Abstract
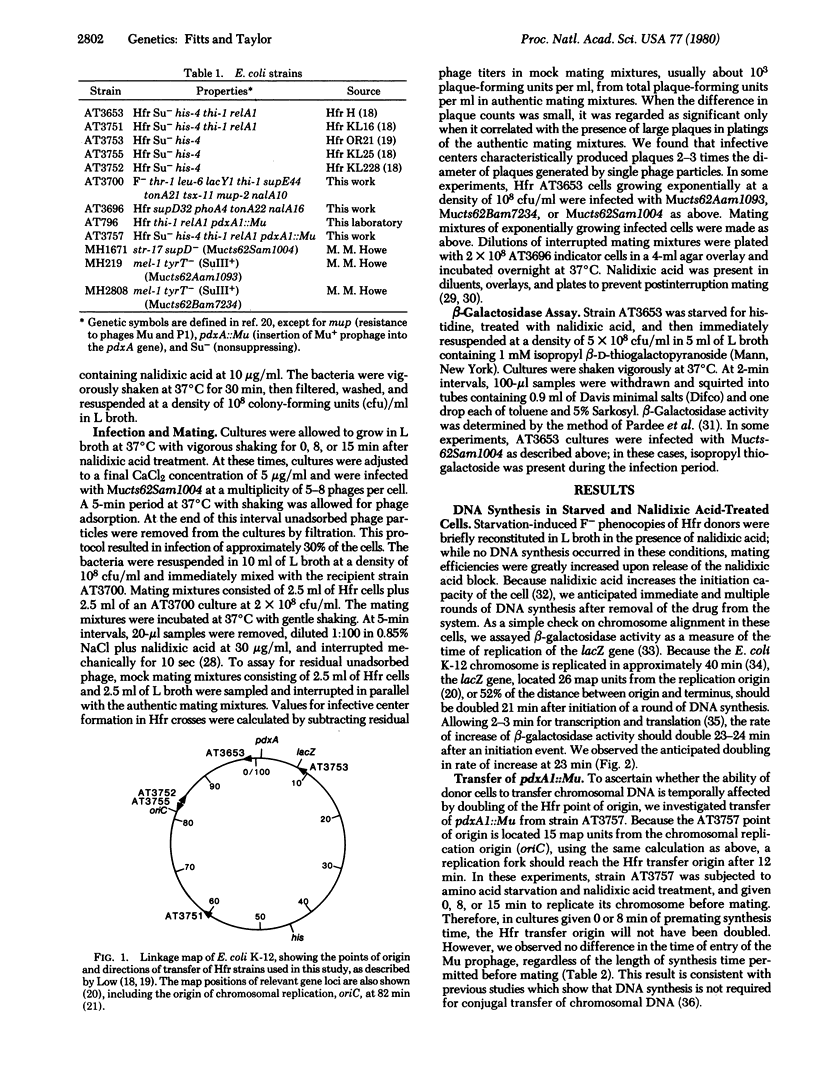
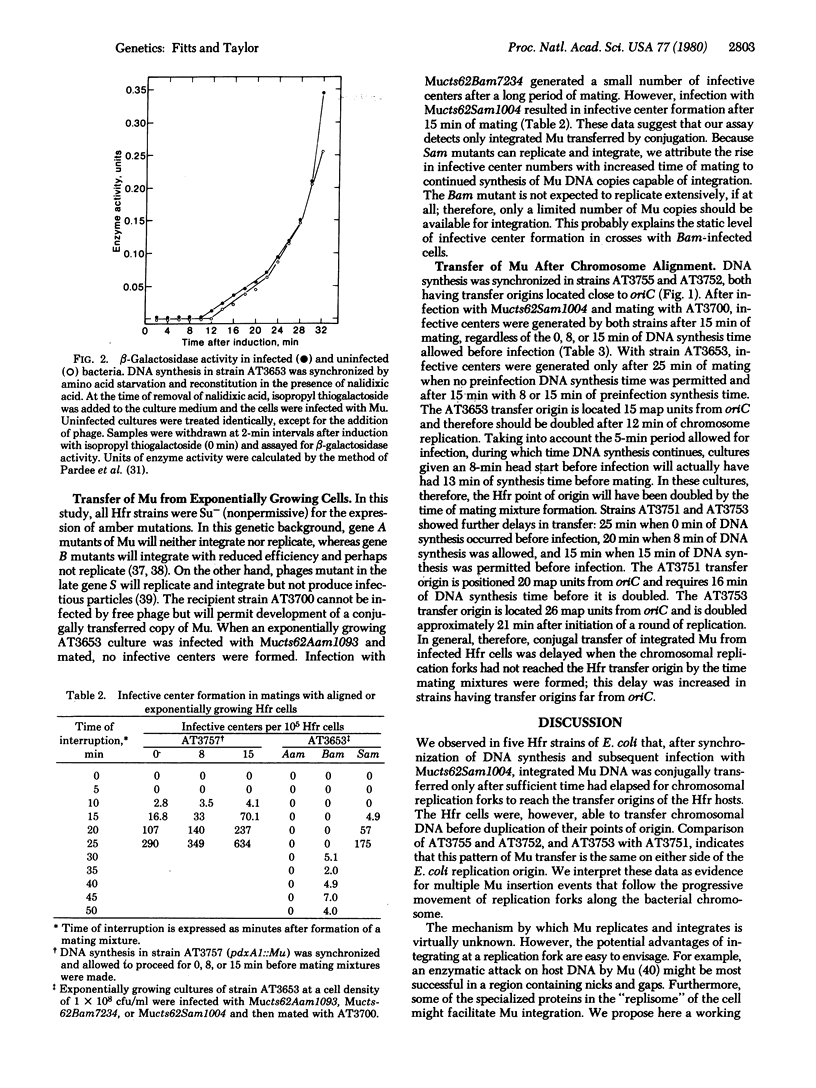
The target site for bacteriophage Mu integration in a lytic cycle of infection was investigated. DNA synthesis in five Hfr strains of Escherichia coli K-12 was synchronized by amino acid starvation and was allowed to proceed for 0, 8, or 15 min before infection. The Hfr cells were then infected with Mu and were subsequently mated with nonimmune F- recipient cells. Mating was interrupted mechanically at 5-min intervals and samples were assayed for infective centers. Conjugal transfer of Mu was delayed in Hfr strains that have transfer origins 15 map units or more from the E. coli replication origin, and the delays increased as the distance between an Hfr point of origin and the replication origin increased. When a gene A mutant of Mu was used for the infection, no infective centers were generated. Infection with a gene B mutant resulted in infective center formation only after long periods of mating. These data are most consistent with a model in which infecting Mu DNA or its progeny integrate at host chromosomal replication forks.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abelson J., Boram W., Bukhari A. I., Faelen M., Howe M., Metlay M., Taylor A. L., Toussaint A., Van de Putte P., Westmaas G. C. Summary of the genetic mapping of prophage Mu. Virology. 1973 Jul;54(1):90–92. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90117-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allet B. Mu insertion duplicates a 5 base pair sequence at the host inserted site. Cell. 1979 Jan;16(1):123–129. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90193-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J., Low K. B., Taylor A. L. Recalibrated linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Mar;40(1):116–167. doi: 10.1128/br.40.1.116-167.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J. Pedigrees of some mutant strains of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):525–557. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.525-557.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouck N., Adelberg E. A. Mechanism of action of nalidixic acid on conjugating bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jun;102(3):688–701. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.3.688-701.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukhari A. I., Froshauer S., Botchan M. Ends of bacteriophage mu DNA. Nature. 1976 Dec 9;264(5586):580–583. doi: 10.1038/264580a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukhari A. I. Reversal of mutator phage Mu integration. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jul 25;96(1):87–99. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90183-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caro L. G., Berg C. M. Chromosome replication in some strains of Escherichia coli K12. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:559–573. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. J., Warren G. J. Conjugal transmission of plasmids. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:99–125. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.000531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniell E., Roberts R., Abelson J. Mutations in the lactose operon caused by bacteriophage Mu. J Mol Biol. 1972 Aug 14;69(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90019-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faelen M., Toussaint A. Bacteriophage Mu-1: a tool to transpose and to localize bacterial genes. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 5;104(3):525–539. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90118-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faelen M., Toussaint A., Couturier M. Mu-1 promoted integration of a -gal phage in the chromosome of E. coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1971;113(4):367–370. doi: 10.1007/BF00272338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faelen M., Toussaint A., De Lafonteyne J. Model for the enchancement of lambde-gal integration into partially induced Mu-1 lysogens. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):873–882. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.873-882.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hane M. W. Some effects of nalidixic acid on conjugation in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):46–56. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.46-56.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe M. M., Bade E. G. Molecular biology of bacteriophage mu. Science. 1975 Nov 14;190(4215):624–632. doi: 10.1126/science.1103291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe M. M., Schumm J. W., Taylor A. L. The S and U genes of bacteriophage mu are located in the invertible G segment of mu DNA. Virology. 1979 Jan 15;92(1):108–124. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90218-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu M. T., Davidson N. Electron microscope heteroduplex study of the heterogeneity of Mu phage and prophage DNA. Virology. 1974 Mar;58(1):229–239. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90157-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahmann R., Kamp D. Nucleotide sequences of the attachment sites of bacteriophage Mu DNA. Nature. 1979 Jul 19;280(5719):247–250. doi: 10.1038/280247a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamp D., Chow L. T., Broker T. R., Kwoh D., Zipser D., Kahmann R. Site-specific recombination in phage mu. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):1159–1167. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuempel P. L., Duerr S. A., Maglothin P. D. Chromosome replication in an Escherichia coli dnaA mutant integratively suppressed by prophage P2. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):902–912. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.902-912.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARK K. G., REPKO T., HOFFMAN E. J. THE EFFECT OF AMINO ACID DEPRIVATION ON SUBSEQUENT DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID REPLICATION. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Sep 17;76:9–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOW B., WOOD T. H. A QUICK AND EFFICIENT METHOD FOR INTERRUPTION OF BACTERIAL CONJUGATION. Genet Res. 1965 Jul;6:300–303. doi: 10.1017/s001667230000416x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low B. Rapid mapping of conditional and auxotrophic mutations in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):798–812. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.798-812.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low K. B. Escherichia coli K-12 F-prime factors, old and new. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):587–607. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.587-607.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARDEE A. B., PRESTIDGE L. S. The initial kinetics of enzyme induction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Apr 29;49:77–88. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90871-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paolozzi L., Ghelardini P., Kepes A., Marcovich H. The mechanism of integration of phage Mu in the chromosome of Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 May 14;88(1):111–116. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91703-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paolozzi L., Jucker R., Calef E. Mechanism of phage Mu-1 integration: nalidixic acid treatment causes clustering of Mu-1-induced mutations near replication origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4940–4943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pato M. L., Glaser D. A. The origin and direction of replication of the chromosome of Escherichia coli B-r. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1268–1274. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razzaki T., Bukhari A. I. Events following prophage Mu induction. J Bacteriol. 1975 May;122(2):437–442. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.2.437-442.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarathy P. V., Siddiqi O. DNA synthesis during bacterial conjugation. II. Is DNA replication in the Hfr obligatory for chromosome transfer? J Mol Biol. 1973 Aug 15;78(3):443–451. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90467-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro J. A. Molecular model for the transposition and replication of bacteriophage Mu and other transposable elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1933–1937. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR A. L. BACTERIOPHAGE-INDUCED MUTATION IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Dec;50:1043–1051. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.6.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Templin A., Margossian L., Clark A. J. Suppressibility of recA, recB, and recC mutations by nonsense suppressors. J Bacteriol. 1978 May;134(2):590–596. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.2.590-596.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waggoner B. T., Pato M. L. Early events in the replication of Mu prophage DNA. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):587–594. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.587-594.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward C. B., Hane M. W., Glaser D. A. Synchronous reinitiation of chromosome replication in E. coli B-r after nalidixic acid treatment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):365–369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijffelman C., Lotterman B. Kinetics of Mu DNA synthesis. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Mar 7;151(2):169–174. doi: 10.1007/BF00338691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Meyenburg K., Hansen F. G., Nielsin L. D., Riise E. Origin of replication, oriC, or the Escherichia coli chromosome on specialized transducing phages lambda asn. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Apr 17;160(3):287–295. doi: 10.1007/BF00332972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


