Abstract
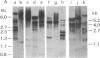
The genome of Mus musculus contains multiple copies (500 -1000) of DNA sequences related to the 35S RNA of intracisternal type A particles (IAPs). Using labeled IAP RNA as a probe in blot-hybridization experiments, we have identified a characteristic electrophoretic pattern of reactive fragments generated by restriction endonuclease cleavage of mouse DNA. From the genomic blots, we deduced a composite restriction map for a 6.5- to 7-kilobase (kb) DNA region containing sequences homologous to the IAP RNA. Units of this type appeared to be interspersed without obvious regularity in nonhomologous flanking regions. A 5.2-kb segment of this unit was inserted directly into plasmid pBR322 from HindIII/EcoRI digest of mouse DNA. The fragment was cloned and then labeled by nick-translation and used to scan a mouse embryo gene library (average 16-kb inserts in lambda Charon 4A); 1% of the library samples hybridized, confirming the extensive reiteration of IAP genetic units. Among six different library isolates containing 6.5- to 7-kb IAP units, some restriction sites were highly conserved whereas others varied in both occurrence and position. Despite this variation, heteroduplexes between the individual isolates showed continuous IAP homology regions of 7 kb. No flanking region homologies were seen in this limited sample. Some evidence suggests that mouse DNA may contain other dispersed sequence elements related to but smaller than the genetic unit defined above.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berstine E. G., Hooper M. L., Grandchamp S., Ephrussi B. Alkaline phosphatase activity in mouse teratoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3899–3903. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callahan R., Benveniste R. E., Sherr C. J., Schidlovsky G., Todaro G. J. A new class of genetically transmitted retravirus isolated from Mus cervicolor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3579–3583. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callahan R., Sherr C. J., Todaro G. J. A new class of murine retroviruses: immunological and biochemical comparison of novel isolates from Mus cervicolor and Mus caroli. Virology. 1977 Jul 15;80(2):401–406. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(77)80015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cory S., Adams J. M. A very large repeating unit of mouse DNA containing the 18S, 28S and 5.8S rRNA genes. Cell. 1977 Aug;11(4):795–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90292-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrlinger H., Anzil A. P., Stavrou D., Heumann R., Hamprecht B., Blinzinger K. Intracisternal A and C particles in mouse neurons: a thin-section study of normal trigeminal ganglion and C1300 neuroblastoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Dec;55(6):1473–1475. doi: 10.1093/jnci/55.6.1473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuff E. L., Callahan R., Howk R. S. Immunological relationship between the structural proteins of intracisternal A-particles of Mus musculus and the M432 retrovirus of Mus cervicolor. J Virol. 1980 Mar;33(3):1211–1214. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.3.1211-1214.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuff E. L., Lueders K. K., Scolnick E. M. Nucleotide sequence relationship between intracisternal type A particles of Mus musculus and an endogenous retrovirus (M432) of Mus cervicolor. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):66–74. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.66-74.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lueders K. K., Kuff E. L. Genetic individuality of intracisternal A-particles of Mus musculus. J Virol. 1979 Apr;30(1):225–231. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.1.225-231.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lueders K. K., Kuff E. L. Sequences associated with intracisternal A particles are reiterated in the mouse genome. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):963–972. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90161-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lueders K. K., Segal S., Kuff E. L. RNA sequences specifically associated with mouse intracisternal A particles. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):83–94. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90319-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Hardison R. C., Lacy E., Lauer J., O'Connell C., Quon D., Sim G. K., Efstratiadis A. The isolation of structural genes from libraries of eucaryotic DNA. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):687–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgard M. V., Keem K., Monahan J. J. Factors affecting the transformation of Escherichia coli strain chi1776 by pBR322 plasmid DNA. Gene. 1978 Jul;3(4):279–292. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90038-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson B. M., Segal S., Lueders K. K., Kuff E. L. RNA associated with murine intracisternal type A particles codes for the main particle protein. J Virol. 1978 Jul;27(1):118–126. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.1.118-126.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice N. R., Straus N. A. Relatedness of mouse satellite deoxyribonucleic acid to deoxyribonucleic acid of various Mus species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3546–3550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. pBR322 restriction map derived from the DNA sequence: accurate DNA size markers up to 4361 nucleotide pairs long. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Aug;5(8):2721–2728. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.8.2721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Gillespie D. Preparative and analytical purification of DNA from agarose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):615–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. G., Blattner F. R. Construction and characterization of the hybrid bacteriophage lambda Charon vectors for DNA cloning. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):555–575. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.555-575.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wivel N. A., Smith G. H. Distribution of intracisternal A-particles in a variety of normal and neoplastic mouse tissues. Int J Cancer. 1971 Jan 15;7(1):167–175. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910070119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong-Staal F., Reitz M. S., Jr, Trainor C. D., Gallo R. C. Murine intracisternal type A particles: a biochemical characterization. J Virol. 1975 Oct;16(4):887–896. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.4.887-896.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. S., Wivel N. A. Analysis of high-molecular-weight ribonucleic acid associated with intracisternal A particles. J Virol. 1973 Feb;11(2):287–298. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.2.287-298.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. S., Wivel N. A. Intracisternal A particle-specific DNA sequences in mammary tumor cells, hybrids, and cybrids derived from laboratory mice and from feral mice of Mus musculus and Mus cervicolor. Virology. 1979 Jul 15;96(1):166–176. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90182-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. S., Wivel N. A. Physicochemical analysis of the deoxyribonucleic acid product of murine intracisternal A particle RNA-directed DNA polymerase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 4;447(2):167–174. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90340-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]