Abstract
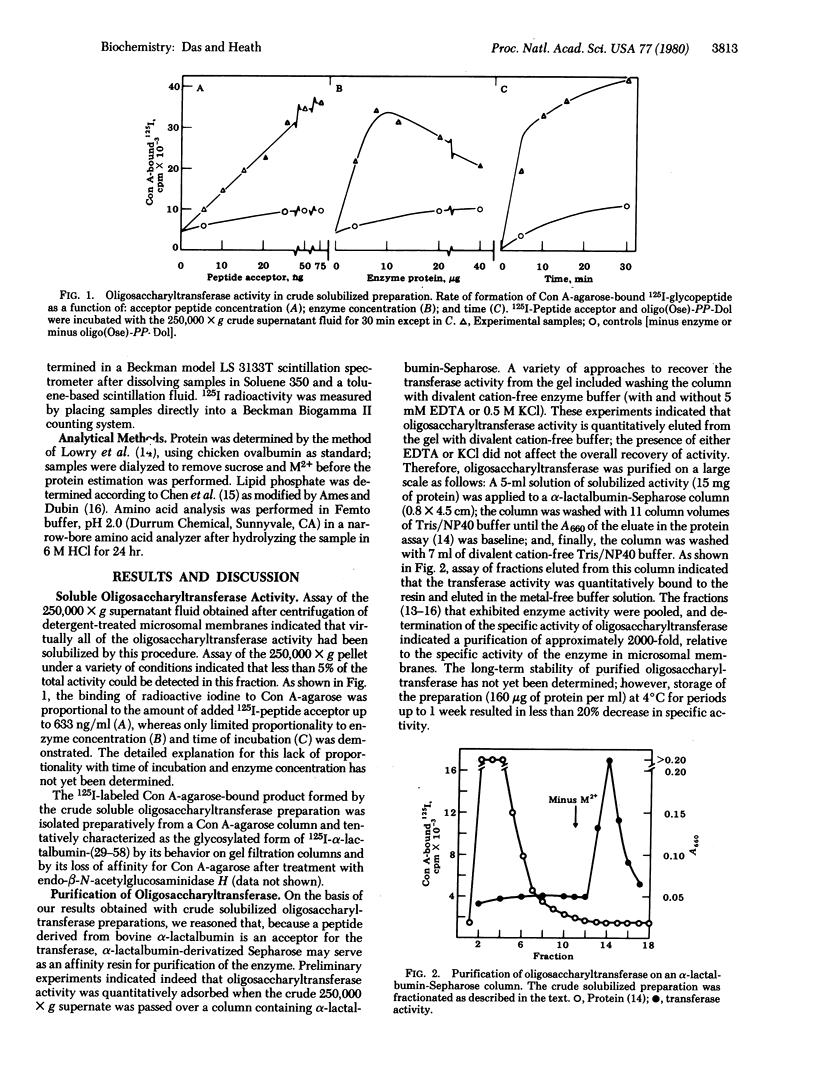
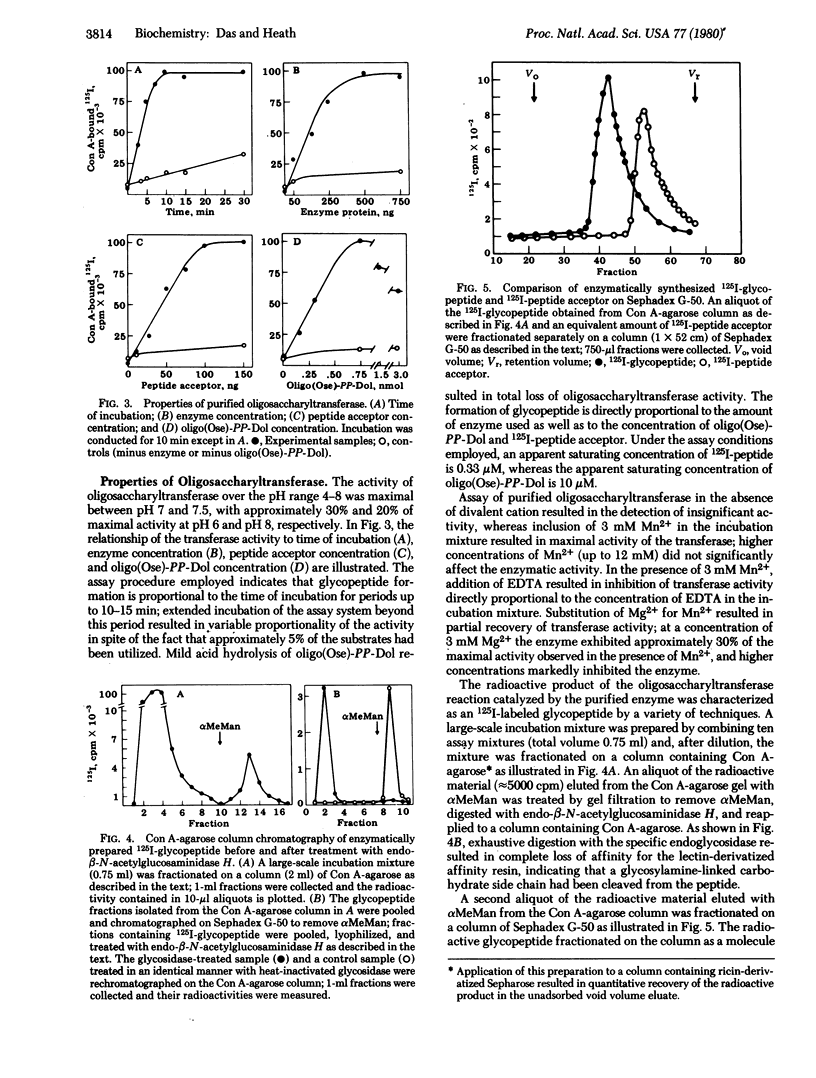
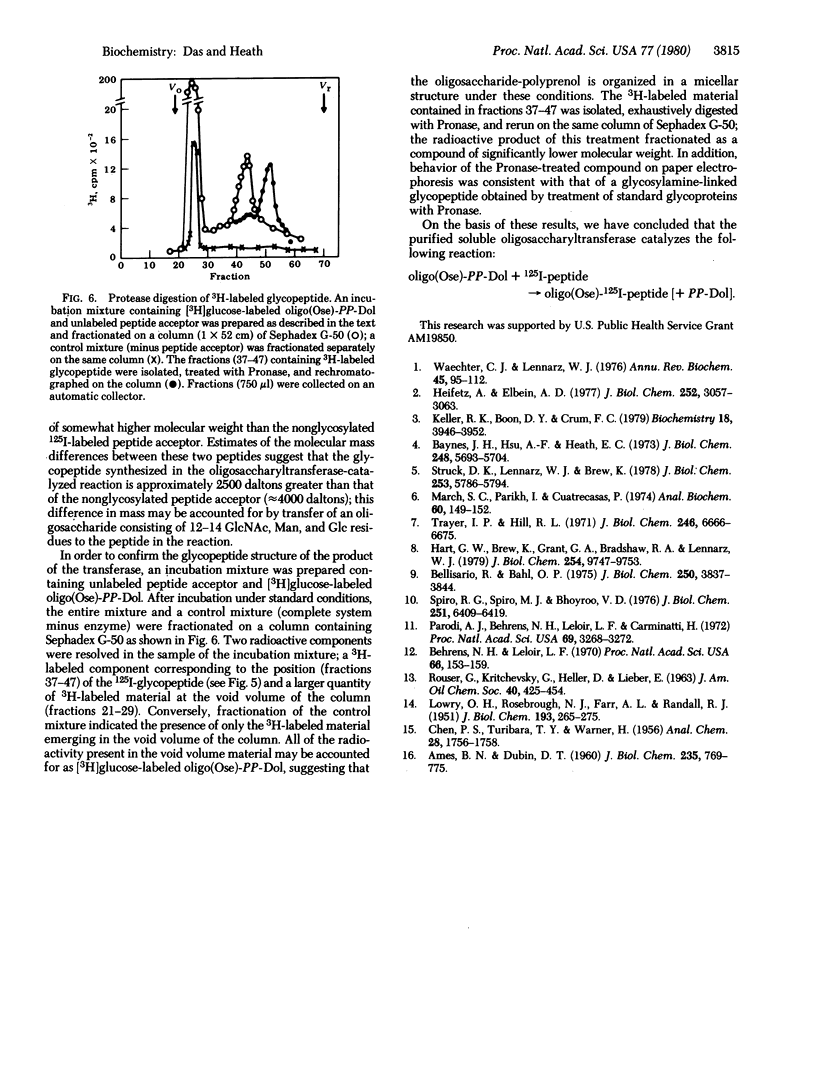
Dolichyldiphosphoryloligosaccharide—protein oligosaccharyltransferase was solubilized from hen oviduct rough endoplasmic reticulum by extraction with 0.2% Nonidet P40. Oligosaccharyltransferase activity was assayed in an incubation mixture containing Glcn-Manx-GlcNAc2-diphosphoryldolichol as an oligosaccharyl donor and the 125I-labeled tryptic peptide consisting of residues 29-58 from bovine α-lactalbumin as acceptor. The transferase was purified approximately 2000-fold by fractionation on a bovine α-lactalbumin-Sepharose column; the active material bound quantitatively to the gel and was eluted by removal of divalent cation from the wash buffer. The product of the transferase activity, 125I-glycopeptide, was determined as concanavalin A-agarose-adsorbed radioactivity by a filter disc assay method. 125I-Labeled concanavalin A-agarose-bound product was characterized as a glycopeptide as follows: (i) gel filtration behavior on Sephadex G-50; (ii) elution from concanavalin A-agarose with 1% α-methyl mannoside; (iii) absence of affinity for ricin-Sepharose and loss of affinity for concanavalin A-agarose after treatment with endo-β-N-acetylglucosaminidase H; (iv) enzymatic synthesis of identical product upon using [3H]oligosaccharyldiphosphoryldolichol and unlabeled peptide acceptor; and (v) digestion of 3H-labeled peptide with Pronase, resulting in the formation of lower molecular weight glycopeptide. Oligosaccharyltransferase activity exhibited an absolute requirement for divalent cations (3 mM Mn2+; Mg2+ was 30% as effective), complete dependence on exogenously supplied peptide acceptor (1.33 μg/ml) and oligosaccharyldiphosphoryldolichol (approximately 10 nmol/ml), and an optimum pH between 7 and 7.5.
