Abstract
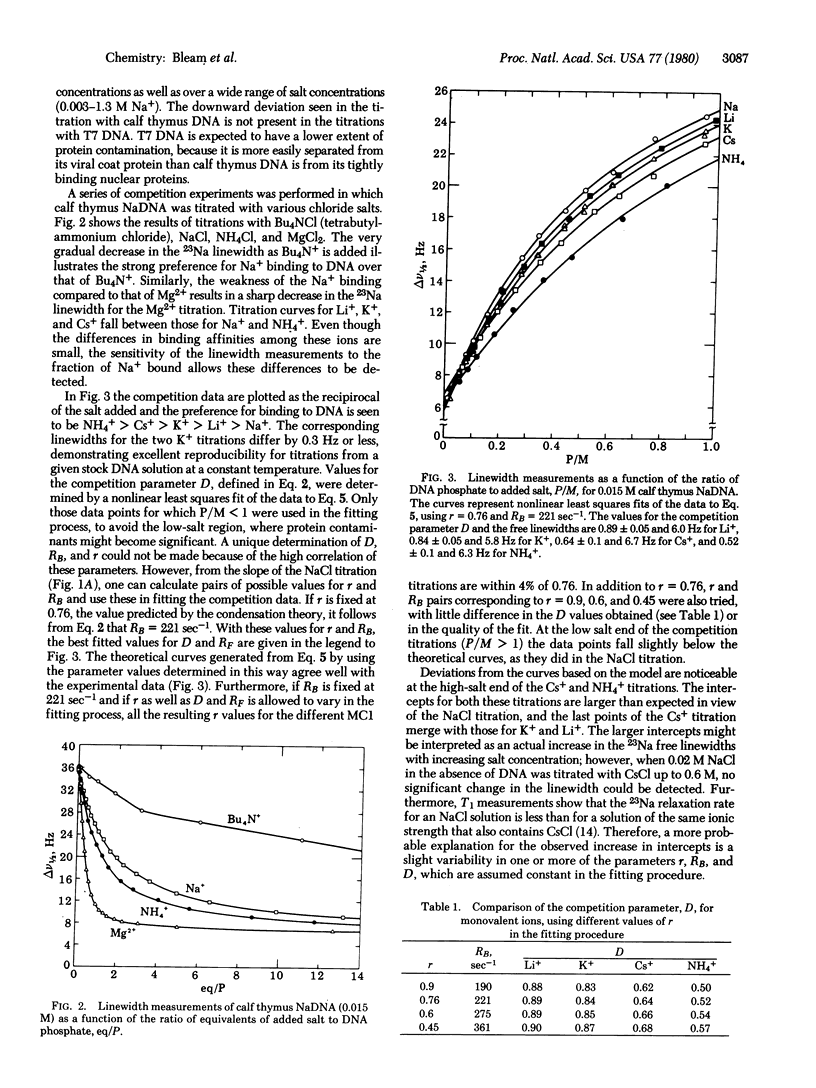
The competition between sodium and various other monovalent cations that bind to helical DNA in aqueous solution has been studied by 23Na NMR. Variations in the sodium linewidth with the concentration of the other ion have been analyzed with an equation that describes the competitive binding in terms of two parameters: r, the total extent of counterion binding, and D, a measure of the binding affinity of a cation relative to sodium. The concentration dependence of these parameters was found to be minimal. In the absence of a competing cation the constancy of r has been demonstrated over a range of DNA phosphate concentrations (0.0025-0.015 M) and NaCl concentrations (0.003-1.3 M). For the cations investigated the range in D values is small (0.5-0.9), and the relative binding affinities follow the order: NH4+ > Cs+ > K+ > Li+ > Na+.
