Abstract
Background
In spite of its high clinical relevance, the relationship between disc degeneration and low back pain is still not well understood. Recent studies have shown that genome-wide gene expression studies utilizing ontology searches provide an efficient and valuable methodology for identification of clinically relevant genes. Here we use this approach in analysis of pain-, nerve-, and neurotrophin-related gene expression patterns in specimens of human disc tissue. Control, non-herniated clinical, and herniated clinical specimens of human annulus tissue were studied following Institutional Review Board approval.
Results
Analyses were performed on more generated (Thompson grade IV and V) discs vs. less degenerated discs (grades I-III), on surgically operated discs vs. control discs, and on herniated vs. control discs. Analyses of more degenerated vs. less degenerated discs identified significant upregulation of well-recognized pain-related genes (bradykinin receptor B1, calcitonin gene-related peptide and catechol-0-methyltransferase). Nerve growth factor was significantly upregulated in surgical vs. control and in herniated vs. control discs. All three analyses also found significant changes in numerous proinflammatory cytokine- and chemokine-related genes. Nerve, neurotrophin and pain-ontology searches identified many matrix, signaling and functional genes which have known importance in the disc. Immunohistochemistry was utilized to confirm the presence of calcitonin gene-related peptide, catechol-0-methyltransferase and bradykinin receptor B1 at the protein level in the human annulus.
Conclusions
Findings point to the utility of microarray analyses in identification of pain-, neurotrophin and nerve-related genes in the disc, and point to the importance of future work exploring functional interactions between nerve and disc cells in vitro and in vivo. Nerve, pain and neurotrophin ontology searches identified numerous changes in proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines which also have significant relevance to disc biology. Since the degenerating human disc is primarily an avascular tissue site into which disc cells have contributed high levels of proinflammatory cytokines, these substances are not cleared from the tissue and remain there over time. We hypothesize that as nerves grow into the human annulus, they encounter a proinflammatory cytokine-rich milieu which may sensitize nociceptors and exacerbate pain production.
Keywords: Low back pain, Neurotrophins, Nerves, Microarray analysis
Background
Low back pain brings the patient to the spine surgeon, but the relationship between disc degeneration and pain production in the disc is still poorly understood. Patients with chronic low back pain do not have the leg pain which results when fragments of herniated disc push on nerves; instead, these patients experience pain that is thought to arise from the disc itself. Although some back pain may be related to lumbosacral anatomy/function spinal anatomy [1], age, and other factors (see Fairbank et al. for a recent systematic review of low back pain classification [2]), discogenic low back pain is not well understood [3-8]. As with all pain, the pain-initiating event results from complex cellular, molecular and functional events at the nociceptors (naked nerve endings) [9,10]. Discogenic pain is believed to result from disc changes (possibly from outer annulus pressure on nerve endings, disc cell dysfunction, products of matrix degradation [11], or unknown events) which influence the nervous system by stimulation of annulus nociceptors.
Recent studies focused over the last decade on molecular events and gene expression patterns related to pain [12], and studies have revealed that genome-wide gene expression studies provide a powerful methodology for identification of clinically relevant genes [13]. The objective of the present study was to perform a genome-wide analysis of annulus tissue from patients with discogenic back pain, compared to disc tissue from control subjects and herniated disc patients, in an analysis of the expression of pain, nerve and neurotrophin-related genes. Ontology searches for these specific topics were utilized in order to avoid searching large gene array data bases gene by gene, and because this technique provides a controlled vocabulary of search terms for gene characteristics [14].
As cell-based therapies for disc degeneration progress, information on pain-, nerve- and neurotrophin-gene expression in disc tissue becomes increasingly important. Findings presented here have potential applications in future treatment modalities, such as perispinal administration of TNF-α inhibitors (such as etanercept/enbrel [15]) or use of specific small molecular antagonists to neurotrophins. New information presented here on the relationship between proinflammatory mediators, nerves and neurotrophins has the potential to contribute to future important antagonist profiles with application to discogenic back pain.
Results
Demographic features of the patient population are summarized in Table 1 which presents spinal site, grade, subject age, and whether surgical specimens were derived from herniated or non-herniated tissue. In the present work, gene expression analyses included three Thompson grade II and five grade III control disc specimens (obtained from Cooperative Human Tissue Network). Surgical specimens were analyzed from three grade II discs (two specimens of which were from herniated discs), four grade III discs (from herniated discs), five grade IV specimens (two of which were from herniated discs), and three grade V specimens (two of which were from herniated discs).
Table 1.
Demographic data on disc tissues*
| Subject number | Site* | Thompson grade | Age (years)/gender | Herniated? | Other information |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
Lumbar |
II |
34/F |
No |
Control |
| 2 |
L3-L4 |
II |
30/M |
No |
Control |
| 3 |
L4-L5 |
II |
54/F |
No |
Surgical specimen |
| 4 |
Lumbar |
II |
34/F |
No |
Control |
| 5 |
L5-S1 |
II |
21/M |
Yes |
Surgical specimen; immuno ** |
| 6 |
L4-L5 |
II |
40/F |
Yes |
Surgical specimen |
| 7 |
L4-L5 |
III |
36/F |
Yes |
Surgical specimen |
| 8 |
C6-C7 |
III |
45/F |
Yes |
Surgical specimen |
| 9 |
L3-L4 |
III |
52/F |
No |
Control |
| 10 |
L3-L4 |
III |
52/F |
No |
Control; immuno |
| 11 |
L3-L4 |
III |
52/F |
No |
Control |
| 12 |
L3-L4 |
III |
52/F |
No |
Control |
| 13 |
L2-L3 |
III |
33/F |
No |
Control |
| 14 |
L5-S1 |
III |
37/M |
Yes |
Surgical specimen; immuno |
| 15 |
L4-L5 |
III |
43/M |
Yes |
Surgical specimen; immuno |
| 16 |
L5-S1 |
IV |
63 F |
No |
Surgical specimen |
| 17 |
L2-L3 |
IV |
65/F |
No |
Surgical specimen |
| 18 |
C5-C6 |
IV |
59/M |
Yes |
Surgical specimen |
| 19 |
L5-S1 |
IV |
45/M |
Yes |
Surgical specimen; immuno |
| 20 |
L5-S1 |
IV |
43/M |
No |
Surgical specimen |
| 21 |
L5-S1 |
V |
72/F |
Yes |
Surgical specimen; immuno |
| 22 |
L4-5 |
V |
41/M |
No |
Surgical specimen; immuno |
| 23 | C6-7 | V | 57/F | Yes | Surgical specimen |
* Note that multiples specimens may have been derived from some subjects. L, lumbar; C, cervical; M, male; F, female; Control discs are normal discs obtained from the Cooperative Human Tissue Network.
** Indicates that specimens were utilized for selected immunohistochemical studies.
The ontology gene expression analysis for pain and nerve categories included a variety of biological processes, molecular functions, and cellular components. To assist the reader in understanding these, Table 2 outlines the categories included in our searches.
Table 2.
Outline of ontology search strategies
|
Pain Ontologies: | |
| A. Biological Process: | |
| 1. Sensory perception | |
| a. Sensory perception of pain: | |
| I. Regulation of sensory perception of pain | |
| II. Detection of chemical stimulus involved | |
| III. Detection of temperature stimulus involved | |
| IV. Detection of mechanical stimulus involved | |
| 2. Ion transport | |
| 3. Inflammatory response | |
| 4. Behavior | |
| 5. Response to pain: | |
| a. Behavioral response to pain | |
| 6. G-protein coupled receptor (protein) signaling pathway | |
| 7. Transmission of nerve impulse | |
| 8. Fatty acid catabolic process | |
| B. Molecular Function: | |
| 1. 1. Carboxyl- or carbamoyl-transferase activity | |
| 2. Opioid peptide activity | |
| 3. Signal transducer activity | |
| a. G-protein coupled receptor activity | |
| b. Galanin receptor activity | |
| c. Bradykinin receptor activity | |
| d. Opioid receptor activity | |
| e. Adrenergic receptor activity | |
| 4. Voltage-gated channel activity | |
| 5. G-protein coupled receptor binding | |
| C. Cellular component | |
| 1. Plasma lipoprotein particle | |
| 2. Axon | |
|
Nerve Ontologies: | |
| A. Biological Process: | |
| 1. Neuron death | |
| a. Neuron apoptosis | |
| i. Positive regulation of neuron apoptosis | |
| ii. Negative regulation of neuron apoptosis | |
| a. Neurotrophin production | |
| iii. Neuroprotection | |
| 2. Neuropeptide signaling pathway |
|
| 3. Transmission of nerve impulse |
|
| 4. Nervous system development: |
|
| a. Nerve development |
|
| b. Neurogenesis |
|
| i. Regulation of neurogenesis |
|
| a. Positive regulation of neurogenesis |
|
| b. Negative regulation of neurogenesis |
|
| ii. Neuron differentiation |
|
| a. Neuron projection development |
|
| i. Axonogenesis regulation: |
|
| a. Positive regulation of axonogenesis |
|
| b. Negative regulation of axonogenesis |
|
| iii. Neuroblast differentiation |
|
| iv. Neuroblast proliferation |
|
| v. Neuron migration |
|
| B. Molecular function: |
|
| 1. Neurotrophin binding: |
|
| a. Nerve growth factor binding |
|
| 2. Neurotrophin receptor activity |
|
| 3. Neurotransmitter receptor activity |
|
| a. Substance P receptor activity |
|
| 4. Calcitonin receptor binding |
|
| 5. Vascular endothelial growth factor (-activated) receptor activity |
|
| 6. Protein kinase activity |
|
| 7. Neuropeptide hormone activity |
|
| 8. Neuropeptide binding |
|
| 9. Ciliary neurotrophic factor receptor binding |
|
| 10. Neurotrophin receptor binding: |
|
| a. Nerve growth factor receptor binding |
|
| C. Cellular component: |
|
| 1. Neuron projection: |
|
| a. Axon |
|
| b. Dendrite |
|
| 2. Endoplasmic reticulum lumen |
|
| 3. Nuclear outer membrane |
In each of our summary tables on gene expression findings (Tables 3, 4 and 5), genes are listed which have relevance to nerves, pain and neurotrophins (listed in section A of Tables 3, 4 and 5), genes with relevance to proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines (listed in section B of Tables 3, 4 and 5) and genes with specificity not only to nerve, pain and neurotrophins but also to the disc itself (listed in section C of the tables).
