Abstract
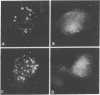
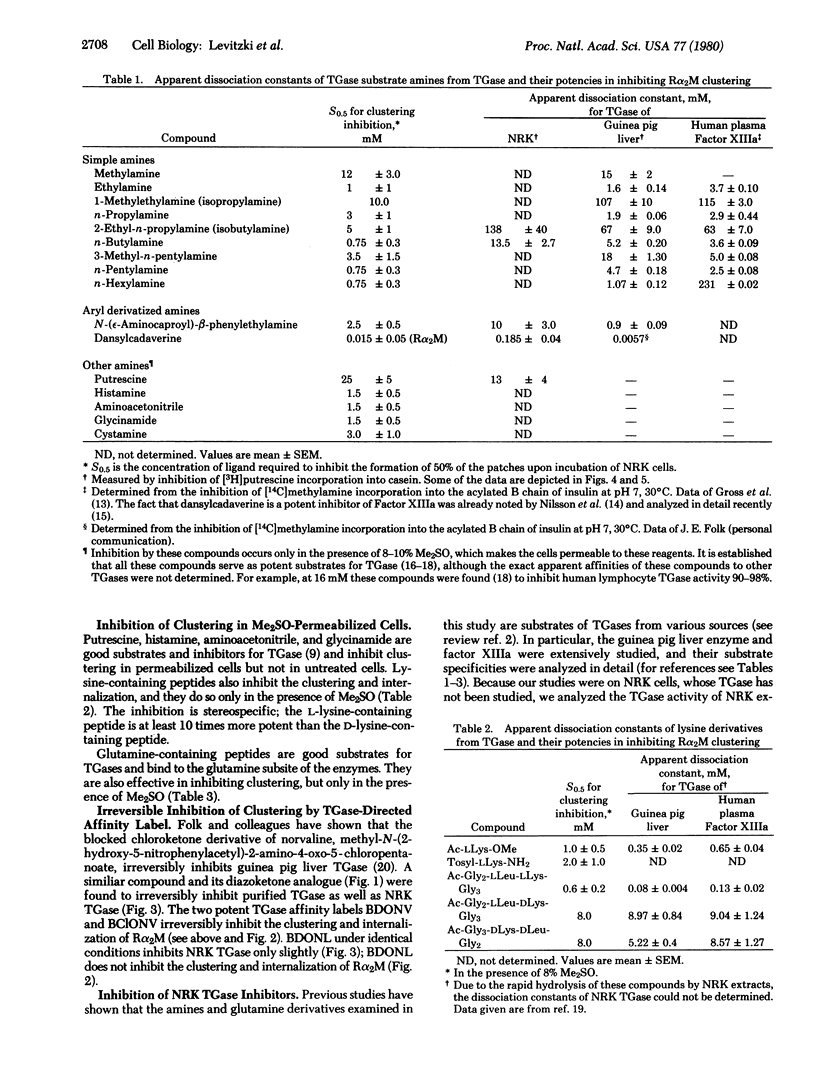
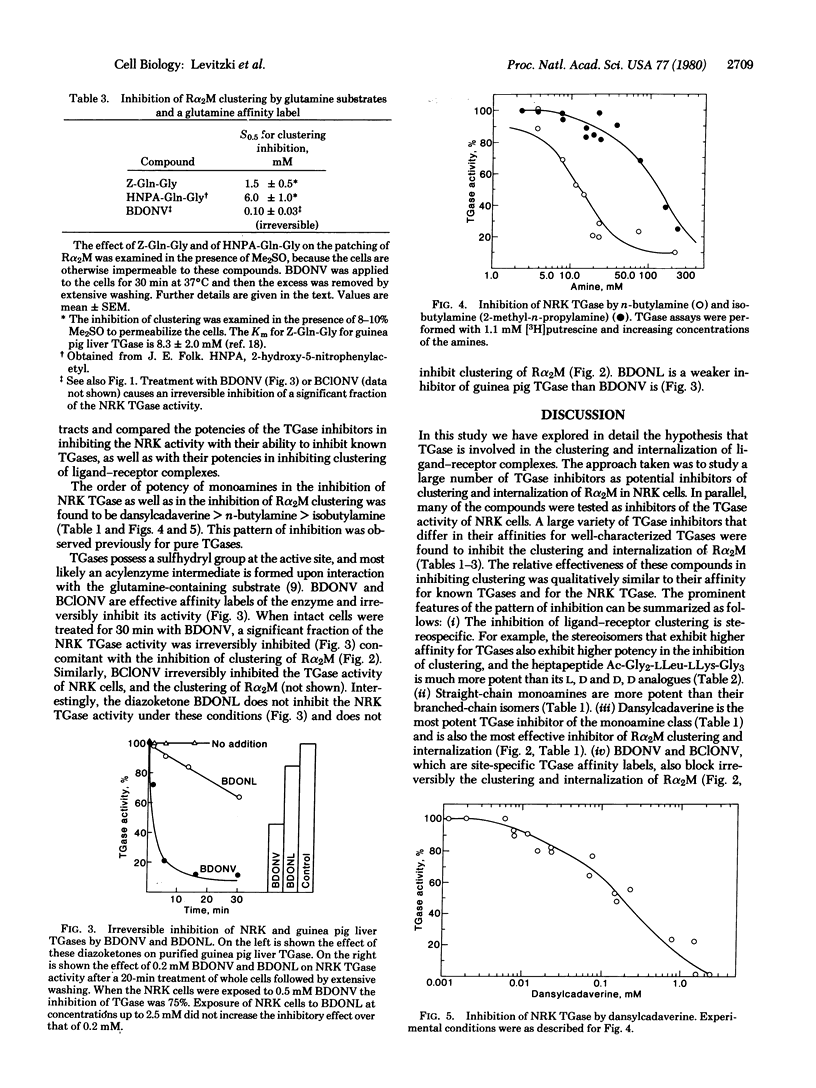
We report evidence that the enzyme transglutaminase (glutaminyl-peptide gamma-glutamyltransferase; R-glutaminyl-peptide:amine gamma-glutamyltransferase, EC2.3.2.13) participates in receptor-mediated endocytosis. Clustering and internalization of rhodamine-labeled alpha 2-macroglobulin (R alpha 2 M) in normal rat kidney (NRK) cells is inhibited by a wide spectrum of compounds that inhibit transglutaminases, including that from NRK cells. The pattern of clustering inhibition resembles the pattern of transglutaminase inhibition as follows: (i) The most potent transglutaminase inhibitors are dansylcadaverine and the transglutaminase-directed affinity label N-benzyloxy-carbonyl-5-diazo-4-oxonorvaline p-nitrophenyl ester; these were also the most potent inhibitors of clustering and internalization of R alpha 2M. (ii) The inhibition of clustering of R alpha 2M occurs in the same concentration range as that required for transglutaminase inhibition. (iii) Linear primary amines are more effective blockers than the iso-chain primary amines. (iv) The transglutaminase affinity label N-benzyloxycarbonyl-5-diazo-4-oxonorvaline p-nitrophenyl ester irreversibly inhibits a significant fraction of the NRK transglutaminase and the clustering and internalization of R alpha 2M. A closely related compound, N-trifluoroacetyl-6-diazo-5-oxonorleucine ethyl ester, does not significantly inhibit transglutaminase or clustering and internalization. (v) Clustering and internalization is inhibited 10-fold more effectively by the heptapeptide Ac-Gly2-LLeu-LLys-Gly3 than by the heptapeptides Ac-Gly2-LLeu-DLys-Gly3 or AcGly3-DLys-DLeu-Gly2. This is the pattern of stereospecificity for the inhibition of purified transglutaminases.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. G., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Localization of low density lipoprotein receptors on plasma membrane of normal human fibroblasts and their absence in cells from a familial hypercholesterolemia homozygote. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2434–2438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P. J., Davies D. R., Levitzki A., Maxfield F. R., Milhaud P., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. H. Transglutaminase is essential in receptor-mediated endocytosis of alpha 2-macroglobulin and polypeptide hormones. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):162–167. doi: 10.1038/283162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folk J. E., Finlayson J. S. The epsilon-(gamma-glutamyl)lysine crosslink and the catalytic role of transglutaminases. Adv Protein Chem. 1977;31:1–133. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60217-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folk J. E., Gross M. Mechanism of action of guinea pig liver transglutaminase. 8. Active site studies with "reporter" group-labeled halomethyl ketones. J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov;246(21):6683–6691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross M., Folk J. E. Activity of guinea pig liver transglutaminase toward ester analogs of amide substrates. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 25;249(10):3021–3025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross M., Whetzel N. K., Folk J. E. Amine binding sites in acyl intermediates of transglutaminases. Human blood plasma enzyme (activated coagulation factor XIII) and guinea pig liver enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3752–3759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand L., Parameswaran K. N., Stenberg P., Tong Y. S., Velasco P. T., Jönsson N. A., Mikiver L., Moses P. Specificity of guinea pig liver transglutaminase for amine substrates. Biochemistry. 