKP, XRCC1/DNA Ligase IIIα, Laser Microirradiation
Abstract
XRCC1 plays a key role in the repair of DNA base damage and single-strand breaks. Although it has no known enzymatic activity, XRCC1 interacts with multiple DNA repair proteins and is a subunit of distinct DNA repair protein complexes. Here we used the yeast two-hybrid genetic assay to identify mutant versions of XRCC1 that are selectively defective in interacting with a single protein partner. One XRCC1 mutant, A482T, that was defective in binding to polynucleotide kinase phosphatase (PNKP) not only retained the ability to interact with partner proteins that bind to different regions of XRCC1 but also with aprataxin and aprataxin-like factor whose binding sites overlap with that of PNKP. Disruption of the interaction between PNKP and XRCC1 did not impact their initial recruitment to localized DNA damage sites but dramatically reduced their retention there. Furthermore, the interaction between PNKP and the DNA ligase IIIα-XRCC1 complex significantly increased the efficiency of reconstituted repair reactions and was required for complementation of the DNA damage sensitivity to DNA alkylation agents of xrcc1 mutant cells. Together our results reveal novel roles for the interaction between PNKP and XRCC1 in the retention of XRCC1 at DNA damage sites and in DNA alkylation damage repair.
Introduction
A characteristic feature of Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) xrcc1 mutant cell lines is the increased frequency of spontaneous and DNA damage-induced sister chromatid exchanges (1–4). This and other DNA repair abnormalities in xrcc1 mutant cells suggested that XRCC1 participates in base excision and single-strand break (SSB)2 repair. The human XRCC1 gene was cloned by complementation of the hypersensitivity of CHO EM9 mutant cells to DNA alkylating agents (1). Although XRCC1 has no known enzymatic activity, it interacts with a number of proteins that are involved in the repair of base damage and single-strand breaks, suggesting that XRCC1 acts as a scaffold that coordinates the assembly and activity of DNA repair enzymes (5).
DNA ligase IIIα was the first XRCC1-interacting protein to be identified (6). These proteins interact via their C-terminal BRCT domains, forming a stable heterodimer (7–11). In xrcc1 mutant cells, the steady state level of DNA ligase IIIα is significantly reduced (7), indicating a role for this interaction in stabilizing DNA ligase IIIα. XRCC1 also interacts with and stabilizes DNA polymerase β (Polβ) (12–16), a key component of the short patch base excision repair (BER) pathway. In contrast, the stability of other XRCC1-interacting proteins, including the DNA glycosylases, OGG1 (17), NEIL1 and NEIL2 (18, 19), AP endonuclease 1 (APE1) (20), PCNA (21), poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases (PARP) 1 and 2 (22, 23), aprataxin (24, 25), polynucleotide kinase 3′-phosphatase (PNKP) (26), and aprataxin-like factor (APLF) (27), is not significantly reduced in the absence of XRCC1.
In accord with the predicted role of XRCC1 as a scaffold that coordinates activities of multiple DNA repair enzymes (5), the binding sites of many but not all interacting proteins have been mapped to discrete regions along the entire length of the XRCC1 polypeptide (Fig. 1). XRCC1 has been identified as a subunit of high molecular weight multiprotein complexes by gel filtration and immunoprecipitation experiments, suggesting that this protein can indeed simultaneously interact with multiple protein partners (28, 29). However, the binding of three DNA repair enzymes, PNKP, aprataxin, and APLF, which are involved in processing DNA termini, appear to be mutually exclusive (24, 26, 27). This notion is supported by the characterization of two distinct XRCC1 protein complexes that contain either PNKP or aprataxin (29).
FIGURE 1.
XRCC1 domain structure and regions involved in protein-protein interactions; replacement of alanine at position 482 with threonine disrupts the binding of XRCC1 to PNKP but not aprataxin or APLF. A, diagram showing the positions of the nuclear localization signal (NLS), N-terminal domain (NTD), and the two BRCT domains (BRCT I and BRCT II) within XRCC1. The regions involved in binding to APE1 (20), PARP1 (23), Polβ (13), PNKP (26), and DNA ligase IIIα (9, 11) and the positions of the amino acid changes that disrupt binding to APE1 (G297V), PARP1 (L316R), Polβ (A160S), PNKP (A482T), and DNA ligase IIIα (P623S) are indicated. B, the effect of replacing alanine with threonine (pGADT7-MutPNK482) at position 482 on the interaction of XRCC1 with PNKP (pGBK-PNK) and DNA ligase IIIα (pGBK-LigIII) was analyzed using the yeast two-hybrid assay. C, the effect of replacing alanine 482 with threonine on the interaction of XRCC1 with PNKP, aprataxin, and APLF. Upper panel, the binding of purified PNKP (PNKP) to glutathione beads liganded by GST (GST), GST fused to wild-type XRCC1 (GST-WT) or GST fused to the A482T mutant version of XRCC1 (pGADT7-MutPNK482). Middle panel, the binding of labeled in vitro translated wild-type XRCC1 (WT) and the A482T mutant version of XRCC1 (MutPNK482) to glutathione beads liganded by GST (GST) and GST fused to APLF (GST-APLF). Lower panel, the binding of labeled in vitro translated wild-type XRCC1 (WT) and the A482T mutant version of XRCC1 (MutPNK482) to glutathione beads liganded by GST (GST) and GST fused to aprataxin (GST-Aprataxin). Pulldown assays were carried out as described under “Experimental Procedures.”
The functional and biological consequences of many of the protein-protein interactions involving XRCC1 have not been clearly delineated. Here we have used a modified version of the yeast two-hybrid genetic screen (30) to identify mutant versions of XRCC1 that are deficient in binding to PARP1, Polβ, PNKP, or DNA ligase IIIα. Notably, the PNKP interaction mutant of XRCC1 is not defective in binding to either aprataxin or APLF, enabling us to delineate functional and biological consequences of the interaction between XRCC1 and PNKP.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Yeast Two-hybrid Assay
A modified version of the yeast two-hybrid assay to screen for human XRCC1 mutants that are defective in interacting with partner proteins was carried out as described by Krejci et al. (30). Briefly, a DNA fragment encoding XRCC1 was subcloned into plasmid pGADT7 to generate pGADT7-XRCC1 that expresses XRCC1 as a GAL4 activation domain fusion protein. pGADT7-XRCC1 (10 μg) was incubated in 0.5 ml of 50 mm sodium pyrophosphate (pH 7), 1 m NaCl, 2 mm EDTA, and 0.5 m hydroxylamine at 75 °C for 30 min. After amplification through Escherichia coli TG1, the mutagenized pGADT7-XRCC1 plasmids were transformed into the haploid yeast strain PJ69-4a and each clone was replica-plated on solid media lacking leucine (−Leu). DNA sequences encoding PARP1, PNKP, DNA ligase IIIα, APE1, and Polβ were amplified by PCR and then subcloned into the plasmid pGBK to generate plasmids that express the XRCC1-interacting proteins as GAL4 DNA binding domain fusion proteins. Isogenic haploid yeast PJ69-4α cells were transformed with pGBK derivatives encoding different XRCC1-interacting proteins followed by selection on solid media lacking tryptophan (−Trp). Each of the PJ69-4α strains expressing a different XRCC1-interacting protein was mated with the replica-plated PJ69-4a strains harboring the mutagenized XRCC1 plasmids. After the selection of diploids (−Trp, −Leu), protein-protein interactions were assessed by growth under either low stringency (15 mm 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole, −Leu, −Trp, −His) or high stringency (−Leu, −Trp, −His, −Ade) medium conditions. XRCC1 plasmids that had lost the ability to interact with one of the 5 bait proteins were recovered using the Yeastmaker yeast plasmid isolation kit (Macherey-Nagel) and then sequenced to identify the mutation site(s).
