Abstract
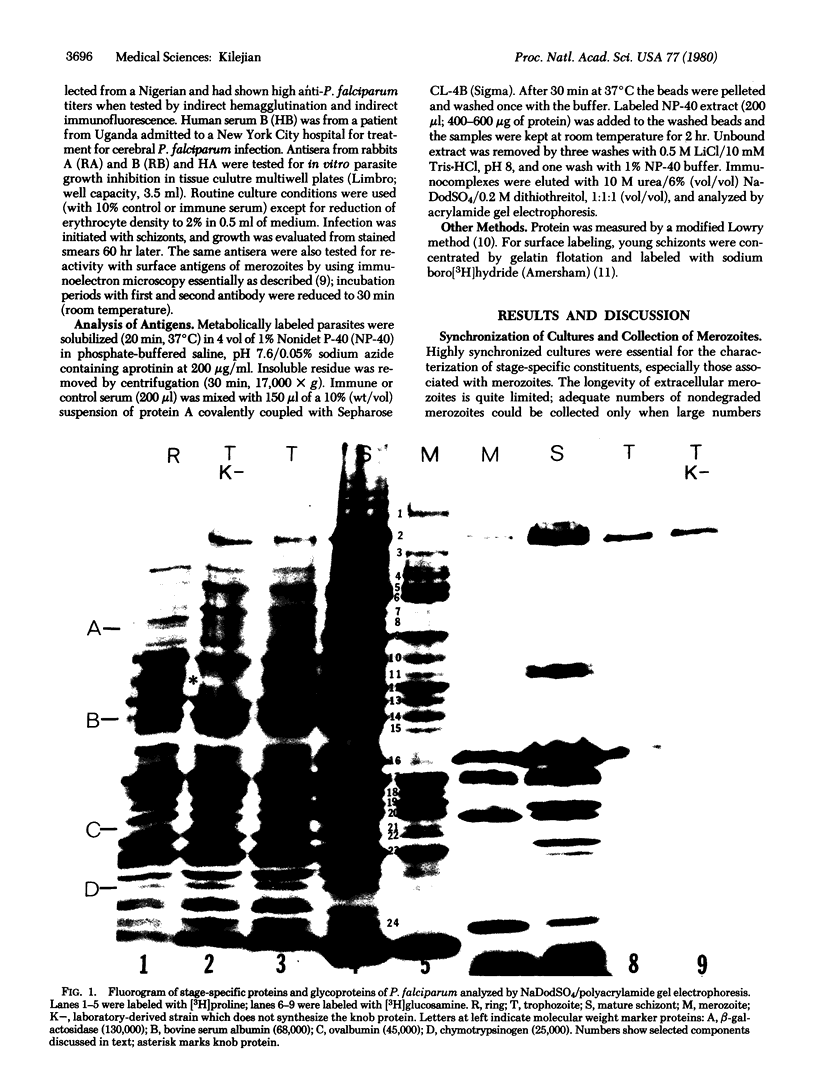
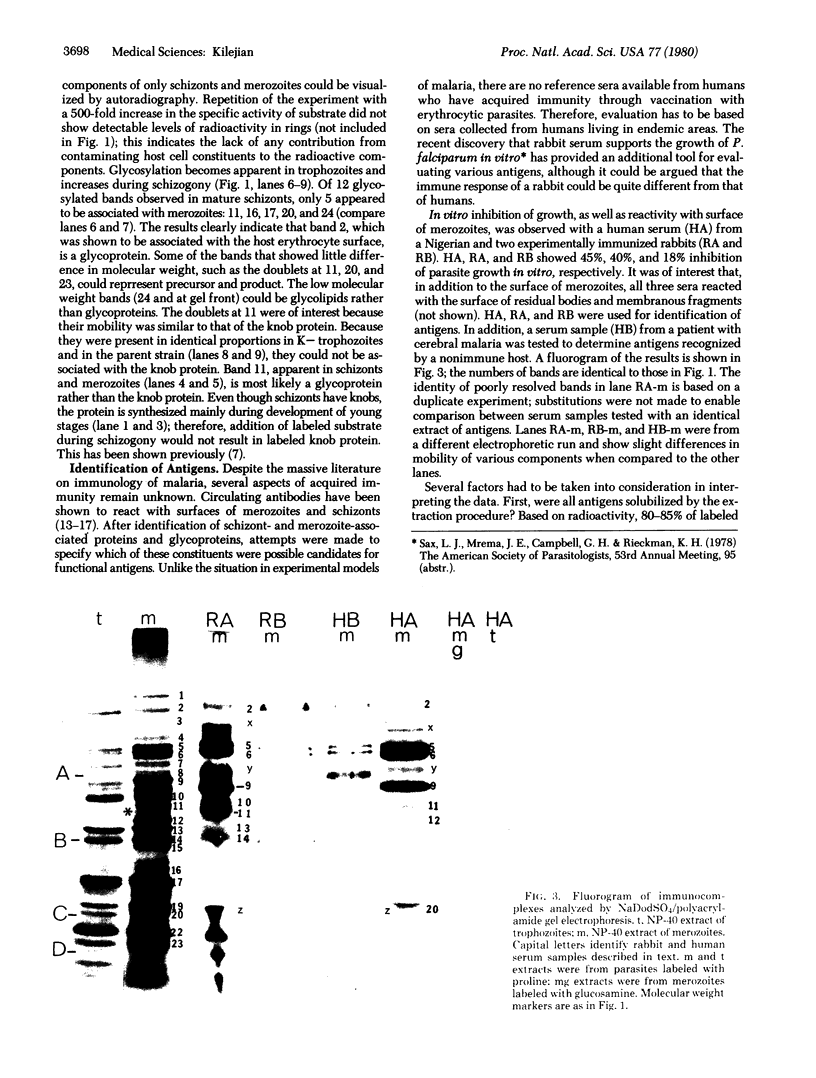
Establishment of highly synchronized cultures of Plasmodium falciparum enabled identification of stage-specific proteins, glycoproteins, and antigens. Comparison of metabolically labeled constituents of rings, trophozoites, mature schizonts, and merozoites indicated the absence of major proteins or glycorproteins unique to rings or trophozoites. A burst of new synthetic activity occurred during schizogony when several schizont- and merozoite-specific proteins and glycoproteins became apparent. In addition to the knob protein, which was previously shown to be associated with protrusions on the host erythrocyte membrane, a major glycoprotein of parasite origin was identified on the surface membrane of schizonts. Analysis of antigens solubilized from different developmental stages indicated that immune sera, which inhibit growth of parasites in vitro, react mainly with merozoite- and schizont-associated antigens.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. N., Brown I. N., Hills L. A. Immunity to malaria. I. Protection against Plasmodium knowlesi shown by monkeys sensitized with drug-suppressed infections or by dead parasites in Freund's adjuvant. Exp Parasitol. 1970 Oct;28(2):304–317. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(70)90101-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabantchik Z. I., Balshin M., Breuer W., Markus H., Rothstein A. A comparison of intact human red blood cells and resealed and leaky ghosts with respect to their interactions with surface labelling agents and proteolytic enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 8;382(4):621–633. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90227-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Butcher G. A., Mitchell G. H., Deans J. A., Langhorne J. Acquired immunity and vaccination in malaria. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1977 Nov;26(6 Pt 2):223–232. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1977.26.223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deans J. A., Dennis E. D., Cohen S. Antigenic analysis of sequential erythrocytic stages of Plasmodium knowlesi. Parasitology. 1978 Dec;77(3):333–344. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000050290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartree E. F. Determination of protein: a modification of the Lowry method that gives a linear photometric response. Anal Biochem. 1972 Aug;48(2):422–427. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen J. B. Concentration from continuous culture of erythrocytes infected with trophozoites and schizonts of Plasmodium falciparum. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1978 Nov;27(6):1274–1276. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1978.27.1274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilejian A. A unique histidine-rich polypeptide from the malaria parasite, Plasmodium lophurae. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 25;249(14):4650–4655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilejian A., Abati A., Trager W. Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium coatneyi: immunogenicity of "knob-like protrusions" on infected erythrocyte membranes. Exp Parasitol. 1977 Jun;42(1):157–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(77)90073-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilejian A. Characterization of a protein correlated with the production of knob-like protrusions on membranes of erythrocytes infected with Plasmodium falciparum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4650–4653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambros C., Vanderberg J. P. Synchronization of Plasmodium falciparum erythrocytic stages in culture. J Parasitol. 1979 Jun;65(3):418–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langreth S. G., Reese R. T. Antigenicity of the infected-erythrocyte and merozoite surfaces in Falciparum malaria. J Exp Med. 1979 Nov 1;150(5):1241–1254. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.5.1241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langreth S. G., Reese R. T., Motyl M. R., Trager W. Plasmodium falciparum: loss of knobs on the infected erythrocyte surface after long-term cultivation. Exp Parasitol. 1979 Oct;48(2):213–219. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(79)90101-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. H., Aikawa M., Dvorak J. A. Malaria (Plasmodium knowlesi) merozoites: immunity and the surface coat. J Immunol. 1975 Apr;114(4):1237–1242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reese R. T., Trager W., Jensen J. B., Miller D. A., Tantravahi R. Immunization against malaria with antigen from Plasmodium falciparum cultivated in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5665–5668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Ullrich R., Wallach D. F., Lightholder J. Two Plasmodium knowlesi-specific antigens on the surface of schizont-infected Rhesus monkey erythrocytes induce antibody production in immune hosts. J Exp Med. 1979 Jul 1;150(1):86–99. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.1.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui W. A., Taylor D. W., Kan S. C., Kramer K., Richmond-Crum S. M., Kotani S., Shiba T., Kusumoto S. Vaccination of experimental monkeys against Plasmodium falciparum: a possible safe adjuvant. Science. 1978 Sep 29;201(4362):1237–1239. doi: 10.1126/science.99814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson G. L., Schenkel R. H., Silverman P. H. Vaccination of rhesus monkeys against malaria by use of sucrose density gradient fractions of Plasmodium knowlesi antigens. Nature. 1974 Feb 1;247(5439):304–305. doi: 10.1038/247304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trager W., Jensen J. B. Human malaria parasites in continuous culture. Science. 1976 Aug 20;193(4254):673–675. doi: 10.1126/science.781840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]