Abstract
AIMS
To test the hypothesis that the clearance (CL) of warfarin, a very highly protein bound drug with capacity-limited metabolism, decreases with age.
METHODS
In a clinical study, a steady-state blood sample was taken from 72 patients (18–89 years) on routine treatment with warfarin. Concentrations of (R)- and (S)-warfarin were determined in plasma (total) and ultrafiltrate (free) by LC-MS/MS. Total and free CL and protein binding were determined and regressed against age and other covariates. In an ex vivo study, warfarin was spiked to plasma samples from 60 healthy subjects (19–87 years) and protein binding was regressed against age and other covariates.
RESULTS
For (R)-warfarin a significant decrease with age was found for both total and free CL (P < 0.001). For (S)-warfarin there was a stronger signal of a decrease with age in free CL (P= 0.005) vs. total CL (P= 0.045). The decrease in CL of (R)- and (S)-warfarin was 0.3–0.5% per year. Other covariates influencing CL were lean body weight for both (R)- and (S)-warfarin and CYP2C9 genotype and blood sampling time for (S)-warfarin. Protein binding of (R)- and (S)-warfarin was not found to change significantly with age in either the clinical or the spiked samples, despite a slight decrease in albumin concentration with age.
CONCLUSIONS
These data support the hypothesis that the CL of (R)- and (S)-warfarin decreases with age. More accurate information was gained when measuring free CL for (S)-warfarin. Warfarin protein binding did not change significantly with age.
Keywords: age, clearance, free, protein binding, (R)-warfarin, (S)-warfarin
WHAT IS ALREADY KNOWN ABOUT THIS SUBJECT
Hepatic drug clearance is thought to be reduced with age. However for highly protein bound drugs, which are cleared by capacity-limited metabolism, studies on total clearance have been conflicting. The hypothesis that protein binding decreases with age has been used to explain this.
Warfarin is a highly protein bound drug, which is cleared by capacity-limited metabolism. There are conflicting or little data on the relationship between adult age and total and free clearance and protein binding of (R)- and (S)-warfarin.
WHAT THIS STUDY ADDS
In a clinical study of 72 patients (18–89 years) on warfarin therapy, both total and free clearance of (R)-warfarin decreased with age. For (S)-warfarin there was a stronger signal of a decrease in free than total clearance. Protein binding was found not to correlate with age for (R)- and (S)-warfarin.
In an ex vivo study, in which warfarin was spiked to plasma samples from 60 healthy subjects (19–87 years), no correlation between protein binding and age was found.
These data support the hypothesis that hepatic drug clearance decreases with age. This should be taken into consideration when individualizing dosing, particularly in the elderly.
Introduction
Medical treatment of elderly people is challenging because of the increased risk of adverse drug reactions with age. As physiological function generally declines with age, it might be expected that hepatic drug clearance (CL) in the elderly shows a predictable decline, as seen for drugs subject to renal clearance. However, this has been the subject of considerable debate [1]. As the choice of the maintenance dose rate of a drug depends on CL, age-related changes in CL should be taken into consideration when prescribing drugs to elderly people.
Hepatic drug clearance has been consistently shown to be impaired with age for drugs with flow-limited metabolism (high CL). For drugs with capacity-limited metabolism (low CL), the effect of ageing on CL is less clear. For those drugs with low protein binding a consistent decrease in CL with ageing is seen, but results are inconsistent for drugs with high protein binding [2]. Butler & Begg hypothesized that the hepatic CL of capacity-limited, highly protein bound drugs is decreased in the elderly and that the conflicting data are a result of CL being estimated using total concentrations rather than free concentrations, which are difficult to measure [2]. Total drug CL reflects both the intrinsic CL of free drug and the extent of protein binding, expressed as the unbound fraction, fu (fu=Cfree/Ctotal), as follows: CLtotal=fu× CLfree. As protein binding may be reduced with age, a decrease in intrinsic (free) CL may be masked by an increase in fu, if only total CL is measured.
To investigate this hypothesis we chose warfarin as an example of a hepatically cleared drug with a very high extent of protein binding (>99%, bound to albumin), which is subject to capacity-limited metabolism. Warfarin is an anticoagulant drug administered as a racemic mixture. The anticoagulant activity of the (S)-enantiomer is 3–7 times that of the (R)-enantiomer and the CL of the (S)-enantiomer is almost twice that of the (R)-enantiomer. (S)-warfarin is metabolized mainly by the CYP2C9 enzyme, and therefore subject to genetic polymorphism, whereas (R)-warfarin is metabolized by various CYP enzymes [3]. In terms of designing a clinical study, warfarin is very suitable in that it is almost completely absorbed orally (>95%) and has a long half-life (20–60 h for (R)-warfarin and 18–35 h for (S)-warfarin) [3] allowing concentrations obtained from a single blood sample from the middle of the dosing interval to represent steady-state concentrations.