Table 3.
Significant differences in pain-, neurotrophin-, nerve-, and disc-related genes in more degenerated discs (Grades iv and v) compared to less degenerated discs (Grades i – iii)
| Gene name | Gene identifier | Fold change | Direction | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
A. Pain-, Neurotrophin- and Nerve-related Genes | ||||
| Adrenergic, beta, receptor kinase 2 |
AI478542 |
1.16 |
Up |
0.045 |
| Ataxin 10 |
AF119662 |
2.62 |
Up |
0.008 |
| Bradykinin receptor B1 |
NM_000710 |
1.09 |
Up |
0.023 |
| Calcitonin gene related peptide |
AI478743 |
1.51 |
Up |
0.035 |
| Catechol-O-methyltransferase |
NM_001670 |
1.17 |
Up |
0.020 |
| Cholinergic receptor, muscarinic 1 |
AI500293 |
1.60 |
Down |
0.042 |
| Clusterin |
M25915 |
12.76 |
Up |
0.010 |
| EGF, latrophilin and seven transmembrane domain containing 1 |
NM_022159 |
1.74 |
Up |
0.040 |
| Endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 2 |
BE889628 |
1.28 |
Up |
0.036 |
| Endoplasmic reticulum protein 44 |
BC005374 |
2.08 |
Up |
0.043 |
| GABA binding protein 2 |
BC002557 |
4.54 |
Down |
0.027 |
| GABA(A) receptor-associated protein |
NM_007278 |
3.78 |
Up |
0.049 |
| Gap junction protein, alpha 1, 43 kDa |
NM_000165 |
4.91 |
Up |
0.017 |
| Glutathione peroxidase 1 |
NM_000581 |
3.42 |
Up |
0.036 |
| Glutamate receptor, metabotropic 1 |
U31216 |
1.06 |
Up |
0.0082 |
| Guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), gamma 10 |
NM_004125 |
2.97 |
Up |
0.049 |
| Guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein) alpha inhibiting activity polypeptide 3 |
J03198 |
3.22 |
Up |
0.021 |
| Guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein) beta polypeptide 1 |
NM_002074 |
4.04 |
Up |
0.015 |
| Heat shock protein 90 kDa alpha (cytosolic), blass B member 1 |
AF275719 |
2.96 |
Up |
0.038 |
| Hydroxysteroid (17-beta) dehydrogenase 4 |
NM_000414 |
1.88 |
Up |
0.049 |
| Kv channel interacting protein 2 |
AF367019 |
1.52 |
Up |
0.027 |
| Neurogenin 2 |
AF022859 |
1.08 |
up |
0.045 |
| Neuron navigator 1 |
N57538 |
2.42 |
Up |
0.009 |
| Neuron navigator 2 |
AA011020 |
1.11 |
Up |
0.043 |
| Neuropilin 2 |
AA295257 |
1.87 |
Up |
0.037 |
| Neuroplastin |
NM_017455 |
2.78 |
Up |
0.048 |
| Opioid growth factor receptor |
AF172449 |
1.31 |
Up |
0.008 |
| Palmitoyl-protein thioesterase 1 |
NM_000310 |
3.04 |
Up |
0.019 |
| PDZ and LIM domain 5 |
AV715767 |
5.1 |
Up |
0.006 |
| Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta |
NM_006238 |
3.31 |
Down |
0.031 |
| Phytanoyl-CoA 2-hydroxylase |
NM_006214 |
2.17 |
Up |
0.049 |
| Potassium channel tetramerisation domain containing 10 |
AS073741 |
2.69 |
Up |
0.036 |
| Potassium channel tetramerisation domain containing 15 |
W73820 |
1.33 |
Up |
0.013 |
| Potassium voltage-gated channel, delayed-rectifier, subfamily S, member 3 |
NM_002252 |
1.66 |
Up |
0.031 |
| Presenilin 1 |
NM_007318 |
1.61 |
Up |
0.024 |
| Regulator of G-protein signaling 5 |
AF159570 |
2.31 |
Up |
0.047 |
| Reticulon 4 (Neurite growth inhibitor) |
AF20999 |
4.61 |
Up |
0.001 |
| Solute carrier family 38, member 1 |
NM_030674 |
2.13 |
Up |
0.039 |
| Solute carrier family 7 (catonic amino acid transporter, y + system), member 1 |
AA148507 |
1.44 |
Up |
0.017 |
| Somatostatin receptor 4 |
NM_001052 |
1.09 |
Down |
0.033 |
| S100 calcium binding protein A4 |
NM_002961 |
7.44 |
Up |
0.010 |
| Thioredoxin domain containing 12 (endoplasmic reticulum) |
AF131758 |
2/42 |
Up |
0.009 |
| Thy-1 cell surface antigen |
AL161958 |
3.48 |
Up |
0.006 |
|
B. Proinflammatory cytokine and chemokine genes: | ||||
| Chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 7 |
AI817041 |
3.32 |
Up |
0.043 |
| Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 12 (stromal cell-derived factor 1) |
NM_000609 |
1.90 |
Up |
0.024 |
| FGF receptor 2 |
T83672 |
1,12 |
Up |
0.020 |
| IL-17A |
NM_002190 |
1.05 |
Up |
0.048 |
| Interferon induced transmembrane protein 1 (9–27) |
NM_003641 |
2.72 |
Up |
0.026 |
| PDGF C |
NM_016205 |
3.07 |
Up |
0.041 |
| PDGF alpha polypeptide |
NM_006206 |
5.73 |
Up |
0.021 |
| PDGF receptor, beta polypeptide |
NM_003609 |
2.10 |
Up |
0.033 |
| PDGF receptor-like |
NM_006207 |
1.82 |
Up |
0.037 |
| TGF beta |
NM_000358 |
6.68 |
Up |
0.035 |
| Latent TGF beta binding protein 1 |
NM_000627 |
3.29 |
Up |
0.016 |
| TNF receptor-associated factor 5 |
NM_004619 |
1.34 |
Up |
0.014 |
| VEGF B |
NM_003377 |
1.09 |
Up |
0.037 |
|
C. Genes with special disc relevance: | ||||
| ADAM metallopeptidase domain 17 |
NM_003183 |
1.56 |
Up |
0.001 |
| Apoptosis-inducing factor, mitochondrion associated, 1 |
NM_004208 |
1.42 |
Up |
0.019 |
| BMP receptor, type II (serine/threonine kinase) |
AI457436 |
1.51 |
Up |
0.027 |
| Calcitonin receptor-like |
AI1478743 |
1.51 |
Up |
0.035 |
| Caspase 2, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase |
AU153405 |
1.63 |
Up |
0.028 |
| Caspase 6, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase |
BC000305 |
1.63 |
Up |
0.048 |
| Collagen, type I, alpha 1 |
K01228 |
2.69 |
Up |
0.046 |
| Collagen, type I, alpha 2 |
NM_000089 |
13.27 |
Up |
0.007 |
| Collagen type III, alpha 1 |
AU144167 |
10.3 |
Up |
0.036 |
| Collagen type IV, alpha 2 |
X05610 |
2.02 |
Up |
0.021 |
| Collagen type V, alpha 1 |
AI9833428 |
1.5 |
Up |
0.039 |
| Collagen type VI, alpha 3 |
NM_004369 |
5.85 |
Up |
0.036 |
| Connective tissue growth factor |
M92934 |
6.47 |
Up |
0.009 |
| EGF-containing fibulin-like extracellular matrix protein 1 |
NM_004105 |
1.49 |
Up |
0.005 |
| Fibronectin 1 |
AK026737 |
16.82 |
Up |
0.017 |
| Fibronectin leucine rich transmembrane protein 2 |
NM_013231 |
2.78 |
Up |
0.023 |
| Hypoxia inducible factor 1, alpha subunit |
NM_001530 |
3.61 |
Up |
0.037 |
| Janus kinase 2 |
AF001362 |
1.3 |
Up |
0.002 |
| Laminen, alpha 5 |
BC003355 |
1.39 |
Up |
0.042 |
| Laminin, beta 1 |
NM_002291 |
2.13 |
Up |
0.045 |
| Lumican |
NM_002345 |
17.58 |
Up |
0.015 |
| Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 |
AF320999 |
4.61 |
Up |
0.0017 |
| Mitogen-activated protein kinase 13 |
BC000433 |
1.37 |
Up |
0.014 |
| Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 3 |
BF971923 |
1.67 |
Up |
0.045 |
| Nitric oxide synthase 3 |
NM_000603 |
4.77 |
Down |
0.030 |
| SPARC (osteonectin), cwcv and Kazal-like domains proteoglycan (testican) 1 |
AF231124 |
2.74 |
Up |
0.027 |
| Thrombospondin 1 |
BF055462 |
1.20 |
Up |
0.033 |
| TIMP metallopeptidase inhibitor 2 |
BF107565 |
3.57 |
Up |
0.034 |
| TIMP metallopeptidase inhibitor 3 |
U67195 |
2.88 |
Up |
0.035 |
| Vimentin | AI520969 | 1.35 | Up | 0.031 |
Table 4.
