Abstract
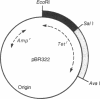
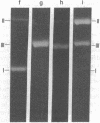
Closed circular DNA interacts with complementary sequences of single-stranded DNA to form displacement loop (D loop) structures in vitro. The site of D-loop formation can be directed by using single-stranded DNA derived from a selected restriction fragment. Circular DNA containing a D loop can then be linearized by cleavage with endonuclease S1. This cleavage appears to remove a limited number of nucleotides from each strand of the circular DNA substrate. Incubation with polynucleotide ligase followed by propagation in vivo leads to circular DNA molecules that bear small, single deletions in the region of the single-stranded DNA sequence chosen for the formation of the D loops. We have utilized these manipulations of DNA to construct tetracycline-sensitive deletion mutants of plasmid pBR322. The level of mutagenesis obtained by the procedure is sufficiently high that selective growth and screening procedures are not necessary for the isolation or identification of mutants. The frequency, variety, and small size of the deletions obtained within the selected target regions present considerable advantage for genetic and biochemical analysis. The method is quite general in rationale and should be immediately applicable to phage and viruses having infectious circular DNA genomes or recombinant DNA species propagated in circular plasmid vectors.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beattie K. L., Wiegand R. C., Radding C. M. Uptake of homologous single-stranded fragments by superhelical DNA. II. Characterization of the reaction. J Mol Biol. 1977 Nov;116(4):783–803. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90271-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L., Carbon J. Biochemical construction and selection of hybrid plasmids containing specific segments of the Escherichia coli genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4361–4365. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godson G. N. Action of the single-stranded DNA specific nuclease S1 on double-stranded DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 21;308(7):59–67. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90122-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerry P., LeBlanc D. J., Falkow S. General method for the isolation of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):1064–1066. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.1064-1066.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward G. S. Gel electrophoretic separation of the complementary strands of bacteriophage DNA. Virology. 1972 Jul;49(1):342–344. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(72)80042-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloman W. K., Radding C. M. Recombination promoted by superhelical DNA and the recA gene of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3910–3914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloman W. K., Wiegand R., Hoessli C., Radding C. M. Uptake of homologous single-stranded fragments by superhelical DNA: a possible mechanism for initiation of genetic recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2394–2398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasamatsu H., Robberson D. L., Vinograd J. A novel closed-circular mitochondrial DNA with properties of a replicating intermediate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2252–2257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., van deSande H. Chain length determination of small double- and single-stranded DNA molecules by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1975 Aug 26;14(17):3787–3794. doi: 10.1021/bi00688a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Méchali M., de Recondo A. M., Girard M. Action of the S1 endonuclease from Aspergillus oryzae on simian virus 40 supercoiled component I DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Oct 15;54(4):1306–1320. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91130-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radding C. M., Beattie K. L., Holloman W. K., Wiegand R. C. Uptake of homologous single-stranded fragments by superhelical DNA. IV. Branch migration. J Mol Biol. 1977 Nov;116(4):825–839. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90273-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenk T. E., Rhodes C., Rigby P. W., Berg P. Biochemical method for mapping mutational alterations in DNA with S1 nuclease: the location of deletions and temperature-sensitive mutations in simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):989–993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):77–90. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tait R. C., Boyer H. W. On the nature of tetracycline resistance controlled by the plasmid pSC101. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):73–81. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90139-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tibbetts C. Physical organization of subgroup B human adenovirus genomes. J Virol. 1977 Nov;24(2):564–579. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.2.564-579.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiegand R. C., Beattie K. L., Holloman W. K., Radding C. M. Uptake of homologous single-stranded fragments by superhelical DNA. III. The product and its enzymic conversion to a recombinant molecule. J Mol Biol. 1977 Nov;116(4):805–824. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90272-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]