Keywords: glycoprotein synthesis, glycosylaminyltransferase, soluble membrane protein
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMES B. N., DUBIN D. T. The role of polyamines in the neutralization of bacteriophage deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:769–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baynes J. W., Hsu A. F., Heath E. C. The role of mannosyl-phosphoryl-dihydropolyisoprenol in the synthesis of mammalian glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 25;248(16):5693–5704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behrens N. H., Leloir L. F. Dolichol monophosphate glucose: an intermediate in glucose transfer in liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 May;66(1):153–159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.1.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellisario R., Bahl O. P. Human chorionic gonadotropin. V. Tissue specificity of binding and partial characterization of soluble human chorionic gonadotropin-receptor complexes. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):3837–3844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart G. W., Brew K., Grant G. A., Bradshaw R. A., Lennarz W. J. Primary structural requirements for the enzymatic formation of the N-glycosidic bond in glycoproteins. Studies with natural and synthetic peptides. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9747–9753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heifetz A., Elbein A. D. Solubilization and properties of mannose and N-acetylglucosamine transferases involved in formation of polyprenyl-sugar intermediates. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 10;252(9):3057–3063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller R. K., Boon D. Y., Crum F. C. N-Acetylglucosamine- 1 -phosphate transferase from hen oviduct: solubilization, characterization, and inhibition by tunicamycin. Biochemistry. 1979 Sep 4;18(18):3946–3952. doi: 10.1021/bi00585a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March S. C., Parikh I., Cuatrecasas P. A simplified method for cyanogen bromide activation of agarose for affinity chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jul;60(1):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90139-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parodi A. J., Behrens N. H., Leloir L. F., Carminatti H. The role of polyprenol-bound saccharides as intermediates in glycoprotein synthesis in liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3268–3272. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro R. G., Spiro M. J., Bhoyroo V. D. Lipid-saccharide intermediates in glycoprotein biosynthesis. II. Studies on the structure of an oligosaccharide-lipid from thyroid. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 25;251(20):6409–6419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struck D. K., Lennarz W. J., Brew K. Primary structural requirements for the enzymatic formation of the N-glycosidic bond in glycoproteins. Studies with alpha-lactalbumin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 25;253(16):5786–5794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trayer I. P., Hill R. L. The purification and properties of the A protein of lactose synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov;246(21):6666–6675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waechter C. J., Lennarz W. J. The role of polyprenol-linked sugars in glycoprotein synthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:95–112. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.000523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