Protein Purification
The DNA sequence change to replace Ala-482 with Thr was made in pFastBac-XRCC1 by site-directed mutagenesis and verified by DNA sequencing. E. coli DH10Bac cells containing the Bacmid (Invitrogen) were transformed with pFastBac-XRCC1A482T plasmid to generate recombinant baculovirus encoding the A482T mutant form of human XRCC1. DNA ligase IIIα-XRCC1 complexes containing either wild-type XRCC1 or the A482T mutant version were purified from insect cells after co-infection with DNA ligase IIIα and XRCC1 baculoviruses as described previously (31). Recombinant human NEIL1, PNKP, and Polβ were purified as described previously (19, 32).
DNA Ligation Assay
A 5′ 32P-labeled 26-mer and an unlabeled 25-mer were annealed to a complementary 51-mer oligonucleotide to generate a duplex with a single ligatable nick. The nicked DNA substrate (2 pmol) and DNA ligase IIIα-XRCC1 (25 or 50 fmol) were incubated in BER buffer (40 mm Hepes-KOH, pH 7.5, 50 mm KCl, 100 μg/ml of bovine serum albumin, 5% glycerol, and 1 mm ATP) at 37 °C for 30 min. After the addition of formamide dye (80% formamide, 20 mm NaOH, 20 mm EDTA, 0.05% bromphenol blue, and 0.05% xylene cyanol), labeled oligonucleotides were separated by denaturing gel electrophoresis as described (33). Labeled oligonucleotides were quantitated by PhosphorImager analysis using ImageQuant software (Amersham Biosciences).
Pulldown Assays
DNA fragments encoding either wild-type XRCC1 or the A482T mutant were subcloned in-frame into the GST expression vector pGSTag (Addgene). Plasmids encoding GST-APLF and GST-aprataxin were gifts from Drs. A. Yasui and S. West, respectively. After expression in E. coli, GST and GST fusion proteins were purified by glutathione affinity chromatography. Glutathione-Sepharose beads (30 μl, Amersham Biosciences) liganded by either GST or GST fusion proteins (2 μg of each) were incubated with purified PNKP (3 nm) as described (31). Bound proteins were detected by immunoblotting with PNKP antibody (Abcam, ab3817) after separation by SDS-PAGE. In similar experiments, glutathione-Sepharose beads (30 μl, Amersham Biosciences) liganded by GST, GST-APLF, or GST-aprataxin were incubated with wild-type and mutant versions of XRCC1 that had been radiolabeled with [35S]methionine by in vitro coupled transcription and translation (TnT7 Kit, Promega). Labeled polypeptides retained by the GST beads were detected in a PhosphorImager after separation by SDS-PAGE.
Magnetic Ni2+ beads (10 μl, Qiagen) were incubated with or without His-tagged PNKP (20 pmol) for 30 min. After washing, the beads were incubated with purified DNA ligase IIIα-XRCC1 complex (5 pmol) with either wild-type XRCC1 or the A482T mutant version for 1 h. Bound proteins were detected by immunoblotting with XRCC1 antibody (GeneTex GTX70262) after separation by SDS-PAGE.
PNKP Phosphatase Activity and SSB Repair Assays
PNKP 3′-phosphatase activity was measured in the presence or absence of DNA ligase IIIα-XRCC1 as described previously (19). To generate a SSB with 3′ and 5′ phosphate termini, an end-labeled 51-mer oligonucleotide containing U at position 26 was annealed to a complementary oligonucleotide and then incubated with uracil-DNA glycosylase and Fapy-DNA glycoslyase (New England Biolabs). The labeled DNA substrate with the SSB (2 pmol) was incubated with Polβ, (50 fmol), PNKP (25 fmol), and DNA ligase IIIα-XRCC1 (25 or 50 fmol) in BER buffer. Labeled oligonucleotides were separated and quantitated as before.
For kinetics studies, the 3′-32P-containing SSB substrate (0.1 nm) and an increasing concentration of unlabeled 3′P-containing SSB substrate (2.5–160 nm) were incubated with 0.5 nm PNKP or PNKP plus DNA ligase IIIα-XRCC1 (0.5 nm) for 5 min at 37 °C. km, Vmax, and kcat values were obtained from Lineweaver-Burk double-reciprocal plots using Sigma Plot (33).
BER Assay with Purified Proteins
A linear 51-bp duplex containing a 5-OHU base lesion at position 26 in one strand (2 pmol) was incubated with NEIL1, PNKP, Polβ, (50 fmol of each), and DNA ligase IIIα-XRCC1 (25 or 50 fmol) for 30 min at 37 °C in BER buffer containing 1 mmol of ATP, 25 mmol of dATP, dTTP, and dGTP, 5 μmol of dCTP, and 10 μmol of [α-32P]dCTP. Labeled oligonucleotides were separated and quantitated as above.
Similar repair reactions were carried with a circular duplex DNA substrate containing a single 5-OHU residue that was generated as described previously (18, 34). Briefly, the plasmid pUC19CPD containing two single-strand nicking sites on the same strand, 32 nucleotides apart, was digested with N.BstNB1 (New England Biolabs) and heated at 65 °C for 10 min to dissociate the 32-mer oligonucleotide (5′-GCG GAT ATT AAT GTG ACG GTA GCG AGT CGC TC-3′) that was removed by annealing with an of excess biotinylated complementary 32-nucleotide oligonucleotide followed by binding to streptavidin-agarose Dynabeads (Sigma). The gapped plasmid was purified by phenol/chloroform extraction and ethanol precipitation, and then annealed with a 5-OHU-containing 5′-phosphorylated 32-nucleotide oligo (5′-pGCG GAT ATT AAT GTG ACG G 5-OHU A GCG AGT CGC TC-3′) at 45 °C in TE buffer containing 50 mm NaCl. After incubation with T4 DNA ligase, the 5-OHU-containing form I plasmid was purified by cesium chloride equilibrium ultracentrifugation in the presence of ethidium bromide. The presence of 5-OHU was verified by treating the plasmid with NEIL1, which converted the form I plasmid into nicked form II. Repair reactions with the circular DNA substrate were carried out under the same conditions as reactions with the linear substrate.
Generation and Characterization of EM9 Cell Lines Ectopically Expressing Wild-type and Mutant XRCC1
DNA fragments encoding wild-type XRCC1 and the A482T mutant version were subcloned into the mammalian expression vector pcDNAHisMax4 so that the human XRCC1 proteins were expressed with an N-terminal peptide encoding the XpressTM epitope and a polyhistidine nickel-binding tag. After transfection, puromycin-resistant cells were selected and screened for XRCC1 expression by immunoblotting. Clones that stably expressed recombinant wild-type XRCC1 and the A482T mutant at levels similar to that of endogenous XRCC1 in parental AA8 cells were selected for further analysis. The steady state levels of XRCC1-interacting proteins, aprataxin, PNKP, Polβ, and DNA ligase IIIα, were determined in these cell lines by immunoblotting.
XRCC1 was immunoprecipitated from nuclear extracts (80 μg) of EM9 cells (1 to 3 × 107 cells) expressing either wild-type XRCC1 or the A482T mutant version with XRCC1 rabbit polyclonal antibody (1 μl, GeneTex GTX70262) as described previously (31). To detect proteins co-immunoprecipitated with XRCC1, membranes were stripped in PBS containing 2% SDS and 0.1 m β-mercaptoethanol for 30 min, washed with PBS for 30 min, and re-probed with a different antibody.