Significant differences in pain-, neurotrophin-, nerve- and disc related gene expression in surgical compared to control (CHTN) specimens
| Gene name | Gene identifier | Fold change | Direction | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
A. Pain-, Neurotrophin-, and Nerve-related genes: | ||||
| Adrenergic, beta, receptor kinase 1 |
NM_001619 |
1.28 |
Down |
0.015 |
| Ataxin 1 |
NM_000332 |
1.89 |
Up |
0.026 |
| Ataxin 10 |
AF119662 |
2.43 |
Up |
0.016 |
| Caireticulin |
NM_004343 |
8.53 |
Up |
0.005 |
| Calcitonin gene-related peptide |
M26095 |
1.21 |
Down |
0.005 |
| Calcium channel, voltage-dependent, gamma subunit 2 (stargazin) |
NM_006078 |
1.18 |
Down |
0.037 |
| Calcium channel, voltage-dependent, P/Q type, alpha 1A subunit |
AA769818 |
1.92 |
Up |
0.023 |
| Calcium channel, voltage-dependent, beta 4 subunit |
NM_000726 |
1.24 |
Down |
0.001 |
| Calmodulin 3 (phosphorylase kinase, delta) |
NM_005184 |
4.29 |
Up |
0.002 |
| Calreticulin |
NM_004343 |
8.53 |
Up |
0.005 |
| Cannabinoid receptor 1 (brain) |
NM_001840 |
1.14 |
Down |
0.021 |
| Catechol-O-methyltransferase |
AW139431 |
1.29 |
Down |
0.035 |
| Chloride intracellular channel 1 |
L08666 |
3.61 |
Up |
0.035 |
| Cholinergic receptor, muscarinic 1 |
AI500293 |
1.99 |
Down |
0.001 |
| Ciliary neurotrophic factor |
NM_000614 |
1.14 |
Down |
0.040 |
| Clusterin |
AI982754 |
20.62 |
Up |
0.008 |
| Early growth response 1 |
NM_001964 |
5.73 |
Up |
0.013 |
| Family with sequence similarity 123, member B |
NM_019000 |
3.45 |
Up |
0.022 |
| Frizzled homolog 8 |
AB043703 |
2.81 |
Up |
0.016 |
| G protein-coupled receptor, family C, group 5, member C |
NM_022036 |
2.32 |
Up |
0.039 |
| G protein-coupled receptor 87 |
NM_023915 |
1.17 |
Down |
0.006 |
| G protein-coupled receptor 98 |
AF037334 |
1.17 |
Down |
0.043 |
| G protein regulated inducer of neurite outgrowth 1 |
AI052709 |
1.05 |
Down |
0.046 |
| GABA binding protein 2 |
BC002557 |
8.78 |
Down |
0.0006 |
| GABA(A) receptor-associated protein |
NM_007278 |
4.04 |
Up |
0.038 |
| GABA A receptor, beta 2 |
NM_021911 |
1.2 |
Down |
0.006 |
| Gap junction protein, alpha 1, 43 kDa |
NM_000165 |
4.1 |
Up |
0.038 |
| Glutamate receptor, ionotropic, delta 2 |
NM_001510 |
1.17 |
Down |
0.046 |
| Glutamate receptor, ionotropic, kainite 5 |
S40369 |
1.28 |
Down |
0.009 |
| Glutamate receptor, ionotropic, N-methyl D-aspartate 2B |
NM_024016 |
1.08 |
Down |
0.017 |
| Glutamate receptor, metabotropic 5 |
D60132 |
1.38 |
Down |
0.007 |
| Guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), alpha inhibiting activity polypeptide 3 |
J03198 |
2.87 |
Up |
0.040 |
| Guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), beta polypeptide 1 |
NM_002074 |
4.36 |
Up |
0.009 |
| Guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), alpha 11 (Gq class) |
NM_002067 |
1.29 |
Up |
0.024 |
| Glutathione peroxidase 1 |
NM_000581 |
3.62 |
Up |
0.028 |
| Low density lipoprotein-related protein 1 |
NM_002332 |
5.26 |
Up |
0.034 |
| Meteorin, glial cell differentiation regulator |
BE965311 |
1.28 |
Down |
0.049 |
| Natriuretic peptide receptor B/guanylate cyclase B |
NM_003995 |
1.55 |
Up |
J0.033 |
| Nerve growth factor, beta polypeptide |
NM_002506 |
1.44 |
Up |
0.03 |
| Netrin 1 |
BF591483 |
1.16 |
Down |
0.041 |
| Neugrin, neurite outgrowth associated |
AL037339 |
2.66 |
Up |
0.028 |
| Neuroligin 1 |
AI912122 |
1.13 |
Down |
0.043 |
| Neuron navigator 1 |
AB032977 |
3.83 |
Up |
0.005 |
| Neuro-oncological ventral antigen 1 |
NM_002515 |
3.1 |
Up |
0.0008 |
| Neuropilin 2 |
BC009222 |
3.28 |
Up |
0.014 |
| Neuroplastin |
NM_017455 |
3.61 |
Up |
0.015 |
| Neurotensin |
NM_006183 |
1.22 |
Down |
0.009 |
| Nexin (serpin peptidase inhibitor, claude E) |
AL541302 |
5.64 |
Up |
0.009 |
| Oligophrenin 1 |
NM_002547 |
2.82 |
Up |
0.048 |
| Opioid growth factor receptor-like 1 |
BE500942 |
2.4 |
Up |
0.023 |
| Palmitoyl-protein thioesterase 1 |
NM_000310 |
3.64 |
Up |
0.005 |
| PDZ and LIM domain 5 |
AV15767 |
5.06 |
Up |
0.006 |
| Potassium large conductance calcium-activated channel, subfamily M, alpha member 1 |
U11058 |
3.44 |
Up |
0.040 |
| Potassium voltage-gated channel, shaker-related subfamily, member 10 |
NM_005549 |
2.02 |
Down |
0.010 |
| Potassium channel tetramerisation domain containing 20 |
AV707142 |
2.34 |
Up |
0.018 |
| Prepronociceptin |
NM_006228 |
1.04 |
Down |
0.027 |
| Regulator of G-protein signaling 3 |
NM_021106 |
2.45 |
Up |
0.039 |
| Regulator of G-protein signaling 12 |
AF030111 |
1.18 |
Down |
0.006 |
| Regulator of G-protein signaling 18 |
AF076642 |
1.3 |
Down |
0.025 |
| Reticulon 4 (Neurite growth inhibitor) |
AB015639 |
5.96 |
Up |
0.004 |
| Roundabout, axon guidance receptor, homolog 3 |
NM_022370 |
1.89 |
Up |
0.025 |
| S100 calcium binding protein A4 |
NM_002961 |
12.85 |
Up |
0.003 |
| S100 calcium binding protein A6 |
NM_014624 |
6.97 |
Up |
0.013 |
| S100 calcium binding protein B |
BC001766 |
3.48 |
Up |
0.009 |
| Sigma non-opioid intracellular receptor 1 |
NM_005866 |
1.64 |
Up |
0.031 |
| Solute carrier family 1 (glutamate/neutral amino acid transporter), member 4 |
W72527 |
4.06 |
Up |
0.001 |
| Solute carrier family 29 (nucleoside transporters), member 1 |
NM_004955 |
2.89 |
0.009 |
|
| Solute carrier family 38, member 1 |
NM_030674 |
2.39 |
Up |
0.015 |
| Synaptopodin |
NM_007286 |
2.24 |
Up |
0.032 |
| Thioredoxin domain containing 5 (endoplasmic reticulum) |
NM_030810 |
6.05 |
Up |
0.002 |
| Thy-1 cell surface antigen |
AL161958 |
3.13 |
Up |
0.013 |
| Voltage-dependent anion channel 2 |
L08666 |
3.61 |
Up |
0.035 |
| Xylosyltransferase 1 |
AI693140 |
6.23 |
Up |
0.004 |
|
B. Proinflammatory cytokine and chemokine genes: | ||||
| Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 2 |
AV648479 |
1.15 |
Down |
0.027 |
| Chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 7 |
AI817041 |
4.13 |
Up |
0.014 |
| FGF 1 (acidic) |
X59065 |
2.17 |
Up |
0.033 |
| FGF 5 |
AB016517 |
1.47 |
Down |
0.015 |
| FGF receptor substrate 2 |
AI708648 |
1.23 |
Down |
0.027 |
| FGF receptor 3 |
NM_000142 |
2.62 |
Up |
0.048 |
| FGF receptor substrate 2 |
AI708648 |
1.23 |
Down |
0.027 |
| IL-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 |
NM_001569 |
3.98 |
Up |
0.010 |
| IL-1 receptor-like 1 |
NM_003856 |
1.16 |
Down |
0.041 |
| IL-31 receptor B1 |
NM_139017 |
1.17 |
Down |
0.025 |
| IL-6 signal transducer (gp130, oncostatin M receptor) |
AW242916 |
1.56 |
Down |
0.032 |
| Interferon gamma receptor 2 |
NM_005534 |
2.25 |
Up |
0.041 |
| Macrophate migration inhibitory factor |
NM_002415 |
5.71 |
Up |
0.004 |
| PDGF C |
NM_016205 |
4.62 |
Up |
0.003 |
| PDGF receptor, alpha polypeptide |
NM_006206 |
6.63 |
Up |
0.011 |
| TGF beta |
NM_000358 |
8.77 |
Up |
0.014 |
| TGF beta receptor 1 |
AA604375 |
3.14 |
Up |
0.023 |
| TNF (ligand) superfamily, member 11 |
AF053712 |
3.28 |
Up |
0.009 |
| TNF alpha-indued protein 6 |
AW188198 |
9.91 |
Up |
0.006 |
| TNF receptor superfamily member 1A |
NM_001065 |
2.01 |
Up |
0.040 |
| TNF receptor superfamily, member 10c, decoy without an intracellular domain |
AK026079 |
1.34 |
Down |
0.014 |
| TNF receptor superfamily, member 10d, decoy without an intracellular domain |
NM_003841 |
1.18 |
Down |
0.039 |
| TNF receptor superfamily, member 12A |
NM_016639 |
2.01 |
Up |
0.046 |
| TNF receptor superfamily, member 25 |
U94506 |
1.16 |
Down |
0.012 |
| TNF receptor-associatee factor 3 |
AI721219 |
1.57 |
Up |
0.046 |
|
C. Genes with special disc relevance: | ||||
| ADAM metallopeptidase domain 17 |
NM_003183 |
1.38 |
Up |
0.025 |
| ADAM metallopeptidase domain 22 |
NM_021723 |
1.18 |
Down |
0.045 |
| BCL2-associated athanogene 5 |
NM_004873 |
1.9 |
Up |
0.028 |
| BMP and activin membrane-bound inhibitor homolog |
NM_012342 |
3.28 |
Up |
0.008 |
| Brevican |
AA622130 |
1.30 |
Down |
0.044 |
| Caspase 6, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase |
BC000305 |
2.05 |
Up |
<0.0001 |
| Collagen type II, alpha 1 |
X)6268 |
53.83 |
Up |
0.009 |
| EGF-containing fibulin-like extracellular matrix protein 2 |
NM_005507 |
11.88 |
Up |
0.012 |
| FGF 5 |
AB016517 |
1.47 |
Down |
0.015 |
| Fibronectin 1 |
AK026737 |
37.09 |
Up |
0.001 |
| Growth arrest specific 1 |
NM_002048 |
5.44 |
Up |
0.006 |
| Growth arrest specific 7 |
BE439987 |
2.56 |
Up |
0.040 |
| Heat shock 70kDa protein 5 |
AW052044 |
1.34 |
Up |
0.047 |
| Heat shock 70kDa protein 8 |
AA704004 |
3.99 |
Up |
0.023 |
| Heat shock protein 90 kDa beta, (group 94), member 1 |
AK025862 |
2.45 |
Up |
0.031 |
| Hypoxia inducible factor 1, alpha subunit |
NM_001530 |
4.41 |
Up |
0.014 |
| Laminin, beta 2 |
X79683 |
3.24 |
Up |
0.029 |
| Latent TGF beta binding protein 1 |
NM_000627 |
3.09 |
Up |
0.024 |
| Lumican |
NM_002345 |
66.35 |
Up |
0.0001 |
| Lysyl oxidase-like 2 |
NM_002318 |
5.06 |
Up |
0.010 |
| Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 |
BF434653 |
1.38 |
Down |
0.018 |
| Mitogen-activated protein kinase 3 |
X60188 |
1.94 |
Up |
0.030 |
| Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 3 |
BF971923 |
1.83 |
Up |
0.016 |
| Mitogen-activated protein kinase 13 |
BC000433 |
1.35 |
Up |
0.020 |
| Mitogen-activated protein kinase 14 |
AA604375 |
3.14 |
Up |
0.023 |
| Proteoglycan 4 |
NM_005807 |
13.72 |
Up |
0.001 |
| PTH 1 receptor |
NM_000316 |
1.77 |
Up |
0.047 |
| Retinoic acid receptor, beta |
NM_000965 |
1.61 |
Up |
0.036 |
| SOD |
NM_000454 |
4.18 |
Up |
0.023 |
| SPARC/osteonectin, cwcv and kazal-like domains proteoglycan (testican) 1 |
AF231124 |
3.00 |
Up |
0.015 |
| Tenascin R |
Y13359 |
1.38 |
Down |
0.014 |
| Thyroid stimulating hormone receptor |
BE045816 |
1.26 |
Down |
0.019 |
| TIMP metallopeptidase inhibitor 3 |
NM_000362 |
12.35 |
Up |
0.001 |
| TIMP metallopeptidase inhibitor 4 |
NM_003256 |
2.43 |
Up |
0.042 |
| Versican | BF218922 | 5.19 | Up | 0.021 |
Table 5.
