Abstract
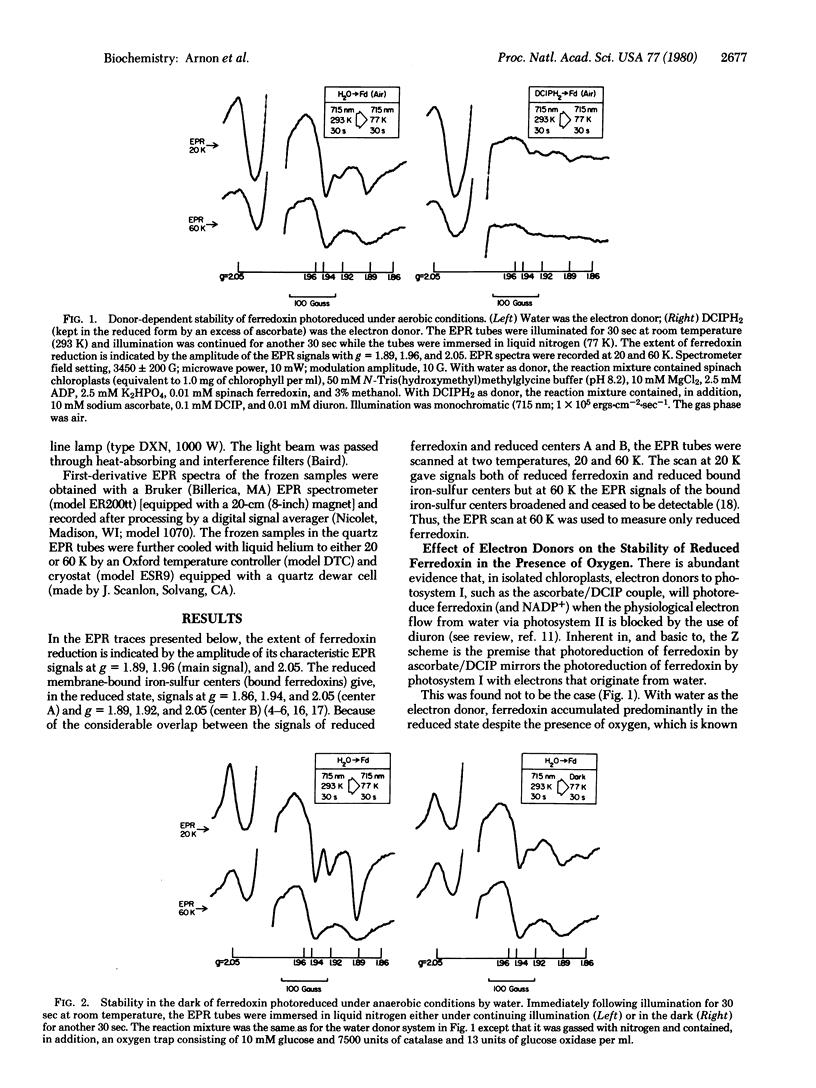
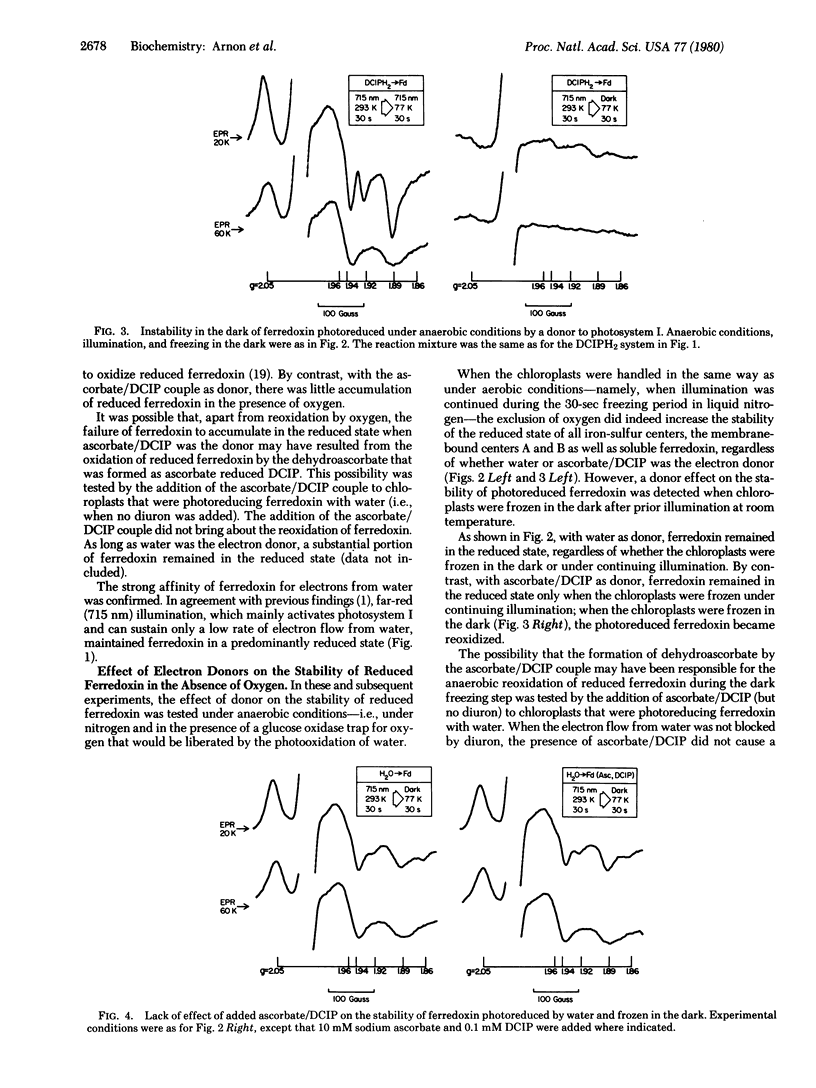
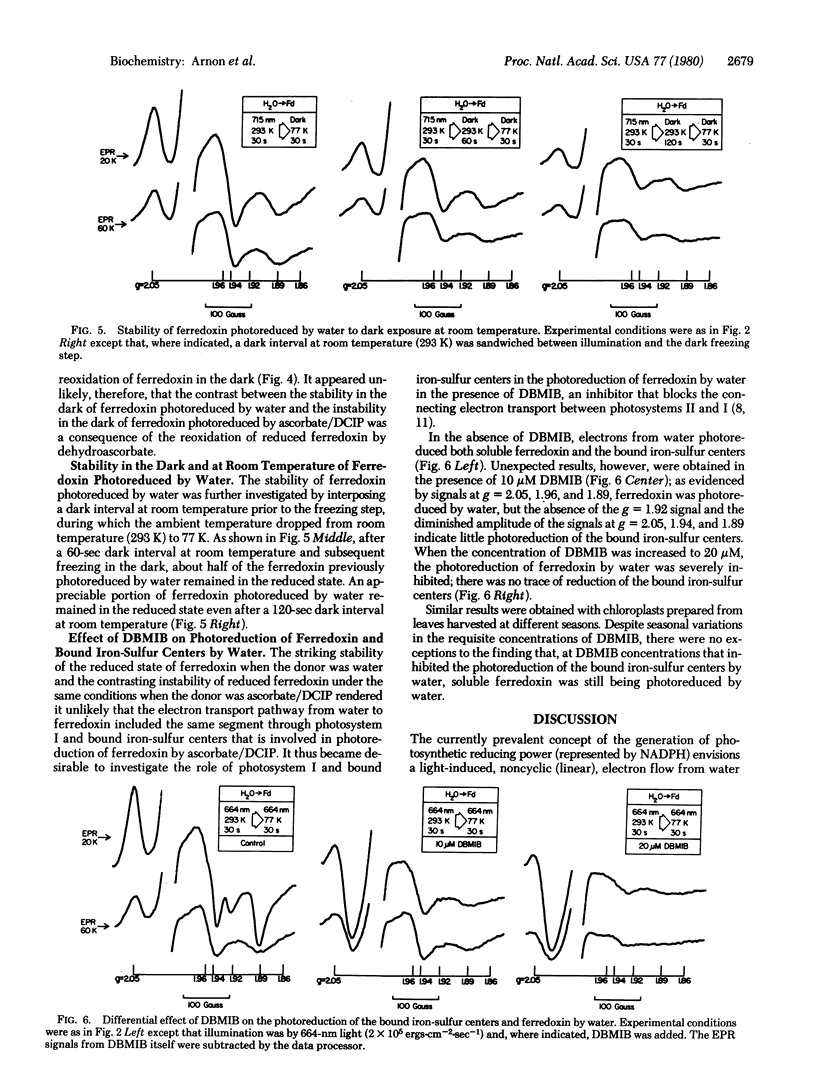
An investigation by paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy of the photoreduction of ferredoxin, oxygenically by water and anoxygenically by a direct electron donor to photosystem I, led to the unexpected findings that different reductive mechanisms may be involved. Ferredoxin photoreduced by water was not reoxidized in the light under aerobic conditions and, under anaerobic conditions, it was remarkably resistant to reoxidation in the dark. By contrast, ferredoxin photoreduced by a donor to photosystem I was readily reoxidized in the light by air and, under anaerobic conditions, by exposure to darkness. Furthermore, when electron transport linking photosystems I and II was inhibited by a plastoquinone antagonist, ferredoxin was photoreduced by water with no evidence for an accompanying photoreduction of the more electronegative bound iron-sulfur centers in chloroplasts. These findings are at variance with the now prevalent concepts of photosynthetic electron transport.
