Abstract
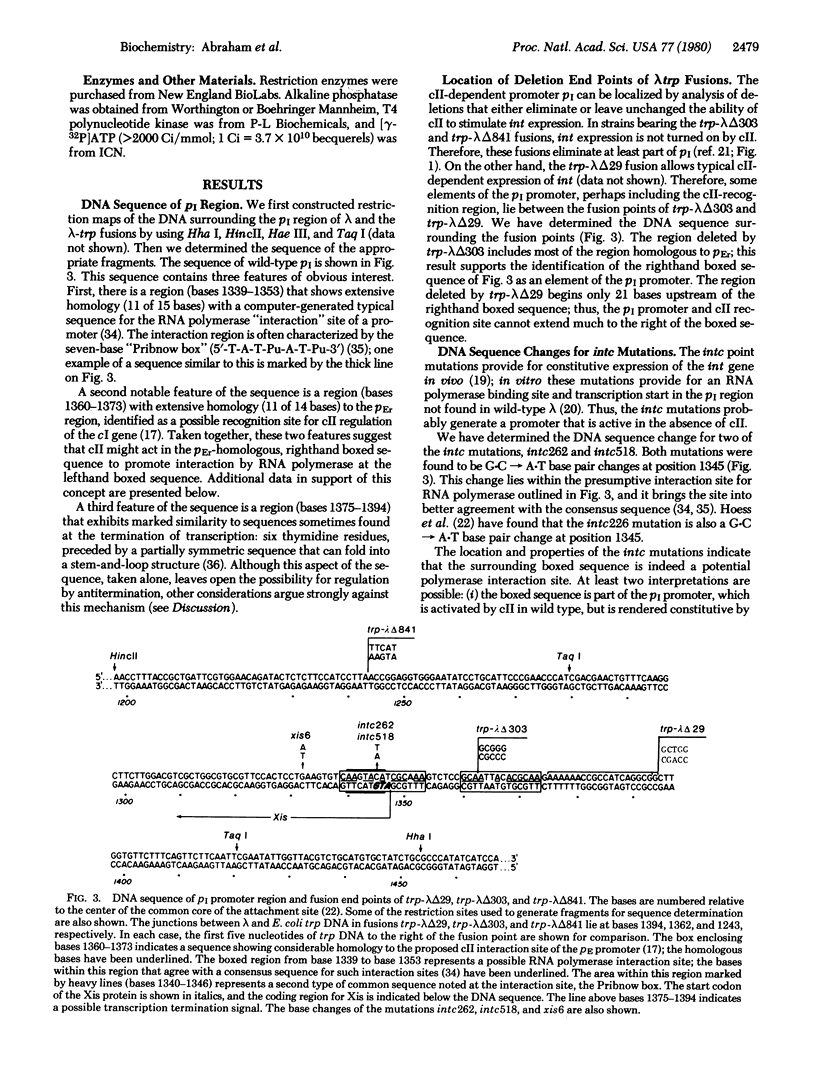
The cII and cIII proteins specified by bacteriophage λ direct the lysogenic response to infection through the coordinate establishment of repression and integration of the viral DNA. The regulatory activity of cII/cIII involves positive regulation of two promoter sites: the pE promoter, turning on expression of the cI protein that maintains lysogeny, and the pI promoter, activating synthesis of the Int protein for integrative recombination. Regulation of the pI promoter provides for differential expression of the Int protein with respect to the excision-specific Xis protein from the closely linked int and xis genes. We have determined the DNA sequence of the pI promoter region for wild-type λ DNA and for two classes of mutations: intc mutations, which result in a high rate of Int synthesis in the absence of cII, and deletion mutations, some of which eliminate cII-activated expression of the int gene. We find a sequence with considerable homology (11 of 15 bases) to a “typical” (computer-generated) promoter sequence, adjacent to a region with striking homology (11 of 14 bases) to part of the pE promoter region. This presumed pI sequence overlaps the start of the xis gene and includes the site of two intc point mutations. A cII-insensitive xis+ deletion partially removes the proposed pI sequence; a deletion that leaves the pI sequence intact but terminates 21 bases upstream does not interfere with cII activation of the int gene. From our results and the analysis of the pE region, we suggest that cII acts in the promoter -35 recognition region to facilitate binding by RNA polymerase at the -10 interaction region. Differential expression of the int and xis genes results because the pI transcript lacks the initiation codon for Xis protein synthesis.