Significant differences in pain-, neurotrophin-, nerve-related and disc genes in herniated discs compared to control (CHTN) discs
| Gene name | Gene identifier | Fold change | Direction | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
A. Pain-, Neurotrophin-, Nerve-related Genes: |
|
|||
| Adrenergic, beta, receptor kinase 1 |
NM-001619 |
1.33 |
Down |
0.042 |
| Ataxin 1 |
NM_000332 |
2.09 |
Up |
0.031 |
| Calcitonin gene related peptide |
M26095 |
1.2 |
Down |
0.040 |
| Calcium channel, voltage-dependent, P/Q type, alpha 1A subunit |
AA769818 |
2.17 |
Up |
0.018 |
| Calcium channel, voltage-dependent, beta 2 subunit |
U80764 |
1.21 |
Up |
0.037 |
| Cannabinoid receptor 1 (brain) |
NM-001840 |
1.16 |
Down |
0.029 |
| Chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 7 |
AI817041 |
4.51 |
Up |
0.012 |
| Cholinergic receptor, muscarinic 1 |
AI500293 |
2.05 |
Down |
0.003 |
| Clusterin |
M25915 |
20.02 |
Up |
0.003 |
| Corticotropin releasing hormone receptor 1 |
X72304 |
1.53 |
Up |
0.035 |
| EPH receptor B3 |
NM_004443 |
1.52 |
Up |
0.037 |
| Family with sequence similarity 134, member B |
NM_019000 |
3.72 |
Up |
0.021 |
| GABA(A) receptor-associated protein |
NM_007278 |
4.39 |
Up |
0.039 |
| GABA A receptor, beta 2 |
NM_021911 |
1.21 |
Down |
0.016 |
| G protein-coupled receptor, family C, group 5, member C |
NM_022036 |
2.64 |
Up |
0.036 |
| G protein-coupled receptor 52 |
NM_005684 |
1.06 |
Down |
0.044 |
| G protein-coupled receptor 161 |
AI703188 |
1.71 |
Up |
0.044 |
| G protein signaling modulator 2 (AGS3-like) |
AW195581 |
1.94 |
Up |
0.040 |
| Glutamate receptor, metabotropic 5 |
D60132 |
1.37 |
Down |
0.026 |
| Glutaminase |
NM_014905 |
3.14 |
Up |
0.014 |
| Glutathione peroxidase 1 |
NM_000581 |
3.94 |
Up |
0.038 |
| Guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), beta polypeptide 1 |
NM_002074 |
4.61 |
Up |
0.013 |
| Guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), gamma 5 |
NM_005274 |
2.62 |
Up |
0.040 |
| Guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), gamma 7 |
AL039870 |
1.54 |
Up |
0.006 |
| Guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), gamma 10 |
AI765321 |
1.49 |
Up |
0.040 |
| Guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), gamma 11 |
NM_004126 |
3.13 |
Up |
0.026 |
| Guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), gamma 12 |
N32508 |
1.86 |
Up |
0.026 |
| Guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), alpha 13 |
AI928136 |
2.80 |
Up |
0.022 |
| Kallidrein-related peptidase 8 |
NM_144506 |
1.21 |
Down |
0.028 |
| Monoglyceride lipase |
BG168471 |
1.79 |
Up |
0.019 |
| Myelin basic protein |
N37023 |
3.28 |
Up |
0.003 |
| Natriuretic peptide receptor B/guanylate cyclase B (atrionatriuretic peptide receptor B) |
NM_003995 |
2.14 |
Up |
0.049 |
| Neogenin homolog 1 |
BF058828 |
1.28 |
Down |
0.022 |
| Nerve growth factor (beta polypeptide) |
NM_002506 |
1.5 |
Up |
0.029 |
| Neural precursor cell expressed, developmentally downregulated 4-like |
AB007899 |
1.23 |
Up |
0.038 |
| Neuromedin U receptor 2 |
AF272363 |
1.09 |
Down |
0.023 |
| Neuro-oncological ventral antigen 1 |
NM_002515 |
3.1 |
Up |
0.001 |
| Neurofibromin 1 |
M60915 |
1.04 |
Up |
0.031 |
| Neuromedin U receptor 2 |
AF272363 |
1.09 |
Down |
0.023 |
| Neuropilin 2 |
AA295257 |
3.92 |
Up |
0.032 |
| Neuroplastin |
NM_017455 |
4.46 |
Up |
0.008 |
| Opioid growth factor receptor-like 1 |
BE500942 |
2.52 |
Up |
0.017 |
| Palmitoyl-protein thioesterase 1 |
NM_000310 |
4.34 |
Up |
0.005 |
| Pancreatic polypeptide receptor 1 |
U42387 |
1.31 |
Down |
0.048 |
| PDZ and LIM domain 5 |
AV715767 |
5.04 |
Up |
0.007 |
| Plexin A1 |
T16388 |
1.51 |
Down |
0.046 |
| Potassium voltage-gated channel, shaker-related subfamily, member 10 |
NM_005549 |
2.36 |
Down |
0.007 |
| Prostaglandin E receptor 2 (subtype EP2), 53 kDa |
NM_000956 |
1.45 |
Up |
0.048 |
| Regulator of G-protein signaling 3 |
NM_021106 |
3.15 |
Up |
0.021 |
| Regulator of G-protein signaling 12 |
AF030111 |
1.18 |
Down |
0.027 |
| Regulator of G-protein signaling 14 |
NM_006480 |
1.13 |
Up |
0.042 |
| Reticulon 4 (neurite growth inhibitor) |
AB015639 |
5.58 |
Up |
0.007 |
| Roundabout, axon guidance receptor, homolog 3 |
NM_022370 |
1.74 |
Up |
0.048 |
| S100 calcium binding protein A6 |
NM_014624 |
9.13 |
Up |
0.017 |
| S100 calcium binding protein A9 |
NM_002965 |
1.93 |
Up |
0.046 |
| S100 calcium binding protein B |
BC001766 |
4.18 |
Up |
0.012 |
| Sigma non-opioid intracellular receptor |
NM_005866 |
2.01 |
Up |
0.022 |
| Solute carrier family 1 (glutamate/neutral amino acid transporter), member 4 |
AI889380 |
2.79 |
Up |
0.013 |
| Solute carrier family 6 (neurotransmitter transporter, creatine), member 8 |
AI820043 |
1.65 |
Down |
0.021 |
| Solute carrier family 22, member 17 |
NM_020372 |
2.62 |
Up |
0.044 |
| Solute carrier family 29 (nucleoside transporters), member 1 |
NM_004955 |
4.03 |
Up |
0.010 |
| Solute carrier family 38, member 1 |
NM_030674 |
2.25 |
Up |
0.023 |
| Solute carrier family 38, member 2 |
NM_018976 |
2.24 |
Up |
0.048 |
| Solute carrier family 44, member 2 |
AI264216 |
1.88 |
Up |
0.020 |
| Syntaxin 1A (brain) |
NM_004603 |
2.46 |
Up |
0.017 |
| Syntaxin binding protein 1 |
NM_003165 |
1.96 |
Up |
0.049 |
| Thy-1 cell surface antigen |
NM_000633 |
2.24 |
Up |
0.025 |
| Xylosyltransferase I |
AI693140 |
6.41 |
Up |
0.007 |
|
B. Proinflammatory cytokine and chemokine genes: |
|
|
|
|
| Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 22 |
NM_002990 |
1.10 |
Down |
0.039 |
| IL 11 receptor, alpha |
NM_147162 |
1.03 |
Down |
0.049 |
| IL 17 receptor C |
BF196320 |
1.11 |
Down |
0.033 |
| IL 27 receptor, alpha |
AI983115 |
1.19 |
Down |
0.042 |
| IL 31 receptor A |
AF106913 |
1.33 |
Down |
0.040 |
| IL-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 |
NM_001569 |
4.30 |
Up |
0.015 |
| IL-23, alpha subunit P19 |
AJ296370 |
1.62 |
Up |
0.023 |
| Interferon gamma receptor 2 |
NM_005534 |
2.79 |
Up |
0.028 |
| Latent TGF beta binding protein 1 |
NM_000627 |
2.61 |
Up |
0.039 |
| Macrophage migration inhibitory factor |
NM_002415 |
5.01 |
Up |
0.034 |
| PDGF receptor, alpha polypeptide |
NM_006206 |
5.96 |
Up |
0.018 |
| TGF beta |
NM_000358 |
12.34 |
Up |
0.011 |
| TGF beta receptor 1 |
NM_000714 |
3.88 |
Up |
0.018 |
| TNF alpha-induced protein 6 |
AW188198 |
14.57 |
Up |
0.002 |
| TNF receptor superfamily, member 11b |
NM_002546 |
3.31 |
Up |
0.034 |
| TNF receptor superfamily, member 12A |
NM_016639 |
2.29 |
Up |
0.042 |
| TNF receptor superfamily, member 25 |
U94506 |
1.13 |
Down |
0.046 |
| TNF receptor-associated factor 3 |
AI721219 |
1.67 |
Up |
0.043 |
| TNF superfamily, member 11 |
AF053712 |
4.32 |
Up |
0.002 |
|
C. Genes with special relevance to the disc: |
|
|||
| ADAM metallopeptidase domain 17 |
NM_003183 |
1.36 |
Up |
0.045 |
| BCL2-associated athanogene 5 |
NM_004873 |
1.95 |
Up |
0.039 |
| Caspase 6, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase |
BC000305 |
