Abstract
Truncated light-harvesting antenna 1 (TLA1) is a nuclear gene proposed to regulate the chlorophyll (Chl) antenna size in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. The Chl antenna size of the photosystems and the chloroplast ultrastructure were manipulated upon TLA1 gene over-expression and RNAi downregulation. The TLA1 over-expressing lines possessed a larger chlorophyll antenna size for both photosystems and contained greater levels of Chl b per cell relative to the wild type. Conversely, TLA1 RNAi transformants had a smaller Chl antenna size for both photosystems and lower levels of Chl b per cell. Western blot analyses of the TLA1 over-expressing and RNAi transformants showed that modulation of TLA1 gene expression was paralleled by modulation in the expression of light-harvesting protein, reaction centre D1 and D2, and VIPP1 genes. Transmission electron microscopy showed that modulation of TLA1 gene expression impacts the organization of thylakoid membranes in the chloroplast. Over-expressing lines showed well-defined grana, whereas RNAi transformants possessed loosely held together and more stroma-exposed thylakoids. Cell fractionation suggested localization of the TLA1 protein in the inner chloroplast envelope and potentially in association with nascent thylakoid membranes, indicating a role in Chl antenna assembly and thylakoid membrane biogenesis. The results provide a mechanistic understanding of the Chl antenna size regulation by the TLA1 gene.
Keywords: Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, Chl antenna size, thylakoid membrane development, TLA1 gene, RNAi, VIPP1 protein
1. Introduction
The absorption of sunlight and the conversion of excitation energy to chemical energy in photosynthesis take place in photosystem II (PSII) and photosystem I (PSI) in the thylakoid membrane of chloroplasts [1]. Distinct pigment–protein complexes are contained within PSI and PSII and perform the functions of light absorption and excitation energy transfer to a photochemical reaction centre [2,3]. Up to 350 chlorophyll a (Chl a) and Chl b molecules can be found in association with PSII, whereas the Chl antenna of PSI may contain up to 300 mainly Chl a molecules [4–6]. Most of these Chl molecules are organized as subunits of the so-called auxiliary chlorophyll a–b light-harvesting complex (LHC), located peripherally to the PS-core complex. In higher plants, there are six such subunits for PSII (LHC b1–b6) and four for PSI (LHC a1–a4) [7]. Several isoforms of these LHC subunits have been identified in the model green microalga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii [8]. The amount of these LHCs in the peripheral Chl antenna determines the size of the functional Chl antenna of the photosystems.
The Chl antenna size is not constant but can vary substantially depending on the developmental, genetic, physiological and environmental conditions. Plants and algae respond to imbalance between the supply and consumption of light energy in the photosynthetic apparatus by a molecular mechanism that alters the size of the Chl antenna [4,9–12]. In general, growth under low-light intensity promotes a large Chl antenna size for both PSII and PSI, which is a survival strategy and a competitive advantage in the wild, where sunlight is often limiting [13]. Growth under high irradiance induces the assembly of photosystems with a smaller Chl antenna size [4,14–16]. Such adjustments of the Chl antenna size in response to irradiance are a guided compensation reaction of the chloroplast to prevent over-excitation of the photosystems and potential photo-oxidative damage [4]. This molecular regulatory mechanism for the adjustment and optimization of the Chl antenna is highly conserved and functions in all organisms with oxygenic and anoxygenic photosynthesis [9,12,17,18].
Accordingly, there are nuclear and plastid genes that define the size and/or regulate the Chl antenna size of photosynthetic organisms [19,20]. Earlier efforts to elucidate the molecular mechanism for the dynamic regulation of the Chl antenna size postulated alteration of the redox state of the plastoquinone pool [10] and/or the operation of a cytosolic signalling transduction pathway for the rapid (order of minutes) regulation of both LHC (LHC proteins) and chlorophyllide a oxygenase (CAO) gene expressions by irradiance [12]. Upregulation and downregulation of the expressions of nuclear LHCB, LHCA (chlorophyl a–b light-harvesting complex) and CAO genes under low and high irradiance, respectively, plays a long-term acclimation role in plants and algae [7,11,12,14,21,22].
Although physiological and biochemical consequences of the function of this molecular mechanism for the regulation of the Chl antenna size are well understood [4,9,23], few nuclear genes have been identified that dynamically modulate the development and define the size of the Chl antenna in the chloroplast [19,20,24]. Earlier work described the isolation and characterization of tla1, a C. reinhardtii DNA insertional mutagenesis strain having a truncated light-harvesting chlorophyll antenna size [19,25–27]. The tla1 mutant possessed a smaller than wild-type Chl antenna size for both photosystems. It also showed lower levels of light-harvesting proteins and of Chl b relative to the wild type [25]. Molecular and genetic analyses revealed that in the tla1 mutant the exogenous plasmid DNA insertion occurred at the end of the 5′ untranslated region (UTR) and just prior to the ATG start codon of the TLA1 gene, which encodes a protein of 213 amino acids, that has a variant of the MPN (Mpr1 Pad1 N-terminal) domain [28]. Thus, the tla1 mutant lacked the in vivo TLA1 promoter and the 5′UTR of the TLA1 gene. In consequence, expression of the TLA1 gene was substantially downregulated at the translational level, and much lower levels of the TLA1 protein were detected in the mutant [26]. Complementation of the tla1 mutant with the TLA1 gene alone was sufficient to restore the wild-type cell pigmentation phenotype [26,27].
The present study is an extension of research from this laboratory [25–27], seeking to elucidate the role of the TLA1 gene in the molecular mechanism for the regulation of the chlorophyll antenna size of photosynthesis. We genetically manipulated the TLA1 gene in a wild-type strain of C. reinhardtii by TLA1 gene over-expression and downregulation, using RNA interference, to study the effect of the TLA1 gene expression on cellular Chl content and Chl antenna size of the photosystems, and also on thylakoid membrane biogenesis and organization without interference from any other background mutations. Results showed that modulation of the TLA1 gene expression impacts chlorophyll content per cell, the chlorophyll antenna size of the photosystems, but also affects accumulation of reaction centre and other thylakoid membrane proteins. The work also provides evidence that TLA1 gene expression affects thylakoid membrane development and organization in the chloroplast, thereby revealing a far broader effect than previously thought.
2. Material and methods
(a). Growth of the algae
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii strains CC503, TLA1 over-expressing lines OE1, OE2 and OE3, TLA1 RNAi transformants Ri6, Ri8 and Ri9 and the chlorophyll-deficient mutant tla1 were grown to the mid-exponential growth phase either in Tris–acetate–phosphate (TAP), pH 7.4 [29,30], or in modified minimal media containing 40 mM Tris–HCl, pH 7.4, supplemented with 25 mM sodium bicarbonate (TBP medium [31]) in culture flasks at 25°C under continuous illumination of 150–300 μmol photons m−2 s−1 provided by cool-white fluorescent lamps. The cultures were stirred continuously to ensure a uniform illumination of the cells and to prevent settling.
Cell density was measured upon counting cells per millilitre culture using a Neubauer ultraplane haemocytometer. Pigments from intact cells were extracted in 80 per cent acetone and cell debris removed by centrifugation at 10 000g for 5 min. The absorbance of the supernatant was measured with a Shimadzu UV-160U spectrophotometer, and the chlorophyll (Chl a and Chl b) concentration of the samples was determined according to Arnon [32], with equations corrected as in Melis et al. [33].
(b). Generation of TLA1 over-expressing lines and TLA1 RNAi transformants
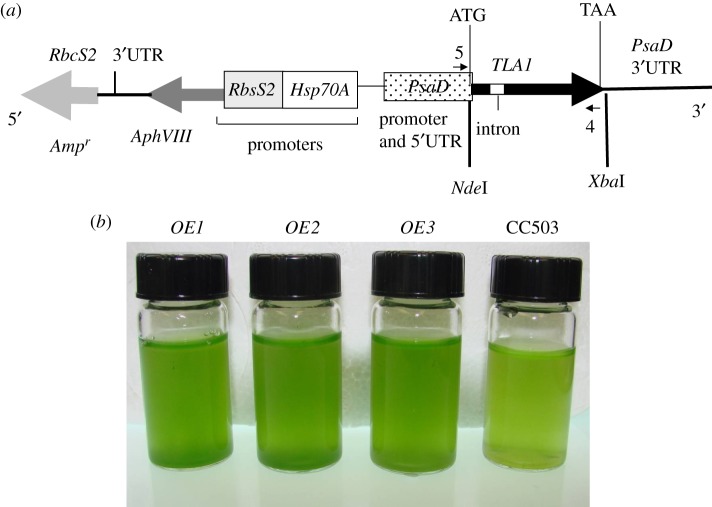
The full-length TLA1 gene (genomic DNA sequence including two exons and a single intron; GenBank accession no. AF534570) was amplified using primer 8 (TLA1 first exon-specific primer; table 1) and primer 9 (TLA1 second exon-specific primer; table 1) on extracted wild-type genomic DNA. Primer 8 and primer 9 had NdeI and XbaI restriction sites added at the 5′ ends, respectively. The 768 bp genomic DNA PCR product (TLA1 gene with the added base pair from the restriction sites) was digested with NdeI and XbaI and cloned into vector pSL18 ([34,35]; figures 1a and 2a). Platinum Taq high-fidelity DNA polymerase (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) was used for the PCR amplification. A 1 kb plus DNA ladder was used as DNA size markers (Invitrogen). The pSL18 plasmid incorporated 5′ and 3′ UTR regions from the PsaD gene of C. reinhardtii, and also contained the ampicillin- and paromomycin-resistance genes [36] as selectable markers (figure 1a). The antibiotic-resistance genes are useful for screening transformants of Escherichia coli and C. reinhardtii on LB + ampicillin and TAP + paromomycin agar plates, respectively. The recombinant pSL18-TLA1 construct from one of the positive E. coli clones was sequenced to confirm the TLA1 gene sequence present. The sequenced pSL18-TLA1 construct was used to transform the CC503 strain by the glass-bead method [37,38], to generate the TLA1 over-expressing lines.
Table 1.