As reviewed in Butler & Begg [2], there is limited information on the CL of warfarin in elderly people. We were unable to find any studies that assessed free warfarin CL based on measurement of free warfarin concentrations. By indirect measurement (inferring free CL by adjusting total CL of rac-warfarin for protein binding), no change in free CL was seen in a single study of 14 patients [4]. Total CL has been shown to be reduced with age [5–9] but in other studies this reduction was only seen for (R)- and not (S)-warfarin [10] or total CL was found unchanged with age [4, 11–13].
Data on the effect of age on plasma protein binding of warfarin is even more limited. We were unable to find any studies that assessed protein binding based on measurement of free warfarin concentrations in patient samples, but four studies involved spiking of racemic warfarin to plasma samples. Hayes et al. [14] showed significantly reduced warfarin binding capacity in 12 elderly healthy subjects compared with nine young controls using high warfarin concentrations and diluted plasma. Abel et al. [15] described a decrease in fu with age in 37 subjects with low albumin concentrations. In contrast, Shepherd et al. [11] did not show a difference in protein binding between 15 elderly and 13 young healthy subjects. The same conclusion was drawn from a study in which warfarin was spiked at a high concentration to plasma samples from 36 patients [12].
The literature therefore contains conflicting data regarding the influence of age on warfarin total and free CL and protein binding. Many of the previous studies did not take warfarin enantiomers and CYP2C9 polymorphism into account, which could limit the conclusions drawn. In addition, analytical technology has only recently become available for measurement of the very low concentrations of free (R)- and (S)-warfarin in clinical samples allowing for free CL to be determined directly. This study thus aimed to determine the influence of age on free and total CL and protein binding of (R)- and (S)-warfarin by direct measurement of total and free concentrations to test the overall hypothesis that warfarin CL decreases with age.
Methods
Study design – clinical study
Patients on stable long term warfarin therapy (>2 weeks) for medical conditions requiring a target International Normalized Ratio (INR) of 2.0–3.5 were identified through the Clinical Haematology department and on General Medicine wards at Christchurch Hospital, New Zealand. It was aimed to recruit 25 patients in each of the age groups 18–39, 40–64 and ≥65 years to allow a decrease in CL of 25% (40% CV [7]) between age groups to be detected with a statistical power (1–β) of 80% and a 5% α value. The patients' demographic characteristics were recorded including gender, age, weight and height as well as indication for warfarin therapy, additional medical problems and concurrent medications. Exclusion criteria were current smoking, consumption of alcohol exceeding three (males) or two (females) standard drinks per day, concomitant treatment with enzyme-inducing drugs or amiodarone (strong enzyme inhibitor), clinical or laboratory evidence of significant liver disease or diseases of malabsorption. At a time of a routine INR measurement, and within 6–22 h of the last warfarin dose, 15 ml blood was collected in BD Vacutainer® K2-EDTA tubes. The blood samples were centrifuged and plasma stored at −80°C for determination of total and free warfarin enantiomer concentrations. The remaining blood cells were stored at −20°C for CYP2C9 genotyping. In addition, a separate 5 ml blood sample was taken for routine analysis of plasma creatinine, albumin, total bilirubin and hepatic enzymes. Ethical approval for the study was obtained from the Upper South A Regional Ethics Committee, New Zealand (Ethics reference URA/08/03/018). Informed written consent was obtained from all patients before participation in the study.
Study design –ex vivo study
Sixty healthy subjects were recruited, including 10 males and 10 females in each of the groups 18–39, 40–64 and ≥65 years as described in Chin et al. [16]. Exclusion criteria included comorbidities, use of any medications in the last 7 days, pregnancy, current smoking, consumption of alcohol exceeding three (males) or two (females) standard drinks per day, or clinical or laboratory evidence of significant liver and renal disease. Plasma aliquots from each subject were allowed to thaw and triplicate samples were spiked with rac-warfarin to concentrations of (R)- and (S)-warfarin of 333 µg l−1. The samples were vortexed and incubated at 37°C for 30 min prior to being assayed for total and free warfarin enantiomer concentrations.