2.48 |
Up |
0.025 |
| Collagen type I, alpha 2 |
NM_000089 |
11.05 |
Up |
0.017 |
| Collagen type II, alpha 1 |
X06268 |
58.92 |
Up |
0.0001 |
| Collagen type III, alpha 1 |
AU144167 |
12.15 |
Up |
0.026 |
| Collagen type VI, alpha 2 |
AL531750 |
3.14 |
Up |
0.018 |
| Collagen type VI, alpha 3 |
NM_004369 |
8.55 |
Up |
0.013 |
| Collagen type VI, alpha 1 |
AA292373 |
3.12 |
Up |
0.037 |
| Collagen type XI, alpha 1 |
NM_001854 |
6.45 |
Up |
0.020 |
| Collagen type IX, alpha 3 |
NM_001853 |
10.38 |
Up |
0.002 |
| EGF receptor pathway substrate 8 |
NM_004447 |
1.55 |
Up |
0.048 |
| EGF-containing fibulin-like extracellular matrix protein 2 |
NM_005507 |
9.96 |
Up |
0.037 |
| Fibronectin 1 |
AK026737 |
52.43 |
Up |
0.0004 |
| Fibronectin leucine rich transmembrane protein 2 |
NM_013231 |
2.61 |
Up |
0.028 |
| Growth arrest-specific 1 |
NM_002048 |
5.45 |
Up |
0.006 |
| Growth arrest-specific 7 |
NM_005890 |
2.04 |
Up |
0.045 |
| Heat shock 70 kDa protein 8 |
AA704004 |
5.36 |
Up |
0.008 |
| Hypoxia indicuble factor 3, alpha subunit |
NM_001530 |
4.32 |
Up |
0.027 |
| Hypoxia inducible factor 1 (HIF1A) |
NM_001530 |
4.32 |
Up |
0.027 |
| Jun oncogene |
NM_002228 |
2.21 |
Up |
0.027 |
| Lumican |
NM_002345 |
79.38 |
Up |
<0.0001 |
| Lysly oxidase-like 2 |
NM_002318 |
5.85 |
Up |
0.009 |
| Mitogen activated protein kinase 1 |
BF434653 |
1.44 |
Down |
0.022 |
| Mitogen-activated protein kinase 3 |
X60188 |
2.28 |
Up |
0.023 |
| Mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 |
AU152505 |
1.41 |
Up |
0.048 |
| Mitogen-activated protein kinase 13 |
BC000433 |
1.32 |
Up |
0.030 |
| Mitogen-activated protein kinase 14 |
NM_001315 |
4.30 |
Up |
0.006 |
| Never in mitosis gene a (NIMA)-related kinase 8 |
AI9365173 |
1.81 |
Up |
0.006 |
| Never in mitosis gene a (NIMA)-related kinase 7 |
AL080111 |
2.43 |
Up |
0.039 |
| Proteoglycan 4 |
NM_005807 |
18.05 |
Up |
0.001 |
| SOD 1, soluble |
NM_000454 |
4.44 |
Up |
0.038 |
| SPARC/osteonectin, cwcv and kazal-like domains proteoclycan (testican) 1 (SPOCK1) |
AF231124 |
3.3 |
Up |
0.010 |
| Thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptor |
D16845 |
1.25 |
Down |
0.004 |
| TIMP metallopeptidase inhibitor 2 |
BF107565 |
2.9 |
Up |
0.046 |
| TIMP metallopeptidase inhibitor 3 |
NM_000358 |
15.36 |
Up |
0.002 |
| Versican |
BF218922 |
6.59 |
Up |
0.013 |
| Vitamin D receptor | AA454701 | 1.19 | Down | 0.039 |
Neurotrophin-, nerve-, and pain-related gene, and disc gene expression patterns in the annulus: expression patterns in more degenerate compared to less degenerate discs
In Table 3, findings are presented for selected relevant genes which were significantly elevated in expression in more degenerated Thompson grade IV and V discs compared to findings in grades I, II and III discs.
Of major interest in Table 3 are a number of genes with high relevance to pain, neurotrophins and nerves. These include significantly upregulated expression in the more degenerated discs of the following: bradykinin receptor B1, calcitonin gene-related peptide, catechol-O-methyltransferase, neuron navigator-1 and −2, neuropilin 2, and reticulon 4 (also known as neurite growth inhibitor). These genes showed up regulation fold changes ranging from 1.09 to 4.61.
A large number of genes in the ion transport grouping showed significant changes in this analysis; 69 genes showed significant up regulation, and 59 significant down regulation (most data not shown).
Genes with specific high relationships to disc cell biology included these significantly upregulated genes in the more degenerated discs: apoptosis-inducing factor (mitochondrion associated), BMP receptor, type II, collagens type I, III, IV, V and VI, connective tissue growth factor, fibronectin, hypoxia inducible factor 1 (HIF1), several of the mitogen-activated protein kinases, SPARC (osteonectin), TGF-ß, lumican and TIMP metallopeptidase inhibitors-2 and −3. These genes showed upregulation fold changes ranging from 1.42 to 17.58. Nitric oxide synthase 3 showed a 4.77 fold downregulation.
Neurotrophin-, nerve-, and pain-related gene, and disc gene expression patterns in the annulus: analysis of expression patterns in surgical compared to control (CHTN) specimens
In Table 4, findings are presented for relevant genes which were significantly upregulated in surgically operated disc specimens compared to expression findings in control (CHTN) discs.
Of high interest in Table 4 are a number of genes with high relevance to pain, neurotrophins and nerves. These include the following: calcitonin gene-related peptide, catechol-O-methyltransferase, ciliary neurotrophic factor, nerve growth factor, neuron navigator 1, neuropilin 2, reticulon 4, and roundabout axon guidance receptor. These genes showed up regulation fold changes ranging from 1.2 to 5.96.
A large number of genes in the ion transport grouping also showed significant changes in this analysis; 87 genes showed significant up regulation, and 73 significant down regulation (most of the gene data in the ion transport group are not shown here).
Genes with specific high relationships to disc cell biology included these significantly upregulated genes in surgical vs. control discs: heat shock proteins, fibronectin 1, versican, lumican, several of the mitogen-activated protein kinases, TIMP metallopeptidase inhibitors-3 and −4, TFG-ß, latent TGF binding protein 1, several of the TNF receptors, and collagen type II alpha 1. These genes showed up regulation fold changes ranging from 1.1 to 66.35. Notable down regulated genes included brevican and FGF 5 (with fold changes of 1.3 and 1.4, respectively).
Neurotrophin-, nerve-, and pain-related gene, and disc gene expression patterns in the annulus: expression patterns in herniated compared to Non-herniated discs
Although not related to discogenic low back pain, we were also interested in evaluating our data in terms of expression patterns which were significantly different in herniated discs vs. non-herniated discs (Table 5).
Of high interest in Table 5 are a number of genes with high relevance to pain, neurotrophins and nerves. These include the following: Calcitonin gene related peptide (down regulated 1.2 fold). Upregulated genes included neuropilin 2, nerve growth factor, reticulon 4, roundabout axon guidance receptor; these genes were upregulated 1.5 to 5.58 fold.
A large number of genes in the ion transport grouping also showed significant changes in this analysis; 98 genes showed significant up regulation, and 39 significant down regulation (most data not shown).
Genes with specific high relationships to disc cell biology included these significantly upregulated genes: a number of the collagens, fibronectin 1, hypoxia inducible factors-1 and −2 (alpha subunit), latent TGF-ß binding protein 1, TGF-ß receptor 1, several of the mitogen-activated protein kinases, proteoglycan 4, SOD, and the apoptosis-associated genes caspase 6 and TNFRSF1A-associated via death domain.
