Abstract
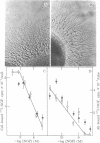
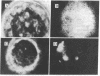
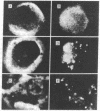
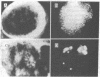
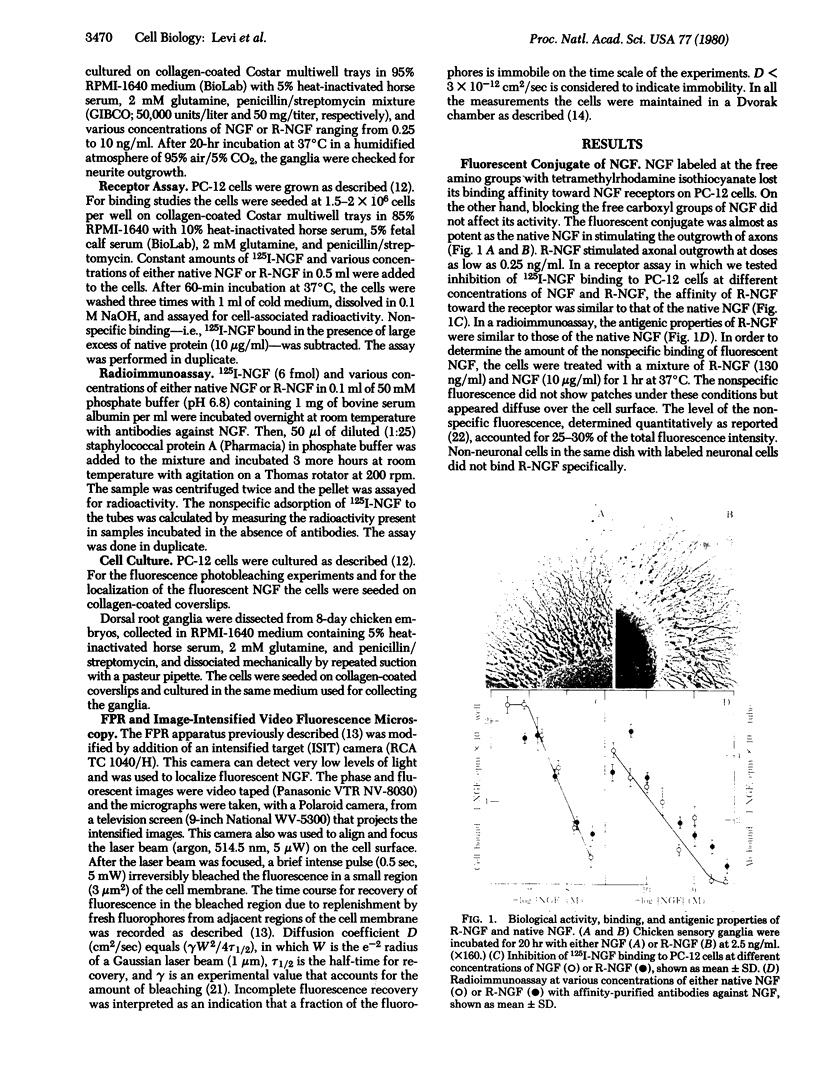
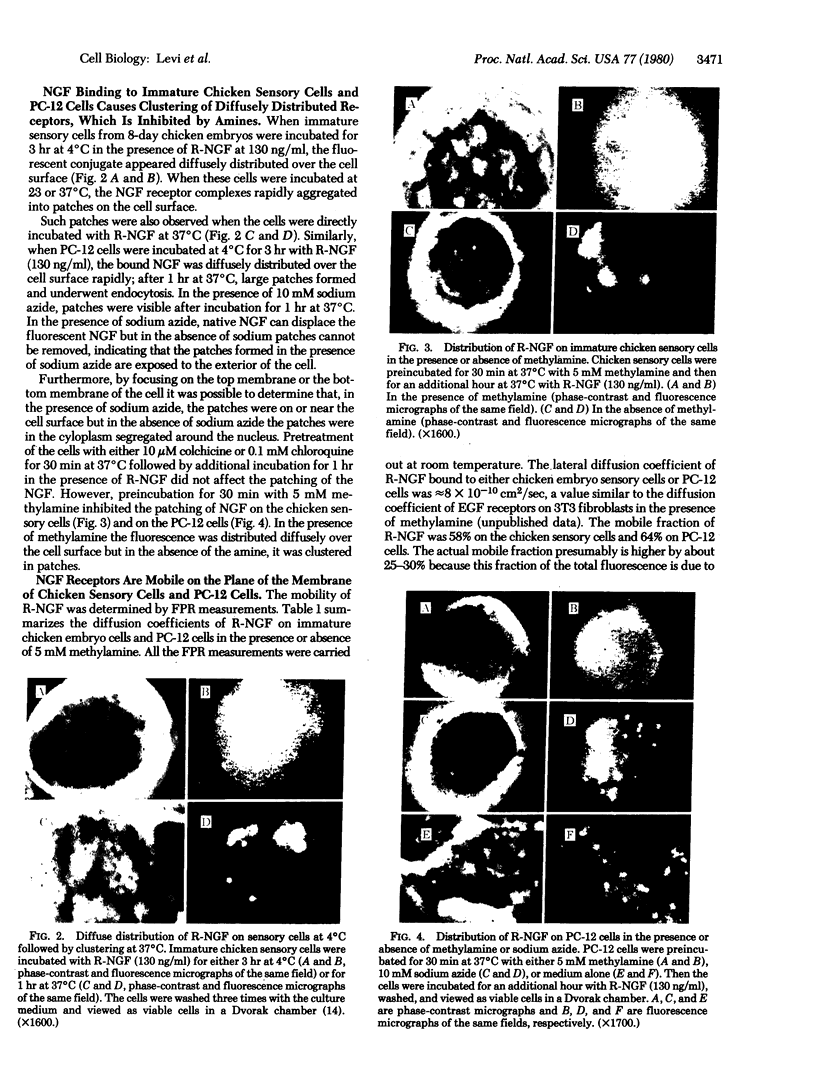
We have prepared a fluorescent conjugate of nerve growth factor (NGF) containing 8--10 rhodamine molecules attached to free carboxyl groups of the protein. This analogue retained full binding capacity toward NGF receptors, full antigenic properties, and the potency to stimulate the differentiation of embryonal chicken sensory ganglia cells in vitro. We have used this analogue to study the mobility and distribution of NGF receptors on embryonal chicken sensory cells from dorsal root ganglia and on a pheochromocytoma cell line (PC-12) that responds to NGF by differentiating along a neuronal pathway. The rhodamine conjugate of nerve growth factor (R-NGF) binds initially to diffusely distributed mobile receptors (D approximately 8 X 10(-10) cm2/sec) on immature sensory and PC-12 cells. At 37 degrees C, the NGF receptor complexes cluster and form immobile visible patches. These patches undergo endocytosis in a process that consumes metabolic energy. Methylamine blocks the formation of visible patches of NGF and the receptors remain dispersed and mobile at 37 degrees C. On differentiated chicken sensory cells, R-NGF binds to diffusely distributed mobile receptors and to aggregated immobile binding sites. These clusters are localized at the tip of the axon, along the axon, and in the main body. The NGF molecules that are internalized at the tip of the axon are transported retrogradely from the peripherey to the cell body.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andres R. Y., Jeng I., Bradshaw R. A. Nerve growth factor receptors: identification of distinct classes in plasma membranes and nuclei of embryonic dorsal root neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2785–2789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelrod D., Koppel D. E., Schlessinger J., Elson E., Webb W. W. Mobility measurement by analysis of fluorescence photobleaching recovery kinetics. Biophys J. 1976 Sep;16(9):1055–1069. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85755-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelrod D., Ravdin P., Koppel D. E., Schlessinger J., Webb W. W., Elson E. L., Podleski T. R. Lateral motion of fluorescently labeled acetylcholine receptors in membranes of developing muscle fibers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4594–4598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocchini V., Angeletti P. U. The nerve growth factor: purification as a 30,000-molecular-weight protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Oct;64(2):787–794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.2.