Determination of total and free (R)- and (S)-warfarin concentrations
Plasma samples were analyzed using a validated, chiral, liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) assay [17]. Briefly, for determination of total concentrations of (R)- and (S)-warfarin, 50 µl plasma was acidified with 5% formic acid and extracted by liquid–liquid extraction with methyl tertbutyl ether using d6-warfarin as internal standard. The supernatant was evaporated and reconstituted in 100 µl 40% methanol. A 5 µl aliquot was injected onto a Chirobiotic V column and detected by MS/MS using negative mode electrospray ionization. Standard curves of 20–2000 µg l−1 of (R)- and (S)-warfarin in plasma were made by quadratic regression, weighted 1/X (r2≥0.998). Intra- and inter-day precision and bias were determined on three separate days at the lower limit of quantification and at three quality control concentrations. Intra- and inter-day coefficients of variation (CV) were ≤7% and biases were ≤9%. The patient samples had total concentrations in the ranges 300–1690 µg l−1 for (R)-warfarin and 130–1020 µg l−1 for (S)-warfarin. Each sample was analyzed in triplicate and the average precision for both patient and spiked samples was <5% CV and all triplicate values were within 80–120% of the mean value.
For determination of free concentrations of (R)- and (S)-warfarin, in brief, 500 µl plasma was ultrafiltrated for 15 min at 32°C and 2000 ×g using Centrifree 30 K ultrafiltration devices (Millipore, Bedford, MA, USA). There was no evidence of non-specific binding to the devices. Ultrafiltrate samples (100 µl) were acidified with 5% formic acid and extracted by liquid–liquid extraction as described above. A 10 µl aliquot of the reconstituted supernatant was injected onto the LC-MS/MS system. Standard curves of 1–20 µg l−1 of (R)- and (S)-warfarin in ultrafiltrate were made by quadratic regression, weighted 1/X (r2≥0.998). Intra- and inter-day CVs were ≤11% and biases were ≤12%. The patient samples had free concentrations in the ranges 2.2–17.5 µg l−1 for (R)-warfarin and 0.8-6.5 µg l−1 for (S)-warfarin. Each sample was ultrafiltrated and analyzed in triplicate. For the patient samples the average precision was <9% CV. Triplicate values were within 80–120% of the mean value for 67/72 (93%) of the samples for (R)-warfarin and 63/72 (88%) for (S)-warfarin. Values outside this range were excluded as outliers. For the spiked plasma samples the average precision was ≤3% CV and all values were within 80–120% of the mean value.
Genotyping for CYP2C9*2 and CYP2C9*3
Genomic DNA was obtained from patient blood samples using a standard NaCl phenol-chloroform extraction. DNA was re-suspended in Tris-EDTA buffer and stored at −20°C until analyzed. Patients were genotyped for the CYP2C9*2 (rs1799853) and CYP2C9*3 (rs1057910) single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), by a two-tube allele-specific polymerase chain reaction (PCR) (Table 1). Each reaction was performed in a total volume of 10 µl containing 200 µm dNTPs, 3 mm MgCl2, 0.5 µm of the control primers β2Mf and β2Mr, 0.5 µm of the two common reverse primers (CYP2C9*2C and CYP2C9*3C), 1 U of Platinum Taq DNA polymerase (5 U µl−1) (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) and ∼50 ng of DNA. Reaction 1 contained 0.5 µm of the wildtype-specific primer CYP2C9*2WT and the mutant-specific primer CYP2C9*3 MU (Table 1). Reaction 2 contained 0.5 µm of the mutant-specific primer CYP2C9*2 MU and the wildtype-specific primer CYP2C9*3WT (Table 1). Thermal cycling conditions comprised an initial denaturation of 2 min at 94°C, followed by 30 cycles of 30 s at 94°C, 30 s at 65°C, 30 s at 72°C and a final extension of 2 min at 72°C. Reactions were visualized using 3% agarose gel electrophoresis. The primers β2Mf and β2Mr amplified a 569 bp region of the beta-2-microglobulin gene (β2M) which served as an internal control for amplification in samples where homozygosity for each SNP of interest resulted in an allele-specific PCR product in only one reaction. The accuracy of CYP2C9*3 genotype assignment was checked by repeat analysis of 5% of samples and by sequencing another 5% of samples. A BLAST search (http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi) found the CYP2C9*2C primer was specific to CYP2C9 whereas the CYP2C9*2 allele-specific primers also exhibited high homology to sequences in CYP2C8, CYP2C18 and CYP2C19. As a result, the CYP2C9*2 allele-specific PCR was further validated by repeat genotyping of all patients for this allele using a predesigned TaqMan SNP genotyping assay (assay ID: C_25625805_10; Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) to ensure CYP2C9 genotypes were correctly assigned. This genotyping was performed in 384-well format following the recommendations of the manufacturer and run on a Roche LightCycler 480. The concordance between the ‘in-house’ and commercial assays was 100%.
