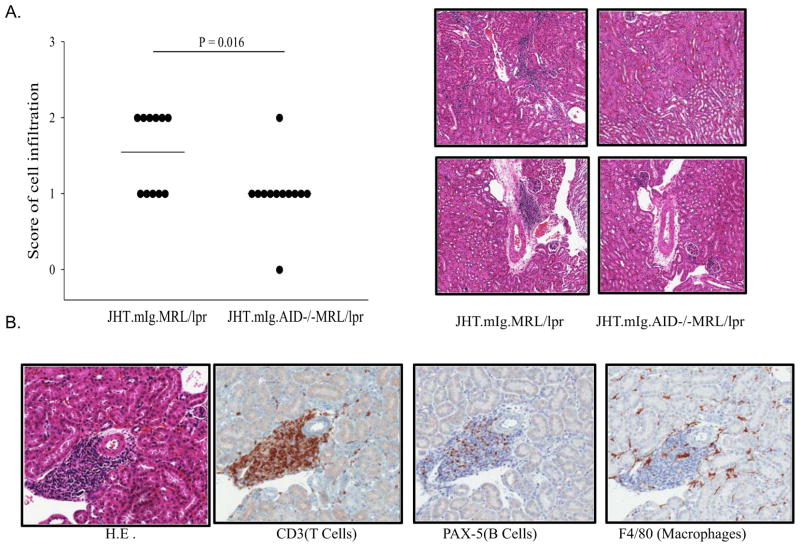
Figure 3.
AID deficiency correlated with a decrease in interstitial T cell infiltration in the kidneys. (A) AID deficiency correlated with a reduction in infiltration of inflammatory cells in the renal interstitium. Each dot represents data from one mouse. JHT.mIg.MRL/lpr mice (N= 11) and JHT.mIg.AID−/−MRL/lpr mice (N = 12) at 5~6 months of age were used. The H&E stain of kidney sections were from representative JHT.mIg.MRL/lpr and AID-deficient counterparts. B. The majority of Infiltrated cells in the renal interstitium were T cells, with some B cells and a few macrophages. The stain of H&E, CD3, PAX5, and F4/80 in kidney sections were from a representative JHT.mIg.MRL/lpr mouse from the same study in (A). Mann-Whitney Rank Sum Test was performed.