1979 May 1;18(9):1756–1765. doi: 10.1021/bi00576a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxfield F. R., Schlessinger J., Shechter Y., Pastan I., Willingham M. C. Collection of insulin, EGF and alpha2-macroglobulin in the same patches on the surface of cultured fibroblasts and common internalization. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):805–810. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90336-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxfield F. R., Willingham M. C., Davies P. J., Pastan I. Amines inhibit the clustering of alpha2-macroglobulin and EGF on the fibroblast cell surface. Nature. 1979 Feb 22;277(5698):661–663. doi: 10.1038/277661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld E. F., Sando G. N., Garvin A. J., Rome L. H. The transport of lysosomal enzymes. J Supramol Struct. 1977;6(1):95–101. doi: 10.1002/jss.400060108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson J. L., Stenberg P., Ljunggren C., Hoffman K. J., Lundén R., Eriksson O., Lorand L. Fibrin-stabilizing factor inhibitors. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1972 Dec 8;202:286–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1972.tb16341.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novogrodsky A., Quittner S., Rubin A. L., Stenzel K. H. Transglutaminase activity in human lymphocytes: early activation by phytomitogens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1157–1161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J., Shechter Y., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. Direct visualization of binding, aggregation, and internalization of insulin and epidermal growth factor on living fibroblastic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2659–2663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrode J., Folk J. E. Stereochemical aspects of amine substrate attachment to acyl intermediates of transglutaminases. Human blood plasma enzyme (activated coagulation factor XIII) and guinea pig liver enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 10;254(3):653–661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shechter Y., Schlessinger J., Jacobs S., Chang K. J., Cuatrecasas P. Fluorescent labeling of hormone receptors in viable cells: preparation and properties of highly fluorescent derivatives of epidermal growth factor and insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2135–2139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willingham M. C., Maxfield F. R., Pastan I. H. alpha 2 Macroglobulin binding to the plasma membrane of cultured fibroblasts. Diffuse binding followed by clustering in coated regions. J Cell Biol. 1979 Sep;82(3):614–625. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.3.614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willingham M. C., Pastan I. The visualization of fluorescent proteins in living cells by video intensification microscopy (VIM). Cell. 1978 Mar;13(3):501–507. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90323-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood D. C., Wood J. Pharmacologic and biochemical considerations of dimethyl sulfoxide. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jan 27;243:7–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb25339.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]