To measure clonogenic survival after DNA alkylation damage, cells were incubated with the DNA alkylating agent ethyl methanesulfonate (EMS, Sigma) for 1 h, washed and then grown in fresh media for 5 to 7 days. Colonies were counted after staining with crystal violet.
Plasmid Construction, Transfection, Laser Microirradiation, and Confocal Microscopy
The plasmid encoding PNKP as an enhanced green fluorescent fusion protein has been described previously (28). DNAs encoding wild-type XRCC1 and the A482T mutant version of XRCC1 were subcloned into the mammalian expression vector, pEYFP-EC1, so that the XRCC1 proteins were expressed as YFP fusion proteins (21). HeLa or EM9 cells (200,000) that had been allowed to adhere to a 35-mm glass bottom culture dish with a 10-mm Microwell (MatTek Corporation, Ashland, MA; number P35G-1.5-10-C) for 24 h in DMEM with 10% FBS, 1% penicillin/streptomycin, and 1% glutamate were transfected with plasmid DNA (1 μg) using the Dreamfect reagent (OZ Biosciences, Marseille, France) according to the manufacturer's standard protocol. Forty-eight h after transfection, cells were subjected to localized microirradiation using a Nikon Eclipse TE2000-E microscope equipped with a CCD camera (Hamamatsu, Tokyo, Japan), a SRS NL100 nitrogen pumped dye laser with Micropoint ablation system (Photonics Instruments, St. Charles, IL) adjusted via passage through a dye to generate a wavelength of 365 nm, and a CSU10 spinning disk system (Yokogawa, Japan). Laser power was attenuated using Velocity software version 5.5.0, build 0 (Improvision/PerkinElmer Life Sciences). Specifically, 1.7% laser intensity was directed to deliver pulses to a delineated rectangular region of interest (94 × 20 pixels, 0.16 μm/pixel) using a Plan Fluor ×60/1.25 numerical aperture oil objective. Galvanometer-driven beam displacers oriented the laser beam, which fired randomly throughout the region until complete exposure was obtained; 300 nm was used for the diffraction limited spot size. At a 10-Hz repetition rate, the laser fired 3-ns pulses with a power of 0.7 nanowatt, measured at the back aperture of the ×60 objective at 365 nm. These conditions generate free radical-induced DNA single-strand breaks in the targeted region, but did not induce γH2AX foci, an indicator of double-strand breaks, in the region of laser damage (35). Throughout the experiment, adherent cells were maintained in a live cell environmental chamber or CO2 enhancement workhead (Slonet Scientific, Segensworth, United Kingdom). Following site-directed laser damage, fluorescence recovery after photobleaching was recorded at various intervals until fluorescence returned to background levels. Data were analyzed using the Velocity software described above and “region of interest fluorescent intensity” was measured at various time intervals (35, 36).
RESULTS
Identification of Protein-Protein Interaction Mutants of XRCC1
Using a modified version of the yeast two-hybrid assay (30), we screened randomly mutagenized pGADT7-XRCC1 plasmids for human XRCC1 mutants that were defective in interacting with partner proteins, PARP1, Polβ, PNKP, APE1, and DNA ligase IIIα, expressed as GAL4 DNA binding domain fusion proteins. Plasmids encoding versions of XRCC1 that were defective in interacting with one partner but retained interactions with the others were selected for DNA sequence analysis. Using this approach, we identified a series of single amino acid changes that disrupted the interaction of XRCC1 with individual bait proteins (Table 1). Notably, all single amino acid changes occurred within a region of XRCC1 that had been identified previously as being required for the interaction with the specific protein (Table 1 and Fig. 1A). Because these amino acid changes only disrupt the interaction with a single partner, we conclude that they do not have a large effect on the overall folding of XRCC1.
TABLE 1.
Amino acid changes within XRCC1 that disrupt interactions with protein partners
The regions of XRCC1 (middle column) that interact with the DNA repair proteins (left column), APE1 (20), PARP1 (23), Polβ (13), PNKP (26), and DNA ligase IIIα (9, 11). The DNA sequence changes and resultant amino acid changes in XRCC1 that disrupt binding to the indicated partner protein are shown in the right column.
| XRCC1 interacting protein | Binding region in XRCC1 | Amino acid change |
|---|---|---|
| APE1 | 183–404 | Glycine 297 (GGC) to valine (GTC) |
| PARP1 | 315–403 | Leucine 316 (CTG) to arginine (CGG) |
| Pol β | 84–183 | Alanine 160 (GCC) to serine (TCC) |
| PNKP | 403–538 | Alanine 482 (GCG) to threonine (ACG) |
| Ligase IIIα | 538–633 | Proline 623 (CCT) to serine (TCT) |
In this study, we chose to focus on the A482T mutant of XRCC1 that is defective in interacting with PNKP but not DNA ligase IIIα (Fig. 1B) or the other XRCC1-interacting proteins tested above (data not shown). Because PNKP preferentially interacts with XRCC1 that has been phosphorylated by casein kinase II (CK2) (37), it is possible that the A482T mutant was detected in the yeast two-hybrid assays because the amino acid substitution prevented XRCC1 phosphorylation by yeast CK2. To examine the effect of the amino acid change in the absence of phosphorylation, wild-type XRCC1 and the A482T mutant were expressed as GST fusion proteins in E. coli and then purified. In accord with the results of the yeast two-hybrid assays (Fig. 1B), the A482T mutant was less effective at binding to in vitro translated PNKP than wild-type XRCC1 (Fig. 1C, upper panel), indicating that the amino acid change disrupts the binding of unmodified XRCC1 with PNKP. Because the regions of XRCC1 that are involved in binding to aprataxin and APLF appear to overlap with each other and the region bound by PNKP (24–27), we examined the interaction of these two proteins with in vitro translated wild-type XRCC1 and the A482T mutant in pulldown assays. The amino acid change in XRCC1 that reduced its binding to PNKP (Fig. 1C, upper panel) had no effect on the interaction with either GST-APLF (Fig. 1C, middle panel) or GST-aprataxin (Fig. 1C, lower panel).
Because XRCC1 participates in base excision and SSB repair as a subunit of the DNA ligase IIIα-XRCC1 complex, we co-expressed DNA ligase IIIα with either wild-type XRCC1 or the A482T mutant in insect cells and purified the resultant complexes (Fig. 2A). As expected, the DNA nick ligation activity of the complex containing the XRCC1 A482T mutant was similar to that of the complex containing wild-type XRCC1 (Fig. 2B). In accord with the protein-protein interaction studies with XRCC1 alone, the binding of the DNA ligase IIIα-XRCC1 complex containing the XRCC1 A482T mutant to PNKP beads was greatly reduced (less than 10%) compared with the complex containing wild-type XRCC1 (Fig. 2C).
FIGURE 2.
Characterization of DNA ligase IIIα-XRCC1 complexes containing either wild-type XRCC1 or the A482T mutant. A, purified DNA ligase IIIα-XRCC1 complexes (150 ng) containing wild-type XRCC1 (lane 1) and the A482T mutant (lane 2). Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and then stained with Coomassie Blue. The bands corresponding to DNA ligase IIIα (LigIII) and XRCC1 (XRCC1) are indicated. B, the joining of a labeled nicked DNA substrate (upper panel and middle panel, lane 1) by DNA ligase IIIα-XRCC1 complexes containing either wild-type XRCC1 (WT, middle panel, lanes 2 and 3) or the A482T mutant (Mut, middle panel, lanes 4 and 5) was measured as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The results of three independent experiments are shown graphically (lower panel). C, upper panel, the binding of DNA ligase IIIα-XRCC1 complexes containing either wild-type XRCC1 (XRCC1-WT) or the A482T mutant (XRCC1-MutPNK482) to magnetic Ni2+ beads with (lanes 3 and 6) or without His-tagged PNKP (lanes 2 and 5). Pulldown assays were carried out as described under “Experimental Procedures.” 10% input of DNA ligase IIIα-XRCC1 complexes with: lane 1, wild-type XRCC1 and lane 4, A482T mutant version. XRCC1 was detected by immunoblotting. The results of two independent experiments are shown graphically with the error bars representing S.D. (lower panel). The binding of XRCC1 is expressed as a percentage of the binding by wild-type XRCC1.
