Abstract
The complete amino acid sequence of th variable (V) region of the mu heavy chain of a human IgM immunoglobulin (Cam) has been determined. The strategy for sequence determination involved sequenator analysis of the CNBr cleavage products of the succinylated carboxymethylated Fab mu fragment, and of tryptic peptides of the CNBr polypeptides and thermolytic subpeptides. The variable region of this heavy chain (VH) belongs to the VHIII subgroup; it has greater than 70% homology with other VHIII sequences and contains the VHIII marker peptide, Phe-Thr-Ile-Ser-Arg (residues 67-71). As more sequences have been published, the number of subgroup-specific residues has diminished to the point that no position is absolutely subgroup specific. An analysis of the available human VH sequences in the V/C switch region showed the likelihood of a human JH segment (residues 101-113) analogous to the J segments in mouse light chains. The JH region is highly conserved, has striking homology to proposed mouse JH regions, and has significant homology to known mouse J lambda and J kappa segments.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adetugbo K., Milstein C., Secher D. S. Molecular analysis of spontaneous somatic mutants. Nature. 1977 Jan 27;265(5592):299–304. doi: 10.1038/265299a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amzel L. M., Poljak R. J. Three-dimensional structure of immunoglobulins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:961–997. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard O., Hozumi N., Tonegawa S. Sequences of mouse immunoglobulin light chain genes before and after somatic changes. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1133–1144. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brack C., Hirama M., Lenhard-Schuller R., Tonegawa S. A complete immunoglobulin gene is created by somatic recombination. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90078-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capra J. D., Kehoe J. M. Hypervariable regions, idiotypy, and the antibody-combining site. Adv Immunol. 1975;20:1–40. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60205-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper S. M., Franklin E. C., Frangione B. Molecular defect in a gamma-2 heavy chain. Science. 1972 Apr 14;176(4031):187–189. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4031.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D. R., Padlan E. A., Segal D. M. Three-dimensional structure of immunoglobulins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:639–667. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.003231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florent G., Lehman D., Lockhart D., Putnam F. W. Identity of the Fc fragments of pathological and normal human immunoglobulin M. Biochemistry. 1974 Jul 30;13(16):3372–3381. doi: 10.1021/bi00713a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
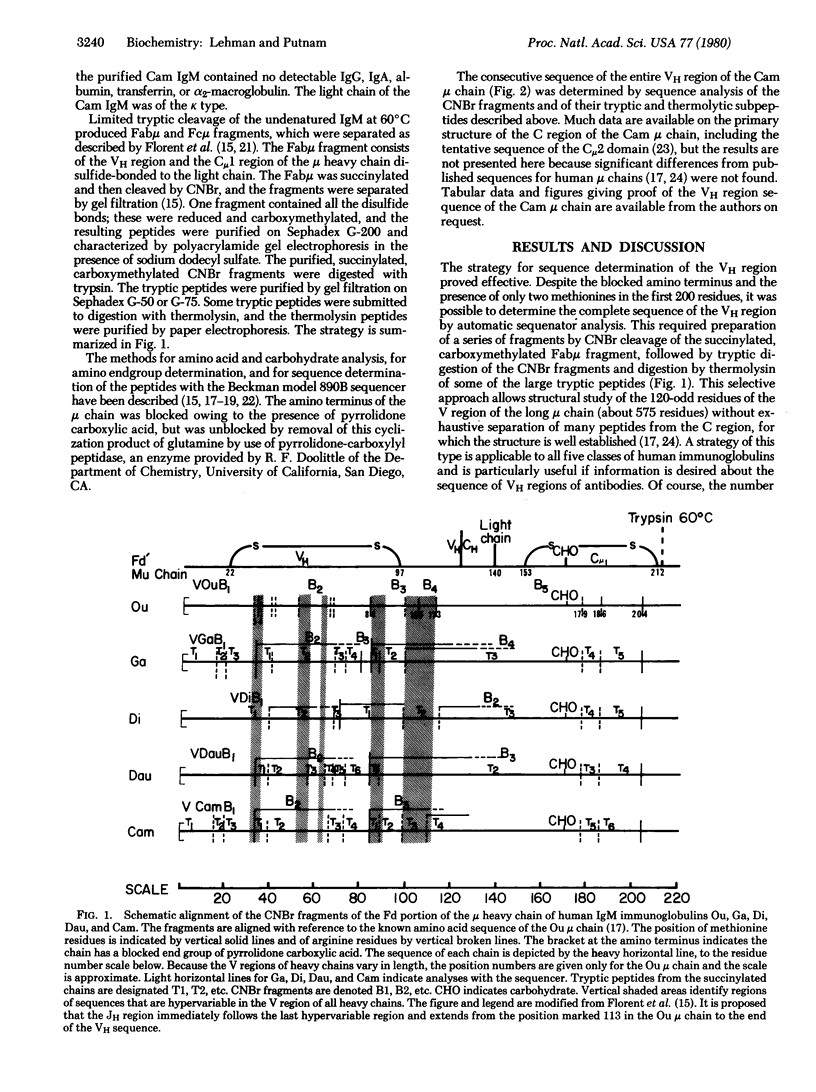
- Florent G., Lehman D., Putnam F. W. The switch point in mu heavy chains of human IgM immunoglobulins. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2482–2498. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin E. C., Prelli F., Frangione B. Human heavy chain disease protein WIS: implications for the organization of immunoglobulin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):452–456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabat E. A., Wu T. T., Bilofsky H. Variable region genes for the immunoglobulin framework are assembled from small segments of DNA--a hypothesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2429–2433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler H., Shimizu A., Paul C., Putnam F. W. Macroglobulin structure: variable sequence of light and heavy chains. Science. 1970 Jul 3;169(3940):56–59. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3940.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler H., Shimizu A., Paul C., Moore V., Putnam F. W. Three variable-gene pools common to IgM, IgG and IgA immunoglobulins. Nature. 