TLA1 gene primers used for cloning TLA1 inverted repeats and full-length gene in pSL72 and pSL18, respectively.
| ‘Primer A’ (TLA1 first exon-specific forward primer; 5′ GTTGATATCAGCGTGAATGGTGTCCTCGT 3′) and ‘primer B’ (TLA1 second exon-specific reverse 5′ GTTGAATTCCCTTGCTGCCATCCTTGCTG 3′); used for generation of the first TLA1 inverted repeat (no. 1; 367 bp, figure 2a) for RNAi cloning in pSL72 vector |
| ‘Primer C’ (TLA1 second exon-specific forward 5′ GTTGGATCCCCTTGCTGCCATCCTTGCTG 3′) and ‘primer D’ (TLA1 first exon-specific reverse primer 5′ GTTTCTAGAAGCGTGAATGGTGTCCTCGT 3′); used for generation of the second TLA1 inverted repeat (no. 2; 367 bp, figure 2a) for RNAi cloning in pSL72 vector |
| ‘Primer 8’ (5′ GGAATTCCATATGACTTTCAGCTGCTC3′) and ‘primer 9’ (5′ GCTCTAGACTTACAGCGCGTTGCC GGGCAAC 3′); used for cloning of full-length TLA1 gene (759 bp) in the pSL18 vector |
Figure 1.
(a,b) Generation of TLA1 over-expressing lines. (a) pSL18-TLA1 gene construct for over-expression of the TLA1 gene. The full-length TLA1 gene (thick black arrow with the small white intron box; 758 bp) was cloned in the pSL18 vector under the control of the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii PsaD promoter (dotted box) and terminator (black line, PsaD 3′ UTR). Upstream from the TLA1 gene, the construct also contained the paromomycin-resistance AphVIII gene (dark grey arrow) and ampicillin-resistance Ampr (light grey arrow) genes. The AphVIII gene was under the control of the Hsp70A (white box) and RbcS2 promoter (grey box). Primer 5 and primer 4 used for PCR and RT-PCR reactions (table 3) are denoted by small black arrows on the map of the pSL18-TLA1 construct. The start (ATG) and the stop codon (TAA) of the TLA1 gene are labelled. (b) Phenotype of three TLA1 over-expressing lines and parental wild-type strain of C. reinhardtii. Minimal media (TBP) liquid cultures of TLA1 over-expressing lines (OE1, OE2 and OE3) and the wild-type CC503 are shown. Cell densities of the four cultures were approximately 5 × 106 cells ml−1. The putative TLA1 over-expressing lines (OE1, OE2 and OE3) showed a slightly darker green coloration compared with the wild type, indicative of greater chlorophyll content in these cells.
Figure 2.
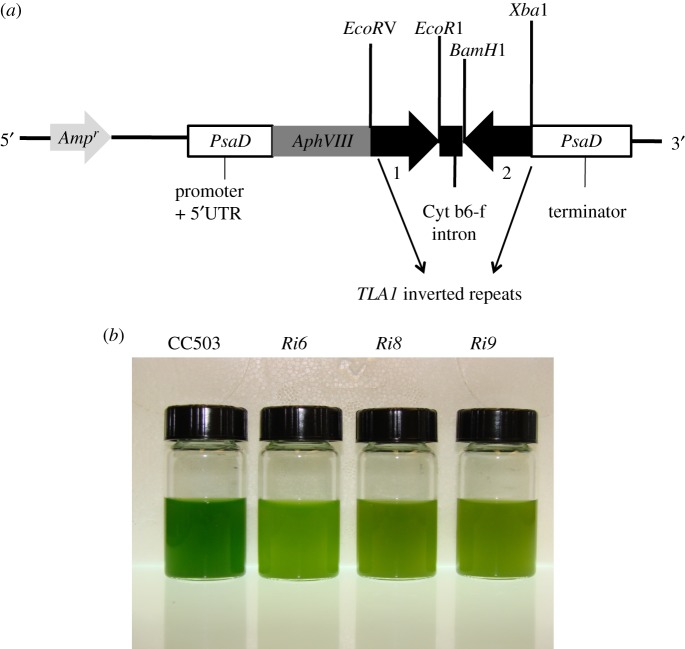
(a,b) Downregulation of expression of TLA1 by RNA interference. (a) pSL72-TLA1 RNAi construct for downregulation of the TLA1 gene. The two reverse complementary inverted repeats (1 and 2) of the TLA1 gene sequence (thick black arrows) were cloned in the pSL72 vector under the control of the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii PsaD promoter and terminator (white boxes). Upstream from the cloned inverted repeats of TLA1, the construct also contained the AphVIII (light grey arrow) and Ampr (dark grey arrow) genes, encoding paromomycin and ampicillin resistance, respectively. The AphVIII gene is also under the control of the PsaD promoter. The cleavage sites of restriction enzymes used for cloning of the two inverted repeats are shown. (b) Phenotype of three TLA1 RNAi transformants and parental wild-type strains of C. reinhardtii. Minimal media (TBP) liquid cultures of TLA1 RNAi transformants (Ri6, Ri8 and Ri9) and the wild-type CC503 are shown. Cell densities of the four cultures were approximately 8 × 106 cells ml−1. The putative TLA1 RNAi transformants (Ri6, Ri8 and Ri9) showed a lighter green coloration compared with the wild type, indicating a lower-level of chlorophyll content in these cells.
Primer A (TLA1 first exon-specific primer, table 1) and primer B (TLA1 second exon-specific primer, table 1) were used to amplify a 367 bp fragment of TLA1 cDNA that constituted fragment number 1 (figure 2a). Primer A had an EcoRV and primer B had an EcoR1 restriction site incorporated in the 5′ end. Primer C (TLA1 second exon-specific primer; table 1) and primer D (TLA1 first exon-specific primer; table 1) were used to amplify a 367 bp fragment of TLA1 cDNA that constituted fragment number 2 (figure 2a). Primer C had a BamH1 and primer D had an XbaI restriction site incorporated in the 5′ end. Fragments 1 and 2 were cloned into vector pSL72 under the control of the constitutive PsaD promoter (figure 2a). The resulting construct was sequenced at the UC Berkeley sequencing facility, and sequenced recombinant construct was used to transform wild-type CC503 strain to generate the TLA1 RNAi transformants.
(c). Nucleic acid extraction, PCR and RT-PCR analysis
Genomic DNA was isolated using a combination of DNeasy plant mini kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA, USA) and phenol chloroform extraction [39]. Total RNA was isolated using the Trizol reagent (Invitrogen). Genomic DNA PCR and RT-PCR analysis was done on the isolated genomic DNA and RNA samples. The one-step RT-PCR kit (Qiagen) was used for RT-PCR experiments. Platinum Taq polymerase (Invitrogen) was used for the PCR amplification. The 1 kb plus DNA ladder was used as DNA size markers (Invitrogen). Primers used for PCR and RT-PCR analysis are listed in table 3.
Table 3.
Primers used for genetic analysis of the CC503 (WT), TLA1 over-expressors and TLA1 RNAi mutants.
| primers | expected product sizes |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| CC503 (WT) | TLA1 over-expressors | TLA1 RNAi mutants | |
| ‘Primer 5’ (5′ACTGCTACTCAC AACAAGCCCAT 3′) and ‘primer 4’ (5′ TTACAGCGCGTTGCC GGGCAAC 3′); probing for the trans-TLA1 gene and transcript with the PsaD 5′UTR | no product | 781 bp genomic DNA product; 665bp cDNA product | N/A |
| ‘Primer 1’ (5′GCCTGCCACAACCTCAGACCA 3′) and ‘primer 4’ (5′ TTACAGCGCGTTGCCGGGCAAC 3′); probing for the TLA1 5′UTR in TLA1 transcript | 687 bp cDNA product | 687 bp cDNA product | N/A |
| ‘Primer 2’ (5′ TTCAGCTGCTCCGCTGACCAAA 3′) and ‘primer 6’ (5′-TTGTTGTCCAGCACCAGCAC 3′); probing for TLA1 transcript | 359 bp cDNA product | N/A | 359 bp cDNA product |
| ‘Primer 3’ (5′ ACGCCACCTTCAACTC 3′) and ‘primer 7’ (5′ CAGGAAGGCATTTGGAAGC 3′); probing for the Actin transcript | 363 bp cDNA product | N/A | 363 bp cDNA product |
(d). Isolation of thylakoid membranes for spectrophotometric analysis
Cells were harvested by centrifugation at 1000g for 3 min at 4°C, the pellet was resuspended in 1–2 ml of growth medium and stored frozen at 80°C until all samples were ready for processing. Samples were thawed on ice and diluted with ice-cold sonication buffer containing 50 mM Tricine (pH 7.8), 10 mM NaCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.2 per cent polyvinylpyrrolidone 40, 0.2 per cent sodium ascorbate, 1 mM aminocaproic acid, 1 mM aminobenzamidine and 100 µM phenylmethylsulphonyl fluoride. Cells were broken by sonication in a Branson 250 cell disrupter operated at 4°C, 3× for 30 s (pulse mode, 50% duty cycle, output power 5) with 30 s cooling intervals. Cell debris and starch grains were removed by centrifugation at 3000g for 4 min at 4°C. The thylakoid membranes were collected by centrifugation of the supernatant at 75 000g for 30 min at 4°C. The thylakoid membrane pellet was resuspended in 50 mM Tricine (pH 7.8), 10 mM NaCl, 5 mM MgCl2 for spectrophotometric measurements.
(e). Isolation of total soluble and cell membrane fractions
CC503 cell fractionation was implemented as described above. The sonicated cell sample was centrifuged at 20 000g for 1 h at 4°C. The supernatant was collected and used as the cell soluble fraction. The membrane pellet was resuspended in a buffer containing 250 mM Tris–HCl (pH 6.8), 20 per cent glycerol, 7 per cent sodium dodecylsulphate (SDS) and 2 M urea for protein analysis. Membrane proteins were solubilized for 30 min in the dark at room temperature, a procedure designed to prevent the formation of protein aggregates during denaturation. Samples were then centrifuged in a micro-centrifuge for 4 min to remove unsolubilized material. The solubilized supernatant was used as the total cell membrane fraction. The total cell, soluble and membrane fractions were used for the TLA1 immunolocalization experiment.
(f). Isolation of intact nuclei, chloroplasts, chloroplast envelope and thylakoid membranes from Chlamydomonas cells for immune-localization experiments
CC503 cells were harvested by centrifugation at 23 000g for 10 min at 4°C. Nuclei were isolated from the pelleted cells following the protocol described by Shimogawara & Muto [40]. For chloroplast isolation, CC503 cells were grown in TAP medium under continuous light (300 µmol photons m−2 s−1) for 2 days and then switched to conditions of light–dark cycles (12 L : 12 D) for synchronous growth. Cells were harvested 4 h past the third L/D cycle by centrifugation at 3000g for 10 min at 4°C. Chloroplasts were isolated from the pelleted cells following the protocol described by Mason et al. [41]. Chloroplast envelopes were isolated by modification of the method of Clemetson & Boschetti [42] as described by Ramazanov et al. [43]. Thylakoid membranes were isolated according to Allen & Staehelin [44].