Table 1.
Primer sequences for a two-tube allele specific assay for the detection of CYP2C9*2 (rs1799853) and CYP2C9*3 (rs1057910)
| Primer | Sequence (5′ to 3′ direction)* | Product size (bp) | Reaction |
|---|---|---|---|
| CYP2C9*2WT | TTGGGATGGGGAAGAGGAGCATTGAGGAgC | 1 | |
| CYP2C9*2 MU | TTGGGATGGGGAAGAGGAGCATTGAGGAgT | 2 | |
| CYP2C9*2C | AGCTAACAACCAGGACTCATAATGAAAGAT | 197 | 1 & 2 |
| CYP2C9*3WT | ATGCTGTGGTGCACGAGGTCCAGAGATAgA | 2 | |
| CYP2C9*3 MU | ATGCTGTGGTGCACGAGGTCCAGAGATAgC | 1 | |
| CYP2C9*3C | CTGGAGAACACACACTGCCAGACACTAGGA | 307 | 1 & 2 |
| β2Mf | TGTAAACACTTGGTGCCTGATATAGCTTGA | 569 | 1 & 2 |
| β2Mr | CATCAGTATCTCAGCAGGTGCCACTAATCT | 1 & 2 |
To increase primer specificity a 3′ penultimate mismatch was included in each of the allele-specific primers. Penultimate mismatches are shown in lower case and 3′ allele-specific bases are shown in upper case bold and underlined. C, common; MU, mutant-specific; WT, wildtype-specific.
Calculation of variables
The clearance (CL) for (R)- and (S)-warfarin was determined as follows: CL =D/(τ×Css) in which D is the daily warfarin dose divided by 2 (the tablet is a racemic mixture of the two enantiomers), τ= 24 h and Css is the steady-state concentration of each warfarin enantiomer. It was assumed that warfarin bioavailability and compliance is complete. The unbound fraction, fu, was calculated as Cfree/Ctotal. Lean body weight (LBW) was calculated as described in Janmahasatian et al. [18] and renal function was determined by calculation of the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) using the re-expressed four-variable Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study equation [19].
Statistical analysis
Results are expressed as mean (SEM). Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS Statistics 17.0. anova was used for comparison of characteristics between age groups. Simple correlation analysis was performed using Pearson's correlation coefficient, r, to express the strength of the relationships. Multiple linear regression was used to model the relationships of CL and protein binding with the other variables measured (age, gender, ethnicity, weight, LBW, eGFR, albumin concentration, CYP2C9 genotype, blood sampling time, concurrent medications). Forward and backwards stepwise methods were used for selecting the predictor variables and the final regression model was determined by block entry of significant variables in a single step. Confidence in normality of residuals was obtained by visual inspection of residual plots. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Clinical study
A total of 72 patients were included in the study. The primary indications for warfarin therapy were venous thromboembolic disease (n= 43), atrial fibrillation (n= 17), prosthetic heart valves (n= 8) and other embolic disorders (n= 4), e.g. transient ischaemic attacks of the central nervous system. The daily warfarin doses ranged from 1.3–12 mg with a mean (SEM) of 5.6 (0.3) mg. The demographic and clinical characteristics of the patients are shown in Table 2. The mean (SEM) age was 61 (2) years for men (range 18–86 years) and 57 (3) years (range 22–89 years) for women. All patients had plasma albumin, bilirubin and liver enzymes within the normal range, except for four patients whose γ-glutamyltransferase concentrations were above three times the upper limit of normal. Seven patients had eGFR <60 ml min−1. A total of 56/72 patients (78%) were receiving concurrent medications, including potential inhibitors of the metabolism of (R)-warfarin (omeprazole n= 20) and (S)-warfarin (fluoxetine n= 2, metronidazole n= 1), which did not differ between age groups (P > 0.57).
Table 2.
