Abstract
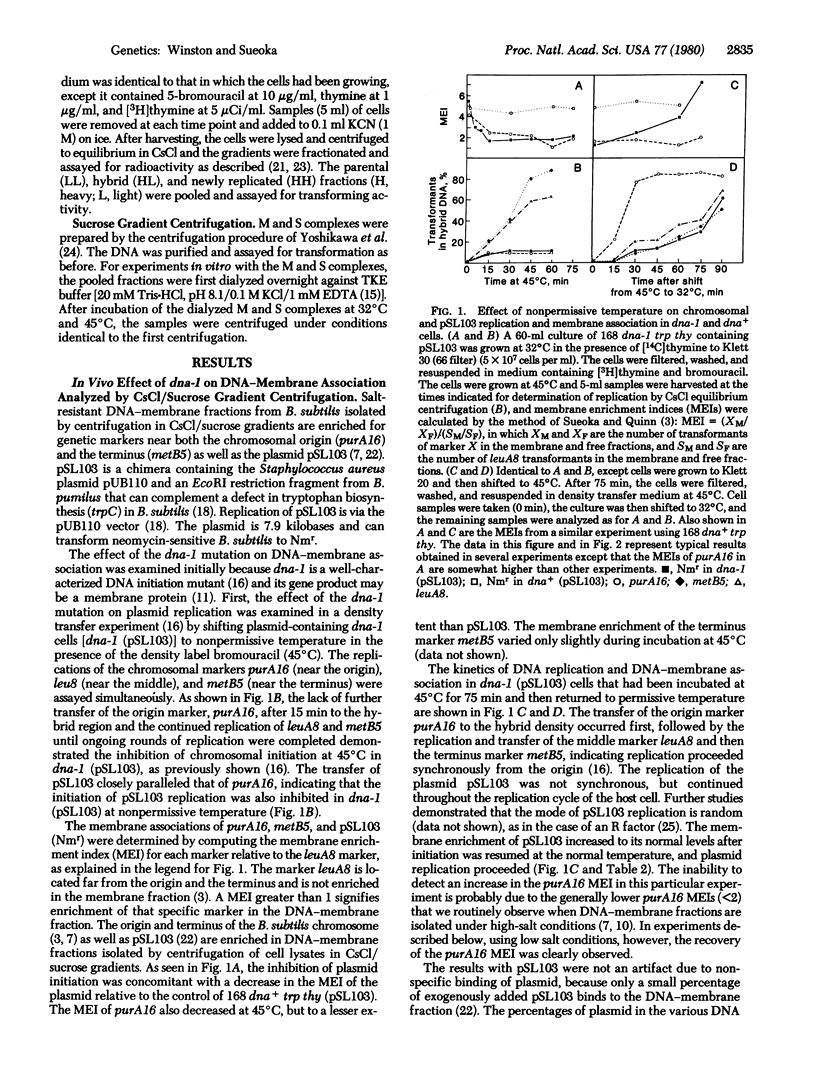
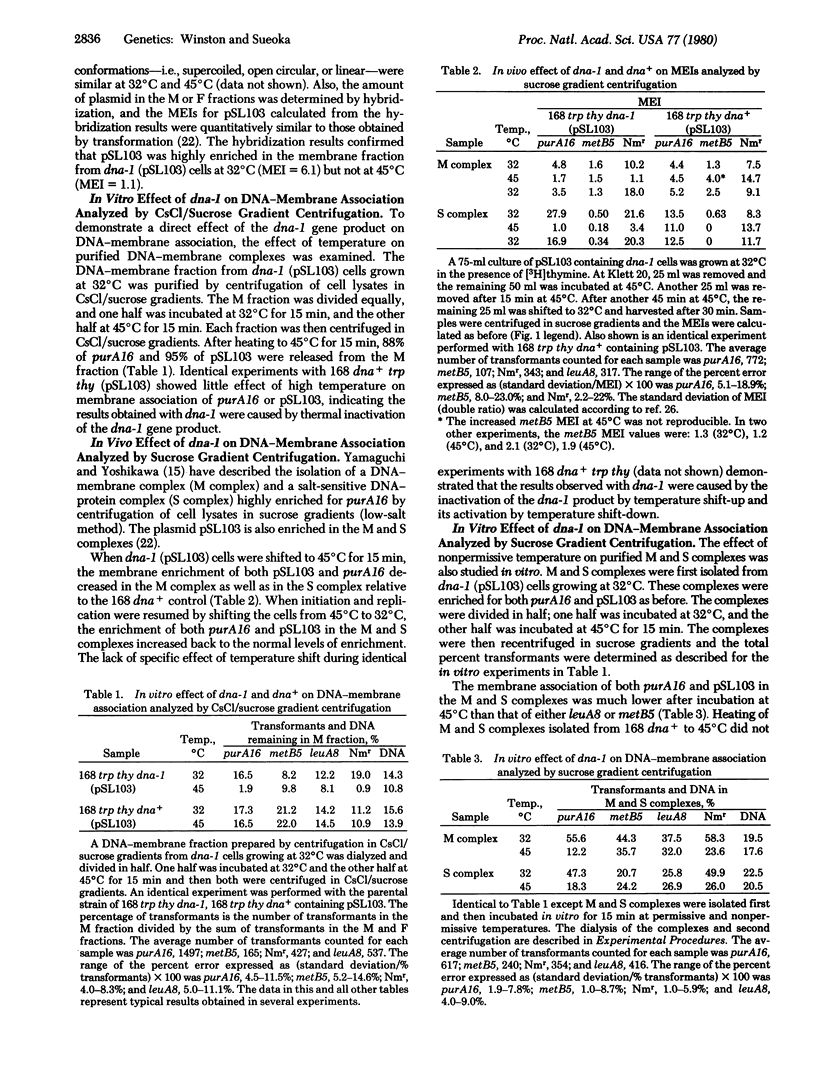
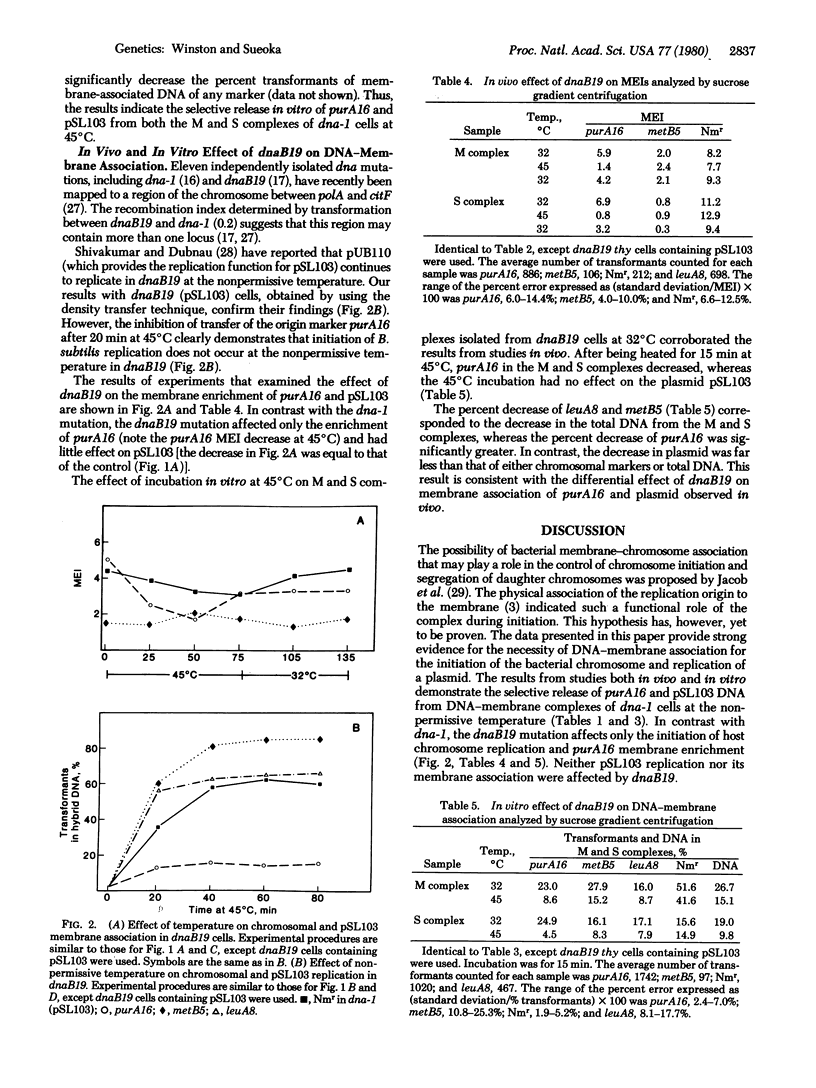
We examined the effect of the inhibition of initiation of DNA replication on the membrane association of the chromosomal origin of replication of Bacillus subtilis and the Staphylococcus aureus-Bacillus pumilus chimeric plasmid pSL103, using temperature-sensitive mutants of B. subtilis that have specifically affected initiation. Inhibition of initiation of the chromosome and pSL103 in the initiation mutant dna-1 results in a decrease in the membrane association of both a marker near the chromosomal origin, purA16, and the plasmid pSL103. The membrane association of both purA16 and pSL103 can be recovered by allowing initiation to resume at the permissive temperature. In another initiation mutant, dnaB19, only the initiation and membrane association of the host chromosome are affected at the nonpermissive temperature, whereas both initiation and membrane association are not affected in the plasmid pSL103. In experiments in vitro, DNA containing the purA16 marker and pSL103 DNA molecules are both selectively released during incubation of purified DNA-membrane complexes prepared from dna-1 cells at the nonpermissive temperature. On the other hand, only purA16 DNA is released in vitro from the DNA-membrane complex prepared from dnaB19 cells. This consistent coupling between initiation and membrane association indicates that DNA-membrane association is critical for the initiation of the B. subtilis chromosome and the plasmid pSL103.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anagnostopoulos C., Spizizen J. REQUIREMENTS FOR TRANSFORMATION IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1961 May;81(5):741–746. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.5.741-746.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beeson J., Sueoka N. Membrane enrichment of genetic markers close to the origin and terminus during the deoxyribonucleic acid replication cycle in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1979 Sep;139(3):911–916. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.3.911-916.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bott K. F., Wilson G. A. Development of competence in the Bacillus subtilis transformation system. J Bacteriol. 1967 Sep;94(3):562–570. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.3.562-570.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding P., Fox C. F. Evidence for stable attachment of DNA to membrane at the replication origin of Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Oct 9;41(1):157–162. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90482-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karamata D., Gross J. D. Isolation and genetic analysis of temperature-sensitive mutants of B. subtilis defective in DNA synthesis. Mol Gen Genet. 1970;108(3):277–287. doi: 10.1007/BF00283358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keggins K. M., Lovett P. S., Duvall E. J. Molecular cloning of genetically active fragments of Bacillus DNA in Bacillus subtilis and properties of the vector plasmid pUB110. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1423–1427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolter R., Helinski D. R. Regulation of initiation of DNA replication. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:355–391. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.002035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan A., Sueoka N. Sequential replication of the Bacillus subtilis chromosome. IV. Genetic mapping by density transfer experiment. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jul 28;27(2):349–368. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90025-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan M. A., Sueoka N. Membrane attachment of the replication origins of a multifork (dichotomous) chromosome in Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1972 Aug 21;69(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90228-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker D. L., Glaser D. A. Chromosomal sites of DNA-membrane attachment in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1974 Aug 5;87(2):153–168. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90140-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rownd R. Replication of a bacterial episome under relaxed control. J Mol Biol. 1969 Sep 28;44(3):387–402. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90368-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shivakumar A. G., Dubnau D. Plasmid replication in DNA Ts mutants of Bacillus subtilis. Plasmid. 1978 Jun;1(3):405–416. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90055-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siccardi A. G., Shapiro B. M. On the process of cellular division in Escherichia coli. IV. Altered protein composition and turnover of the membranes of thermosensitive mutants defective in chromosomal replication. J Mol Biol. 1971 Mar 28;56(3):475–490. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90395-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder R. W., Young F. E. Association between the chromosome and the cytoplasmic membrane in Bacillus subtilis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 May 8;35(3):354–362. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90506-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sueoka N., Hammers J. M. Isolation of DNA-membrane complex in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4787–4791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sueoka N., Quinn W. G. Membrane attachment of the chromosome replication origin in Bacillus subtilis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:695–705. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sueoka N., Yoshikawa H. The chromosome of Bacillus subtilis. I. Theory of marker frequency analysis. Genetics. 1965 Oct;52(4):747–757. doi: 10.1093/genetics/52.4.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomizawa J., Selzer G. Initiation of DNA synthesis in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:999–1034. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.005031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada C., Yura T. Phenethyl alcohol resistance in Escherichia coli. 3. A temperature-sensitive mutation(dnaP) affecting DNA replication. Genetics. 1974 Jun;77(2):199–220. doi: 10.1093/genetics/77.2.199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White K., Sueoka N. Temperature-sensitive DNA synthesis mutants of Bacillus subtilis--appendix: theory of density transfer for symmetric chromosome replication. Genetics. 1973 Feb;73(2):185–214. doi: 10.1093/genetics/73.2.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White K., Sueoka N. Temperature-sensitive DNA synthesis mutants of Bacillus subtilis--appendix: theory of density transfer for symmetric chromosome replication. Genetics. 1973 Feb;73(2):185–214. doi: 10.1093/genetics/73.2.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston S., Matsushita T. Permanent loss of chromosome initiation in toluene-treated Bacillus subtilis cells. J Bacteriol. 1975 Sep;123(3):921–927. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.3.921-927.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi K., Yoshikawa H. Chromosome--Membrane association in Bacillus subtilis. III. Isolation and characterization of a DNA-protein complex carrying replication origin markers. J Mol Biol. 1977 Feb 25;110(2):219–253. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi K., Yoshikawa H. Topography of chromosome membrane junction in Bacillus subtilis. Nat New Biol. 1973 Aug 15;244(137):204–206. doi: 10.1038/newbio244204a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa H., Yamaguchi K., Seiki M., Ogasawara N., Toyoda H. Organization of the replication-origin region of the Bacillus subtilis chromosome. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):569–576. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