(g). Spectrophotometric analyses
The concentration of the photosystems in thylakoid membranes was estimated spectrophotometrically from the amplitude of the light-minus-dark absorbance difference signal at 700 nm (P700) for PSI, and 320 nm (QA) for PSII [45,46]. The functional light-harvesting Chl antenna size of PSI and PSII was measured from the kinetics of P700 photo-oxidation and QA photo-reduction, respectively [47].
(h). Cell protein SDS–PAGE and Western blot analysis
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii cells from the different strains were harvested, washed twice with fresh growth medium and resuspended in TEN buffer, containing 10 mM Tris–HCl, 10 mM EDTA and 150 mM NaCl, pH 8. Following sonication, the crude cell extract was incubated in the presence of solubilization buffer [46]. Gel lanes were loaded with an equal amount of Chl, in the range of 1–2 nmol Chl, as indicated. SDS–PAGE analysis was performed according to Laemmli [48] on a 12.5 per cent acrylamide gel, using the Fermentas pre-stained protein ladder (Glen Burnie, MD). A constant current of 15 mA was applied to the electrophoresis for a 3 h period. Gels were stained with 1 per cent Coomassie brilliant blue R for protein visualization.
Electrophoretic transfer of the SDS–PAGE resolved proteins onto nitrocellulose was carried out for 2 h at a constant current of 400 mA in the transfer buffer (25 mM Tris, 192 mM glycine and 20% methanol). The Chlamydomonas anti-TLA1 polyclonal antibodies (made against the full-length recombinant TLA1 protein), spinach anti-LHC antibodies, Arabidopsis anti-D1 and anti-D2 antibodies (made against a synthetic peptide having the highly conserved C-terminal sequence of the D2 protein from plants), Chlamydomonas anti-VIPP1 (anti-vesicle-inducing protein in plastid 1), anti-Rubisco and anti-NAB1 (anti-nucleic acid-binding protein 1) antibodies were used for Western blot analysis of the different TLA1 over-expressing strains, TLA1 RNAi transformants and the wild-type strain. The anti-TLA1 immune serum was diluted with the antibody buffer (Tris-buffered saline, 0.005% Tween 20 and 1% bovine serum albumin, pH 7.4) to a ratio of 1 : 3000 before use as the primary probe. Primary LHC, D1, D2, VIPP1 and NAB1 antibodies were used in 1 : 25 000, 1 : 30 000, 1 : 50 000, 1 : 100 000 and 1 : 3000 dilutions, respectively, using the earlier-mentioned antibody buffer. Primary Rubisco antibodies were used in 1 : 50 000 dilutions. The secondary antibodies used for this Western blot analysis were conjugated to horseradish peroxidase (BioRad, Hercules, CA) and diluted to a ratio ranging from 1 : 30 000 to 1 : 50 000 with the antibody buffer. Western blots were developed for visualization via the Supersignal West chemiluminescent substrate kit (Pierce, Rockford, IL, USA).
(i). Transmission electron microscopy
Cultures of CC503, OE1, Ri6 and tla1 were grown to mid-exponential phase (5 × 106 cells ml−1), concentrated by centrifugation and fixed for 1 h in a mixture containing 0.1 M cacodylate buffer (pH 7.4) and glutaraldehyde (added to a final concentration of 3% in the cacodylate buffer). Fixed cells were washed three times with 0.1 M cacodylate buffer, pH 7.4 upon shaking gently for 10 min on an orbital shaker. Following the wash, cells were transferred to the secondary fixative mix (1% OsO4 and 1.6% potassium ferricyanide, dissolved in 0.1 M sodium cacodylate buffer, pH 7.4 and incubated for 2 h). Cells were rinsed twice with cacodylate buffer for 10 min each, then rinsed three times with distilled water for 10 min each. Cells were stained with 2 per cent uranyl acetate (in water) under vacuum for about half an hour. After staining, the cells were dehydrated with increasing concentrations of ethanol, followed by dehydration in 100 per cent acetone. The dehydrated cells were then infiltrated and embedded in resin. Sections were cut to approximately 500 µm diameter and 60 nm thickness. Therefore, 100 sections were required to traverse a cell along its short axis (approx. 6 µm). Sections were collected on 100 mesh copper grid and slot grids. Sections were dried and poststained with 2 per cent methanolic uranyl acetate for 7 min, then with lead citrate for an additional 7 min. Sections were dried and examined under Tecnai 12 transmission electron microscopy (TEM) at 100 kV.
3. Results
(a). Generation and screening of TLA1 over-expressing and RNAi transformants
The full-length coding region of the TLA1 gene (759 bp) was amplified using primers 8 and 9 (table 1) on genomic DNA and cloned into the pSL18 vector under control of a constitutive PsaD promoter (figure 1a; see also §2). The resulting recombinant construct was used to transform wild-type CC503 strain to generate the TLA1 over-expressing lines. Two reverse complementary cDNA fragments (367 bp) of the TLA1 gene were cloned into the pSL72 vector to generate the pSL72-TLA1 RNAi construct (figure 2a; table 1; see also §2). The resulting recombinant construct was used to transform the wild-type CC503 strain to generate the TLA1 RNAi transformants. TLA1 over-expressing and RNAi transformant line colonies were selected on TAP agar plates in the presence of 10 μM paromomycin and screened for dark green and pale green coloration, respectively. Three independent lines of putative TLA1 over-expressing lines (figure 1b) and RNAi transformant strains (figure 2b) were randomly selected from a batch of 300 isolated transformants (from each group) and further analysed for chlorophyll content and composition, as well as Chl antenna size, upon autotrophic growth in minimal TBP liquid media (figures 1b and 2b).
(b). Chlorophyll content and photosystem Chl antenna size measurements
Compared with the green phenotype of the CC503 wild type, TLA1 over-expressing strains (OE1, OE2 and OE3) had a dark green coloration (figure 1b), whereas TLA1 RNAi transformants (Ri6, Ri8 and Ri9) had a pale green coloration (figure 2b). The TLA1 over-expressing lines and the RNAi transformants were tested for their Chl/cell and Chl a/Chl b ratios. Chl/cell in the TLA1 over-expressing lines (3.1–3.4 × 10−15 mol cell−1) was slightly greater than that in the wild type (3 × 10−15 mol cell−1) while that of the TLA1 RNAi transformants ranged between 0.9 × 10−15 and 2 × 10−15 mol cell−1 (table 2). The wild-type C. reinhardtii has a Chl a/Chl b ratio of 2.6, whereas the TLA1 over-expressing lines and the TLA1 RNAi transformants have a Chl a/Chl b ratio ranging between 2.3–2.5 and 3–6, respectively. Table 2 also shows Chl-to-PSII (Chl/QA) and Chl-to-PSI (Chl/P700) ratios, as measured from the light-minus-dark difference spectra of the various strains. The wild-type strain contained about 521 Chl molecules per QA molecule, whereas the TLA1 over-expressing lines and the TLA1 RNAi transformants had a Chl/QA ratio ranging between 525–537 and 410–494, respectively (table 2). Hence, the TLA1 over-expressing lines resemble the wild-type strain in having similar Chl and QA content in their thylakoids. In the TLA1 RNAi transformants, the Chl relative to QA content was lowered by about 20–25%. The wild-type strain contained 547 Chl molecules per P700 molecule, whereas the TLA1 over-expressing lines and the TLA1 RNAi transformants had a Chl/P700 ratio ranging between 560–610 and 361–459, respectively. Thus, in the TLA1 over-expressing lines, the Chl content was slightly greater relative to the P700 content in the thylakoid membrane, by about 2–12%, whereas in the TLA1 RNAi transformants the Chl content was considerably lower (16–34%) relative to P700 content in the thylakoids. These measurements suggested a smaller Chl antenna size for both photosystems in the TLA1 RNAi transformants. The functional light-harvesting Chl antenna size of PSI and PSII in the wild type and the TLA1 over-expressing lines and TLA1 RNAi transformants was determined from the kinetics of P700 photo-oxidation and QA photo-reduction ([49]; table 2). This method assigns Chl molecules to each reaction centre in proportion with the rate of light absorption by the respective photosystem. Rates of light utilization by the photosystems were measured from the kinetics of QA photo-reduction and P700 photo-oxidation in isolated thylakoid membranes suspended in the presence of the herbicide DCMU [47]. In the TLA1 over-expressing strains, the PSI and PSII Chl antenna sizes were slightly greater by 2–14% and 1–4%, respectively, compared with that in the wild-type strain. In the TLA1 RNAi transformants, the PSI Chl antenna size was smaller by 15–50%, whereas the PSII Chl antenna size was smaller by 11–26%, compared with that in the wild type. Overall, PSI Chl antenna size was attenuated more than that of PSII (table 2).
Table 2.
Chlorophyll content and composition, and Chl antenna size of the photosystems in TLA1 over-expressing and RNAi transformant lines. The error measurements are s.e.m.
| strain | Chl content, mol/cell × 10−15 | Chl a/Chl b ratio | Chl/QA ratio | Chl/P700 ratio | PSII Chl antenna size | PSI Chl antenna size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC503 | 3.0 ± 0.1 | 2.6 ± 0.1 | 521 ± 3 | 547 ± 11 | 220 ± 4 | 237 ± 3 |
| OE1 | 3.4 ± 0.2 | 2.2 ± 0.2 | 537 ± 5 | 610 ± 7 | 229 ± 2 | 269 ± 5 |
| OE2 | 3.3 ± 0.25 | 2.3 ± 0.12 | 530 ± 7 | 599 ± 4 | 225 ± 4 | 260 ± 2 |
| OE3 | 3.1 ± 0.5 | 2.5 ± 0.1 | 525 ± 2 | 560 ± 3 | 222 ± 4 | 243 ± 4 |
| Ri6 | 0.9 ± 0.4 | 6.0 ± 0.17 | 410 ± 12 | 361 ± 9 | 163 ± 7 | 118 ± 6 |
| Ri8 | 1.0 ± 0.5 | 5.3 ± 0.22 | 425 ± 14 | 384 ± 11 | 170 ± 10 | 121 ± 4 |
| Ri9 | 2.0 ± 0.38 | 3.0 ± 0.12 | 494 ± 5 | 459 ± 5 | 195 ± 12 | 201 ± 2 |
(c). Genetic analysis of TLA1 over-expressing lines and TLA1 RNAi transformants
Total genomic DNA and RNA were isolated from the TLA1 over-expressing lines (OE1, OE2 and OE3) and the wild-type strain. PCR and RT-PCR analysis was done on the isolated genomic DNA and RNA using primer 5 (PsaD 5′UTR-specific forward primer; table 3; figure 3a,b) and primer 4 (TLA1 second exon-specific reverse primer; table 3; figure 3a,b). A genomic DNA PCR product of 781 bp and a cDNA product of 665 bp were obtained in all the TLA1 over-expressing strains, which were missing from the wild-type samples, as the wild-type strain lacks the trans-TLA1 gene with the PsaD 5′UTR. This result shows that the TLA1 over-expressing lines possess the trans-TLA1 gene under the control of the PsaD promoter and are expressing it. RT-PCR was also performed on the TLA1 over-expressing lines using primer 1 (TLA1 5′UTR-specific forward primer; table 3 and figure 3c) and primer 4 (TLA1 second exon-specific reverse primer; table 3 and figure 3c) as a control experiment. A cDNA product of 687 bp was obtained in all of the TLA1 over-expressing lines and the wild type (figure 3c). This result offers evidence of the presence and expression of the native TLA1 gene in all the strains examined.
