Abstract
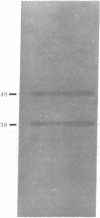
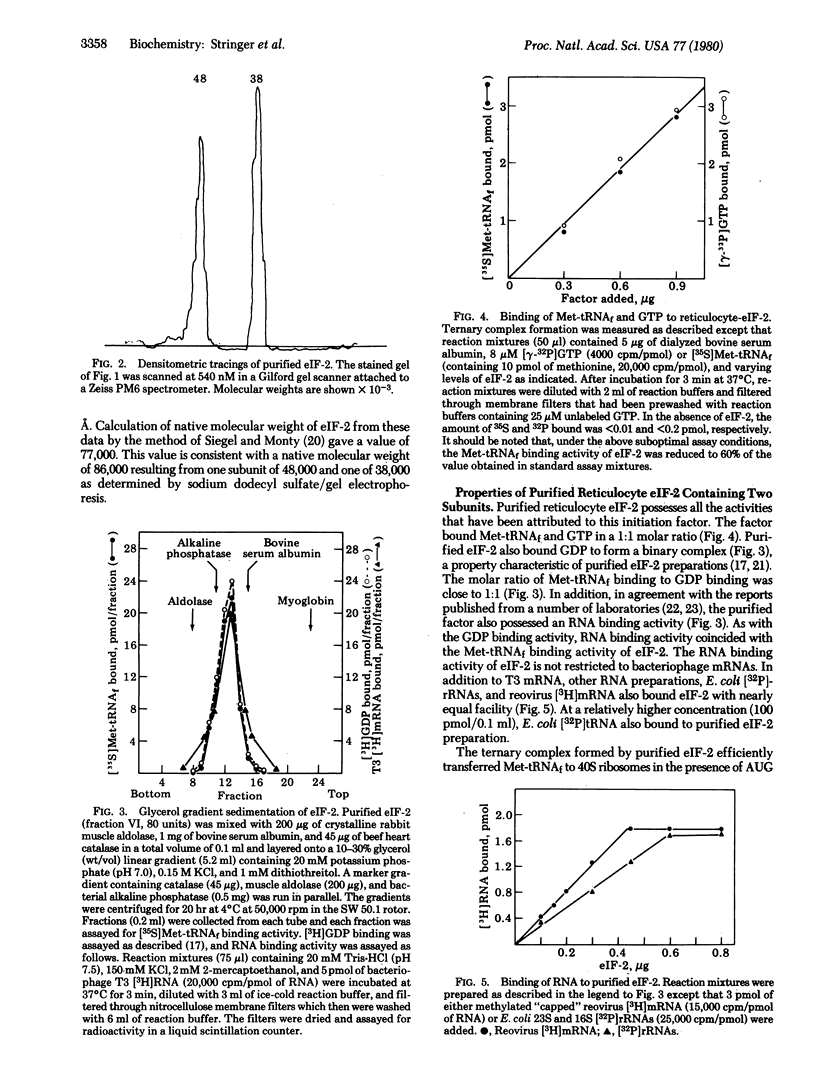
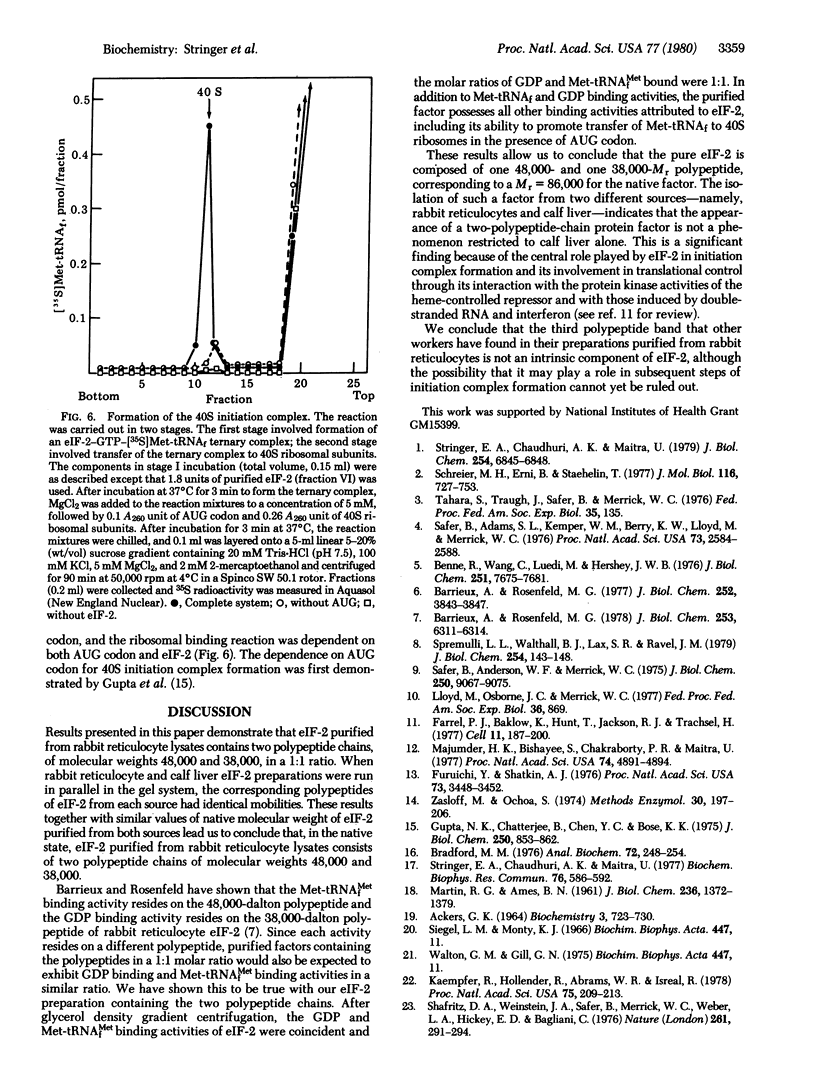
Eukaryotic initiation factor 2 (eIF-20) purified from rabbit reticulocyte lysates consists of equimolar amounts of two polypeptide chains of Mr 48,000 and 38,000. Determination of the molecular weight of the native factor gave a value which is consistent with a Mr of 86,000 indicating that the factor is composed of one Mr 48,000 and one Mr 38,000 polypeptide. The purified factor exhibited all the binding activities characteristic of eIF-2. The factor formed ternary complexes with Met-tRNAfMet and GTP; it bound GDP to form a binary complex; and it also possessed the property of binding a wide variety of RNA species, including reoviral mRNA, phage T3 mRNA, rRNAs, and tRNA. Furthermore, the ternary complex formed by purified eIF-2 interacted with the 40S ribosomal subunit in the presence of AUG codon to form a 40S initiation complex. These results indicate that all binding activities attributed to eIF-2 are contained in the 48,000- and 38,000-dalton polypeptides.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ACKERS G. K. MOLECULAR EXCLUSION AND RESTRICTED DIFFUSION PROCESSES IN MOLECULAR-SIEVE CHROMATOGRAPHY. Biochemistry. 1964 May;3:723–730. doi: 10.1021/bi00893a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali S. Y. Analysis of matrix vesicles and their role in the calcification of epiphyseal cartilage. Fed Proc. 1976 Feb;35(2):135–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrieux A., Rosenfeld M. G. Characterization of GTP-dependent Met-tRNAf binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3843–3847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrieux A., Rosenfeld M. G. mRNA-induced dissociation of initiation factor 2. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 25;253(18):6311–6314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benne R., Wong C., Luedi M., Hershey J. W. Purification and characterization of initiation factor IF-E2 from rabbit reticulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 10;251(23):7675–7681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Balkow K., Hunt T., Jackson R. J., Trachsel H. Phosphorylation of initiation factor elF-2 and the control of reticulocyte protein synthesis. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):187–200. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90330-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi Y., Shatkin A. J. Differential synthesis of blocked and unblocked 5'-termini in reovirus mRNA: effect of pyrophosphate and pyrophosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3448–3452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta N. K., Chatterjee B., Chen Y. C., Majumdar A. Protein synthesis in rabbit reticulocytes. A study of Met-tRNA f Met binding factor(s) and Met-tRNA f Met binding to ribosomes and AUG codon. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 10;250(3):853–862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaempfer R., Hollender R., Abrams W. R., Israeli R. Specific binding of messenger RNA and methionyl-tRNAfMet by the same initiation factor for eukaryotic protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):209–213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majumder H. K., Bishayee S., Chakraborty P. R., Maitra U. Ribonuclease III cleavage of bacteriophage T3RNA polymerase transcripts to late T3 mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4891–4894. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safer B., Adams S. L., Kemper W. M., Berry K. W., Lloyd M., Merrick W. C. Purification and characterization of two initiation factors required for maximal activity of a highly fractionated globin mRNA translation system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2584–2588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safer B., Anderson W. F., Merrick W. C. Purification and physical properties of homogeneous initiation factor MP from rabbit reticulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1975 Dec 10;250(23):9067–9075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier M. H., Erni B., Staehelin T. Initiation of mammalian protein synthesis. I. Purification and characterization of seven initiation factors. J Mol Biol. 1977 Nov;116(4):727–753. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90268-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafritz D. A., Weinstein J. A., Safer B., Merrick W. C., Weber L. A., Hickey E. D., Baglioni C. Evidence for role of m7G5'-phosphate group in recognition of eukaryotic mRNA by initiation factor IF-M3. Nature. 1976 May 27;261(5558):291–294. doi: 10.1038/261291a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spremulli L. L., Walthall B. J., Lax S. R., Ravel J. M. Partial purification of the factors required for the initiation of protein synthesis in wheat germ. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 10;254(1):143–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer E. A., Chaudhuri A., Maitra U. Association of a GDP binding activity with initiation factor eIF-2 from calf liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 May 23;76(2):586–592. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90764-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer E. A., Chaudhuri A., Maitra U. Purified eukaryotic initiation factor 2 from calf liver consists of two polypeptide chains of 48,000 and 38,000 daltons. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):6845–6848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton G. M., Gill G. N. Preferential regulation of protein synthesis initiation complex formation by purine nucleotides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 20;447(1):11–19. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zasloff M., Ochoa S. Purification of eukaryotic initiation factor 1 (EIF1) from Artemia salina embryos. Methods Enzymol. 1974;30:197–206. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)30022-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]