Abstract
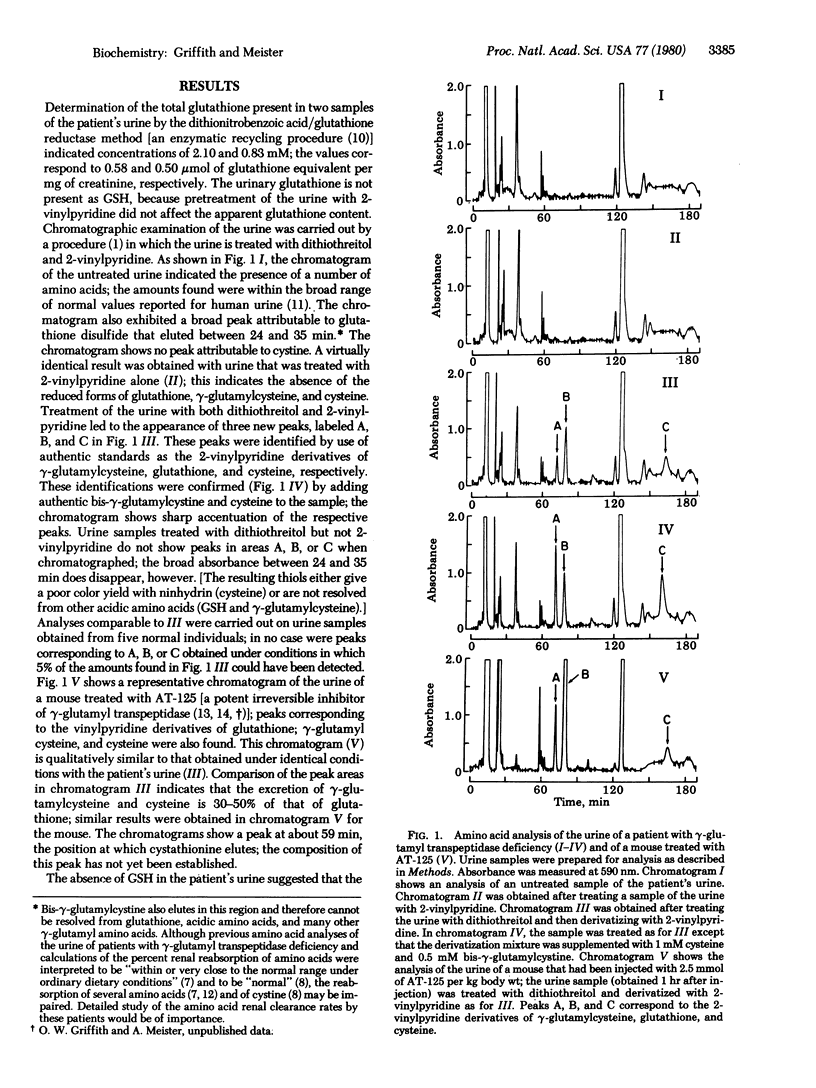
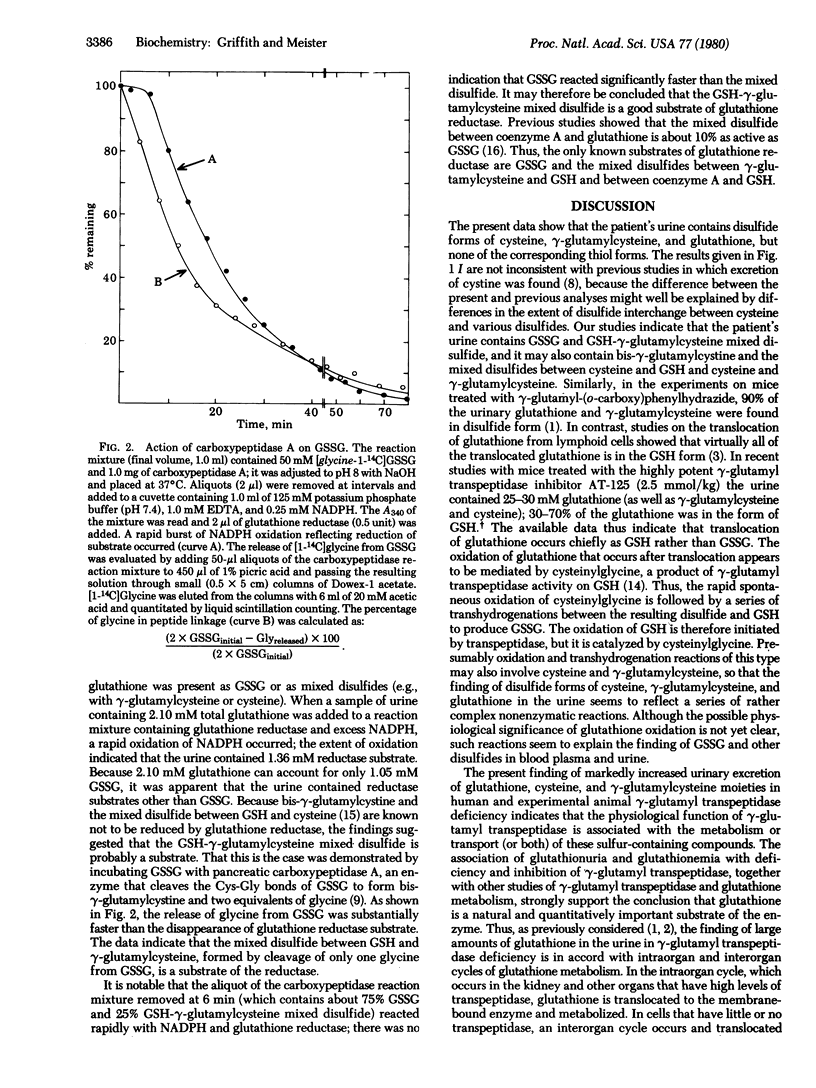
Animals treated with potent gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase inhibitors and a patient with severe gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase deficiency excrete much larger than normal amounts of glutathione, gamma-glutamylcysteine, and cysteine in their urine; these compounds were found in disulfide forms. The findings indicate that the metabolic function of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase is associated with the metabolism or transport (or both) of cysteine, gamma-glutamylcysteine, and glutathione, and that gamma-glutamylcysteine is a physiological substrate of the enzyme. The occurrence of gamma-glutamylcysteine in urine and other considerations suggest that this dipeptide is formed as an extracellular metabolite of glutathione in addition to its recognized role as an intrcellular precursor of glutathione. The dipeptide may be formed by a pathway involving transpeptidation or by cleavage of the Cys-Gly bond of glutathione. In the course of this work it was found that the mixed disulfide between glutathione and gamma-glutamylcysteine is a good substrate of glutathione reductase.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen L., Meck R., Yunis A. The inhibition of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase from human pancreatic carcinoma cells by (alpha S,5S)-alpha-amino-3-chloro-4,5-dihydro-5-isoxazoleacetic acid (AT-125; NSC-163501). Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1980 Jan;27(1):175–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlberg I., Mannervik B. Purification by affinity chromatography of yeast glutathione reductase, the enzyme responsible for the NADPH-dependent reduction of the mixed disulfide of coenzyme A and glutathione. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Oct 13;484(2):268–274. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(77)90083-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S. H., Wilken D. R. Participation of the unsymmetrical disulfide of coenzyme A and glutathione in an enzymatic sulfhydryl-disulfide interchange. I. Partial purification and properties of the bovine kidney enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1966 Sep 25;241(18):4251–4260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith O. W., Bridges R. J., Meister A. Evidence that the gamma-glutamyl cycle functions in vivo using intracellular glutathione: effects of amino acids and selective inhibition of enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5405–5408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith O. W., Bridges R. J., Meister A. Transport of gamma-glutamyl amino acids: role of glutathione and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6319–6322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith O. W., Meister A. Glutathione: interorgan translocation, turnover, and metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5606–5610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith O. W., Meister A. Translocation of intracellular glutathione to membrane-bound gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase as a discrete step in the gamma-glutamyl cycle: glutathionuria after inhibition of transpeptidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):268–272. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith O. W., Novogrodsky A., Meister A. Translocation of glutathione from lymphoid cells that have markedly different gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2249–2252. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagenfeldt L., Arvidsson A., Larsson A. Glutathione and gamma-glutamylcysteine in whole blood, plasma and erythrocytes. Clin Chim Acta. 1978 Apr 17;85(2):167–173. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(78)90236-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häberle D., Wahlländer A., Sies H. Assessment of the kidney function in maintenance of plasma glutathione concentration and redox state in anaesthetized rats. FEBS Lett. 1979 Dec 15;108(2):335–340. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80558-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister A., Tate S. S. Glutathione and related gamma-glutamyl compounds: biosynthesis and utilization. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:559–604. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman J. D., Goodman S. I., Mace J. W., Patrick A. D., Tietze F., Butler E. J. Glutathionuria: inborn error of metabolism due to tissue deficiency of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jul 8;65(1):68–74. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80062-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sies H., Koch O. R., Martino E., Boveris A. Increased biliary glutathione disulfide release in chronically ethanol-treated rats. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jul 15;103(2):287–290. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81346-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson G. A., Meister A. Utilization of L-cystine by the gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase-gamma-glutamyl cyclotransferase pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):1985–1988. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tietze F. Enzymic method for quantitative determination of nanogram amounts of total and oxidized glutathione: applications to mammalian blood and other tissues. Anal Biochem. 1969 Mar;27(3):502–522. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90064-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright E. C., Stern J., Ersser R., Patrick A. D. Glutathionuria: gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase deficiency. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1980;2(1):3–7. doi: 10.1007/BF01805554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