Immunohistochemical studies
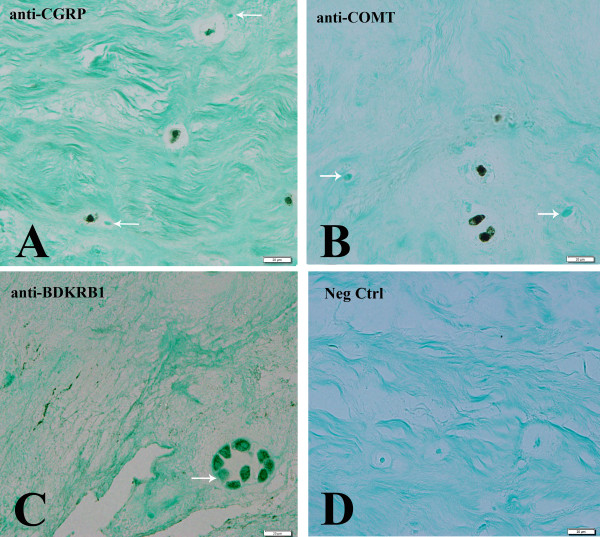
Paraffin-embedded annulus tissue was available for several of the subjects studied here (subjects # 5, 10, 14, 15, 19, 21 and 22 (Table 1) which enabled us to perform immunolocalization studies for products of three of the genes of special interest here (calcitonin gene-related peptide, catechol-0-methyltransferase and bradykinin receptor B1). For each of these immunolocalizations, cells were present with localization in single cells, clusters of cells, and both rounded and spindle-shaped cells in the outermost region of the annulus. Representative images are shown in Figures 1A-C; Figure 1D presents a negative control with the absence of any localization. Note that in Figures 1A-C adjacent cells were occasionally present which showed no localization.
Figure 1 .
Immunohistochemical localizations of calcitonin gene-related peptide, catechol-0-methyltransferase and bradykinin receptor B1: Representative images showing localization of calcitonin gene-related peptide (Figure 1A), catechol-0-methyltransferase (Figure 1B) and bradykinin receptor B1 (Figure 1C) in annulus regions of the human disc. Figure 1D illustrates a negative control. Arrows mark nearby cells which did not show localization.
Discussion
In the present study we performed a genome-wide microarray analysis of human annulus tissue from patients with discogenic back pain compared to disc tissue from control subjects or compared to and herniated disc patients we had a special focus upon analysis of the expression of pain, nerve and neurotrophin-related genes. Ontology searches were an efficient search technique for identification of pain, and nerve-related genes [14]. Although there is a large body of clinical literature on low back pain, molecular studies are few, and those in the literature primarily focus upon population-based genetic studies of polymorphisms (SNPs) (see [13] for a review of pain and spinal disease). To the best of our knowledge, the present work is the first (non-SNP) genome-wide study of pain, neurotrophin and nerve-related genes in disc degeneration.
Pain-related genes
Several well-recognized pain-related genes were found to have significant elevations in our analyses. Bradykinin receptor B1, calcitonin gene-related peptide and catechol-0-methyltransferase were significantly elevated in more degenerated discs (grade IV and V) compared to less degenerated (grades I-III) discs (Table 1). Bradykinin receptor B1 is formed after tissue injury and mediates hyperalgesia in chronic inflammation, but has very low expression in healthy tissue expression [16]. Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) has been found to be elevated in sensory nerves innervating inflamed tissue [17], in dorsal root ganglia and spinal cord in sciatic nerve injuries in the rat model by Orita et al. [18]. In the latter work, application or antibodies to nerve growth factor or its receptors TrkA or p75NTR blocked CGRP expression. Catechol-0-methyltransferase (COMT) codes for a protein which is important in catabolic pathways of a number of pain-relevant neurotransmitters, including noradrenalin, adrenaline and dopamine [19]. In the present analyses comparing surgically operated discs to control discs (Table 4) and herniated to control discs, calcitonin gene-related peptide was the only one of these genes which was significant, and in these comparisons it was downregulated 1.2-fold. The COMT gene is very interesting since patients with a specific polymorphism identified by Zubieta et al. showed higher sensory and affective pain ratings [20].
Our ability to perform immunolocalization studies on human annulus tissues to determine the presence of bradykinin receptor B1, calcitonin gene-related peptide and catechol-0-methyltransferase (Figure 1) added strength to the present study, and confirmed the presence of products of these gene at the protein level within human disc tissue.
Neurotrophin-related genes
Neurotrophins were also identified in the present analyses, including nerve growth factor in our studies of surgical vs. control discs, and herniated vs. control discs (significantly upregulated, Tables 4 and 5, respectively), and ciliary neurotrophic factor (down regulated, Table 4, surgical vs. control discs).
Studies have recently shown production of several neurotrophins by disc cells. Gigante et al. reported the presence of nerve growth factor (NGF) mRNA and the high affinity tyrosine kinase A receptor (trkA) and the low affinity p75 receptor in the rounded cells in the disc annulus and nucleus pulposus [21]. Recently Abe et al. reported on the expression of nerve growth factor (NGF) by human disc cells in control disc tissue in vivo and in vitro in cells from control discs using immunocytochemistry [22]. Nerve growth factor was found to be high in the outer annulus and herniated disc tissue. That work also demonstrated that the proinflammatory cytokines IL-1 and TNF-alpha had stimulatory effects on NGF. These authors suggested that such actions may play a role in nerve sprouting into the disc and may be associated with discogenic pain. Recent in vitro work from our lab has also confirmed that exposure of disc cells to IL-1ß in three-dimensional culture (which more accurately mimics the in vivo condition) results in elevated production of nerve growth factor by human annulus cells [23].
Ciliary neurotrophic factor whose expression is reported here, has not previously been known to be expressed in the human disc. Work from previous studies has shown that it can act as both a neuroprotective agent [24] and a trophic factor for motor neurons [25].
Nerve-related genes
Several nerve-related genes should be mentioned in our analyses, including neuron navigator-1 and −2, neuropilin 2, reticulon 4 (neurite growth inhibitor), roundabout axon guidance receptor, homolog 3, and neural precursor cell expressed (developmentally down regulated 4-like) (Tables 3, 4 and 5). These genes also have not previously been known to be expressed in the human disc.
Neuron navigator 1 is a microtubule-associated protein involved in neuronal migration [26], and neuron navigator 2 is required for all-trans retinoic acid-mediated neurite outgrowth and axonal elongation [27]. Neuropilin 2 was significantly upregulated in all of our disc comparisons (Tables 34 and 5). Neuropilin 2 is another gene which we have found to be significantly upregulated in cultured annulus cells exposed to IL-1ß [23]. Neuropilin-1 and neuropilin-2 are membrane proteins implicated in aspects of neurodevelopment. They are semaphorin III receptors as shown by the work of Kolodkin et al. [28], and are expressed in overlapping populations of neurons in the embryonic nervous system. Semaphorin III is a protein which, when secreted in vitro, results in the collapse of neuronal growth cones and chemorepulsion of neurites. It is also needed for correct sensory afferent innervation [29]. Expression of this gene by annulus cells may provide evidence that annulus cells express this gene to block neurite ingrowth into the disc.
Roundabout (ROBO1) is a gene which encodes a receptor which is a member of the neural cell adhesion molecule family. It functions as an axon guidance receptor [30]. We found upregulation of this gene in surgical vs. control specimens (Table 4) and in herniated vs. control specimens (Table 5).
Reticulon 4 (neurite growth inhibitor) was identified with upregulation in each of our analyses, with 4.6 fold (Table 3, more degenerated discs vs. less degenerated discs), 5.96 fold (Table 4, surgical vs. control discs) and 5.58 fold (Table 5, herniated vs. control discs) changes. This gene, also called NOGO, is a neurite outgrowth inhibitor [31].
Genes related to proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines
In Tables 34 and 5, in the section headed “Genes with special disc relevance” we have listed many proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines identified in our analyses. These deserve special mention here because a large number of proinflammatory cytokines are well recognized as products of disc cells themselves in vivo (see [32-36] for an introduction to this field). Many chemokines are also produced by disc cells (our unpublished data). It is very important to note in the present study that many proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines are now known to induce or exacerbate inflammatory and neuropathic pain and hyperalgesia [37-39]. We suggest here that this is an exceptionally important aspect of low back pain that has here-to-fore been little recognized. The degenerating human disc is primarily an avascular tissue site into which disc cells have contributed high levels of proinflammatory cytokines which are not cleared from the tissue and remain there over time. We suggest that as nerves grow into the human annulus, they encounter a proinflammatory cytokine-rich milieu which exacerbates pain production.
Kim et al. using in vitro work has suggested that disc cells themselves are involved in inflammatory activities, and suggested that interactions between annulus cells and nerve cells enhances the production of growth factors responsible for neovascularization and nerve ingrowth into the disc [40]. Previous research by Aoki et al. showed that disc inflammation potentially promoted axonal regeneration of dorsal root ganglion neurons innervating the disc in a rat model [41]. Using gene correlations, recent work by Lee et al. suggests that IL-1ß is generated during degeneration of the disc, and this stimulates expression of agents such as nerve growth factor, which result in nerve in growth into the disc [42].
It is important to recognize that proinflammatory cytokine production within the degenerating disc can also be exacerbated by repeated disc injury, which may lead to persistent proinflammatory cytokine elevation [43]; thus repeated disc injury may also influence neuroinflammation and pain.
A final important comment from the joint literature on proinflammatory mediators concerns the fact that release of these agents in damaged tissue and in the spinal cord is known to sensitize the peripheral terminals of nociceptors [44]. It is possible that similar hyper excitability of pain transmitting neurons results from proinflammatory cytokines in the disc matrix during degeneration; proinflammatory cytokines likely to be at play here are IL-1ß and TNF-α.
Genes which share high importance to the disc itself
It was interesting that many genes were identified in our analyses which have relevance to the nerve, neurotrophin and pain ontology and to disc biology itself (as shown in section C of Tables 34 and 5). These included extracellular matrix (ECM) components, such as collagens, fibronectin, laminin, thrombospondin, brevican, proteoglycans, and versican, and also genes related to matrix degradation (metallopepdiases and TIMP metallopeptidase inhibitors), growth factors (connective tissue growth factor), nitric oxide synthase 3 (ENOS), SOD, and hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha subunit. Also important to disc biology were the vitamin D receptor gene, growth arrest specific genes (important to cell senescence), apoptosis-related genes, and BMP receptor type II. Although some of these gene products may be resident only in sites of neurovascular ingrowth, many may influence the disc ECM itself and disc cell functions. Such findings point to the importance of future research directed towards identifying functional interactions between disc and nerve cells in vivo and in vitro. For example, it has long been recognized that there is an accumulation of fibronectin fragments in the aging/degenerating disc, and these fragments initiate signaling pathways which can increase MMP expression causing a cycle of matrix destruction [45-50]. Strong up regulation of fibronectin was present in our analyses (16.8 fold upregulation in more degenerated vs. healthier discs (Table 3), 37.0 fold upregulation in surgical vs. control discs (Table 4), and a 52.4 fold up regulation in herniated vs. control discs (Table 5).