Effect of XRCC1-PNKP Interaction on PNKP Activity and Repair Reactions Reconstituted with Purified Proteins
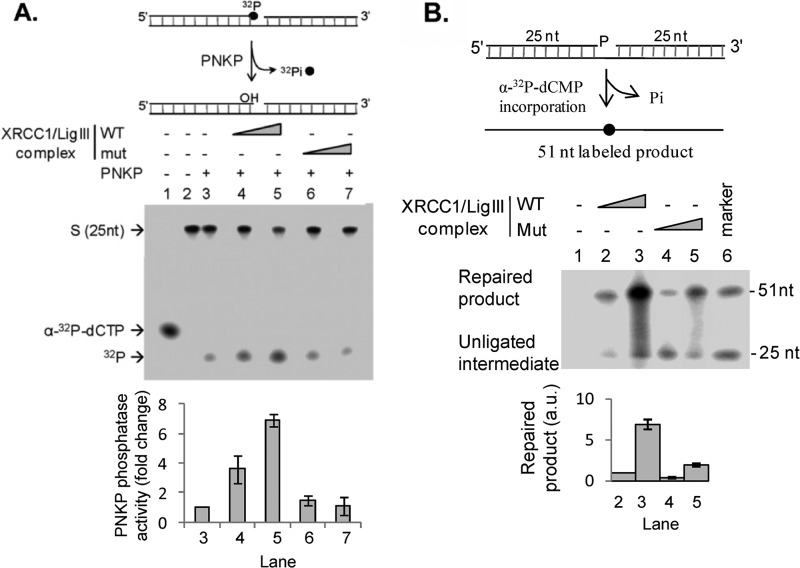
In initial studies, we examined the effect of DNA ligase IIIα-XRCC1 on PNKP 3′-phosphatase activity, which is required for the repair of single-strand breaks generated by oxidative DNA damage (38). The complex containing wild-type XRCC1 enhanced removal of the 3′-phosphate group by more than 6-fold at a 2:1 ratio of DNA ligase IIIα-XRCC1 complex to PNKP, whereas the complex containing the A482T mutant did not significantly increase the 3′-phosphatase activity of PNKP under similar conditions (Fig. 3A). Thus, the interaction with DNA ligase IIIα does not prevent XRCC1 from interacting with PNKP and enhancing its 3′-phosphatase activity (26). To determine the mechanism by which XRCC1 stimulates PNKP, we calculated kinetic parameters for the 3′-phosphatase activity of PNKP in the presence and absence of the wild-type DNA ligase IIIα-XRCC1 complex (Table 2). The km and kcat values for PNKP of 17.9 nm and 25.3 min−1, respectively, were similar to those reported previously (19). In the presence of DNA ligase IIIα-XRCC1, there was almost a 2-fold decrease in km but only a moderate increase in kcat (Table 2). Thus, the stimulation of PNKP activity by XRCC1 is primarily due to enhanced substrate binding.
FIGURE 3.
The interaction with XRCC1 enhances the 3′-phosphatase activity of PNKP and the joining of single-strand breaks with 3′- and 5′-phosphate termini. A, the removal of labeled 3′-phosphate groups from a single strand break (upper panel and middle panel) by PNKP was measured in the absence (middle panel, lane 3) or presence of DNA ligase IIIα-XRCC1 complexes containing wild-type XRCC1 (WT, middle panel, lanes 4 and 5) and the A482T mutant version (Mut, middle panel, lanes 6 and 7) as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Lane 2, labeled DNA substrate alone. The positions of [α-32P]dCTP (lane 1), 25-mer with labeled 3′-phosphate (S), and labeled phosphate (32P) are indicated on the left. The results of three independent experiments are shown graphically with the error bars representing S.D. (lower panel). PNKP phosphatase activity is expressed as fold-change compared with the activity of PNKP alone (lane 3). B, repair of a DNA substrate containing a single nucleotide gap with 3′- and 5′-phosphate termini (upper panel). PNKP and Polβ were incubated with the DNA substrate, [α-32P]dCTP and DNA ligase IIIα-XRCC1 complexes containing either wild-type XRCC1 (WT, middle panel, lanes 2 and 3) or the A482T mutant version (Mut, middle panel, lanes 4 and 5), as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Lane 6, end-labeled 25- and 51-mer oligonucleotides (marker). The positions of the labeled unligated intermediate and repaired product are indicated on the left. The results of three independent experiments are shown graphically with the error bars representing S.D. (lower panel). The amount of repaired product is expressed as arbitrary units determined by PhosphorImager analysis.
TABLE 2.
Kinetic parameters for PNKP; effect of DNA ligase IIIα−XRCC1
kcat values were calculated using the equation Kcat = Vmax/ [E], where E is PNKP concentration.
| Reaction | km | kcat | kcat/km |
|---|---|---|---|
| nm | min−1 | nm−1 min−1 | |
| PNKP only | 17.9 ± 1.4 | 25.3 ± 0.9 | 1.4 |
| PNKP plus XRCC1-ligase III | 10.1 ± 1.1 | 32.8 ± 2.1 | 3.2 |
In many instances, ionizing radiation generates SSB breaks with 3′-phosphoglycolate or 3′-phosphate termini. To mimic this situation, we constructed a DNA substrate that contains a 1-nucleotide gap with 3′- and 5′-phosphate termini and examined the role of the interaction between PNKP and XRCC1 in the repair of this substrate in reconstituted reactions that require the sequential activities of PNKP, Polβ, and DNA ligase IIIα-XRCC1. The repair reactions with the DNA ligase IIIα-XRCC1 complex containing wild-type XRCC1 were significantly more efficient than those with the DNA ligase IIIα-XRCC1 complex containing the XRCC1 A482T mutant (about 6-fold, Fig. 3B, compare lanes 3 and 5). Thus, the XRCC1 subunit of the DNA ligase IIIα-XRCC1 complex stimulates the first step of the repair reaction, removal of the 3′-phosphate group generating the 3′-OH termini required for DNA synthesis by Polβ and subsequent ligation by DNA ligase IIIα-XRCC1.
In addition to participating in the repair of DNA single-strand breaks, both PNKP and DNA ligase IIIα-XRCC1 are components of an APE1-independent BER pathway (19). This repair pathway is initiated by the removal of an oxidized base such as 5′-OHU by either NEIL1 or NEIL2 (18, 19). Cleavage of the resultant abasic site by the DNA glycosylase generates a 1-nucleotide gap with both 3′- and 5′-phosphate termini. In reconstituted reactions with both linear (Fig. 4A) and circular DNA substrates (Fig. 4B) containing a single 5′-OHU, disruption of the interaction between XRCC1 and PNKP significantly reduced the efficiency of the repair reaction (about 3-fold).
FIGURE 4.
