Abstract
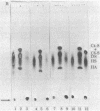
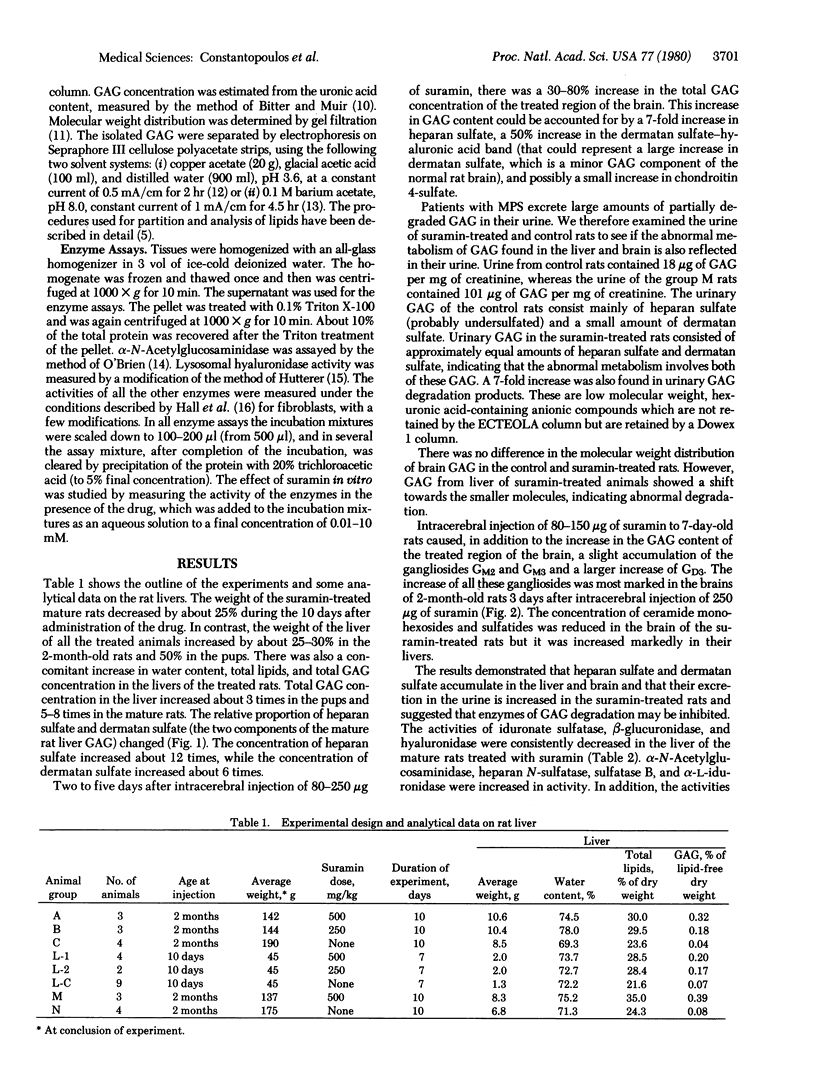
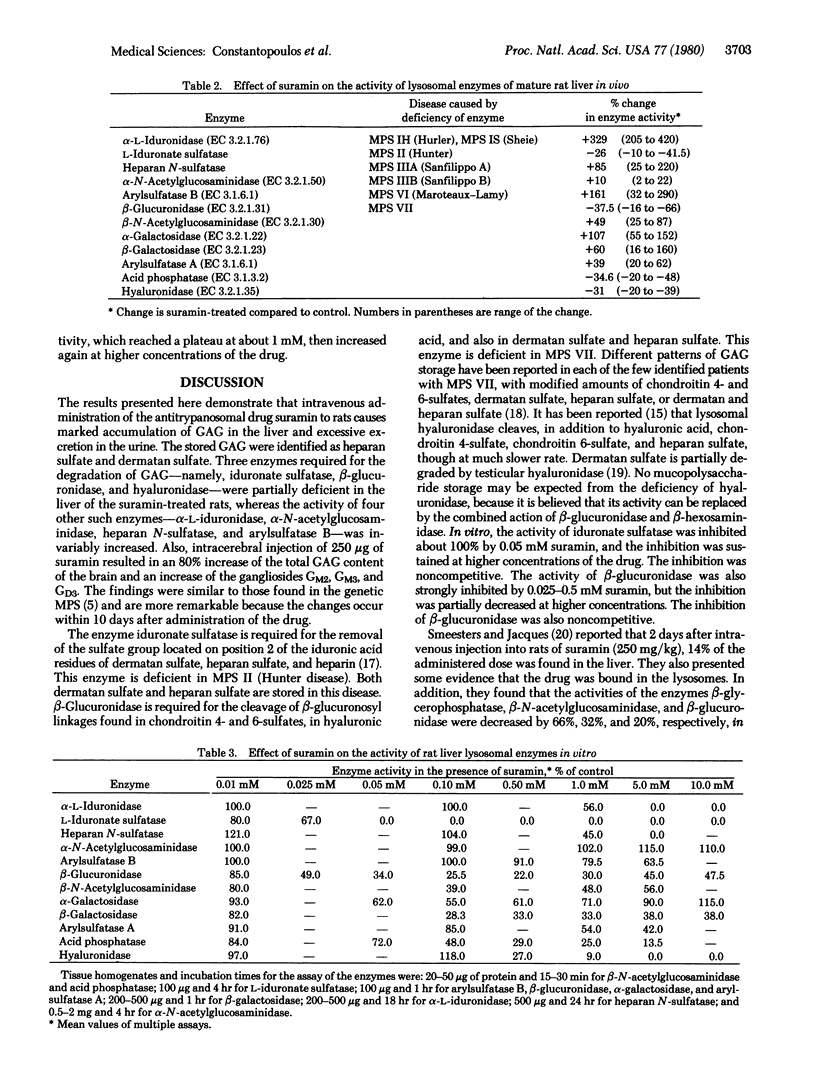
Intracerebral injection of the trypanocidal drug suramin in rats caused the formation of membranous neuronal and neuroglial inclusions. Here we show that intravenous administration suramin, 500 mg/kg, to 2-month-old rats causes a 5- to 8-fold increase of glycosaminoglycan concentration in the liver within 10 days and a 6-fold increase in urinary glycosaminoglycan excertion. The excess glycosaminoglycans consist of heparan sulfate and dermatan sulfate. Intracerebral injection of 250 micrograms of suramin results in a small increase of glycosaminoglycan and larger increase of ganglioside GM2, GM3, and GD3 concentrations in the treated region of the brain. The activities of the lysosomal enzymes iduronate sulfatase, beta-glucuronidase, and hyaluronidase in the liver of the suramin-treated mature rats were consistently decreased, whereas those of alpha-L-iduronidase, heparan N-sulfatase, arylsulfatase B, and others were considerably increased. The activity of iduronate sulfatase was completely inhibited in vitro by suramin at concentrations of 50 microM or higher. The activity of beta-glucuronidase was also strongly inhibited by low concentrations of suramin, but this inhibition was partially decreased at higher concentrations of the drug. The inhibition of both enzymes by suramin was noncompetitive. The suramin-treated rat may be a useful experimental animal model of mucopolysaccharidosis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BITTER T., MUIR H. M. A modified uronic acid carbazole reaction. Anal Biochem. 1962 Oct;4:330–334. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(62)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach G., Eisenberg F., Jr, Cantz M., Neufeld E. F. The defect in the Hunter syndrome: deficiency of sulfoiduronate sulfatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):2134–2138. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.2134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady R. O., O'Brien J. S., Bradley R. M., Gal A. E. Sphingolipid hydrolases in brain tissue of patients with generalized gangliodosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jun 9;210(1):193–195. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90079-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. S. Comparative biochemistry and drug design for infectious disease. Science. 1979 Sep 7;205(4410):964–971. doi: 10.1126/science.382357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constantopoulos G., Dekaban A. S., Carroll W. R. Determination of molecular weight distribution of acid mucopolysaccharides by sephadex gel filtration. Anal Biochem. 1969 Oct 1;31(1):59–70. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90241-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constantopoulos G., Dekaban A. S. Neurochemistry of the mucopolysaccharidoses: brain lipids and lysosomal enzymes in patients with four types of mucopolysaccharidosis and in normal controls. J Neurochem. 1978 May;30(5):965–973. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb12388.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constantopoulos G., McComb R. D., Dekaban A. S. Neurochemistry of the mucopolysaccharidoses: brain glycosaminoglycans in normals and four types of mucopolysaccharidoses. J Neurochem. 1976 May;26(5):901–908. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb06471.