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calissano P., Monaco G., Castellani L., Mercanti D., Levi A. Nerve growth factor potentiates actomyosin adenosinetriphosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2210–2214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. 125I-labeled human epidermal growth factor. Binding, internalization, and degradation in human fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1976 Oct;71(1):159–171. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Anderson R. G., Brown M. S. Coated pits, coated vesicles, and receptor-mediated endocytosis. Nature. 1979 Jun 21;279(5715):679–685. doi: 10.1038/279679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorden P., Carpentier J. L., Cohen S., Orci L. Epidermal growth factor: morphological demonstration of binding, internalization, and lysosomal association in human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5025–5029. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Tischler A. S. Establishment of a noradrenergic clonal line of rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells which respond to nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendry I. A., Stöckel K., Thoenen H., Iversen L. L. The retrograde axonal transport of nerve growth factor. Brain Res. 1974 Mar 15;68(1):103–121. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90536-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horii Z. I., Varon S. Nerve growth factor action on membrane permeation to exogenous substrates in dorsal root ganglionic dissociates from the chick embryo. Brain Res. 1977 Mar 18;124(1):121–133. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90868-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koppel D. E., Axelrod D., Schlessinger J., Elson E. L., Webb W. W. Dynamics of fluorescence marker concentration as a probe of mobility. Biophys J. 1976 Nov;16(11):1315–1329. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85776-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVI-MONTALCINI R., MEYER H., HAMBURGER V. In vitro experiments on the effects of mouse sarcomas 180 and 37 on the spinal and sympathetic ganglia of the chick embryo. Cancer Res. 1954 Jan;14(1):49–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R., Angeletti P. U. Nerve growth factor. Physiol Rev. 1968 Jul;48(3):534–569. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1968.48.3.534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R. The nerve growth factor: its mode of action on sensory and sympathetic nerve cells. Harvey Lect. 1966;60:217–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxfield F. R., Schlessinger J., Shechter Y., Pastan I., Willingham M. C. Collection of insulin, EGF and alpha2-macroglobulin in the same patches on the surface of cultured fibroblasts and common internalization. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):805–810. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90336-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxfield F. R., Willingham M. C., Davies P. J., Pastan I. Amines inhibit the clustering of alpha2-macroglobulin and EGF on the fibroblast cell surface. Nature. 1979 Feb 22;277(5698):661–663. doi: 10.1038/277661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKanna J. A., Haigler H. T., Cohen S. Hormone receptor topology and dynamics: morphological analysis using ferritin-labeled epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5689–5693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J., Shechter Y., Cuatrecasas P., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. Quantitative determination of the lateral diffusion coefficients of the hormone-receptor complexes of insulin and epidermal growth factor on the plasma membrane of cultured fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5353–5357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shechter Y., Schlessinger J., Jacobs S., Chang K. J., Cuatrecasas P. Fluorescent labeling of hormone receptors in viable cells: preparation and properties of highly fluorescent derivatives of epidermal growth factor and insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2135–2139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein S. C., Steinman R. M., Cohn Z. A. Endocytosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:669–722. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.003321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skaper S. D., Bottenstein J. E., Varon S. Effects of nerve growth factor on cyclic AMP levels in embryonic chick dorsal root ganglia following factor deprivation. J Neurochem. 1979 Jun;32(6):1845–1851. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb02299.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenen H., Angeletti P. U., Levi-Montalcini R., Kettler R. Selective induction by nerve growth factor of tyrosine hydroxylase and dopamine- -hydroxylase in the rat superior cervical ganglia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jul;68(7):1598–1602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.7.1598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yankner B. A., Shooter E. M. Nerve growth factor in the nucleus: interaction with receptors on the nuclear membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1269–1273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]