Figure 3.
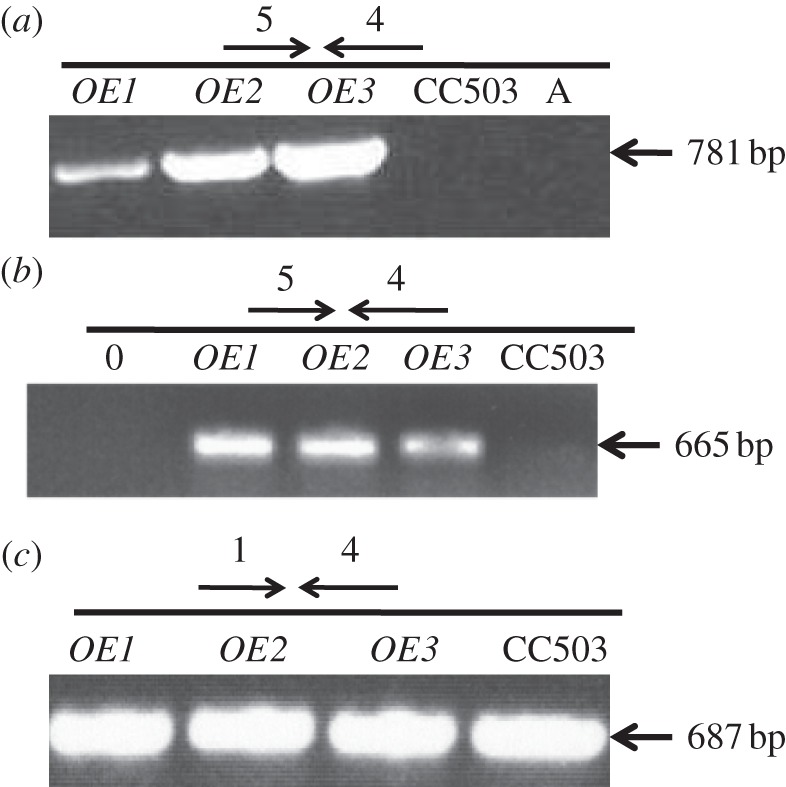
(a–c) Molecular genetic analysis of TLA1 over-expressing lines and the wild-type CC503. (a) PCR analysis of the TLA1 over-expressing strains and wild type using the cell's genomic DNA as template. Primer 5 (PsaD 5′UTR-specific forward primer, table 3) and primer 4 (TLA1 3′UTR-specific reverse primer, table 3) were used to probe for the presence/absence of the full-length trans-TLA1 gene (781 bp product) in the three TLA1 over-expressing lines (OE1, OE2 and OE3) and CC503 (WT) strain. (b) RT-PCR analysis of the TLA1 over-expressing lines and WT using cDNA template. Primer 5 (PsaD 5′UTR-specific forward primer, table 3) and primer 4 (TLA1 3′UTR-specific reverse primer, table 3) were used to probe for the presence/absence of the full-length trans-TLA1 transcript (665 bp product) in the three TLA1 over-expressing lines (OE1, OE2 and OE3) and CC503 (WT) strain. (c) RT-PCR analysis of the TLA1 over-expressing strains and WT using cDNA template. Primer 1 (TLA1 5′UTR-specific forward primer, table 3) and primer 4 (TLA1 3′UTR-specific reverse primer, table 3) were used to probe for the presence of the full-length cis-TLA1 transcript (687 bp product) in the three TLA1 over-expressing lines (OE1, OE2 and OE3) and CC503 (WT) strain.
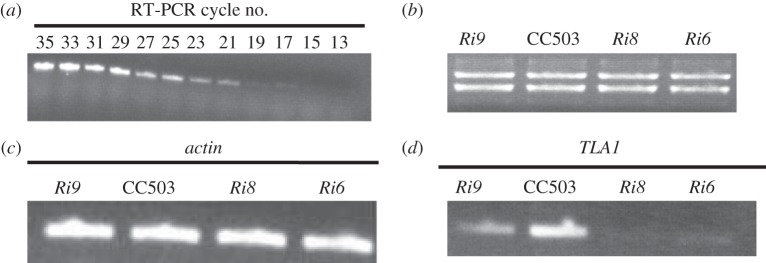
RNA was isolated from the wild-type strain CC503, and cycle-RT-PCR was performed using cycles ranging from 13 to 35, and also using primer 2 (TLA1 first exon-specific forward primer, table 3; figure 4a) and primer 6 (TLA1 second exon-specific reverse primer, table 3 and figure 4a). The products obtained from these cycles were subjected to DNA gel electrophoresis to identify a desired cycle in which the RT-PCR product concentration would be in the linear range. Cycle number 27 was selected for further semi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis, using Actin- and TLA1-specific primers. Total cell RNA from the TLA1 RNAi transformant and wild-type strains were subjected to RNA gel electrophoresis to check for quality and concentration of the RNA preparations (figure 4b). Primer 3 and primer 7 (Actin gene-specific; table 3 and figure 4c) were used for semi-quantitative RT-PCR (using cycle 27) analysis of Actin transcripts (363 bp product) in the three TLA1 RNAi transformants (Ri6, Ri8 and Ri9) and the wild-type strain. Results from this analysis showed that the transcript level of Actin is the same in all strains. Primer 2 (TLA1 first exon-specific forward primer; table 3 and figure 4d) and primer 6 (TLA1 second exon-specific reverse primer; table 3 and figure 4d) were used for semi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis of TLA1 transcripts (359 bp product) in the three TLA1 RNAi transformants (Ri6, Ri8 and Ri9) and the wild-type strain. The TLA1 transcript level was significantly lower in all TLA1 RNAi transformants particularly Ri6 and Ri8 compared with that in the wild-type strain (figure 4d).
Figure 4.
(a–d) Transcript analysis in the TLA1 RNAi transformants and the wild-type CC503 strain. (a) Cycle RT-PCR analysis of the wild-type CC503 using RNA template. Primer 2 (TLA1 first exon-specific forward primer; table 3) and primer 6 (TLA1 second exon-specific reverse primer; table 3) were used in RT-PCR cycles ranging from 13 to 35. Cycle number 27 was selected for further semi-quantitative analysis of RT-PCR products obtained using Actin and TLA1-specific primers. (b) RNA agarose gel showing equal loading of total cell RNA from TLA1 RNAi transformants and the wild-type CC503. Three microgram of total cell RNA from the TLA1 RNAi transformants and WT strain were loaded on the gel. (c) Semi-quantitative RT-PCR product analysis using Actin-specific primers on cDNA template. Primer 3 and primer 7 (Actin gene-specific; table 3) were used for semi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis (cycle 27) of Actin transcripts (363 bp product) in the three TLA1 RNAi transformants (Ri6, Ri8 and Ri9) and the WT. (d) Semi-quantitative RT-PCR product analysis using TLA1-specific primers on cDNA template. Primer 2 (TLA1 first exon-specific forward primer; table 3) and primer 6 (TLA1 second exon-specific reverse primer; table 3) were used for semi-quantitative RT-PCR (cycle 27) analysis of TLA1 transcripts (359 bp product) in the three TLA1 RNAi transformants (Ri6, Ri8 and Ri9) and the WT. Note the diminished amounts of TLA1 transcripts in the RNAi transformants.
(d). Western blot analysis of photosynthetic proteins in TLA1 over-expressing and RNAi transformant lines
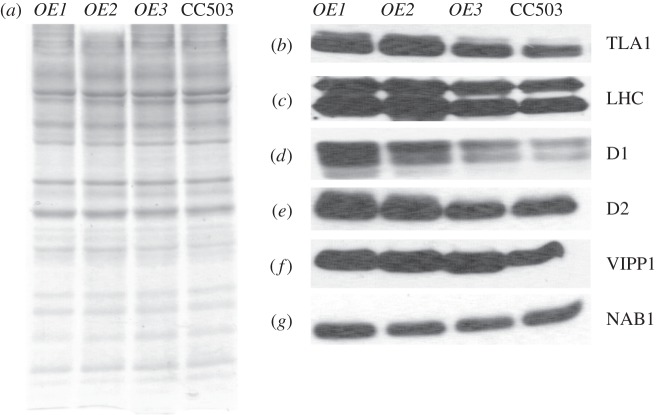
Total cell protein extracts from the three TLA1 over-expressing lines (OE1, OE2 and OE3) and wild-type strain were resolved on a 12.5 per cent SDS–PAGE gel. Lanes were loaded on an equal protein basis (figure 5a). Western blot analysis of the total cell extract from these samples was performed with specific polyclonal antibodies raised against the Chlamydomonas recombinant TLA1 protein, spinach LHC proteins (recognizes both LHCA and LHCB), Arabidopsis PSII reaction centre D1 and D2 proteins, Chlamydomonas VIPP1 and Chlamydomonas NAB1 proteins (figure 5b–g). Results showed that the amount of TLA1, LHCs, D1, D2 and VIPP1 proteins were increased in OE1 and OE2 and to a lesser extent in OE3, when compared with that in the CC503 wild type (figure 5b–g). OE3 showed a minimal change in the earlier-mentioned protein levels compared with that in the wild type strain. The Western blot analysis results indicated that TLA1 over-expression is not only affecting the Chl antenna size by regulating the amount of LHC proteins associated with the photosystems (figure 5b,c), but it is also affecting the concentration of D1 and D2 reaction centre proteins (figure 5d,e), and the amount of the VIPP1 protein, which is involved in thylakoid biogenesis/maintenance (figure 5f). TLA1 over-expression did not have an effect on the amount of NAB1 protein, which plays a role in LHC biosynthesis in the cytosol, therefore, indirectly affecting the Chl antenna size in C. reinhardtii (figure 5g).