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorfman A., Matalon R. The mucopolysaccharidoses (a review). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):630–637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fransson L. A., Rodén L. Structure of dermatan sulfate. I. Degradation by testicular hyaluronidase. J Biol Chem. 1967 Sep 25;242(18):4161–4169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. W., Liebaers I., Di Natale P., Neufeld E. F. Enzymic diagnosis of the genetic mucopolysaccharide storage disorders. Methods Enzymol. 1978;50:439–456. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(78)50048-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hata R., Nagai Y. A rapid and micro method for separation of acidic glycosaminoglycans by two-dimensional electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1972 Feb;45(2):462–468. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90208-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutterer F. Degradation of mucopolysaccharides by hepatic lysosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 28;115(2):312–319. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90430-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kampine J. P., Kanfer J. N., Gal A. E., Bradley R. M., Brady R. O. Response of sphingolipid hydrolases in spleen and liver to increased erythrocytorhexis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Feb 14;137(1):135–139. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(67)90016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder I. G. Radioactive substrates for iduronate sulfatase and alpha-L-iduronidase. Methods Enzymol. 1978;50:150–154. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(78)50013-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd J. B., Beck F. Lysosomes and congenital malformations. Biochem J. 1969 Dec;115(5):32P–34P. doi: 10.1042/bj1150032p. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld E. F., Lim T. W., Shapiro L. J. Inherited disorders of lysosomal metabolism. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:357–376. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.002041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien J. S. Sanfilippo syndrome: profound deficiency of alpha-acetylglucosaminidase activity in organs and skin fibroblasts from type-B patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1720–1722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees S. Membranous neuronal and neuroglial inclusions produced by intracerebral injection of Suramin. J Neurol Sci. 1978 Mar;36(1):97–109. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(78)90164-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVENNERHOLM L. CHROMATOGRAPHIC SEPARATION OF HUMAN BRAIN GANGLIOSIDES. J Neurochem. 1963 Sep;10:613–623. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1963.tb08933.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanovich V., Gore I. A micromethod for the determination of acid mucopolysaccharides in vascular tissue. J Chromatogr. 1967 Dec;31(2):473–478. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)86097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuchmann-Duplessis H., Mercier-Parot L. Influence de la suramine sur la survie péri-natale et post-natale de la souris. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1973;167(12):1717–1721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]