Demographic and clinical characteristics [mean (SEM)] of patients in the clinical study and healthy subjects in the ex vivo study
| Clinical study | Ex vivo study | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | All (n= 72) | 18–39 years (n= 10) | 40–64 years (n= 33) | ≥65 years (n= 29) | P value* | All (n= 60) |
| Age (years) | 59 (2) | 30 (2) | 54 (1) | 75 (1) | <0.001 | 51 (2) |
| Weight (kg) | 86 (2) | 79 (8) | 93 (4) | 82 (3) | 0.06 | 71 (2) |
| LBW (kg) | 57 (2) | 54 (6) | 58 (2) | 58 (2) | 0.74 | 50 (2) |
| Plasma albumin concentration (g l−1) | 43 (0.3) | 45 (0.6) | 43 (0.4) | 43 (0.6) | 0.08 | 45 (0.3) |
| Estimated GFR (ml min−1 1.73 m−2) | 75 (2) | 90 (11) | 76 (2) | 68 (3) | 0.002 | 77 (1) |
| Sampling time (h) | 15 (0.4) | 14 (1) | 14 (0.7) | 16 (0.6) | 0.14 | N/A |
| CYP2C9 genotype (% *1/*1) | 71 | 70 | 74 | 68 | 0.87 | N/A |
| Gender (% male) | 58 | 50 | 48 | 72 | 0.14 | 50 |
| Ethnicity (% NZ European) | 90 | 90 | 91 | 89 | 0.99 | 90 |
anova between age groups in clinical study.
Genotyping for CYP2C9 showed the following distribution: *1/*1 (n= 50, 70%), *1/*2 (n= 14, 20%), *1/*3 (n= 5, 7%), *2/*3 (n= 2, 3%) and not available (n= 1). These allele frequencies are in agreement with frequencies reported in other Caucasian cohorts [20]. For statistical analysis of the influence of CYP2C9 genotype on (S)-warfarin clearance, patients with *1/*2 and *1/*3 were grouped together and the two patients with *2/*3 genotype were excluded.
The main focus of the study was to investigate changes in warfarin clearance with age. Figure 1 shows the variation in total and free CL of (R)- and (S)-warfarin with age. A gradual decline in CL with age is apparent, but there is a large variability, particularly for (S)-warfarin. The multiple regression models for total and free CL of (R)- and (S)-warfarin are shown in Table 3. The regression analysis was performed both on untransformed CL and log CL. This did not impact the conclusions drawn and for simplicity untransformed CL is presented in Table 3. As seen, after correcting for LBW, a decrease in CL with age was highly significant for both total and free (R)-warfarin (P < 0.001 in both cases). For (S)-warfarin, following correction for CYP2C9 genotype, a decrease was just significant for total CL (P= 0.045), whereas the signal was statistically stronger for free CL (P= 0.005). Sampling time (h post dose) also contributed to the models of (S)-warfarin CL. Age was associated with a decline in total CL of both (R)- and (S)-warfarin of 0.02 ml min−1 per year of age, which for a subject with a LBW of 57 kg, a CYP2C9*1/*1 genotype and a blood sample taken 15 h post dose, corresponds to a decrease of 0.5% per year for (R)-warfarin and 0.3% for (S)-warfarin. The corresponding decrease in free CL was 0.5% for (R)-warfarin and 0.4% for (S)-warfarin.
Figure 1.
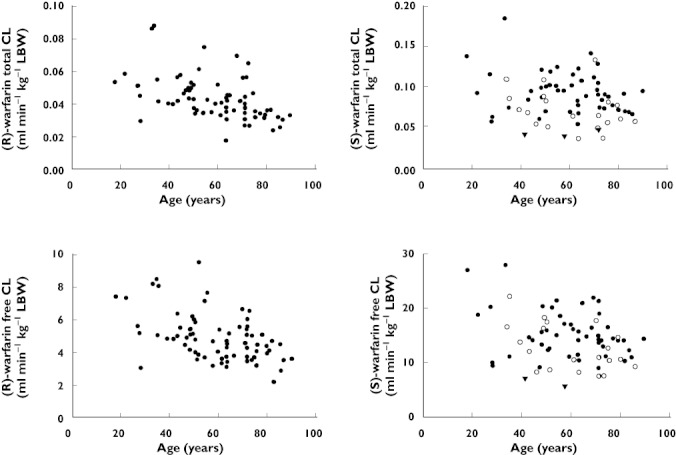
Total and free clearance (CL) per kg lean body weight (LBW) for (R)- and (S)-warfarin vs. age in 72 patients on long term warfarin therapy. For (S)-warfarin; CYP2C9 genotype *1/*1 (•),*1/*2 or *1/*3 (○) and *2/*3 (▾)
Table 3.