Keywords: promoter structure, RNA regulation, bacteriophage λ cII, cIII proteins
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S., Gottesman M. Control of transcription termination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:967–996. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.004535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belfort M., Wulff D. The roles of the lambda c3 gene and the Escherichia coli catabolite gene activation system in the establishment of lysogeny by bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):779–782. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett G. N., Yanofsky C. Sequence analysis of operator constitutive mutants of the tryptophan operon of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1978 May 15;121(2):179–192. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(78)80004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brachet P., Thomas R. Mapping and functional analysis of y and CII mutants. Mutat Res. 1969 Mar-Apr;7(2):257–260. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(69)90041-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S., Echols H. Positive regulation of integrative recombination by the cII and cIII genes of bacteriophase lambda. Virology. 1977 Jun 15;79(2):312–319. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90358-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Court D., Green L., Echols H. Positive and negative regulation by the cII and cIII gene products of bacteriophage lambda. Virology. 1975 Feb;63(2):484–491. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90321-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echols H. Developmental pathways for the temperate phage: lysis vs lysogeny,. Annu Rev Genet. 1972;6(0):157–190. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.06.120172.001105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echols H., Green L. Establishment and maintenance of repression by bacteriophage lambda: the role of the cI, cII, and c3 proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2190–2194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enquist L., Honigman A., Hu S. L., Szybalski W. Expression of lambda int gene function in ColE1 hybrid plasmids carrying the C fragment of bacteriophage lambda. Virology. 1979 Jan 30;92(2):557–560. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer R., Takeda Y., Echols H. Transcription of the int gene of bacteriophage lambda. New RNA polymerase binding site and RNA start generated by int-constitutive mutations. J Mol Biol. 1979 Apr 15;129(3):509–514. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90510-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. R., Howe M. New mutations in the S cistron of bacteriophage lambda affecting host cell lysis. Virology. 1969 May;38(1):200–202. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90148-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman M. E., Yarmolinsky M. B. Integration-negative mutants of bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 14;31(3):487–505. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90423-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman M. M., Hicks M. L., Gellert M. Genetics and function of DNA ligase in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1973 Jul 15;77(4):531–547. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90221-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarneros G., Echols H. New mutants of bacteriophage lambda with a specific defect in excision from the host chromosome. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 14;47(3):565–574. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90323-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heffernan L., Benedik M., Campbell A. Regulatory structure of the insertion region of bacteriophage lambda. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):1127–1134. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herskowitz I. Control of gene expression in bacteriophage lambda. Annu Rev Genet. 1973;7:289–324. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.07.120173.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoess R. H., Foeller C., Bidwell K., Landy A. Site-specific recombination functions of bacteriophage lambda: DNA sequence of regulatory regions and overlapping structural genes for Int and Xis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2482–2486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honigman A., Hu S. L., Szybalski W. Regulation of integration by coliphage lambda: activation of int transcription by the cII and cIII proteins. Virology. 1979 Jan 30;92(2):542–556. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90156-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M. O., Fischer R., Herskowitz I., Echols H. Location of the regulatory site for establishment of repression by bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):150–154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamp D., Kahmann R., Zipser D., Roberts R. J. Mapping of restriction sites in the attachment site region of bacteriophage lambda. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Sep 9;154(3):231–248. doi: 10.1007/BF00571278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzir N., Oppenheim A., Belfort M., Oppenheim A. B. Activation of the lambda int gene by the cii and ciii gene products. Virology. 1976 Oct 15;74(2):324–331. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90339-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotewicz M., Chung S., Takeda Y., Echols H. Characterization of the integration protein of bacteriophage lambda as a site-specific DNA-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1511–1515. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMacken R., Mantei N., Butler B., Joyner A., Echols H. Effect of mutations in the c2 and c3 genes of bacteriophage lambda on macromolecular synthesis in infected cells. J Mol Biol. 1970 May 14;49(3):639–655. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90288-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pribnow D. Nucleotide sequence of an RNA polymerase binding site at an early T7 promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):784–788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichardt L., Kaiser A. D. Control of lambda repressor synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2185–2189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer G. E., Walkinshaw M. D., Arnott S. A computer aided oligonucleotide analysis provides a model sequence for RNA polymerase-promoter recognition in E.coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Oct;5(10):3759–3773. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.10.3759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz E., Scherer G., Hobom G., Kössel H. Nucleotide sequence of cro, cII and part of the O gene in phage lambda DNA. Nature. 1978 Mar 30;272(5652):410–414. doi: 10.1038/272410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada K., Campbell A. Int-constitutive mutants of bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):237–241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., O'Neill M., de Crombrugghe B. Interaction site of Escherichia coli cyclic AMP receptor protein on DNA of galactose operon promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5090–5094. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