Figure 5.
(a–g) Protein analysis of the TLA1 over-expressing lines and the CC503 wild-type strain. (a) SDS–PAGE of total cell protein extracts from the TLA1 over-expressing lines (OE1, OE2 and OE3) and the WT strain. Lanes were loaded on an equal protein basis (30 µg of protein per lane). (b–g) Western blot analysis of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii total cell protein extracts. Lanes, loaded as in (a), were probed with (b) TLA1-specific, (c) LHC-specific, (d) D1 reaction centre protein-specific, (e) D2 reaction centre protein-specific, (f) VIPP1-specific and (g) NAB1-specific polyclonal antibodies.
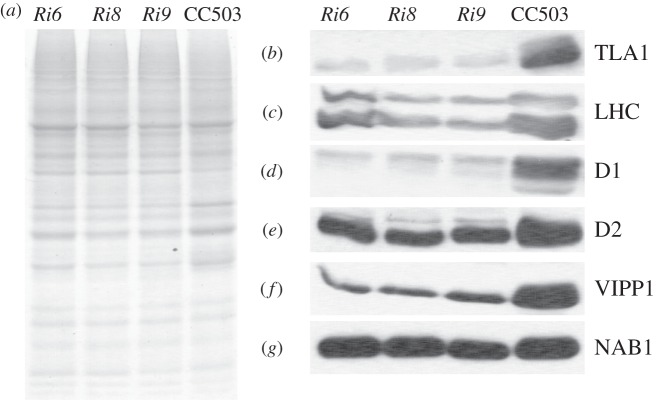
Total cell protein extracts from three TLA1 RNAi transformants (Ri6, Ri8 and Ri9) and wild-type strain were also resolved on a 12.5 per cent SDS–PAGE gel. Lanes were loaded on an equal protein basis (figure 6a). Western blot analysis of the total cell extracts from the different strains was performed with the same set of specific polyclonal antibodies as those used in figure 5b to probe the TLA1 over-expressing lines (figure 6b–g). Results showed that the amount of TLA1, LHCs, D1, D2 and VIPP1 proteins were significantly decreased in the RNAi transformants compared with that in the CC503 wild-type strain (figure 6b–f). Like the TLA1 over-expressing strains, downregulation in the amount of TLA1 expression did not have an effect on the amount of NAB1 protein in the RNAi transformants (figure 6g). It is concluded that a cause-and-effect relationship exists between changes in TLA1 expression and LHC, D1, D2 and VIPP1 abundance in the chloroplast, providing an explanation of the mechanism and strengthening the notion of the TLA1 protein as a regulator of Chl content and Chl antenna size in photosynthesis [25–27].
Figure 6.
(a–g) Protein analysis of the TLA1 RNAi transformants and the CC503 wild-type strain. (a) SDS–PAGE of total cell protein extracts from the TLA1 RNAi transformants (Ri6, Ri8 and Ri9) and the WT strain. Lanes were loaded on an equal protein basis (25 µg of protein per lane). (b–g) Western blot analysis of C. reinhardtii total cell protein extracts. Lanes, loaded as in (a) were probed with (b) TLA1-specific, (c) LHC-specific, (d) D1 reaction centre protein-specific, (e) D2 reaction centre protein-specific, (f) VIPP1-specific and (g) NAB1-specific polyclonal antibodies.
(e). Localization of TLA1 protein in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
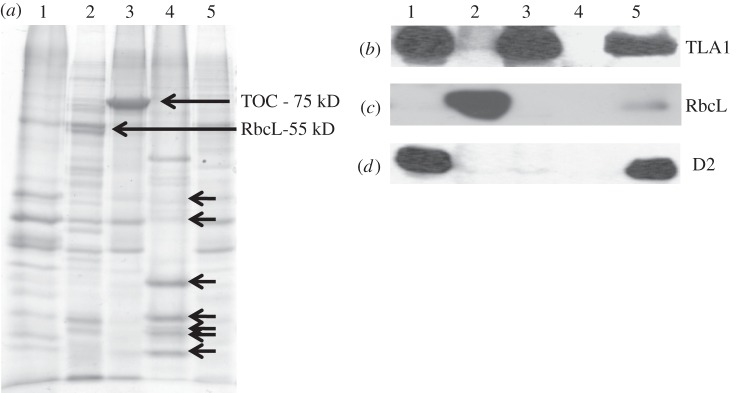
Total soluble and membrane fractions were isolated and probed with the TLA1 antibodies. Figure 7a shows the SDS–PAGE profile of these fractions with lanes loaded on equal protein basis. The corresponding Western blot analysis (figure 7b) showed that the TLA1 protein is enriched in the membrane fraction (M) and not present in the soluble fraction (S). Further fractionation of CC503 Chlamydomonas cells and isolation of chloroplasts, chloroplast envelopes, thylakoid membranes and nuclei was also undertaken (see §2). Total membrane fraction (figure 8a, lane 1), soluble stroma fraction (lane 2), chloroplast envelope (lane 3), nuclei (lane 4) and total cell extract (lane 5) were loaded on a 12.5 per cent SDS–PAGE gel. Lanes were loaded on an equal protein basis (figure 8a). Rubisco protein enrichment (RbcL-55 kD) was used as a marker protein for the soluble chloroplast fraction (figure 8a, lane 2). TOC75 (translocon of outer envelope of chloroplast, MW = 75 kD) was used as a marker for the chloroplast envelope (figure 8a, lane 3). The nuclei preparation showed enrichment in histone proteins, denoted by black arrows in figure 8a (lane 4) [50,51]. The D2 protein was used as a marker protein for the total membrane fraction (figure 8a, lane 1). Western blot analysis of the earlier-mentioned samples was performed with TLA1-specific polyclonal antibodies and also with Chlamydomonas RbcL-specific and D2-specific antibodies. The Western blot analysis showed that the TLA1 protein is enriched in the total membrane and chloroplast envelope fractions (figure 8b, lanes 1 and 3) and is absent from the isolated stroma-soluble fraction and from the nuclei preparation (figure 8b, lanes 2 and 4). These results suggest precipitation of the TLA1 protein with the relatively heavier membrane fractions, suggesting either membrane (envelope?) association or formation of a larger complex, probably in association with other membrane proteins, all of which pellet in the course of the differential centrifugation for the isolation of the cellular fractions.
Figure 7.
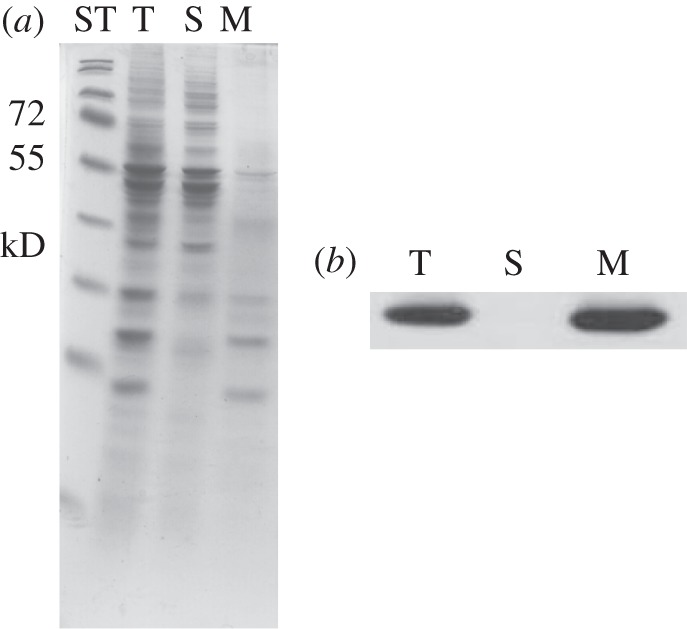
(a,b) Cell fractionation and Western blot analysis of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii soluble and membrane fractions, probed with TLA1-specific polyclonal antibodies. (a) SDS–PAGE of total cell protein extracts from different cell fractions of CC503 (WT) strain: lane T, total cell extract; lane S, soluble fraction and lane M, membrane fraction. ST denotes standard molecular weight protein markers. (b) Western blot analysis of the total, soluble and membrane fractions of C. reinhardtii. Lanes were loaded as in (a) and probed with the TLA1-specific antibodies.
Figure 8.
(a–d) Cell fractionation and Western blot analysis of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii cellular compartments, probed with anti-TLA1, anti-RbcL and anti-D2 polyclonal antibodies. (a) SDS–PAGE of total cell protein extracts from different cell fractions of the CC503 (WT) strain: lane 1, thylakoid membrane fraction; lane 2, stroma soluble fraction; lane 3, chloroplast envelopes; lane 4, isolated nuclei and lane 5, total cell protein extract. Lanes were loaded on an equal protein basis (30 µg of protein per lane). The Rubisco large subunit (RbcL MW = 55 kD) is pointed with an arrow in lane 2. The ‘translocon’ of the outer envelope membrane (Toc MW = 75 kD) is pointed with an arrow in lane 3, suggesting fraction enrichment in the chloroplast envelope. The short black arrows in lane 4 denote histone proteins present in C. reinhardtii. (b–d) Western blot analysis of different C. reinhardtii cell fractions. Lanes were loaded as in panel (a), and probed with (b) TLA1-specific, (c) RbcL-specific and (d) D2-specific polyclonal antibodies.
(f) Transmission. electron microscopy studies of cells of different Chlamydomonas reinhardtii strains
Size and composition of the Chl antenna has been shown to influence the formation of grana stacks in chloroplasts [52–54]. Accordingly, TEM was undertaken to assess the status of thylakoid membrane development and organization in TLA1 over-expressing (OE1) and TLA1 RNAi transformants (Ri6). TEM images revealed systematic differences in the arrangement and organization of thylakoid membranes among the wild-type CC503 cell (figure 9a), OE1 (figure 9b) and Ri6 (figure 9c). The OE1 strain (figure 9b) showed dense packing of grana, similar to that found in the CC503 control (figure 9a). By contrast, the TLA1 RNAi transformant Ri6 showed comparatively disorganized and less-compact arrangement of the thylakoid membranes with more free-floating stroma-exposed lamellae punctuated with few pseudograna (figure 9c). Although cells used for TEM studies were harvested from cultures that had approximately the same cell density (5 × 106 cells ml−1), RNAi transformants, e.g. the Ri6, were seen to apparently possess more starch grains compared with those in the wild-type and TLA1 over-expressing lines. This may be viewed as an indication of metabolic differences between the Ri6 transformant lines and those of the wild-type and OE1 over-expressing [54,55]. The potential significance of this phenomenon was not further investigated in this work.