Multiple regression analysis of total and free clearance (CL) of (R)- and (S)-warfarin
| Predictor | b | SE (b) | P value | Adjusted r2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (R)-warfarin total CL (ml min−1) | |||||
| Constant | 1.404 | 0.436 | 0.002 | ||
| LBW (kg) | 0.037 | 0.006 | <0.001 | 0.33 | |
| Age (years) | −0.018 | 0.004 | <0.001 | 0.45 | (Δr2age= 0.13) |
| (R)-warfarin free CL (ml min−1) | |||||
| Constant | 158.7 | 48.1 | 0.002 | ||
| LBW (kg) | 3.939 | 0.633 | <0.001 | 0.33 | |
| Age (years) | −2.013 | 0.490 | <0.001 | 0.46 | (Δr2age= 0.13) |
| (S)-warfarin total CL (ml min−1) | |||||
| Constant | 2.411 | 1.106 | 0.033 | ||
| LBW (kg) | 0.063 | 0.013 | <0.001 | 0.26 | |
| CYP2C9 genotypea | −1.212 | 0.352 | 0.001 | 0.34 | |
| Sampling time (h) | 0.108 | 0.010 | 0.025 | 0.37 | |
| Age (years) | −0.020 | −0.196 | 0.045 | 0.40 | (Δr2age= 0.03) |
| (S)-warfarin free CL (ml min−1) | |||||
| Constant | 392.5 | 182.4 | 0.035 | ||
| LBW (kg) | 10.32 | 2.08 | <0.001 | 0.26 | |
| CYP2C9 genotypea | −162.0 | 58.0 | 0.007 | 0.31 | |
| Age (years) | −4.636 | 1.582 | 0.005 | 0.36 | (Δr2age= 0.05) |
| Sampling time (h) | 21.72 | 7.78 | 0.007 | 0.42 |
A value of 1 was assigned to *1/*1 and a value of 2 to *1/*2 or *1/*3.
LBW was the best descriptor for body size and successively superior to weight, weight0.75 and BMI in terms of explained variance of warfarin CL. Gender, ethnicity, albumin concentrations, eGFR or concomitant administration of potential enzyme inhibitors did not make significant contributions to any of the regression models. There were no statistically significant correlations between age and: weight, LBW, CYP2C9 genotype, sampling time, gender or ethnicity. When examined within age groups, likewise, there were no significant differences as shown in Table 2. A slight decline in albumin of 0.05 g l−1 per year was seen with age (r=−0.33, P= 0.006). In addition, eGFR declined with increasing age by 0.52 ml min−1 1.73 m−2 per year (r=−0.49, P < 0.001).
There was no significant correlation of protein binding (expressed as fu) with age for (R)- and (S)-warfarin (Figure 2). This remained when gender, LBW, albumin concentration and eGFR were included as covariates in the regression model. For the entire group of patients, the mean (SEM) fu was 0.92 (0.02) % for (R)-warfarin and 0.60 (0.01) % for (S)-warfarin corresponding to a protein binding of 99.1% for (R)-warfarin and 99.4% for (S)-warfarin.
Figure 2.
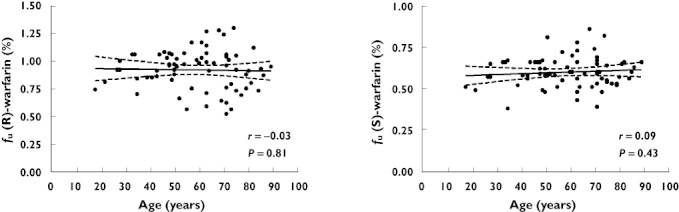
Mean and 95% CI from linear regression analysis of fu of (R)- and (S)-warfarin vs. age in steady-state plasma samples from 72 patients on long term warfarin therapy
Ex vivo study
The demographic and clinical characteristics of the 60 healthy subjects (age range 19–87 years) are shown in Table 2. The results obtained by spiking warfarin to plasma samples were similar to those obtained from the patient study in that there was no significant correlation between fu and age (Figure 3). In the healthy subjects, fu did correlate with albumin concentrations (r=−0.46, P < 0.001). In addition, free fatty acids (FFAs) were measured in this study and were found to correlate with fu (r=−0.76, P < 0.001). However, age was not a significant predictor of fu even after including these covariates in the regression model.
Figure 3.