Possible limitations to the present analyses include the fact that some specimens, noted as “controls” in Table 1, were obtained from the Cooperative Human Tissue Network (CHTN). Although these were shipped quickly to our lab post-autopsy as quickly as possible via CHTN, delays might result in potential alterations in mRNA levels during our study. The reader should note that in order to carefully investigate this issue, in Table 4 we compared findings in surgical specimens vs. those obtained from CHTN. As would be expected in different sized microarray group comparisons with ontology searchers, Table 4 does differ in some respects from data presented in Table 3. It is also worth noting that in our laboratory, CHTN specimens are also routinely used for derivation of disc cells in vitro, and in our hands over 98% of CHTN specimens yielded viable cells.
Another point for the reader to note is that our tables have reported gene expression fold changes which in some cases were less than 2.0, a level which is commonly used. Since we feel that smaller changes in important genes may be clinically relevant, we have reported these changes in our data tables.
Conclusions
Even though our three study groups were not large, the present analysis showed that microarray analysis could successfully be used to examine key pain-, neurotrophin- and nerve-related genes in specimens of human disc tissue. Many genes were found in these ontology searches which held significance not only for nerves, pain and neurotrophins, but also for disc ECM, signaling and functional components. Key findings included confirmation of the presence of calcitonin gene-related peptide, catechol-0-methyltransferase and bradykinin receptor B1 at the protein level in the human annulus using immunohistochemistry, and identification of significant changes in a number of proinflammatory and chemokine genes identified from nerve, neurotrophin and pain ontology searches. Since the disc is primarily avascular, and since disc cells themselves produce proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines which are not removed from the tissue, we hypothesize that as nerves grow into the human annulus, they encounter a proinflammatory cytokine-rich milieu which may sensitize nociceptors and exacerbate pain production. Findings reported here point to the importance of future studies of the functional interactions between disc and nerve cells in vivo and in vitro.
Methods
Clinical study population
Experimental study of human disc specimens was approved prospectively by the authors’ Human Subjects Institutional Review Board. The need for informed consent was waived by the ethical board since disc tissue was removed as part of routine surgical practice. Scoring of disc degeneration utilized a modification of the Thompson scoring system [51] incorporating author ENH’s radiologic, MRI and surgical findings. The Thompson system scores disc degeneration over the spectrum from a healthy disc (Thompson grade I) to discs with advanced degeneration (grade V, the most advanced stage of degeneration) [51]. Patient specimens were derived from surgical disc procedures performed on individuals with herniated discs and degenerative disc disease. Surgical specimens were transported to the laboratory in sterile tissue culture medium. Non-surgical, control donor disc specimens were obtained via the National Cancer Institute Cooperative Human Tissue Network (CHTN); they were shipped overnight to the laboratory in sterile tissue culture medium and processed as described below. Specimen procurement from the CHTN was included in our approved protocol by our human subjects Institutional Review Board.
Microarray analysis
Disc tissue was snap frozen in liquid nitrogen, pulverized (BioPulverizer, BioSpec Products, Inc., Bartlesville, OK, USA), and homogenized via the FastPrep-24 instrument (MP Biomedicals L.L.C., Santa Ana, CA, USA). Total RNA was isolated via a modified version of TRIzol Reagent (Life Technologies: Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA), and prepared for microarray hybridization using the GeneChip 3’ IVT Express Kit (Affymetrix, Santa Clara, CA). In brief, total RNA was reverse transcribed to synthesize cDNA, converted to double stranded DNA, subjected to transcription generating biotin-labeled amplified RNA (cRNA) and hybridized to the DNA microarray in the Affymetrix Fluidics Station 400. Affymetrix human U133 X3P arrays were used. The GCOS Affymetrix GeneChip Operating System (version 1.2, Affymetrix, Santa Clara, CA 95051) was used for determining gene expression levels. mRNA from annulus tissue from each subject was analyzed separately (i.e., samples were not pooled).
Statistical analysis
The GCOS Affymetrix GeneChip Operating System (version 1.2, Affymetrix, Santa Clara, CA) was used for determining gene expression levels. GeneSifterTM web-based software (VizX Labs, Seattle, WA, USA) was used to analyze all microarray data. Using GC-RMA (Robust multi-array average), Affymetrix ‘.cel’ files were uploaded to the GeneSifterTM web site and normalized, and corrected for false discovery rate (FDR). Using the student t-test (2 tailed, unpaired), statistical significance was determined (p < 0.05).
Gene Ontology (GO) searches were employed in our analyses to select genes of interest and groups of critically important genes. This approach lets one avoid searching through results gene by gene, and provides a controlled vocabulary of search terms for gene characteristics. In our analyses, Gene Ontologies (GO) were generated by GeneSifterTM based on the Gene Ontology Consortium. Searches were performed in the present study on “pain” and “nerve”; for each, ontologies were searched under “biological process”, “molecular function” (the activities of the gene product at the molecular level), and “cellular component” (parts or cells or the extracellular milieu). To aid the reader in visualizing the key terms covered in these ontology grouping, details are provided in Table 2.
Gene array data for the human disc specimens analyzed here have been uploaded to the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) website [GEO:GSE23130] and may be accessed there.
Immunohistochemistry
Bradykinin receptor B1 (BDKRB1) and calcitonin gene related peptide (CGRP) Immunohistochemistry: Disc specimens were fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin, embedded undecalcified, paraffin sections cut at 4 μm, collected on PLUS slides(Cardinal Health, Dublin, OH) and dried at 60°C. Sections were deparaffinized in xylene (Cardinal) and rehydrated through graded alcohols (AAPER, Shelbyville, KY) to distilled water. Antigen retrieval was performed using Biocare Antigen Decloaker Solution, pH 6.0 (Biocare Medical, Concord, CA) for 20 minutes at 95°C followed by cooling for 20 minutes. The remainder of the procedure was performed using the Dako Autostainer Plus (Dako, Carpenteria, CA) automated stainer. Endogenous peroxidase was blocked using 3% H202 (Sigma, St Louis, MO). Slides were incubated for 30 minutes with Serum-Free Protein Block (Dako); blocking solution was drained from slides and primary antibody applied. Sections were incubated for one hour with anti-Bradykinin receptor B1 (BDKRB1) (Novus Biologicals, Littleton, CO) at a 1:50 dilution, or with for one hour with anti-calcitonin gene related peptide (CGRP) (Abcam, Cambridge, MA) at a 1:100 dilution. Secondary antibody was 4 + Biotinylated Universal Goat Link (Biocare) for 10 minutes followed by 4+ streptavidin HRP Label (Biocare) for 10 minutes and DAB (Dako) for 5 minutes. Slides were removed from stainer, rinsed in water, counterstained with light green, dehydrated, cleared and mounted with resinous mounting media. Universal Rabbit Negative (Dako, Carpinteria, CA) was used as a negative control.
Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) immunohistochemistry did not require antigen retrieval. Sections were prepared as described above, and incubated for one hour with anti-catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) (Lifespan Biosciences, Seattle, WA) at a 1:200 dilution. The secondary antibody and negative control utilized were as described above.
Positive control human tissues were also included with each immunolocalization run; for bradykinin receptor B1 this was brain, for calcitonin gene related peptide this was thyroid, and for catechol-O-methyltransferase, adrenal.
Abbreviations
GO: Gene ontologies; GC-RMA: Robust multi-array average; HIF1: Hypoxia inducible factor 1; TGF-ß: Transforming growth factor beta; TIMP: Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases; CHTN: Cooperative Human Tissue Network; TNFα: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; SNP: Single nucleotide polymorphism; CGRP: Calcitonin gene-related peptide; COMT: Catechol-0-methyltransferase; NGF: Nerve growth factor; IL-1: Interleukin-1; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; ECM: Extracellular matrix.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
HEG and ENH are responsible for study concept and design. ENH contributed surgical disc specimens and disc grades. GLH performed gene searches and analyses. JAI performed immunohistochemistry. HEG identified critical genes and wrote the manuscript, and all authors approved the final manuscript.
Contributor Information
Helen E Gruber, Email: helen.gruber@carolinashealthcare.org.
Gretchen L Hoelscher, Email: gretchen.hoelscher@carolinashealthcare.org.
Jane A Ingram, Email: jane.ingram@carolinashealthcare.org.
Edward N Hanley, Jr, Email: edward.hanley@carolinashealthcare.org.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to than the Brooks Center for Back Pain Research for general laboratory support. We thank Synthia Bethea for expert technical assistance in mRNA isolation and processing, Nury Steuerwald, Ph.D. (Director) and Judy Vachris in the Molecular Biology Core for excellent assistance with microarray processing, and Natalia Zinchenko for expert assistance with histology.
References
- Vora AJ, Koerr KD, Wolfer LR. Functional anatomy and pathophysiology of axial low back pain: Disc, posterior elements, sacroiliac joint, and associated pain generators. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2010;21:679–709. doi: 10.1016/j.pmr.2010.07.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbank J, Gwilym SE, France JC, Daffner SD, Dettori J, Hermsmeyer J. et al. The role of classification of chronic low back pain. Spine. 2012;36:S19–S42. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e31822ef72c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Cosamalon J, del Valle ME, Calavia MG, Garcia-Suarez O, Lopez-Muniz A, Otero J. et al. Intervertebral disc, sensory nerves and neurotrophins: who is who in discogenic pain? J Anat. 2010;217:1–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2010.01227.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurri H, Karppinen J. Discogenic pain. Pain. 2004;112:225–228. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2004.08.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyodo H, Sato T, Sasaki H, Tanaka Y. Discogenic pain in acute nonspecific low-back pain. Eur Spine J. 2005;14:573–577. doi: 10.1007/s00586-004-0844-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki Y, Takahashi K, Ohtori S, Moriya H. In: Spinal Reconstruction - Clinical Examples of Applied Basic Science, Biomechanics, and Engineering. Lewandowski KUYMJ, Kalfas IH, Park P, McLain RF, Trantolo DJ, editor. Informa Healthcare, New York; 2007. Scientific basis of interventional therapies for discogenic pain: Neural mechanisms of discogenic pain; pp. 219–236. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Y, Abdi S. Diagnosis and minimally invasive treatment of lumbar discogenic pain - A review of the literature. Clin J Pain. 2006;22:468–481. doi: 10.1097/01.ajp.0000208244.33498.05. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng B, Wu W, Hou S, Li P, Zhang C, Yang Y. The pathogenesis of discogenic low back pain. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87B:62–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauben D. Central nervous system modulation of spinal pain: Pain sensitization and implications for surgical selection. SpineLine. 2005. pp. 7–12.