Figure 9.
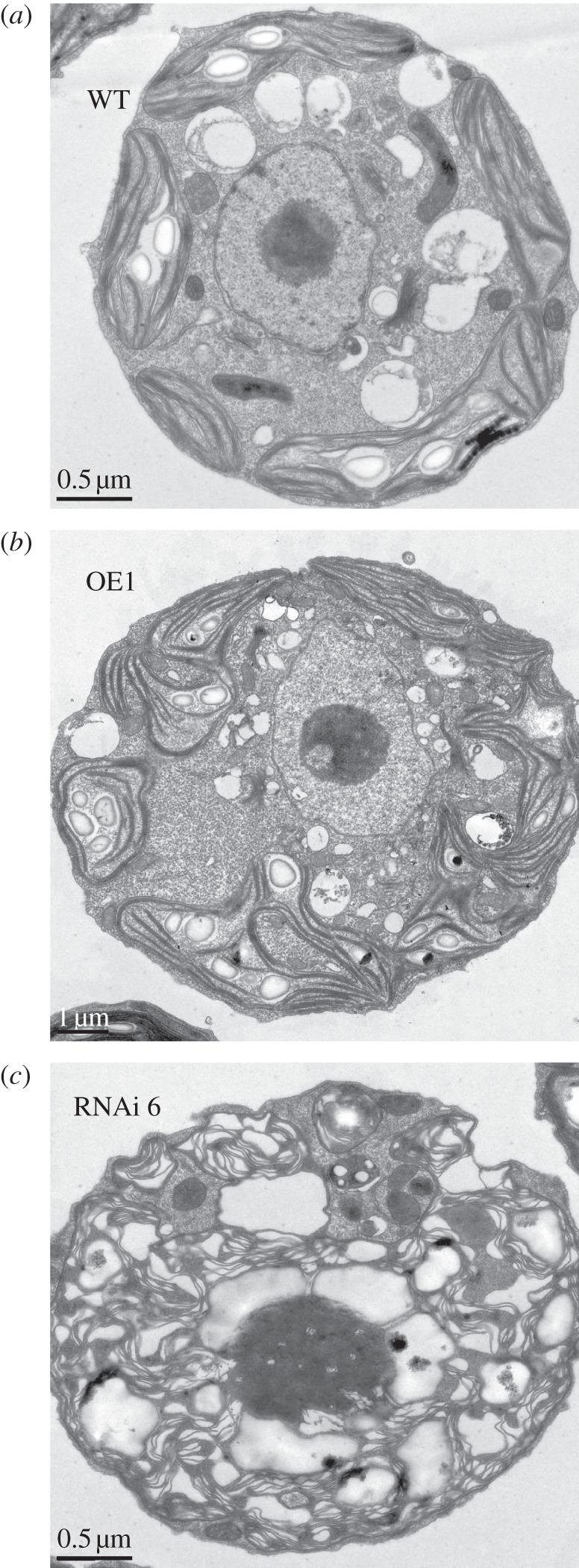
Transmission electron micrographs of different Chlamydomonas reinhardtii strains. (a) CC503 (WT) cell. (b) TLA1 over-expressing (OE1) line. (c) TLA1 RNAi transformant Ri6 cell. Note the well-developed appressed membranes (grana) in the TLA1 over-expressing (OE1) line, and the disorganized thylakoids with fewer appressed membranes in the TLA1 RNAi transformant.
4. Discussion
The ability of the photosynthetic apparatus to regulate the size of the functional Chl antenna was first recognized in pioneering work by Bjorkman et al. [56], more than 30 years ago. In spite of the substantial number of physiological and biochemical studies on this phenomenon (reviewed in [4,5,9]), genes and mechanism for the regulation of the Chl antenna size of photosynthesis have not been fully elucidated. Earlier DNA insertional mutagenesis work from this laboratory identified the novel TLA1 gene (GenBank accession no. AF534570 and AF534571) as a genetic determinant of cellular Chl content and photosystem Chl antenna size [25–27].
The mechanism by which the TLA1 gene regulates the Chl antenna size of photosynthesis is not currently understood, although it is likely to regulate the expression of other genes that directly affect the functional interaction between cell and organelle. For example, it may act by an as yet unknown mechanism for the regulation of expression of nuclear genes that are directly responsible for the biosynthesis of Chl and/or assembly of the LHC proteins. This notion is supported by findings in this work. For example, in the TLA1 RNAi transformants, TLA1 protein level, total amount of Chl, abundance of LHC polypeptides and levels of Chl b were all downregulated (figure 6b,c; table 2), presumably as a consequence of downregulation in the amount of the TLA1 protein. In the TLA1 over-expressing strains, a slight increase in the amount of the TLA1 protein, total Chl, LHC proteins and Chl b content were observed (figure 5b,c; table 2). The number of Chl molecules per QA was lower in the TLA1 RNAi transformants and slightly higher in the TLA1 over-expressing lines relative to that in the wild type (table 2). Interestingly, the amount of the reaction centre proteins (D1 and D2) were also lowered in the TLA1 RNAi transformants but were higher in the TLA1 over-expressing strains, respectively, relative to the wild type (figures 5d,e and 6d,e). The number of Chl molecules per P700 showed a similar trend as that of Chl per QA (data not shown). More directly, kinetic spectrophotometric analysis showed that the Chl antenna size of the photosystems is smaller in the TLA1 RNAi transformants and slightly larger in the TLA1 over-expressing strains, relative to that in the wild type. The PSI Chl antenna size was more pronouncedly reduced than that of PSII in the TLA1 RNAi transformants (table 2). It is noted that cellular Chl content and Chl antenna size of the photosystems in the TLA1 RNAi transformants are similar to those measured earlier with the tla1 mutant [25]. The latter, like the TLA1 RNAi transformants here, possessed a lower number of photosynthetic electron transport chains per chloroplast, when compared with that in the wild-type strain [25].
Interestingly, both in the tla1 mutant described earlier [25] and in the RNAi lines described here, the decrease in Chl content was proportionally larger than the change in Chl antenna size, implying a phenotype consistent with a restriction on chlorophyll biosynthesis. This would explain the dual effect on the truncated size of the Chl antenna and the diminished abundance in reaction centre proteins on a per cell basis. It is understood that when chlorophyll supply is restricted reaction centre assembly takes precedence over antenna, and hence the antenna size is smaller.
Nucleic acid binding protein 1 (NAB1) is a cytosolic protein that plays an important role in regulation of the expression of the light-harvesting antenna of PSII at the post-transcriptional level by binding largely to LHCBM6 and to a lesser extent to LHCBM4 mRNA in C. reinhardtii [54]. Absence of the NAB1 protein leads to an increase in the apoprotein amount of LHCB (LHCBM4 and LHCBM6), which is peripherally associated with the PSII antenna, leading to an increase in the size of the PSII Chl antenna size [54]. Western blot analysis of the TLA1 RNAi transformants and the TLA1 over-expressing lines with the NAB1-specific antibodies did not reveal any difference in the level of the NAB1 proteins, suggesting that TLA1 and NAB1 function in a different signal transduction pathway in the regulation of the Chl antenna size of photosynthesis.
VIPP1 is a conserved protein in higher plants, algae and cyanobacteria, and has been shown to play a role in thylakoid membrane biogenesis/maintenance in higher plants and algae [57–59]. VIPP1 was localized in both chloroplast inner envelope and thylakoid membranes. The Arabidopsis VIPP1-less mutant (hcf155) cannot grow photo-autotrophically owing to aberrant thylakoids and is deficient in the formation of vesicles that bud-off from the inner chloroplast envelope [58,60]. It is known that vesiculation of the inner chloroplast envelope membrane provides a pathway by which diglyceride lipids are transported from the site of synthesis at the inner envelope to the developing thylakoids [59]. The VIPP1-less mutant is also chlorophyll-deficient, and has a dysfunctional photosynthetic electron transport chain [58]. In the cyanobacteria Synechocystis 6803, loss of photosynthetic activity and aberrant thylakoid membranes were due to loss of VIPP1 [60]. In this work, Western blot analysis of the TLA1 RNAi transformants and the TLA1 over-expressing lines with the VIPP1 primary antibodies showed that the amount of VIPP1 protein is drastically reduced in the TLA1 RNAi transformants and increased in the TLA1 over-expressing lines (figures 5f and 6f). These results suggested that TLA1 and VIPP1 function in the same signalling transduction pathway for the regulation of the Chl antenna size and electron transport chain of photosynthesis.
TLA1 was originally deemed to be a soluble protein lacking a chloroplast or mitochondrial targeting/transit peptide, hence presumed to be localized in the cytoplasm of the cell. However, cell fractionation studies in this work showed that it co-isolates with the cell membrane fraction (figures 7 and 8). The TLA1 protein sequence does possess a single hydrophobic domain comprising 27 amino acids between residues 42 and 69, theoretically long enough to qualify as a transmembrane domain [26]. This hydrophobic domain of 27 amino acids is highly conserved in similar proteins of unknown function from other diverse organisms. This hydrophobic domain can theoretically be used for single-span membrane attachment of the TLA1. This observation might explain the Western blot analysis results in this study, which showed that the TLA1 protein is enriched in the cellular membrane and chloroplast envelope fraction but not present in the soluble stroma or nucleus. Alternatively, the TLA1 protein could be anchored to the membrane via a different anchoring membrane protein or a lipid. Interestingly, the TLA1 homologue in Arabidopsis (AT5G55940) was predicted to be localized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) [61].