Effect of the interaction between XRCC1 and PNKP on the NEIL1-initiated, APE-independent repair of 5-OHU in reconstituted repair reactions. A, repair of a 5-OHU residue in a linear duplex oligonucleotide (upper panel). B, the repair of a 5-OHU residue in a covalently closed circular duplex (upper panel). NEIL1, PNKP, and Polβ were incubated with the DNA substrate, [α-32P]dCTP or dTTP as indicated, and DNA ligase IIIα-XRCC1 complexes containing either wild-type XRCC1 (WT, middle panel, lanes 2 and 3) or the A482T mutant (Mut, middle panel, lanes 4 and 5) as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Lane 6, end-labeled 32-mer (marker). The positions of the labeled unligated intermediate and repaired product are indicated on the left. The results of three independent experiments are shown graphically with the error bars representing S.D. (lower panel). The amount of repaired product is expressed as arbitrary units determined by PhosphorImager analysis.
The Interaction between PNKP and XRCC1 Is Critical for Cell Survival following DNA Damage
To determine the contribution of the interaction between XRCC1 and PNKP to cell survival after DNA damage, we isolated derivatives of CHO xrcc1 EM9 cells that stably express tagged versions of either wild-type XRCC1 (Fig. 5A, lane 3) or the A482T mutant (Fig. 5A, lane 4) at levels about 2-fold higher than endogenous XRCC1 (Fig. 5A, lane 1). As expected (7, 16), expression of both wild-type XRCC1 (Fig. 5A, lane 3) and the A482T version (Fig. 5A, lane 4) resulted in increased steady levels of Polβ and DNA ligase IIIα but had no significant effect on the steady state levels of PNKP. Because XRCC1 and PNKP co-exist in a large multiprotein complex (28, 29), we asked whether they were associated in cell extracts. In immunoprecipitation experiments, less PNKP (about 40%) was co-immunoprecipitated by XRCC1 antibody from extracts of cells expressing the XRCC1 A482T compared with cells expressing wild-type XRCC1 (Fig. 5B, compare lanes 3 and 4), whereas similar amounts of DNA ligase IIIα, Polβ, and aprataxin were co-immunoprecipitated. As expected, expression of wild-type XRCC1 complemented the sensitivity of CHO xrcc1 EM9 cells to ethyl methanesulfonate (Fig. 5C), a DNA alkylating agent. In contrast, expression of the A482T mutant only partially corrected the DNA damage sensitivity of the xrcc1 cells. Thus, the interaction between XRCC1 and PNKP makes a significant contribution to the repair of DNA damage caused by DNA alkylating agents.
FIGURE 5.

Effect of disrupting the interaction with PNKP on the ability of exogenous XRCC1 to correct the DNA damage-sensitive phenotype of xrcc1 mutant EM9 cells. A, the steady state levels of XRCC1, PNKP, Polβ, DNA ligase IIIα, and β-actin were determined by immunoblotting of whole cell extracts (45 μg) from: lane 1, wild-type parental AA8 cells; lane 2, xrcc1 mutant EM9 cells; lane 3, EM9 cells stably expressing Xpress-tagged wild-type XRCC1; lane 4, EM9 cells stably expressing Xpress-tagged A482T XRCC1. B, the indicated proteins were detected by immunobloting of nuclear extracts (8 μg) from lane 1, EM9 cells stably expressing Xpress-tagged wild-type XRCC1 (WT) and lane 2, EM9 cells stably expressing Xpress-tagged A482T XRCC1 (MutPNK). Nuclear extracts (80 μg) from lane 3, EM9 cells stably expressing Xpress-tagged wild-type XRCC1 (WT) and lane 4, EM9 cells stably expressing Xpress-tagged A482T XRCC1 (MutPNK) were incubated with XRCC1 antibody and the immunoprecipitates were probed for DNA ligase IIIα (DNA Lig III), XRCC1, Polβ, PNKP (PNK), and aprataxin by immunoblotting (upper panel). The results of three independent immunoprecipitation experiments are shown graphically with the error bars representing S.D. (lower panel). The amount of co-immunoprecipitated PNKP was determined by determining the ratios of co-immunoprecipitated PNKP to immunoprecipitated wild-type and mutant XRCC1 and expressing these ratios as percentage of the ratio obtained with wild-type XRCC1. C, effect of ethyl methanesulfonate (EMS) on the survival of AA8 cells (triangle), EM9 cells (circle), EM9 cells stably expressing Xpress-tagged wild-type XRCC1 (square) and EM9 cells stably expressing Xpress-tagged A482S XRCC1 (×). The graphs represent the compilation of 4 independent experiments with error bars representing S.D.
Role of the Interaction between PNKP and XRCC1 in the Recruitment and Retention of These Factors at in Vivo Damage Sites
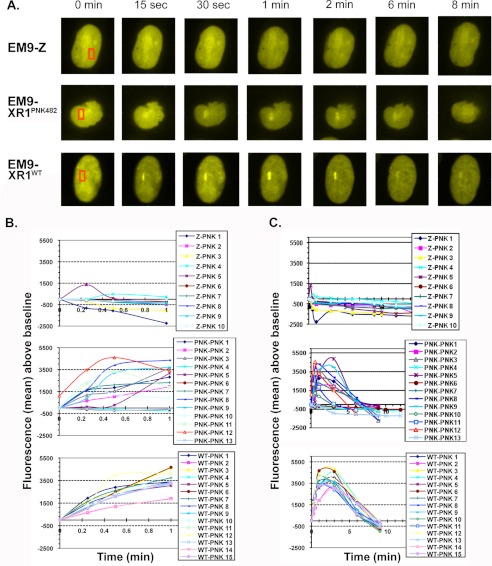
In agreement with published studies (28), recruitment of EYFP-tagged PNKP to localized sites of DNA damage induced by laser microirradiation was more or less absent in xrcc1 mutant EM9 cells, as compared with EM9 cells expressing wild-type XRCC1 (Fig. 6). Surprisingly, there was no difference in the initial recruitment of PNKP in EM9 cells expressing the XRCC1 A482T mutant (Fig. 6B). However, the average retention time of EYFP-PNKP was greater in the cells expressing wild-type XRCC1 (6.7 ± 1.2 min) than in cells expressing the A482T mutant (3.7 ± 2.8 min, p = 0.0008 as determined by single factor analysis of variance), although there was noticeable variability among individual cells expressing the mutant version of XRCC1 (Fig. 6C). Thus, the interaction with XRCC1 increases the length of time that PNKP is stably associated at DNA damage sites.
FIGURE 6.
Role of XRCC1 and the interaction between XRCC1 and PNKP in the recruitment and retention of EYFP-PNKP to sites of laser-induced DNA damage. A, representative cells showing the recruitment and retention EYFP-PNKP to sites of laser-induced DNA damage (red box) in xrcc1 mutant EM9 cells (upper panel), EM9 cells stably expressing Xpress-tagged A482T XRCC1 (XR1PNK482, middle panel), and EM9 cells stably expressing Xpress-tagged wild-type XRCC1 (XR1WT, lower panel). B, initial recruitment of EYFP-PNKP to the damaged site in EM9 cells expressing no (Z, top), the A482T mutant (PNK, middle), or wild-type (WT, bottom) XRCC1 protein. C, retention of EYFP-PNKP at the damaged site (see panel B). The results of 10 to 15 independent cells from the three cell lines are shown graphically in panels B and C.
