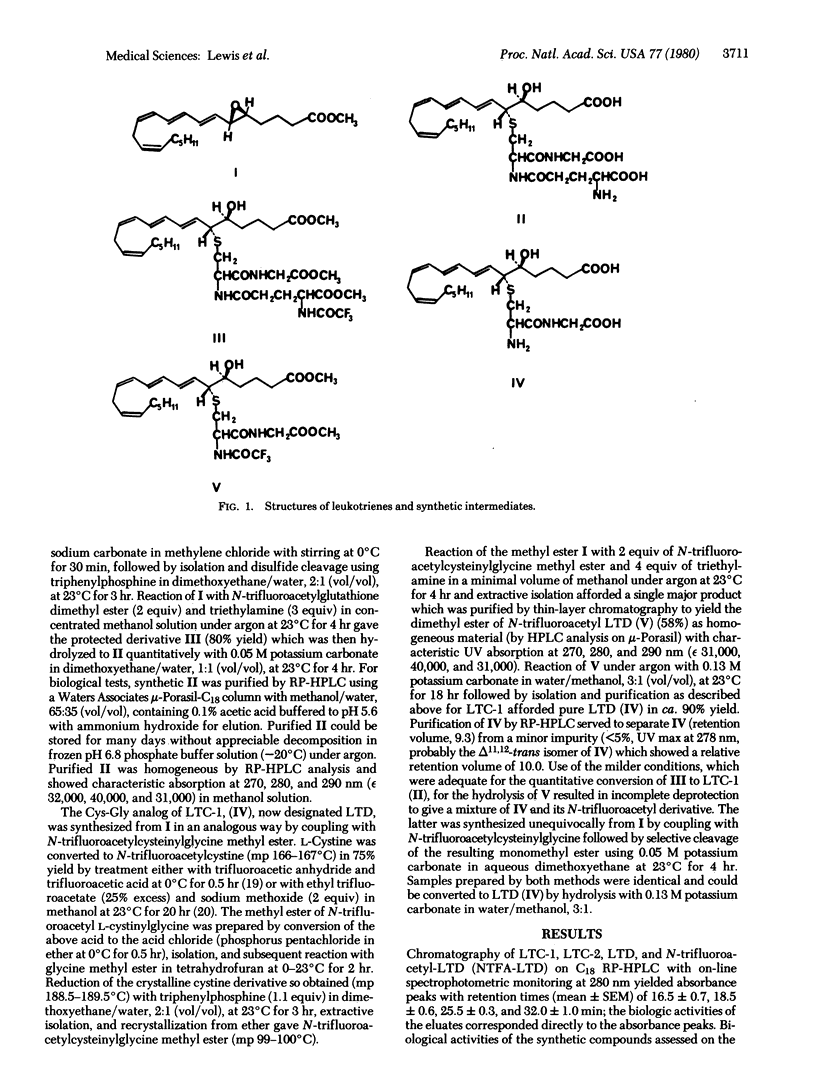
Abstract
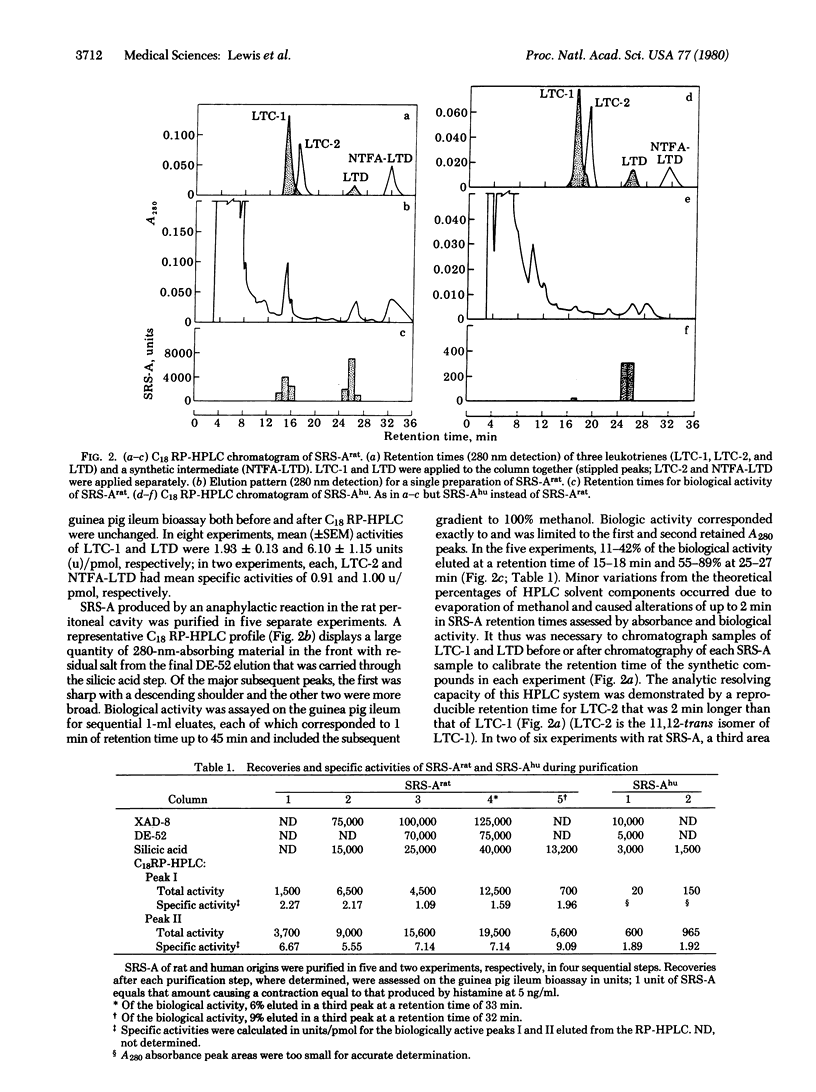
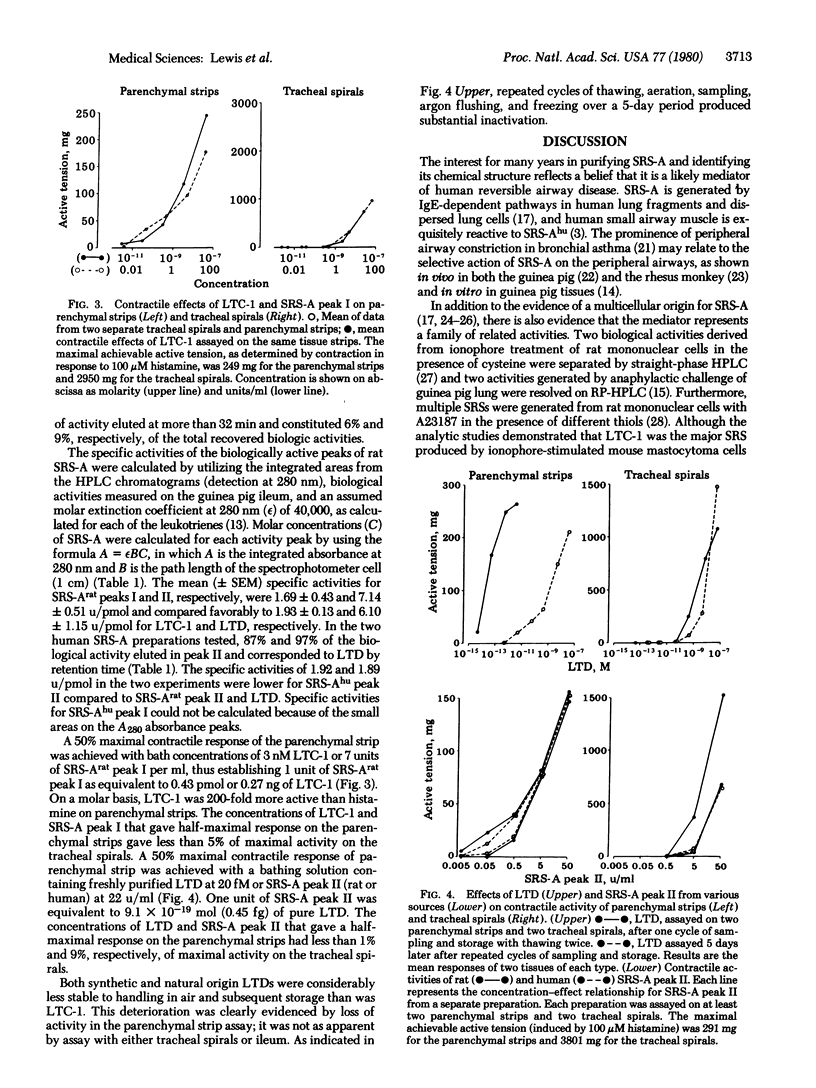
Slow reacting substance(s) of anaphylaxis (SRS-A) was isolated from both human (lung) and rat sources and compared with three synthetic SRS-As of known structure—leukotrienes (LTs) C-1, C-2, and D. Reversed-phase liquid chromatography was used both as a final purification step and a means of comparison of biologically derived and synthetic substances. Two major peaks of SRS-A activity of both rat and human origin corresponded chromatographically with LTC-1 and LTD, respectively, and had equivalent specific activities on the guinea pig ileum. With guinea pig ileum, the specific activities (units/pmol) for synthetic leukotrienes and anaphylactic peaks were (mean ± SEM): synthetic LTC-1, 1.93 ± 0.13; SRS-Arat peak I, 1.69 ± 0.43; synthetic LTD, 6.10 ± 1.15; SRS-Arat peak II, 7.14 ± 0.51; and SRS-Ahu peak II, 1.90. Both synthetic LTC-1 and LTD and their SRS-A natural counterparts had a preferential contractile activity on guinea pig peripheral airway compared to central airways and were at least 200 times more active than histamine on peripheral airways on a molar basis. Leukotriene D is the major SRS-A of human lung and accounts for almost all of the biological activity. It likely is formed from leukotriene C-1 in vivo by an enzymic process of the well-known γ-glutamyltransferase type.