- McHugh JM, McHugh WB. Pain: Neuroanatomy, chemical mediators, and clinical implications. AACN Clin Issues Adv Pract Acute Crit Care. 2000;11:168–178. doi: 10.1097/00044067-200005000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuertz K, Stachi E, Boos N. The influence of matrix degradation products on pain development in the intervertebral disc. Eur Spine J. 2008;17:1555. Abstract. [Google Scholar]
- Gu J, Zhuo M, Caterina M, MacDermott AB, Malmnbert A, Neugebauer V. et al. Molecular pain, a new era of pain research and medicine. Mol Pain. 2005;1:1. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-1-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim DH, Schwartz CE. The genetics of pain: implications for evaluation and treatment of spinal disease. Spine J. 2010;10:827–840. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2010.05.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- The Gene Ontology Consortium. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Nature Genet. 2000;25:25–29. doi: 10.1038/75556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobinick EL, Britschgi-Davoodifar S. Perispinal TNF-alpha inhibition for discogenic pain. Swiss Med Weekly. 2003;133:170–177. doi: 10.4414/smw.2003.10163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dray A, Perkins M. Bradykinin and inflammatory pain. Trends Neurosci. 1993;16:99–104. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(93)90133-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnerer J, Schuligal R, Stein D. Increased content and transport of substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide in sensory nerves innervating inflamed tissue: evidence for a regulatory function of nerve growth factor in vivo. Neurosci. 1992;49:693–698. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90237-V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orita S, Ohtori S, Nagata M, Horii M, Yamashita M, Yamauchi K. et al. Inhibiting nerve growth factor or its receptors downregulates calcitonin gene-related peptide expression in rat lumbar dorsal roog ganglia innervating injured intervertebral discs. J Orthop Res. 2010;28:1614–1620. doi: 10.1002/jor.21170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S, Skorpen F. Variation in the COMT gene: implications for pain perception and pain treatment. Pharmaco Economics. 2009;10:669–684. doi: 10.2217/pgs.09.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubieta J-K, Heitzeg MM, Smith YR, Bueller JA, Xu K, Xu Y. et al. COMT val158met genotype affects u-opioid neurotransmitter responses to a pain stressor. Science. 2003;299:1240–1243. doi: 10.1126/science.1078546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigante A, Bevilacqua C, Pagnotta A, Manzotti S, Toesca A, Greco F. Expression of NGF, Trka and p75 in human cartilage. Eur J Histochem. 2003;47:339–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abe Y, Akeda K, An HS, Aoki Y, Pichika R, Muehleman C. et al. Proinflammatory cytokines stimulate the expression of nerve growth factor by human intervertebral disc cells. Spine. 2007;32:635–642. doi: 10.1097/01.brs.0000257556.90850.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruber HE, Hoelscher GL, Bethea S, Hanley EN. Interleukin 1b exposure significantly upregulates neurotrophin gene expression for brain-derived neurotrophic factor, neurotrophin 3 and neuropilin 2 during 3D culture of human annulus cells. Spine J. 2011;11(10S):33S–34S. [Google Scholar]
- Emerich DF, Winn SR, Hantraye PM, Peschanski M, Chen C-Y, McDermott PBEE. et al. Protective effect of encapsulated cells producing neurotrophic factor CNTF in a monkey model of Huntington's disease. Nature. 1997;386:395–399. doi: 10.1038/386395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbin GG, Manthorpe MM, Varon SS. Purification of the chick eye ciliary neuronotrophic factor. J Neurochem. 1984;43:1468–1478. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb05410.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Lopez MJ, Alcantara S, Mascarno C, Perez-Branguli F, Ruiz-Lozano P, Maes T. et al. Mouse neuron navigator 1, a novel microtubule-associated protein involved in neuronal migration. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2005;28:599–612. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2004.09.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muley PD, McNeill EM, Marzinke MA, Knobel KM, Barr MM, Clagett-Dame M. The atRA-responsive gene neuron navigator 2 functions in neurite outgrowth and axonal elongation. Dev Neurobiol. 2008;68:1441–1453. doi: 10.1002/dneu.20670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodkin AL, Levengood DV, Rowe EG, Tai Y-T, Giger RJ, Ginty DD. Neuropilin is a semaphorin III receptor. Cell. 1997;90:753–762. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80535-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tessier-Lavigne M, Goodman CS. The molecular biology of axon guidance. Science. 1996;274:1123–1133. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5290.1123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd T, Brose K, Mitchell KJ, Fetter RD, Tessier-Lavigne M, Goodman CS. et al. Roundabout controls axon crossing of the CNS midline and defines a novel subfamily of evolutionarily conserved guidance receptors. Cell. 1998;92:205–215. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80915-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spillmann AA, Bandtlow CE, Lottspeich F, Keller F, Schwab ME. Identification and characterization of a bovine neurite growth inhibitor (bNI-220) J Biol Chem. 1998;273:19283–19293. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.30.19283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akyol S, Senel Eraslan B, Etyemez H, Tanriverdi T, Hanci M. Catabolic cytokine expressions in patients with degenerative disc disease. Turkish Neurosurg. 2010;20:492–499. doi: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.3394-10.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyland JA, Le Maitre C, Freemont AJ. Investigation of the role of IL-1 and TNF in matrix degradation in the intervertebral disc. Rheumatol. 2008;47:809–814. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/ken056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shamji MF, Setton LA, Jarvin W, So S, Chen J, Jing L. et al. Proinflammatory cytokine expression profiles in degenerated and herniated human intervertebral disc tissue. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:1974–1982. doi: 10.1002/art.27444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabr MA, Jing L, Helbling AR, Sinclair M, Allen KD, Shamji MF. et al. Interleukin-17 synergizes with IFNg or TNFa to promote inflammatory mediator release and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) expression in human intervertebral disc cells. J Orthop Res. 2011;29:1–7. doi: 10.1002/jor.21206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeMaitre CL, Hoyland JA, Freemont AJ. Catabolic cytokine expression in degenerate and herniated human intervertebral discs: IL-1ß and TNFa expression profile. 2007. http://arthritis-research.com/content/9/4/R77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sommer C, Kress M. Recent findings on how proinflammatory cytokines cause pain: peripheral mechanisms in inflammatory and neuropathic hyperalgesia. Neurosci Lett. 2004;361:184–187. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2003.12.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boddeke EW. Involvement of chemokines in pain. Eur J Pharmacol. 2001;429:115–119. doi: 10.1016/S0014-2999(01)01311-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson C, Undem B, Bullock B, Winchurch RA. Neuropeptide regulation of proinflammatory cytokine responses. J Leukocyte Biol. 1998;63:602–605. doi: 10.1002/jlb.63.5.602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon HJ, Kim JH, Lee HS, Chotai S, Kang JD, Suh JK, Park YK. Annulus fibrosus cells interact with neuron-like cells to modulate production of growth factors and cytokines in symptomatic disc degeneration. Spine. 2012;37:2–9. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e31820cd2d8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki Y, Ohtori S, Ino H, Duoya H, Ozawa T, Saito T. et al. Disc inflammation potentially promotes axonal regeneration of dorsal root ganglion neurons innervating lumbar intervertebral disc in rats. Spine. 2004;29:2621–2626. doi: 10.1097/01.brs.0000146051.11574.b4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee JM, Song JY, Baek M, Jung H-Y, Kang H, Han IB. et al. Interleukin-1b induces angiogenesis and innervation in human intervertebral disc degeneration. J Orthop Res. 2011;29:265–269. doi: 10.1002/jor.21210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich JA, Liebenberg EC, Thuillier DU, Lotz JC. ISSLS Prize Winner: Repeated disc injury causes persistent inflammation. Spine. 2007;32:2812–2819. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e31815b9850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaible HG, Schmelz M, Tegeder I. Pathophysiology and treatment of pain in joint disease. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2006;58:323–342. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2006.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oegema TRJ, Johnson SL, Aguiar DJ, Ogilvie JW. Fibronectin and its fragments increase with degeneration in the human intervertebral disc. Spine. 2000;25:2742–2747. doi: 10.1097/00007632-200011010-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nerlich AG, Bachmeier BE, Boos N. Expression of fibronectin and TGF-b1 mRNA and protein suggest altered regulation of extracellular matrix in degenerated disc tissue. Eur Spine J. 2005;14:7–26. doi: 10.1007/s00586-004-0745-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson DG, Li X, Balian G. A fibronectin fragment alters the metabolism by rabbit intervertebral disc cells in vitro. Spine. 2005;30:1242–1246. doi: 10.1097/01.brs.0000164097.47091.4c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xia M, Zhu Y. Fibronectin fragment activation of ERK increasing integrin a5 and b1 subunit expression to degenerate nucleus pulposus cells. J Orthop Res. 2011;29:556–561. doi: 10.1002/jor.21273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aota Y, An HS, Homandberg G, Thonar EJMA, Andersson GBJ, Pichika R. et al. Differential effects of fibronectin fragment on proteoglycan metabolism by intervertebral disc cells: A comparison with articular chondrocytes. Spine. 2005;30:722–728. doi: 10.1097/01.brs.0000157417.59933.db. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulai JI, Chen H, Im H-J, Kumar S, Hanning C, Hegde PS. et al. NF-kB mediates the stimulation of cytokine and chemokien expression by human articular chondrocytes in response to fibronectin fragments. J Immunol. 2005;174:5781–5788. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.9.5781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson JP, Pearce RH, Schechter MT, Adams ME, Tsang IKY, Bishop PB. Preliminary evaluation of a scheme for grading the gross morphology of the human intervertebral disc. Spine. 1990;15:411–415. doi: 10.1097/00007632-199005000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]