To further explore the role of the XRCC1-PNKP interaction at in vivo DNA damaged sites, we performed similar experiments using HeLa cells that had been transfected with EYFP tagged versions of either wild-type XRCC1 or the A482T mutant (Fig. 7). Although there was no significant difference in the kinetics of recruitment of wild-type XRCC1 and the A482T mutant to the site of laser irradiation within the first minute (Fig. 7B), the point of maximal fluorescent intensity at the site of laser irradiation of the XRCC1 A482T mutant was reached much earlier and the retention time at the damaged site (4.1 ± 1.8 and 25 ± 3.5 min, respectively) was dramatically reduced compared with wild-type XRCC1 (18 ± 4.2 min, p = 5.5 × 10−8 and 76 ± 7.0 min, p = 3.9 × 10−13, respectively) (Fig. 7C). Thus, under conditions that introduce DNA base damage and SSBs but not double-strand breaks (28), the interaction between PNKP and XRCC1 is not critical for the initial recruitment of these factors to DNA damage, but does influence the stable association of these factors at DNA damaged sites.
FIGURE 7.
Comparison of the recruitment and retention of wild-type XRCC1 and the A482T mutant to sites of laser-induced DNA damage. A, representative cells showing the recruitment and retention of wild-type XRCC1 (XR1WT, upper panel) and the A482T mutant version (XR1PNK482, lower panel) fused to EYFP to sites of laser-induced DNA damage (red box) in HeLa cells. B, initial recruitment of the wild-type or A482T mutant EYFP-XRCC1 fusion proteins to the damaged site. C, retention of the wild-type or A482T mutant EYFP-XRCC1 fusion proteins at the damaged site. The results of 9 or 10 independent cells transfected with either wild-type XRCC1 or the A482T mutant of XRCC1 are shown graphically in panels B and C.
DISCUSSION
Although XRCC1 plays a pivotal role in DNA repair via multiple interactions with different repair enzymes (5), the functional and biological relevance of many of these interactions have not been described. In this study, we have used a modified version of the yeast two-hybrid genetic screen (30) to identify mutant versions of XRCC1 that are selectively defective in interacting with a single protein partner. Notably, the single amino acid changes that disrupt interactions with PARP1, Polβ, PNKP, APE1, or DNA ligase IIIα occur within regions of the XRCC1 polypeptide that had been previously implicated in the specific protein-protein interaction (8–10, 13, 20, 23, 26). Although there is atomic resolution structural information for several different regions of XRCC1 (39–41), only the amino acid change that disrupts the interaction with DNA ligase IIIα occurs within one of these locations, the BRCT II domain (40). The amino acid change that disrupts the interaction with Polβ occurs in an unstructured region that is immediately adjacent to that which has been shown to make direct contact with Polβ, suggesting that the interface between Polβ and XRCC1 extends beyond that determined by x-ray crystallography and NMR (41, 42).
In this study, we have focused on a mutant version of XRCC1 that is defective in interacting with PNKP. PNKP binds to a region in XRCC1 between the two BRCT domains that is phosphorylated at multiple serine and threonine residues by CK2 (26, 37). Notably, PNKP binds specifically to phosphorylated XRCC1 via an FHA domain that interacts with a multiply phosphorylated XRCC1 peptide (residues 515–526) (43). Two other XRCC1 partner proteins, APLF and aprataxin, which also participate in the processing of DNA termini, contain similar FHA domains that presumably bind in a similar manner to the phosphorylated XRCC1 peptide (29, 43, 44). Recently, it has been shown that unmodified and phosphorylated XRCC1 interact with different regions of PNKP but the region of unmodified XRCC1 mediating the interaction with PNKP was not identified (45). Here, we have identified an amino acid change, alanine 482 to threonine, within a region of XRCC1 that is phosphorylated at multiple sites in vivo (37) that disrupts the interaction between unmodified XRCC1 and PNKP. This confirms that the interaction interface between XRCC1 and PNKP extends beyond that involving the XRCC1-phosphorylated peptide (residues 515–526) and the FHA domain of PNKP (43). Notably, the alanine 482 to threonine change has no detectable effect on interactions with either APLF or aprataxin Thus, whereas the interactions of PNKP, APLF, and aprataxin with XRCC1 are almost certainly mutually exclusive because they bind to overlapping sites in XRCC1, the effect of replacing alanine 482 with threonine is specific for the interaction with PNKP, suggesting a specific requirement for Ala-482 within the PNKP interaction interface.
Almost all of the studies describing interactions of XRCC1 with its multiple partner proteins have utilized XRCC1 that has been expressed and purified in the absence of DNA ligase IIIα. Here, we have compared the activity of wild-type and mutant versions of XRCC1 in the context of the DNA ligase IIIα-XRCC1 complex and shown that, in accord with published studies for XRCC1 alone (26), the 3′-phosphatase activity of PNKP is stimulated by interaction with XRCC1 when it is complexed with DNA ligase IIIα. The interaction of PNKP with the DNA ligase IIIα-XRCC1 complex, which increases PNKP activity primarily by enhancing DNA substrate binding, also increased the efficiency of reconstituted repair reactions utilizing DNA substrates representing key DNA lesion types generated by reactive oxygen species, including nonligatable single-strand breaks and oxidized base lesions that are repaired via a NEIL1-initiated, APE1-independent BER reaction (19).
Because both wild-type XRCC1 and the A482T mutant interact with Polβ and DNA ligase IIIα, expression of these proteins in xrcc1 mutant cells at a level similar to endogenous XRCC1 restored the steady state levels of Polβ and DNA ligase IIIα to that observed in the parental wild-type cell line as expected (7, 16). Furthermore, similar amounts of aprataxin were co-immunoprecipitated with wild-type XRCC1 and the A482T mutant, whereas less PNKP was co-immunoprecipitated with the A482T mutant. Thus, replacement of alanine 482 with threonine reduces the amount of XRCC1 complexed with PNKP but has no effect on the amount complexed with apraxatin (29). Taken together with our in vitro binding results, we conclude that the replacement of alanine 482 with threonine reduces but does not totally abolish the interaction between XRCC1 and PNKP, presumably because the interaction interface between the phosphorylated peptide segment in XRCC1 and the PNKP FHA domain remains intact. The reduced binding between XRCC1 and PNKP correlates with the inability of the A482T mutant to fully complement the sensitivity of xrcc1 mutant cells to DNA alkylation damage, providing a molecular explanation for previous studies showing that knockdown of PNKP levels resulted in increased sensitivity to methyl methanesulfonate (46). The increased DNA damage sensitivity of the EM9 cells expressing the XRCC1 A482T mutant was only observed at the highest doses of ethyl methanesulfonate, suggesting that PNKP may only participate in the repair of a subset of lesions generated by high levels of DNA alkylating agents rather than the major base adducts generated by DNA alkylation. Unlike BER initiated by the NEIL DNA glycosylases (18, 19), the repair of alkylated bases, which is initiated by the methyl purine DNA glycosylase, involves APE1 not PNKP (47). At high concentrations of DNA alkylating agents, it is possible that the number of abasic sites generated either by the action of the methyl purine DNA glycosylase or increased spontaneous loss of alkylated bases exceeds the capacity of APE1. We suggest that the cleavage of these abasic sites by NEIL DNA glycosylases or other mechanisms generates single-strand breaks with 3′-phosphate and/or 5′-hydroxyl termini that require PNKP activity prior to rejoining.
There are contradictory reports as to the roles of XRCC1 and PNKP in their recruitment to DNA damaged sites. PNKP did not form H2O2-induced nuclear foci in xrcc1 mutant EM9 cells (37) and less PNKP was recruited to localized sites of damage induced by laser microirradiation in these same mutant cells (28). In contrast, PNKP was required for the efficient recruitment of XRCC1 to DNA single-strand breaks with modified 3′-termini (14). It is likely that differences in the experimental approaches, including the types of DNA damage, account for these apparently contradictory observations. Under the conditions used in this study, the recruitment of PNKP to localized DNA damaged sites was dependent upon XRCC1. Surprisingly, no defect in initial PNKP recruitment was observed in cells expressing the XRCC1 A482T mutant. Because the protein-protein interaction is weakened rather than abolished, it is possible that any modest defect in recruitment was masked because of high levels of expression of the tagged PNKP protein following transient transfection. Interestingly, disruption of the interaction between XRCC1 and PNKP decreased the retention time of PNKP at damaged sites, suggesting that this interaction plays an important role in the stability of the multiprotein repair complex assembled at damage sites.