Keywords: human lung, rat peritoneal leukocytes, peripheral airways, synthetic leukotrienes
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROCKLEHURST W. E. Occurrence of an unidentified substance during anaphylactic shock in cavy lung. J Physiol. 1953 Apr 28;120(1-2):16P–17P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROCKLEHURST W. E. Slow reacting substance and related compounds. Prog Allergy. 1962;6:539–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach M. K., Brashler J. R., Brooks C. D., Neerken A. J. Slow reacting substances: comparison of some properties of human lung SRS-A and two distinct fractions from ionophore-induced rat mononuclear cell SRS. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):160–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach M. K., Brashler J. R., Gorman R. R. On the structure of slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis: evidence of biosynthesis from arachidonic acid. Prostaglandins. 1977 Jul;14(1):21–38. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(77)90154-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach M. K., Brashler J. R. In vivo and in vitro production of a slow reacting substance in the rat upon treatment with calcium ionophores. J Immunol. 1974 Dec;113(6):2040–2044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drazen J. M., Austen K. F. Effects of intravenous administration of slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxis, histamine, bradykinin, and prostaglandin F2alpha on pulmonary mechanics in the guinea pig. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jun;53(6):1679–1685. doi: 10.1172/JCI107719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drazen J. M., Lewis R. A., Wasserman S. I., Orange R. P., Austen K. F. Differential effects of a partially purified preparation of slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxis on guinea pig tracheal spirals and parenchymal strips. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jan;63(1):1–5. doi: 10.1172/JCI109262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drazen J. M., Schneider M. W. Comparative responses of tracheal spirals and parenchymal strips to histamine and carbachol in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jun;61(6):1441–1447. doi: 10.1172/JCI109063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarström S., Murphy R. C., Samuelsson B., Clark D. A., Mioskowski C., Corey E. J. Structure of leukotriene C. Identification of the amino acid part. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Dec 28;91(4):1266–1272. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91203-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakschik B. A., Falkenhein S., Parker C. W. Precursor role of arachidonic acid in release of slow reacting substance from rat basophilic leukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4577–4581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. A., Goetzl E. J., Wasserman S. I., Valone F. H., Rubin R. H., Austen K. F. The release of four mediators of immediate hypersensitivity from human leukemic basophils. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 1):87–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. A., Wasserman S. I., Goetzi E. J., Austen K. F. Formation of slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxis in human lung tissue and cells before release. J Exp Med. 1974 Nov 1;140(5):1133–1146. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.5.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden E. R. The chronicity of acute attacks of asthma--mechanical and therapeutic implications. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1975 Jul;56(1):18–26. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(75)90030-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister A., Tate S. S. Glutathione and related gamma-glutamyl compounds: biosynthesis and utilization. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:559–604. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michoud M. C., Pare P. D., Orange R. P., Hogg J. C. Airway sensitivity to slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxis, histamine, and antigen in Ascaris sensitive monkeys. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Mar;119(3):419–424. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.119.3.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris H. R., Taylor G. W., Piper P. J., Sirois P., Tippins J. R. Slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxis: purification and characterisation. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 15;87(2):203–206. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80332-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse H. C., 3rd, Bloch K. J., Austen K. F. Biologic properties of rat antibodies. II. Time-course of appearance of antibodies involved in antigen-induced release of slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis (SRS-A rat); association of this activity with rat IgGa. J Immunol. 1968 Oct;101(4):658–663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy R. C., Hammarström S., Samuelsson B. Leukotriene C: a slow-reacting substance from murine mastocytoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4275–4279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orange R. P., Chang P. L. The effect of thiols on immunologic release of slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis. I. Human lung. J Immunol. 1975 Oct;115(4):1072–1077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orange R. P., Murphy R. C., Austen K. F. Inactivation of slow reacting substance of anaphylaxins (SRS-A) by arylsulfatases. J Immunol. 1974 Jul;113(1):316–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orange R. P., Murphy R. C., Karnovsky M. L., Austen K. F. The physicochemical characteristics and purification of slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxis. J Immunol. 1973 Mar;110(3):760–770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orange R. P., Stechschulte D. J., Austen K. F. Immunochemical and biologic properties of rat IgE. II. Capacity to mediate the immunologic releas of histamine an slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxis (SRS-A). J Immunol. 1970 Nov;105(5):1087–1095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orning L., Hammarström S., Samuelsson B. Leukotriene D: a slow reacting substance from rat basophilic leukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2014–2017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson N. A., Wasserman S. I., Said J. W., Austen K. F. Release of chemical mediators from partially purified human lung mast cells. J Immunol. 1976 Oct;117(4):1356–1362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