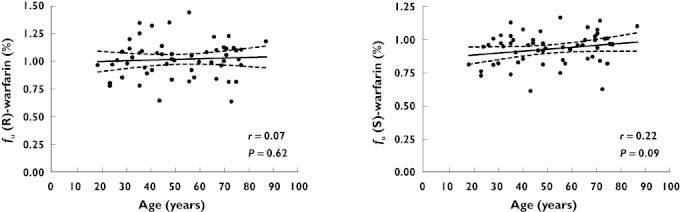
Mean and 95% CI from linear regression analysis of fu of (R)- and (S)-warfarin vs. age in spiked plasma samples from 60 healthy subjects
Discussion
In this study both free and total CL of (R)- and (S)-warfarin were found to be reduced with age. This is the first study to investigate directly the impact of age on free CL of warfarin in a substantial number of patients. The only other study by Routledge et al. from 1979 [4] inferred free CL by adjusting total concentrations of rac-warfarin for protein binding and no correlation with age was observed. This discrepancy might be due to the small number of patients (n= 14), or the fact that it was an indirect measure of free CL of rac-warfarin using the technology available at the time. For total CL, several studies have shown impaired CL with age, although not consistently as described in the introduction. However, the studies in which there was no statistically significant change with age [4, 11–13] only investigated rac-warfarin and did not take CYP2C9 genotypes into account. Since the start of our study three population pharmacokinetic models of (R)- and (S)-warfarin have been published, which also show that total CL decreases with age [21–23]. The decline in CL associated with age was 0.3–0.5% per year in our study. This is slightly less than a decline of 0.6–1% per year as shown in other studies [5, 8, 21–23].
The calculation of CL was based on a single steady-state plasma concentration from a sample taken 6–22 h post dose. For (R)-warfarin the blood sampling time did not influence the estimation of CL, but for (S)-warfarin, which has a shorter half-life, sampling time contributed to the regression model. Importantly, sampling time did not correlate with age or differ between age groups, and therefore did not affect the association of age and clearance. In other studies this potential issue has been avoided by having more restrictive intervals for sampling time. For (S)-warfarin CL, CYP2C9 genotype was also an important covariate as expected from previous studies.
Overall, warfarin CL was shown to decline with age and for (S)-warfarin more accurate information was gained by determining free CL. The hypothesis as put forward in the Butler & Begg paper [2] was that that hepatic clearance declines with age and the warfarin CL data presented here supports this hypothesis. It was also hypothesized that protein binding decreases with age, resulting in changes with age being more apparent for free than for total CL. However, in the data reported here, protein binding did not change with age, in either the clinical samples or the spiked samples from healthy subjects, despite a slight decrease in albumin concentrations with age. This could explain why no difference was seen in age-related changes of free and total CL of (R)-warfarin and only relatively minor improvement was seen by measuring free CL of (S)-warfarin. The other studies that have measured warfarin protein binding and age (all following spiking of warfarin to plasma samples) have either found no change [11, 12] or a reduction with age [14, 15].
In the ex vivo study free fatty acid (FFA) concentrations were found to correlate strongly with fu. FFA concentrations did not correlate with age, which is similar to that reported by others [24]. However, even after including FFA in the regression model, age was not a significant predictor of protein binding. In the clinical study FFA concentrations were not measured, but based on the finding in the ex vivo study, these are unlikely to impact on the contribution of age to protein binding.
In conclusion, these data support the hypothesis that the CL of (R)- and (S)-warfarin decreases with age. More accurate information was gained when measuring free CL for (S)-warfarin. Warfarin protein binding did not change significantly with age.
Acknowledgments
Financial support for this study is gratefully acknowledged from the Lotteries Grants Board and Health Research Council (ref. 08/322) of New Zealand. RLR is the recipient of a Sir Charles Hercus Health Research Fellowship from the Health Research Council of New Zealand. The clinical staff at the Christchurch Haemostasis Clinic is gratefully acknowledged for the assistance in recruitment of patients.
Competing Interests
There are no competing interests to declare.