Keywords: photosynthetic mechanisms, photosystems I and II
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARNON D. I., TSUJIMOTO H. Y., MCSWAIN B. D. ROLE OF FERREDOXIN IN PHOTOSYNTHETIC PRODUCTION OF OXYGEN AND PHOSPHORYLATION BY CHLOROPLASTS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jun;51:1274–1282. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.6.1274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnon D. I. COPPER ENZYMES IN ISOLATED CHLOROPLASTS. POLYPHENOLOXIDASE IN BETA VULGARIS. Plant Physiol. 1949 Jan;24(1):1–15. doi: 10.1104/pp.24.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnon D. I., Chain R. K. Regulation of ferredoxin-catalyzed photosynthetic phosphorylations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4961–4965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnon D. I., Chain R. K. Role of oxygen in ferredoxin-catalyzed cyclic photophosphorylations. FEBS Lett. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):297–302. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80606-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnon D. I. Ferredoxin and photosynthesis. Science. 1965 Sep 24;149(3691):1460–1470. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3691.1460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnon D. I., Tsujimoto H. Y., Hiyama T. Electron paramagentic resonance studies of photosynthetic electron transport: photoreduction of ferredoxinand membrane-bound iron-sulfur centers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3826–3830. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bearden A. J., Malkin R. The bound ferredoxin of chloroplasts: a role as the primary electron acceptor of photosystem I. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Feb 16;46(3):1299–1305. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(72)80116-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draber W., Trebst A., Harth E. On a new inhibitor of photosynthetic electron-transport in isolated chloroplasts. Z Naturforsch B. 1970 Oct;25(10):1157–1159. doi: 10.1515/znb-1970-1018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. C., Heathcote P. Effects of glycerol on the redox properties of the electron acceptor complex in spinach photosystem I particles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Mar 7;590(1):89–96. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(80)90148-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. C., Reeves S. G., Cammack R. Determination of the oxidation-reduction potential of the bound iron-sulphur proteins of the primary electron acceptor complex of photosystem I in spinach chloroplasts. FEBS Lett. 1974 Dec 1;49(1):111–114. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80644-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. C., Reeves S. G., Telfer A. The detection of a bound ferredoxin in the photosynthetic lamellae of blue-green algae and other oxygen evolving photosynthetic organisms. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Apr 2;51(3):593–596. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91355-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. C., Telfer A., Lord A. V. Evidence for the role of a bound ferredoxin as the primary electron acceptor of photosystem I in spinach chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jun 23;267(3):530–537. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90181-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ke B., Hansen R. E., Beinert H. Oxidation-reduction potentials of bound iron-sulfur proteins of photosystem I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2941–2945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkin R., Bearden A. J. Primary reactions of photosynthesis: photoreduction of a bound chloroplast ferredoxin at low temperature as detected by EPR spectroscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jan;68(1):16–19. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.1.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHIN M., TAGAWA K., ARNON D. I. CRYSTALLIZATION OF FERREDOXIN-TPN REDUCTASE AND ITS ROLE IN THE PHOTOSYNTHETIC APPARATUS OF CHLOROPLASTS. Biochem Z. 1963;338:84–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer K., Mathis P., Acker S., van Best J. A. Electron acceptors associated with P-700 in Triton solubilized photosystem I particles from spinach chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jul 6;503(1):120–134. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(78)90166-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuvalov V. A., Dolan E., Ke B. Spectral and kinetic evidence for two early electron acceptors in photosystem I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):770–773. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAGAWA K., ARNON D. I. Ferredoxins as electron carriers in photosynthesis and in the biological production and consumption of hydrogen gas. Nature. 1962 Aug 11;195:537–543. doi: 10.1038/195537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagawa K., Arnon D. I. Oxidation-reduction potentials and stoichiometry of electron transfer in ferredoxins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 2;153(3):602–613. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(68)90188-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto H. Y., Hiyama T., Arnon D. I. Affinity of ferredoxin for electrons from water and the regulation of cyclic photophosphorylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Mar 13;93(1):215–222. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80268-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VERNON L. P., ZAUGG W. S. Photoreductions by fresh and aged chloropasts: requirement for ascorbate and 2, 6-dichlorophenolindophenol with aged chloroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1960 Sep;235:2728–2733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