In our studies, XRCC1 (∼76 min) was retained at the damaged site much longer than PNKP (∼7 min). This is consistent with studies showing that, whereas Polβ, DNA ligase IIIα, PCNA, and CAF1 dissociate at a similar time, XRCC1 remains at the damaged site (48, 49). Remarkably, disruption of the interaction with PNKP dramatically reduced the retention of XRCC1 at the damaged sites, suggesting that this interaction during the initial repair phase is required for the subsequent stable association of XRCC1 at the lesion. It is assumed that the fraction of XRCC1 retained at the damaged site has some as yet undefined function after completion of DNA repair. Because the association of XRCC1 with chromatin prevents its degradation (16), it is possible that the retention of XRCC1 at repaired sites ensures that the level of this key DNA repair protein corresponds to the levels of DNA damage.
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs. West and Yasui for reagents and Dr. Krejci for assistance with the yeast two-hybrid screen.
This work was supported, in whole or in part, by National Institutes of Health Grants R01 ES 012512 (to A. E. T.), R01 CA81063 (to S. M.), R01 GM052504 (to T. E.), and P01 CA 92584 (to A. E. T., S. M., and T. E.) and by the Intramural Research Program of the NIA, National Institutes of Health.
- SSB
- single-strand break
- BER
- base excision repair
- APE1
- AP endonuclease 1
- APLF
- aprataxin-like factor
- CK2
- casein kinase II
- MPG
- methyl purine DNA glycosylase
- PARP
- poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase
- PNKP
- polynucleotide kinase 3′-phosphatase
- Polβ
- DNA polymerase β
- EYFP
- enhanced yellow fluorescent protein.
REFERENCES
- 1. Thompson L. H., Brookman K. W., Jones N. J., Allen S. A., Carrano A. V. (1990) Molecular cloning of the human XRCC1 gene, which corrects defective DNA strand-break repair and sister chromatid exchange. Mol. Cell. Biol. 10, 6160–6171 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Shen M. R., Zdzienicka M. Z., Mohrenweiser H., Thompson L. H., Thelen M. P. (1998) Mutations in hamster single-strand break repair gene XRCC1 causing defective DNA repair. Nucleic Acids Res. 26, 1032–1037 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Zdzienicka M. Z., van der Schans G. P., Natarajan A. T., Thompson L. H., Neuteboom I., Simons J. W. (1992) A Chinese hamster ovary cell mutant (EM-C11) with sensitivity to simple alkylating agents and a very high level of sister chromatid exchanges. Mutagenesis 7, 265–269 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Thompson L. H., Brookman K. W., Carrano A. V., Dillehay L. E. (1982) Role of DNA repair in mutagenesis of Chinese hamster ovary cells by 7-bromomethylbenz[a]anthracene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 534–538 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Caldecott K. W. (2003) XRCC1 and DNA strand break repair. DNA Repair 2, 955–969 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Caldecott K. W., McKeown C. K., Tucker J. D., Ljungquist S., Thompson L. H. (1994) An interaction between the mammalian DNA repair protein XRCC1 and DNA ligase III. Mol. Cell. Biol. 14, 68–76 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Caldecott K. W., Tucker J. D., Stanker L. H., Thompson L. H. (1995) Characterization of the XRCC1-DNA ligase III complex in vitro and its absence from mutant hamster cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 23, 4836–4843 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Dulic A., Bates P. A., Zhang X., Martin S. R., Freemont P. S., Lindahl T., Barnes D. E. (2001) BRCT domain interactions in the heterodimeric DNA repair protein XRCC1-DNA ligase III. Biochemistry 40, 5906–5913 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Nash R. A., Caldecott K. W., Barnes D. E., Lindahl T. (1997) XRCC1 protein interacts with one of two distinct forms of DNA ligase III. Biochemistry 36, 5207–5211 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Mackey Z. B., Ramos W., Levin D. S., Walter C. A., McCarrey J. R., Tomkinson A. E. (1997) An alternative splicing event which occurs in mouse pachytene spermatocytes generates a form of DNA ligase III with distinct biochemical properties that may function in meiotic recombination. Mol. Cell. Biol. 17, 989–998 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Taylor R. M., Wickstead B., Cronin S., Caldecott K. W. (1998) Role of a BRCT domain in the interaction of DNA ligase IIIα with the DNA repair protein XRCC1. Curr. Biol. 8, 877–880 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Dianova I. I., Sleeth K. M., Allinson S. L., Parsons J. L., Breslin C., Caldecott K. W., Dianov G. L. (2004) XRCC1-DNA polymerase β interaction is required for efficient base excision repair. Nucleic Acids Res. 32, 2550–2555 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Kubota Y., Nash R. A., Klungland A., Schär P., Barnes D. E., Lindahl T. (1996) Reconstitution of DNA base excision-repair with purified human proteins. Interaction between DNA polymerase β and the XRCC1 protein. EMBO J. 15, 6662–6670 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Parsons J. L., Dianova I. I., Allinson S. L., Dianov G. L. (2005) DNA polymerase β promotes recruitment of DNA ligase III α-XRCC1 to sites of base excision repair. Biochemistry 44, 10613–10619 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Caldecott K. W., Aoufouchi S., Johnson P., Shall S. (1996) XRCC1 polypeptide interacts with DNA polymerase β and possibly poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase, and DNA ligase III is a novel molecular “nick-sensor” in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 24, 4387–4394 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Parsons J. L., Tait P. S., Finch D., Dianova I. I., Allinson S. L., Dianov G. L. (2008) CHIP-mediated degradation and DNA damage-dependent stabilization regulate base excision repair proteins. Mol. Cell 29, 477–487 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Marsin S., Vidal A. E., Sossou M., Ménissier-de Murcia J., Le Page F., Boiteux S., de Murcia G., Radicella J. P. (2003) Role of XRCC1 in the coordination and stimulation of oxidative DNA damage repair initiated by the DNA glycosylase hOGG1. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 44068–44074 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Das A., Wiederhold L., Leppard J. B., Kedar P., Prasad R., Wang H., Boldogh I., Karimi-Busheri F., Weinfeld M., Tomkinson A. E., Wilson S. H., Mitra S., Hazra T. K. (2006) NEIL2-initiated, APE-independent repair of oxidized bases in DNA. Evidence for a repair complex in human cells. DNA Repair 5, 1439–1448 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Wiederhold L., Leppard J. B., Kedar P., Karimi-Busheri F., Rasouli-Nia A., Weinfeld M., Tomkinson A. E., Izumi T., Prasad R., Wilson S. H., Mitra S., Hazra T. K. (2004) AP endonuclease-independent DNA base excision repair in human cells. Mol. Cell 15, 209–220 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Vidal A. E., Boiteux S., Hickson I. D., Radicella J. P. (2001) XRCC1 coordinates the initial and late stages of DNA abasic site repair through protein-protein interactions. EMBO J. 20, 6530–6539 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Fan J., Otterlei M., Wong H. K., Tomkinson A. E., Wilson D. M., 3rd (2004) XRCC1 co-localizes and physically interacts with PCNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 32, 2193–2201 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Schreiber V., Amé J. C., Dollé P., Schultz I., Rinaldi B., Fraulob V., Ménissier-de Murcia J., de Murcia G. (2002) Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-2 (PARP-2) is required for efficient base excision DNA repair in association with PARP-1 and XRCC1. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 23028–23036 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Masson M., Niedergang C., Schreiber V., Muller S., Menissier-de Murcia J., de Murcia G. (1998) XRCC1 is specifically associated with poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase and negatively regulates its activity following DNA damage. Mol. Cell. Biol. 18, 3563–3571 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Date H., Onodera O., Tanaka H., Iwabuchi K., Uekawa K., Igarashi S., Koike R., Hiroi T., Yuasa T., Awaya Y., Sakai T., Takahashi T., Nagatomo H., Sekijima Y., Kawachi I., Takiyama Y., Nishizawa M., Fukuhara N., Saito K., Sugano S., Tsuji S. (2001) Early-onset ataxia with ocular motor apraxia and hypoalbuminemia is caused by mutations in a new HIT superfamily gene. Nat. Genet. 29, 184–188 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Gueven N., Becherel O. J., Kijas A. W., Chen P., Howe O., Rudolph J. H., Gatti R., Date H., Onodera O., Taucher-Scholz G., Lavin M. F. (2004) Aprataxin, a novel protein that protects against genotoxic stress. Hum. Mol. Genet. 13, 1081–1093 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Whitehouse C. J., Taylor R. M., Thistlethwaite A., Zhang H., Karimi-Busheri F., Lasko D. D., Weinfeld M., Caldecott K. W. (2001) XRCC1 stimulates human polynucleotide kinase activity at damaged DNA termini and accelerates DNA single-strand break repair. Cell 104, 107–117 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Iles N., Rulten S., El-Khamisy S. F., Caldecott K. W. (2007) APLF (C2orf13) is a novel human protein involved in the cellular response to chromosomal DNA strand breaks. Mol. Cell Biol. 27, 3793–3803 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Hanssen-Bauer A., Solvang-Garten K., Sundheim O., Peña-Diaz J., Andersen S., Slupphaug G., Krokan H. E., Wilson D. M., 3rd, Akbari M., Otterlei M. (2011) XRCC1 coordinates disparate responses and multiprotein repair complexes depending on the nature and context of the DNA damage. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 52, 623–635 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Luo H., Chan D. W., Yang T., Rodriguez M., Chen B. P., Leng M., Mu J. J., Chen D., Songyang Z., Wang Y., Qin J. (2004) A new XRCC1-containing complex and its role in cellular survival of methyl methanesulfonate treatment. Mol. Cell. Biol. 24, 8356–8365 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Krejci L., Damborsky J., Thomsen B., Duno M., Bendixen C. (2001) Molecular dissection of interactions between Rad51 and members of the recombination-repair group. Mol. Cell. Biol. 21, 966–976 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 31. Della-Maria J., Zhou Y., Tsai M. S., Kuhnlein J., Carney J. P., Paull T. T., Tomkinson A. E. (2011) Human Mre11/human Rad50/Nbs1 and DNA ligase IIIα-XRCC1 protein complexes act together in an alternative nonhomologous end joining pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 33845–33853 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Hazra T. K., Izumi T., Boldogh I., Imhoff B., Kow Y. W., Jaruga P., Dizdaroglu M., Mitra S. (2002) Identification and characterization of a human DNA glycosylase for repair of modified bases in oxidatively damaged DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99, 3523–3528 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Hegde M. L., Theriot C. A., Das A., Hegde P. M., Guo Z., Gary R. K., Hazra T. K., Shen B., Mitra S. (2008) Physical and functional interaction between human oxidized base-specific DNA glycosylase NEIL1 and flap endonuclease 1. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 27028–27037 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Hegde M. L., Banerjee S., Hegde P. M., Bellot L. A., Hazra T. K., Boldogh I., Mitra S. (August 17, 2012) J. Biol. Chem. 10.1074/jbc.M112.384032 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Muniandy P. A., Thapa D., Thazhathveetil A. K., Liu S. T., Seidman M. M. (2009) Repair of laser-localized DNA interstrand cross-links in G1 phase mammalian cells. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 27908–27917 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Berquist B. R., Singh D. K., Fan J., Kim D., Gillenwater E., Kulkarni A., Bohr V. A., Ackerman E. J., Tomkinson A. E., Wilson D. M., 3rd (2010) Functional capacity of XRCC1 protein variants identified in DNA repair-deficient Chinese hamster ovary cell lines and the human population. Nucleic Acids Res. 38, 5023–5035 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Loizou J. I., El-Khamisy S. F., Zlatanou A., Moore D. J., Chan D. W., Qin J., Sarno S., Meggio F., Pinna L. A., Caldecott K. W. (2004) The protein kinase CK2 facilitates repair of chromosomal DNA single-strand breaks. Cell 117, 17–28 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Breslin C., Caldecott K. W. (2009) DNA 3′-phosphatase activity is critical for rapid global rates of single-strand break repair following oxidative stress. Mol. Cell. Biol. 29, 4653–4662 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Marintchev A., Mullen M. A., Maciejewski M. W., Pan B., Gryk M. R., Mullen G. P. (1999) Solution structure of the single-strand break repair protein XRCC1 N-terminal domain. Nat. Struct. Biol. 6, 884–893 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Cuneo M. J., Gabel S. A., Krahn J. M., Ricker M. A., London R. E. (2011) The structural basis for partitioning of the XRCC1-DNA ligase IIIα BRCT-mediated dimer complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 39, 7816–7827 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Cuneo M. J., London R. E. (2010) Oxidation state of the XRCC1 N-terminal domain regulates DNA polymerase β binding affinity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 107, 6805–6810 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Gryk M. R., Marintchev A., Maciejewski M. W., Robertson A., Wilson S. H., Mullen G. P. (2002) Mapping of the interaction interface of DNA polymerase β with XRCC1. Structure 10, 1709–1720 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Ali A. A., Jukes R. M., Pearl L. H., Oliver A. W. (2009) Specific recognition of a multiply phosphorylated motif in the DNA repair scaffold XRCC1 by the FHA domain of human PNK. Nucleic Acids Res. 37, 1701–1712 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Kanno S., Kuzuoka H., Sasao S., Hong Z., Lan L., Nakajima S., Yasui A. (2007) A novel human AP endonuclease with conserved zinc finger-like motifs involved in DNA strand break responses. EMBO J. 26, 2094–2103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Lu M., Mani R. S., Karimi-Busheri F., Fanta M., Wang H., Litchfeld D. W., Weinfeld M. (2010) Independent mechanisms of stimulation of polynucleotide kinase/phosphatase by phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated XRCC1. Nucleic Acids Res. 38, 510–521 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Rasouli-Nia A., Karimi-Busheri F., Weinfeld M. (2004) Stable down-regulation of human polynucleotide kinase enhances spontaneous mutation frequency and sensitizes cells to genotoxic agents. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101, 6905–6910 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Xia L., Zheng L., Lee H. W., Bates S. E., Federico L., Shen B., O'Connor T. R. (2005) Human 3-methyladenine-DNA glycosylase. Effect of sequence context on excision, association with PCNA, and stimulation by AP endonuclease. J. Mol. Biol. 346, 1259–1274 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Lan L., Nakajima S., Oohata Y., Takao M., Okano S., Masutani M., Wilson S. H., Yasui A. (2004) In situ analysis of repair processes for oxidative DNA damage in mammalian cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101, 13738–13743 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Okano S., Lan L., Caldecott K. W., Mori T., Yasui A. (2003) Spatial and temporal cellular responses to single-strand breaks in human cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 23, 3974–3981 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]