REFERENCES
- 1.McLean AJ, Le Couteur DG. Aging biology and geriatric clinical pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 2004;56:163–84. doi: 10.1124/pr.56.2.4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Butler JM, Begg EJ. Free drug metabolic clearance in elderly people. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2008;47:297–321. doi: 10.2165/00003088-200847050-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Dollery C. Therapeutic Drugs. 2nd edn. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone; 1999. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Routledge PA, Chapman PH, Davies DM, Rawlins MD. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of warfarin at steady state. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1979;8:243–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1979.tb01009.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Mungall DR, Ludden TM, Marshall J, Hawkins DW, Talbert RL, Crawford MH. Population pharmacokinetics of racemic warfarin in adult patients. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1985;13:213–27. doi: 10.1007/BF01065653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Wynne H, Cope L, Kelly P, Whittingham T, Edwards C, Kamali F. The influence of age, liver size and enantiomer concentrations on warfarin requirements. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1995;40:203–7. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Loebstein R, Yonath H, Peleg D, Almog S, Rotenberg M, Lubetsky A, Roitelman J, Harats D, Halkin H, Ezra D. Interindividual variability in sensitivity to warfarin-Nature or nurture? Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2001;70:159–64. doi: 10.1067/mcp.2001.117444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kamali F, Khan TI, King BP, Frearson R, Kesteven P, Wood P, Daly AK, Wynne H. Contribution of age, body size, and CYP2C9 genotype to anticoagulant response to warfarin. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2004;75:204–12. doi: 10.1016/j.clpt.2003.10.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sconce EA, Khan TI, Wynne HA, Avery P, Monkhouse L, King BP, Wood P, Kesteven P, Daly AK, Kamali F. The impact of CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genetic polymorphism and patient characteristics upon warfarin dose requirements: proposal for a new dosing regimen. Blood. 2005;106:2329–33. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-03-1108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Herman D, Locatelli I, Grabnar I, Peternel P, Stegnar M, Mrhar A, Breskvar K, Dolzan V. Influence of CYP2C9 polymorphisms, demographic factors and concomitant drug therapy on warfarin metabolism and maintenance dose. Pharmacogenomics J. 2005;5:193–202. doi: 10.1038/sj.tpj.6500308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Shepherd AMM, Hewick DS, Moreland TA, Stevenson IH. Age as a determinant of sensitivity to warfarin. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1977;4:315–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1977.tb00719.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chan E, McLachlan AJ, Pegg M, MacKay AD, Cole RB, Rowland M. Disposition of warfarin enantiomers and metabolites in patients during multiple dosing with rac-warfarin. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1994;37:563–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1994.tb04305.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hotraphinyo K, Triggs EJ, Maybloom B, Maclaine-Cross A. Warfarin sodium: steady-state plasma levels and patient age. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1978;5:143–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1978.tb00664.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hayes MJ, Langman MJ, Short AH. Changes in drug metabolism with increasing age: 1. warfarin binding and plasma proteins. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1975;2:69–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1975.tb00474.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Abel J, Roth E, Sellers E, Ray A. Drug-plasma protein binding in Kutchin Athapaskan indians. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1982;32:436–41. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1982.186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chin PKL, Jensen BP, Larsen HS, Begg EJ. Adult age and ex vivo protein binding of lorazepam, oxazepam and temazepam in healthy subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2011;72:985–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2011.04036.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Jensen B, Chin P, Begg E. Quantification of total and free concentrations of R- and S-warfarin in human plasma by ultrafiltration and LC-MS/MS. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2011;401:2187–93. doi: 10.1007/s00216-011-5303-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Janmahasatian S, Duffull SB, Ash S, Ward LC, Byrne NM, Green B. Quantification of lean bodyweight. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2005;44:1051–65. doi: 10.2165/00003088-200544100-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Levey AS, Coresh J, Greene T, Stevens LA, Zhang Y, Hendriksen S, Kusek JW, Van Lente F for the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology, Collaboration. Using standardized serum creatinine values in the modification of diet in renal disease study equation for estimating glomerular filtration rate. Ann Inter Med. 2006;145:247–54. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-145-4-200608150-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Scott SA, Khasawneh R, Peter I, Kornreich R, Desnick RJ. Combined CYP2C9, VKORC1 and CYP4F2 frequencies among racial and ethnic groups. Pharmacogenomics. 2010;11:781–91. doi: 10.2217/pgs.10.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hamberg AK, Dahl ML, Barban M, Scordo MG, Wadelius M, Pengo V, Padrini R, Jonsson EN. A PK-PD model for predicting the impact of age, CYP2C9, and VKORC1 genotype on individualization of warfarin therapy. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2007;81:529–38. doi: 10.1038/sj.clpt.6100084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hamberg AK, Wadelius M, Lindh JD, Dahl ML, Padrini R, Deloukas P, Rane A, Jonsson EN. A pharmacometric model describing the relationship between warfarin dose and INR response with respect to variations in CYP2C9, VKORC1, and age. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2010;87:727–34. doi: 10.1038/clpt.2010.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lane S, Al-Zubiedi S, Hatch E, Matthews I, Jorgensen AL, Deloukas P, Daly AK, Park BK, Aarons L, Ogungbenro K, Kamali F, Hughes D, Pirmohamed M. The population pharmacokinetics of R- and S-warfarin: effect of genetic and clinical factors. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2011;73:66–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2011.04051.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Richieri GV, Kleinfeld AM. Unbound free fatty acid levels in human serum. J Lipid Res. 1995;36:229–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


