Abstract
Production of various forms of nonintegrated viral DNA was measured in cultured mouse cells carrying different Fv-1 alleles early after infection with N-tropic or B-tropic retroviruses. Quantitative analyses were performed by agarose gel electrophoresis, transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper, and molecular hybridization. In permissive infection of Fv-1n cells (NIH Swiss and DBA mouse strains) with N-tropic virus and of Fv-1b cells (BALB/c and C57BL/6 strains) with B-tropic virus, form III (double-stranded linear) DNA first appeared at 3-4 hr and reached a maximum at 8-10 hr; two form I (closed circle) DNAs appeared at 7-8 hr and reached a maximum at or beyond 12 hr. In the two Fv-1b cells infected with N-tropic virus and in DBA (Fv-1n) cells infected with B-tropic virus, formation of the two form I DNAs was quantitatively restricted but formation of form III DNA was unaltered. In Fv-1n NIH Swiss mouse embryo cells infected with B-tropic virus, the level of form III DNA was markedly depressed and hence the two form I DNAs were not detectable. In C57BL/6 cells as well as in DBA/2 cells 12 hr after infection, the quantity of form III DNA varied directly with the amount of restricted virus, whereas the quantity of form I DNA varied according to the square of the amount of restricted virus. The significance of these results for understanding the molecular basis of retrovirus replication and its restriction by the Fv-1 gene is discussed.
Full text
PDF


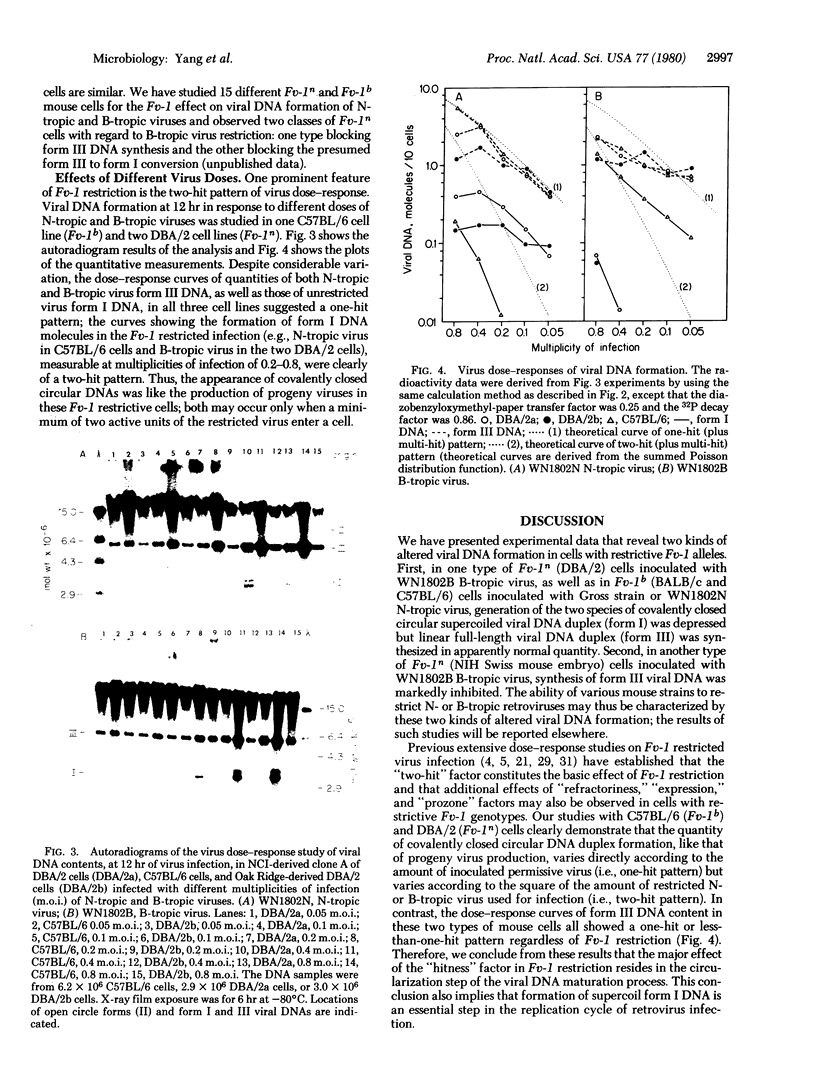

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Stark G. R. Method for detection of specific RNAs in agarose gels by transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and hybridization with DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5350–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjers B. M., Bassin R. H., Rein A., Gerwin B. I., Duran-Troise G. Mechanism of restriction of murine leukemia viruses varies between different strains of Fv-1n mice. Int J Cancer. 1979 Nov 15;24(5):600–607. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910240513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Declève A., Niwa O., Gelmann E., Kaplan H. S. Replication kinetics of N- and B-tropic murine leukemia viruses on permissive and nonpermissive cells in vitro. Virology. 1975 Jun;65(2):320–332. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90038-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guntaka R. V., Richards O. C., Shank P. R., Kung H. J., Davidson N. Covalently closed circular DNA of avian sarcoma virus: purification from nuclei of infected quail tumor cells and measurement by electron microscopy and gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1976 Sep 15;106(2):337–357. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90090-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Huebner R. J. Host-range restrictions of murine leukemia viruses in mouse embryo cell cultures. J Virol. 1970 Feb;5(2):221–225. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.2.221-225.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins N., Schindler J., Hynes R. Six-NB-tropic murine leukemia viruses derived from a B-tropic virus of BALB/c have altered p30. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):309–318. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.309-318.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu I. C., Yang W. K. DNA transfection of ecotropic murine leukemia viruses in mouse cell cultures. Cancer Res. 1977 Jun;37(6):1709–1714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu I. C., Yang W. K., Tennant R. W., Brown A. Transfection of Fv-1 permissive and restrictive mouse cells with integrated DNA of murine leukemia viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1451–1455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Besmer P., Chu L., Baltimore D. Growth of pseudotypes of vesicular stomatitis virus with N-tropic murine leukemia virus coats in cells resistant to N-tropic viruses. J Virol. 1973 Sep;12(3):659–662. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.3.659-662.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolicoeur P., Baltimore D. Effect of Fv-1 gene product on proviral DNA formation and integration in cells infected with murine leukemia viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2236–2240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolicoeur P., Baltimore D. Effect of Fv-1 gene product on synthesis of N-tropic and B-tropic murine leukemia viral RNA. Cell. 1976 Jan;7(1):33–39. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90252-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolicoeur P., Rassart E. Effect of Fv-1 gene product on synthesis of linear and supercoiled viral DNA in cells infected with murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):183–195. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.183-195.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krontiris T. G., Soeiro R., Fields B. N. Host restriction of Friend leukemia virus. Role of the viral outer coat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Sep;70(9):2549–2553. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.9.2549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilly F. Fv-2: identification and location of a second gene governing the spleen focus response to Friend leukemia virus in mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1970 Jul;45(1):163–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonell M. W., Simon M. N., Studier F. W. Analysis of restriction fragments of T7 DNA and determination of molecular weights by electrophoresis in neutral and alkaline gels. J Mol Biol. 1977 Feb 15;110(1):119–146. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80102-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niwa O., Decléve A., Kaplan H. S. Conversion of restrictive mouse cells to permissiveness during sequential and mixed double infection by murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1976 Oct 1;74(1):140–153. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90136-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odaka T. Inheritance of susceptibility to Friend mouse leukemia virus. V. Introduction of a gene responsible for susceptibility in the genetic complement of resistant mice. J Virol. 1969 Jun;3(6):543–548. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.6.543-548.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus T., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. A major genetic locus affecting resistance to infection with murine leukemia viruses. I. Tissue culture studies of naturally occurring viruses. J Exp Med. 1971 Jun 1;133(6):1219–1233. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.6.1219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus T., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. A major genetic locus affecting resistance to infection with murine leukemia viruses. IV. Dose-response relationships in Fv-1-sensitive and resistant cell cultures. Virology. 1975 Jun;65(2):333–342. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90039-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray U., Soeiro R., Fields B. N. Host restriction of Friend Leukemia virus coat protein synthesis. J Virol. 1976 Apr;18(1):370–373. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.1.370-373.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rein A., Kashmiri S. V., Bassin R. H., Gerwin B. L., Duran-Troise G. Phenotypic mixing between N- and B-tropic murine leukemia viruses: infectious particles with dual sensitivity to Fv-1 restriction. Cell. 1976 Mar;7(3):373–379. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90166-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Humphrey J. B., Lilly F. A major genetic locus affecting resistance to infection with murine leukemia viruses. 3. Assignment of the Fv-1 locus to linkage group 8 of the mouse. J Exp Med. 1973 Mar 1;137(3):850–853. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.3.850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shank P. R., Varmus H. E. Virus-specific DNA in the cytoplasm of avian sarcoma virus-infected cells is a precursor to covalently closed circular viral DNA in the nucleus. J Virol. 1978 Jan;25(1):104–104. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.1.104-104.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sveda M. M., Soeiro R. Host restriction of Friend leukemia virus: synthesis and integration of the provirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2356–2360. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanstrom R., Shank P. R. X-Ray Intensifying Screens Greatly Enhance the Detection by Autoradiography of the Radioactive Isotopes 32P and 125I. Anal Biochem. 1978 May;86(1):184–192. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90333-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. M., Illmensee R., Summers J. Efficeint transcription of RNA into DNA by avian sarcoma virus polymerase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 6;442(3):324–330. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tennant R. W., Otten J. A., Brown A., Yang W. K., Kennel S. J. Characterization of Fv-1 host range strains of murine retroviruses by titration and p30 protein characteristics. Virology. 1979 Dec;99(2):349–357. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tennant R. W., Schluter B., Myer F. E., Otten J. A., Yang W. K., Brown A. Genetic evidence for a product of the Fv-1 locus that transfers resistance to mouse leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1976 Dec;20(3):589–596. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.3.589-596.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tennant R. W., Schluter B., Yang W., Brown A. Reciprocal inhibition of mouse leukemia virus infection by Fv-1 allele cell extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4241–4245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A. Structure of the intermediates leading to the integrated provirus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 21;473(1):39–55. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(77)90006-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang W. K., Tennant R. W., Rascati R. J., Otten J. A., Schluter B., Kiggans J. O., Jr, Myer F. E., Brown A. Transfer of Fv-1 locus-specific resistance to murine N-tropic and B-tropic retroviruses by cytoplasmic RNA. J Virol. 1978 Aug;27(2):288–299. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.2.288-299.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]