1970 Sep 26;227(5265):1318–1320. doi: 10.1038/2271318a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y. S., Low T. L., Infante A., Putnam F. W. Complete covalent structure of a human IgA1 immunoglobulin. Science. 1976 Sep 10;193(4257):1017–1020. doi: 10.1126/science.821146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y. S., Putnam F. W. Primary structure of a human IgA1 immunoglobulin. I. Isolation, composition, and amino acid sequence of the chymotryptic peptides. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2839–2849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Max E. E., Seidman J. G., Leder P. Sequences of five potential recombination sites encoded close to an immunoglobulin kappa constant region gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3450–3454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putnam F. W., Florent G., Paul C., Shinoda T., Shimizu A. Complete amino acid sequence of the Mu heavy chain of a human IgM immunoglobulin. Science. 1973 Oct 19;182(4109):287–291. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4109.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putnam F. W., Titani K., Whitley E., Jr Chemical structure of light chains: amino acid sequence of type K Bence-Jones proteins. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1966 Nov 22;166(1003):124–137. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1966.0088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao D. N., Rudikoff S., Krutzsch H., Potter M. Structural evidence for independent joining region gene in immunoglobulin heavy chains from anti-galactan myeloma proteins and its potential role in generating diversity in complementarity-determining regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2890–2894. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakano H., Rogers J. H., Hüppi K., Brack C., Traunecker A., Maki R., Wall R., Tonegawa S. Domains and the hinge region of an immunoglobulin heavy chain are encoded in separate DNA segments. Nature. 1979 Feb 22;277(5698):627–633. doi: 10.1038/277627a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schilling J., Clevinger B., Davie J. M., Hood L. Amino acid sequence of homogeneous antibodies to dextran and DNA rearrangements in heavy chain V-region gene segments. Nature. 1980 Jan 3;283(5742):35–40. doi: 10.1038/283035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidman J. G., Leder A., Nau M., Norman B., Leder P. Antibody diversity. Science. 1978 Oct 6;202(4363):11–17. doi: 10.1126/science.99815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toraño A., Putnam F. W. Complete amino acid sequence of the alpha 2 heavy chain of a human IgA2 immunoglobulin of the A2m (2) allotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):966–969. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker P. W., Marcu K. B., Newell N., Richards J., Blattner F. R. Sequence of the cloned gene for the constant region of murine gamma 2b immunoglobulin heavy chain. Science. 1979 Dec 14;206(4424):1303–1306. doi: 10.1126/science.117549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. C., Fudenberg H. H., Pink J. R. Heavy-chain variable regions in normal and pathological immunolobulins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1143–1146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe S., Barnikol H. U., Horn J., Bertram J., Hilschmann N. Die Primärstruktur eines monoklonalen IgM-Immunoglobulins (Makroglobulin Gal.), II. Die Aminosäuresequenz der H-Kette (mu-Typ,Subgruppe HIII), Struktur des gesamten IgM-Moleküls. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1973 Oct-Nov;354(10-11):1505–1509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigert M., Gatmaitan L., Loh E., Schilling J., Hood L. Rearrangement of genetic information may produce immunoglobulin diversity. Nature. 1978 Dec 21;276(5690):785–790. doi: 10.1038/276785a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]