Keywords: 23Na NMR, alkali metal ions, condensation theory
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. F., Record M. T., Jr, Hart P. A. Sodium-23 NMR studies of cation-DNA interactions. Biophys Chem. 1978 Jan;7(4):301–316. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(78)85007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P., Bauer W. Supercoiling in closed circular DNA: dependence upon ion type and concentration. Biochemistry. 1978 Feb 21;17(4):594–601. doi: 10.1021/bi00597a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan A., Kilkuskie R., Hanlon S. Correlations between the duplex winding angle and the circular dichroism spectrum of calf thymus DNA. Biochemistry. 1979 Jan 9;18(1):84–91. doi: 10.1021/bi00568a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustavsson H., Siegel G., Lindman B., Fransson L. A. 23Na+ NMR in solutions of mucopolysaccharides. FEBS Lett. 1978 Feb 1;86(1):127–130. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80113-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanlon S., Brudno S., Wu T. T., Wolf B. Structural transitions of deoxyribonucleic acid in aqueous electrolyte solutions. I. Reference spectra of conformational limits. Biochemistry. 1975 Apr 22;14(8):1648–1660. doi: 10.1021/bi00679a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov V. I., Minchenkova L. E., Schyolkina A. K., Poletayev A. I. Different conformations of double-stranded nucleic acid in solution as revealed by circular dichroism. Biopolymers. 1973;12(1):89–110. doi: 10.1002/bip.1973.360120109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James T. L., Noggle J. H. 23Na nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation studies of sodium ion interaction with soluble RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Mar;62(3):644–649. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.3.644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kielman H. S., van der Hoeven J. M., Leyte J. C. Nuclear magnetic relaxation of 23Na and 7Li ions in polyphosphate solutions. Biophys Chem. 1976 Jan;4(1):103–111. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(76)80011-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurland R., Newton C., Nir S., Papahadjopoulos D. Specificity of Na+ binding to phosphatidylserine vesicles from a 23Na NMR relaxation rate study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Feb 20;551(1):137–147. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning G. S. Limiting laws and counterion condensation in polyelectrolyte solutions. IV. The approach to the limit and the extraordinary stability of the charge fraction. Biophys Chem. 1977 Sep;7(2):95–102. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(77)80002-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning G. S. The molecular theory of polyelectrolyte solutions with applications to the electrostatic properties of polynucleotides. Q Rev Biophys. 1978 May;11(2):179–246. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Record M. T., Jr, Anderson C. F., Lohman T. M. Thermodynamic analysis of ion effects on the binding and conformational equilibria of proteins and nucleic acids: the roles of ion association or release, screening, and ion effects on water activity. Q Rev Biophys. 1978 May;11(2):103–178. doi: 10.1017/s003358350000202x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuben J., Shporer M., Gabbay E. J. The Alkali Ion-DNA Interaction as Reflected in the Nuclear Relaxation Rates of Na and Rb. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):245–247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellman J. A. Electrical double layer, zeta potential, and electrophoretic charge of double-stranded DNA. Biopolymers. 1977 Jul;16(7):1415–1434. doi: 10.1002/bip.1977.360160704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spegt P., Tondre C., Weill G., Zana R. NMR and density study of Co2+ site binding by polyelectrolytes. Biophys Chem. 1973 Dec;1(2):55–61. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(73)80001-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spegt P., Weill G. Magnetic resonance distinction between site bound and atmospherically bound paramagnetic counterions in polyelectrolyte solutions. Biophys Chem. 1976 Mar;4(2):143–149. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(76)85004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss U. P., Helfgott C., Pink H. Interactions of polyelectrolytes with simple electrolytes. II. Donnan equilibria obtained with DNA in solutions of 1-1 electrolytes. J Phys Chem. 1967 Jul;71(8):2550–2556. doi: 10.1021/j100867a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf B., Hanlon S. Structural transitions of deoxyribonucleic acid in aqueous electrolyte solutions. II. The role of hydration. Biochemistry. 1975 Apr 22;14(8):1661–1670. doi: 10.1021/bi00679a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