For many years, all proteins destined for internal chloroplast compartments were thought to possess a chloroplast transit peptide (cTP) and use the Toc/Tic protein import machinery. However, new large-scale proteomic studies have revealed the existence of several proteins that lack cleavable transit peptide pre-sequences but reach internal chloroplast compartments nevertheless [62,63]. The initial suggestion that the chloroplast proteome consists of a large fraction of proteins lacking a cTP [62] was interpreted in two ways. First, these proteins might not possess any cleavable targeting pre-sequence (i.e. non-canonical Cp proteins) and, second, they carry these target sequences, but current prediction algorithms fail to recognize them. Recent results by Armbruster et al. [63] indicated that about 11.2 per cent of chloroplast proteins in Arabidopsis are non-canonical chloroplast proteins (lack a well-defined cTP) and are localized in the inner compartment of chloroplasts. It is clear that at least two classes of non-canonical chloroplast proteins exist: one localized is the chloroplast inner envelope and the other in the ER-dependent Cp import process [63]. Examples of non-canonical chloroplast proteins in inner chloroplast envelope include the chloroplast envelope quinone oxidoreductase homologue (ceQORH) protein [64–66] and Tic32/IEP32 that was identified as another inner chloroplast envelope protein without an apparent cTP [67]. ceQORH uses an internal 40 amino acids long sequence for chloroplast localization that does not resemble any conserved chloroplast localization sequence [64]. Non-canonical chloroplast proteins that are localized in the chloroplast via ER and Golgi apparatus are encountered in organisms that have complex plastids, including many algae and apicomplexan parasites [68]. Examples include a recently identified alpha carbonic anhydrase (CAH1) protein in the model plant Arabidopsis [69]. The Arabidopsis alpha CAH1 protein has been found to localize in the chloroplast stroma, although it was predicted to have a secretory/ER transit peptide [63,69,70]. On the basis of its similarities to Cp protein transport in primitive organisms, the CAH1 pathway might represent an ancestral co-translational targeting mechanism that arose prior to the evolution of the now dominant post-translational Toc/Tic system [69]. Given this background, it is possible that the TLA1 protein is localized in the chloroplast envelope and budding thylakoid membrane (figures 7 and 8), where it exerts a pivotal role in thylakoid membrane biogenesis and Chl antenna assembly. This scenario would require future specific in vitro import and red fluorescent protein or green fluorescent protein-fusion assays to test for the specific sub-cellular destination of the TLA1 protein.
TEM revealed substantial differences in thylakoid membrane ultrastructure between the TLA1 RNAi transformants and the wild-type and OE strains. The thylakoid organization of the former showed less-compact arrangement of membranes compared with that of the wild-type and OE strains. The TLA1 RNAi transformants did not possess properly appressed grana membranes but showed a rather disorganized thylakoid membrane system (figure 9a–c). Proteins of the LHC and the VIPP1 are known to play a role in thylakoid membrane biogenesis and organization. Hence, the TEM results along with the Western blot analysis showing reduction in LHC and VIPP1 proteins in the TLA1 RNAi transformants might indicate that the TLA1 protein regulates the organization of the thylakoid membranes in the chloroplast via regulation of expression of these two proteins. The work described here provides new insight into the modus operandi of the TLA1 gene, not only as a component of a novel signal transduction pathway for the regulation of the Chl antenna size, but also as a regulator of thylakoid membrane biogenesis and organization in chloroplasts.
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by the US Department of Energy Hydrogen and Fuel Cells Program grant no. DE-FG36-05GO15041. Authors wish to acknowledge Reena Zalpuri of the UC Berkeley, Electron Microscope Laboratory for help with the TEM, Dr Roberto Bassi (University of Verona, Italy) for provision of the spinach LHC antibodies, Dr Michael Schroda (University of Freiburg, Freiburg, Germany) for the Chlamydomonas VIPP1 antibodies, Dr James V. Moroney (Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge, USA) for the Chlamydomonas RbcL antibodies and Dr Olaf Kruse (University of Bielefeld, Germany) for the Chlamydomonas NAB1 antibodies.
References
- 1.Duysens L. N. M., Amsez J., Kamp B. M. 1961. Two photochemical systems in photosynthesis. Nature 190, 510–511 10.1038/190510a0 (doi:10.1038/190510a0) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Simpson D. J., Knoetzel J. 1996. Light-harvesting complexes of plants and algae: introduction, survey and nomenclature. In Oxygenic photosynthesis: the light reactions (eds Ort D. R., Yocum C. F.), pp. 493–506 Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers [Google Scholar]
- 3.Pichersky E., Jansson S. 1996. The light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b-binding polypeptides and their genes in angiosperm and gymnosperm species. In Oxygenic photosynthesis: the light reactions (eds Ort D. R., Yocum C. F.), pp. 507–521 Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers [Google Scholar]
- 4.Melis A. 1991. Dynamics of photosynthetic membrane composition and function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1058, 87–106 10.1016/S0005-2728(05)80225-7 (doi:10.1016/S0005-2728(05)80225-7) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Melis A. 1996. Excitation energy transfer: functional and dynamic aspects of LHC (cab) proteins. In Oxygenic photosynthesis: the light reactions (eds Ort D. R., Yocum C. F.), pp. 523–538 Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers [Google Scholar]
- 6.Neidhardt J., Benemann J. R., Zhang L., Melis A. 1998. Photosystem-II repair and chloroplast recovery from irradiance stress: relationship between chronic photoinhibition, light-harvesting chlorophyll antenna size and photosynthetic productivity in Dunaliella salina (green algae). Photosynth. Res. 56, 175–184 10.1023/A:1006024827225 (doi:10.1023/A:1006024827225) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Jansson S., et al. 1992. A nomenclature for the genes encoding the chlorophyll a/b-binding proteins of higher plants. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 10, 242–253 10.1007/BF02668357 (doi:10.1007/BF02668357) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Elrad D., Grossman A. R. 2004. A genome's-eye view of the light-harvesting polypeptides of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Curr. Genet. 45, 61–75 10.1007/s00294-003-0460-x (doi:10.1007/s00294-003-0460-x) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Anderson J. M. 1986. Photoregulation of the composition, function and structure of thylakoid membranes. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 37, 93–136 10.1146/annurev.pp.37.060186.000521 (doi:10.1146/annurev.pp.37.060186.000521) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Escoubas J. M., Lomas M., LaRoche J., Falkowski P. G. 1995. Light intensity regulation of cab gene transcription is signaled by the redox state of the plastoquinone pool. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 92, 10 237–10 241 10.1073/pnas.92.22.10237 (doi:10.1073/pnas.92.22.10237) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Huner N. P. A., Oquist G., Sarhan F. 1998. Energy balance and acclimation to light and cold. Trends Plant Sci. 3, 224–230 10.1016/S1360-1385(98)01248-5 (doi:10.1016/S1360-1385(98)01248-5) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Masuda T., Tanaka A., Melis A. 2003. Chlorophyll antenna size adjustments by irradiance in Dunaliella salina involve coordinate regulation of chlorophyll a oxygenase (CAO) and LHCb gene expression. Plant Mol. Biol. 51, 757–771 10.1023/A:1022545118212 (doi:10.1023/A:1022545118212) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kirk J. T. O. 1994. Light and photosynthesis in aquatic ecosystems, 2nd edn Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press [Google Scholar]
- 14.Maxwell D. P., Falk S., Huner N. P. A. 1995. Photosystem II excitation pressure and development of resistance to photoinhibition. 1. Light harvesting complex II abundance and zeaxanthin content in Chlorella vulgaris. Plant Physiol. 107, 687–694 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Webb M. R., Melis A. 1995. Chloroplast response in Dunaliella salina to irradiance stress. Effect on thylakoid membrane assembly and function. Plant Physiol. 107, 885–893 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Tanaka A., Melis A. 1997. Irradiance-dependent changes in the size and composition of the chlorophyll a-b light-harvesting complex in the green alga Dunaliella salina. Plant Cell Physiol. 38, 17–24 10.1093/oxfordjournals.pcp.a029080 (doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.pcp.a029080) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Nakada E., Asada Y., Arai T., Miyake J. 1995. Light penetration into cell suspensions of photosynthetic bacteria and relation to hydrogen production. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 80, 53–57 10.1016/0922-338X(95)98176-L (doi:10.1016/0922-338X(95)98176-L) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Yakovlev A. G., Taisova A. S., Fetisova Z. G. 2002. Light control over the size of an antenna unit building block as an efficient strategy for light harvesting in photosynthesis. FEBS Lett. 512, 129–132 10.1016/S0014-5793(02)02238-X (doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(02)02238-X) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mitra M., Melis A. 2008. Optical properties of microalgae for enhanced biofuels production. Opt. Express 16, 21 807–21 820 10.1364/OE.16.021807 (doi:10.1364/OE.16.021807) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kirst H., Garcia-Cerdan J. G., Zurbriggen A., Melis A. 2012. Assembly of the light-harvesting chlorophyll antenna in the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii requires expression of the TLA2-CpFTSY gene. Plant Physiol. 158, 930–945 10.1104/pp.111.189910 (doi:10.1104/pp.111.189910) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ohtsuka T., Ito H., Tanaka A. 1997. Conversion of chlorophyll b to chlorophyll a and the assembly of chlorophyll with apoproteins by isolated chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 113, 137–147 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wilson K. E., Huner N. P. A. 2000. The role of growth rates, redox-state of the plastoquinone pool and the trans-thylakoid pH in photoacclimation of Chlorella vulgaris to growth irradiance and temperature. Planta 212, 93–102 10.1007/s004250000368 (doi:10.1007/s004250000368) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Melis A., Neidhardt J., Benemann J. R. 1999. Dunaliella salina (Chlorophyta) with small chlorophyll antenna sizes exhibit higher photosynthetic productivities and photon use efficiencies than normally pigmented cells. J. Appl. Phycol. 10, 515–52 10.1023/A:1008076231267 (doi:10.1023/A:1008076231267) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Melis A. 2009. Solar energy conversion efficiencies in photosynthesis: minimizing the chlorophyll antennae to maximize efficiency. Plant Sci. 177, 272–280 10.1016/j.plantsci.2009.06.005 (doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2009.06.005) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Polle J. E. W., Kanakagiri S., Melis A. 2003. tla1, a DNA insertional transformant of the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with a truncated light-harvesting chlorophyll antenna size. Planta 217, 49–59 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Tetali S., Mitra M., Melis A. 2007. Development of the light-harvesting chlorophyll antenna in the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii is regulated by the novel TLA1 gene. Planta 225, 813–829 10.1007/s00425-006-0392-z (doi:10.1007/s00425-006-0392-z) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Mitra M., Melis A. 2010. Genetic and biochemical analysis of the TLA1 gene in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Planta 231, 729–740 10.1007/s00425-009-1083-3 (doi:10.1007/s00425-009-1083-3) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Mitra M., Ng S., Melis A. 2012. The TLA1 protein family members contain a variant of the plain MOV34/MPN domain. Am. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2, 1–18 10.3923/ajbmb.2012.1.18 (doi:10.3923/ajbmb.2012.1.18) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sueoka N. 1960. Mitotic replication of deoxyribonucleic acids in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 46, 83–91 10.1073/pnas.46.1.83 (doi:10.1073/pnas.46.1.83) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Harris E. H. 1989. The Chlamydomonas source book: a comprehensive guide to biology and laboratory use. San Diego, CA: Academic Press; [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Polle J. E. W., Benemann J. R., Tanaka A., Melis A. 2000. Photosynthetic apparatus organization and function in wild type and a Chl b-less mutant of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Dependence on carbon source. Planta 211, 335–344 10.1007/s004250000279 (doi:10.1007/s004250000279) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Arnon D. 1949. Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenol oxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol. 24, 1–15 10.1104/pp.24.1.1 (doi:10.1104/pp.24.1.1) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Melis A., Spangfort M., Andersson B. 1987. Light-absorption and electron-transport balance between PSII and PSI in spinach chloroplasts. Photochem. Photobiol. 45, 129–136 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1987.tb08413.x (doi:10.1111/j.1751-1097.1987.tb08413.x) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Fischer N., Rochaix J. D. 2001. The flanking regions of PsaD drive efficient gene expression in the nucleus of the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Mol. Genet. Genomics 265, 888–894 10.1007/s004380100485 (doi:10.1007/s004380100485) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Pollock S. V., Colombo S. L., Prout D. L., Godfrey A. C., Moroney J. V. 2003. Rubisco activase is required for optimal photosynthesis in the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii in a low-CO2 atmosphere. Plant Physiol. 133, 1854–1861 10.1104/pp.103.032078 (doi:10.1104/pp.103.032078) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sizova I., Fuhrmann M., Hegemann P. 2001. A Streptomyces rimosus aphVIII gene coding for a new type phosphotransferase provides stable antibiotic resistance to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Gene 277, 221–229 10.1016/S0378-1119(01)00616-3 (doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(01)00616-3) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Debuchy R., Purton S., Rochaix J. D. 1989. The arginosuccinate lyase gene of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: an important tool for nuclear transformation and for correlating the genetic and molecular maps of the ARG7 locus. EMBO J. 8, 2803–2809 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kindle K. L. 1990. High-frequency nuclear transformation of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 87, 1228–1232 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1228 (doi:10.1073/pnas.87.3.1228) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Davies J., Weeks D. P., Grossman A. R. 1992. Expression of the arylsulfatase gene from the 2-tubulin promoter in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Nucleic Acids Res. 20, 2959–2965 10.1093/nar/20.12.2959 (doi:10.1093/nar/20.12.2959) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Shimogawara K., Muto S. 1992. Purification of Chlamydomonas 28-kDa ubiquitinated protein and its identification as ubiquitinated histone H2B. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 294, 193–199 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90157-R (doi:10.1016/0003-9861(92)90157-R) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Mason C. B., Bricker T. M., Moroney J. V. 2006. A rapid method for chloroplast isolation from the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Nat. Protocols 1, 2227–2230 10.1038/nprot.2006.348 (doi:10.1038/nprot.2006.348) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Clemetson J. M., Boschetti A. 1988. Chloroplast envelope proteins from Chlamydomonas: separation into outer and inner envelopes and analysis by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 943, 371–374 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90570-6 (doi:10.1016/0005-2736(88)90570-6) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ramazanov Z., Mason C. B., Geraghty A. M., Spalding M. H., Moroney J. V. 1993. The low CO,-inducible 36-kilodalton protein is localized to the chloroplast envelope of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii . Plant Physiol. 101, 1195–1199 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Allen K. D., Staehelin L. A. 1994. Polypeptide composition, assembly and phosphorylation patterns of the photosystem II antenna system of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Planta 194, 42–54 10.1007/BF00201033 (doi:10.1007/BF00201033) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Melis A., Brown J. S. 1980. Stoichiometry of system I and system II reaction centers and of plastoquinone in different photosynthetic membranes. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 77, 4712–4716 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4712 (doi:10.1073/pnas.77.8.4712) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Smith B. M., Morrissey P. J., Guenther J. E., Nemson J. A., Harrison M. A., Allen J. F., Melis A. 1990. Response of the photosynthetic apparatus in Dunaliella salina (green algae) to irradiance stress. Plant Physiol. 93, 1433–1440 10.1104/pp.93.4.1433 (doi:10.1104/pp.93.4.1433) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Melis A. 1989. Spectroscopic methods in photosynthesis: photosystem stoichiometry and chlorophyll antenna size. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 323, 397–409 10.1098/rstb.1989.0019 (doi:10.1098/rstb.1989.0019) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Laemmli U. K. 1970. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227, 680–685 10.1038/227680a0 (doi:10.1038/227680a0) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Melis A., Anderson J. M. 1983. Structural and functional organization of the photosystems in spinach chloroplasts: antenna size, relative electron transport capacity and chlorophyll composition. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 724, 473–484 [Google Scholar]
- 50.Morris R. L., Keller L. R., Zweidler A., Rizzo P. J. 1990. Analysis of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii histones and chromatin. J. Protozool. 37, 117–123 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Waterborg J. H., Robertson A. J., Tatar D. L., Borza C. M., Davie J. R. 1995. Histones of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 109, 393–407 10.1104/pp.109.2.393 (doi:10.1104/pp.109.2.393) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Allen J. F., Forsberg J. 2001. Molecular recognition in thylakoid structure and function. Trends Plant Sci. 6, 317–326 10.1016/S1360-1385(01)02010-6 (doi:10.1016/S1360-1385(01)02010-6) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Yang D. H., Andersson B., Aro E. M., Ohad I. 2001. The redox state of the plastoquinone pool controls the level of the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b binding protein complex II (LHC II) during photoacclimation: cytochrome b(6)f deficient Lemna perpusilla plants are locked in a state of high-light acclimation. Photosynth. Res. 68, 163–174 10.1023/A:1011849919438 (doi:10.1023/A:1011849919438) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Mussgnug J. H., et al. 2005. NAB1 is an RNA binding protein involved in the light-regulated differential expression of the light-harvesting antenna of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Cell 17, 3409–3421 10.1105/tpc.105.035774 (doi:10.1105/tpc.105.035774) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Grossman A. 2000. Acclimation of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii to its nutrient environment. Protist 151, 201–224 10.1078/1434-4610-00020 (doi:10.1078/1434-4610-00020) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Bjorkman, et al. 1972. Effect of light intensity during growth of Atriplex patula on the capacity of photosynthetic reactions, chloroplast components and structure. Camegie Inst. Yearbook 71, 115–135 [Google Scholar]
- 57.Li H. M., Kaneko Y., Keegstra K. 1994. Molecular cloning of a chloroplastic protein associated with both the envelope and thylakoid membranes. Plant Mol. Biol. 25, 619–632 10.1007/BF00029601 (doi:10.1007/BF00029601) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Kroll D., Meierhoff K., Bechtold N., Kinoshita M., Westphal S., Vothknecht U. C., Soll J., Westhoff P. 2001. VIPP1, a nuclear gene of Arabidopsis thaliana essential for thylakoid membrane formation. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 98, 4238–4242 10.1073/pnas.061500998 (doi:10.1073/pnas.061500998) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Liu C., Willmund F., Whitelegge J. P., Hawat S., Knapp B., Lodha M., Schroda M. 2005. J-Domain protein CDJ2 and HSP70B are a plastidic chaperone pair that interacts with vesicle-inducing protein in plastids 1. Mol. Biol. Cell 16, 1165–1177 10.1091/mbc.E04-08-0736 (doi:10.1091/mbc.E04-08-0736) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Gao H., Xu X. 2009. Depletion of VIPP1 in Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 affects photosynthetic activity before the loss of thylakoid membranes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 292, 63–70 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2008.01470.x (doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2008.01470.x) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Dunkley T. P. J., et al. 2006. Mapping the Arabidopsis organelle proteome. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 103, 6518–6523 10.1073/pnas.0506958103 (doi:10.1073/pnas.0506958103) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Kleffmann T., Russenberger D., von Zychlinski A., Christopher W., Sjolander K., Gruissem W., Baginsky S. 2004. The Arabidopsis thaliana chloroplast proteome reveals pathway abundance and novel protein functions. Curr. Biol. 14, 354–362 10.1016/j.cub.2004.02.039 (doi:10.1016/j.cub.2004.02.039) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Armbruster U., et al. 2009. Chloroplast proteins without cleavable transit peptides: rare exceptions or a major constituent of the chloroplast proteome? Mol. Plant 2, 1325–1335 10.1093/mp/ssp082 (doi:10.1093/mp/ssp082) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Miras S., Salvi D., Ferro M., Grunwald D., Garin J., Joyard J., Rolland N. 2002. Non-canonical transit peptide for import into the chloroplast. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 47 770–47 778 10.1074/jbc.M207477200 (doi:10.1074/jbc.M207477200) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Miras S., Salvi D., Piette L., Seigneurin-Berny D., Grunwald D., Reinbothe C., Joyard J., Reinbothe S., Rolland N. 2007. Toc159- and Toc75-independent import of a transit sequence-less precursor into the inner envelope of chloroplasts. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 29 482–29 492 10.1074/jbc.M611112200 (doi:10.1074/jbc.M611112200) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Ferro M., Salvi D., Brugiere S., Miras S., Kowalski S., Louwagie M., Garin J., Joyard J., Rolland N. 2003. Proteomics of the chloroplast envelope membranes from Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Cell Proteomics 2, 325–345 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Nada A., Soll J. 2004. Inner envelope protein 32 is imported into chloroplasts by a novel pathway. J. Cell Sci. 117, 3975–3982 10.1242/jcs.01265 (doi:10.1242/jcs.01265) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Jarvis P. 2008. Targeting of nucleus-encoded proteins to chloroplasts in plants. New Phytol. 179, 257–285 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2008.02452.x (doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2008.02452.x) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Villarejo A., et al. 2005. Evidence for a protein transported through the secretory pathway en route to the higher plant chloroplast. Nat. Cell Biol. 7, 1124–1140 10.1038/ncb1330 (doi:10.1038/ncb1330) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Radhamony R. N., Theg S. M. 2006. Evidence for an ER to Golgi to chloroplast protein transport pathway. Trends Cell Biol. 16, 385–387 10.1016/j.tcb.2006.06.003 (doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2006.06.003) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]