Abstract
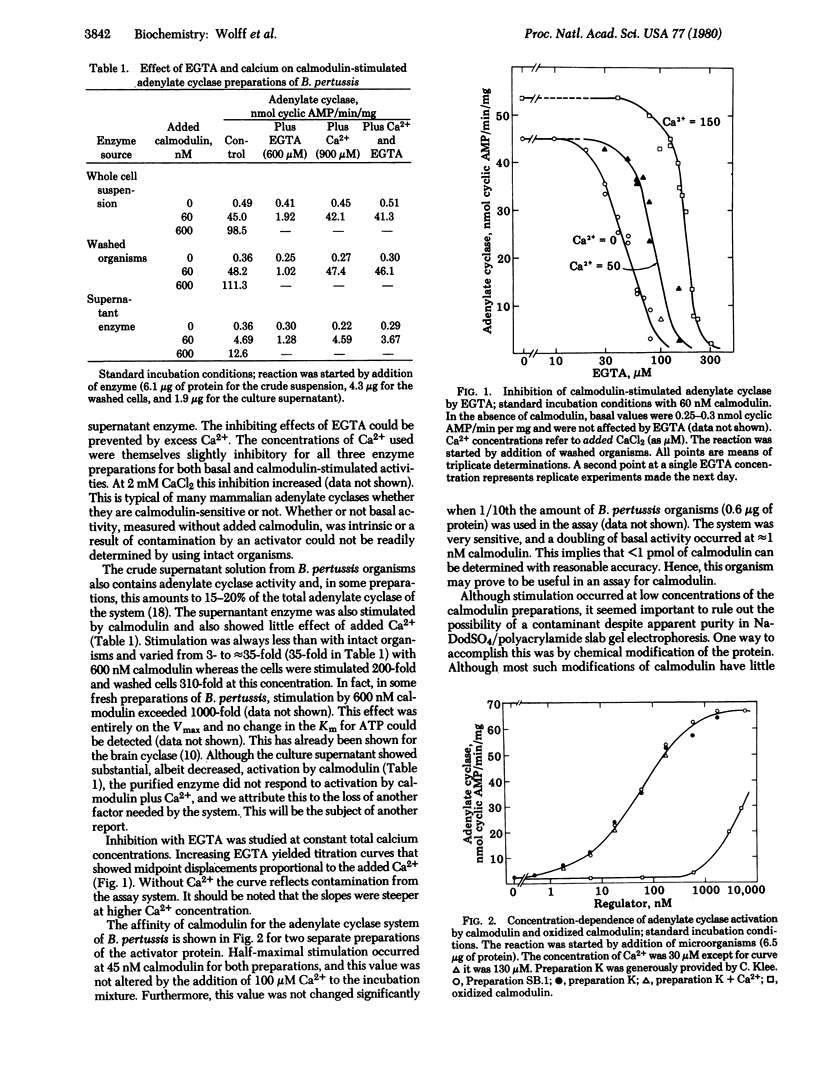
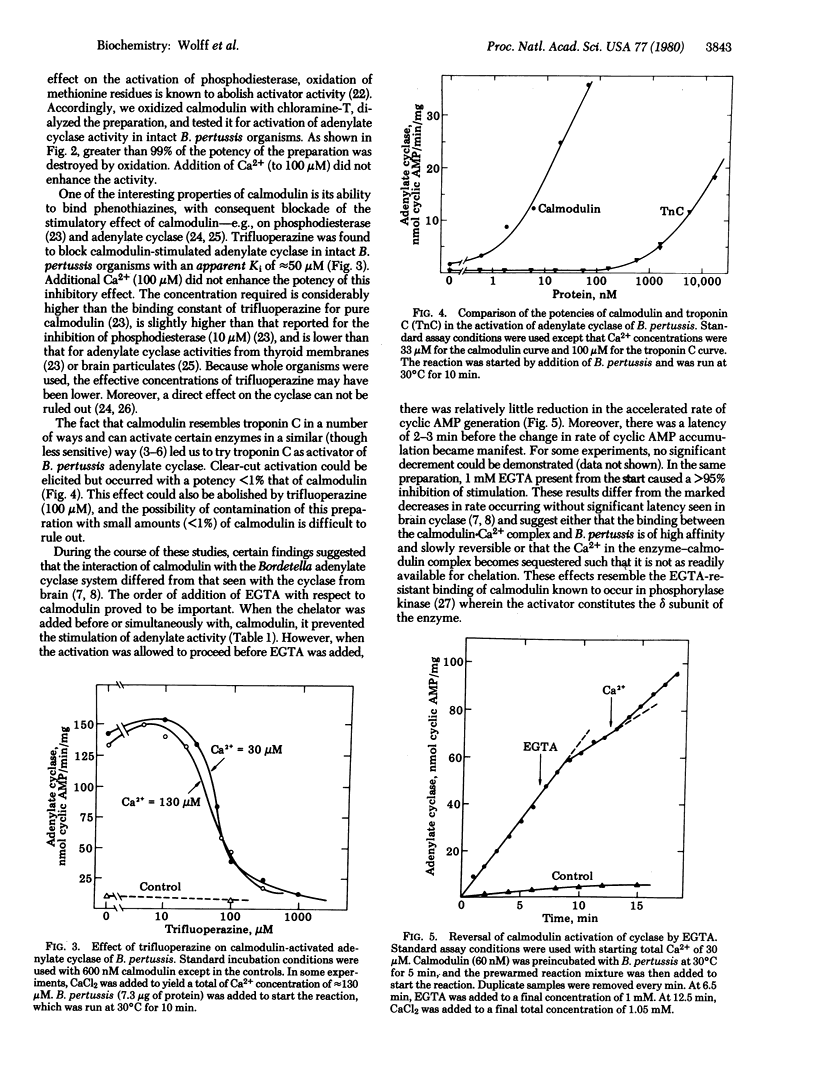
The adenylate cyclase of Bordetella pertussis is stimulated 100- to 1000-fold in a dose-dependent manner by calf brain calmodulin. The system has the following properties. (i) The activation is prevented by ethylene glycol bis(beta-aminoethyl ether)-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid and restored by Ca2+. (ii) Oxidation of the methionine residues of calmodulin abolishes the ability to activate the cyclase. (iii) Trifluoperazine inhibits calmodulin-activated cyclase. (iv) A troponin C preparation stimulates the B. pertussis cyclase with < 0.01 the potency of calmodulin. Although calmodulin has not been demonstrated in prokaryotes, this is an example of a (eukaryotic) calmodulin effect in a prokaryote.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berkowitz S. A., Katagiri J., Binder H. K., Williams R. C., Jr Separation and characterization of microtubule proteins from calf brain. Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 13;16(25):5610–5617. doi: 10.1021/bi00644a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostrom C. O., Brostrom M. A., Wolff D. J. Calcium-dependent adenylate cyclase from rat cerebral cortex. Reversible activation by sodium fluoride. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 25;252(16):5677–5685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostrom C. O., Huang Y. C., Breckenridge B. M., Wolff D. J. Identification of a calcium-binding protein as a calcium-dependent regulator of brain adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):64–68. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostrom M. A., Brostrom C. O., Breckenridge B. M., Wolff D. J. Calcium-dependent regulation of brain adenylate cyclase. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1978;9:85–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostrom M. A., Brostrom C. O., Breckenridge B. M., Wolff D. J. Regulation of adenylate cyclase from glial tumor cells by calcium and a calcium-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 10;251(15):4744–4750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung W. Y., Bradham L. S., Lynch T. J., Lin Y. M., Tallant E. A. Protein activator of cyclic 3':5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase of bovine or rat brain also activates its adenylate cyclase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Oct 6;66(3):1055–1062. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90747-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung W. Y. Calmodulin plays a pivotal role in cellular regulation. Science. 1980 Jan 4;207(4426):19–27. doi: 10.1126/science.6243188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Burchell A., Foulkes J. G., Cohen P. T., Vanaman T. C., Nairn C. Identification of the Ca2+-dependent modulator protein as the fourth subunit of rabbit skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase. FEBS Lett. 1978 Aug 15;92(2):287–293. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80772-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evain D., Klee C., Anderson W. B. Chinese hamster ovary cell population density affects intracellular concentrations of calcium-dependent regulator and ability of regulator to inhibit adenylate cyclase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3962–3966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett E. L., Underhill L. H., Cook G. H., Manclark C. R., Wolff J. A protein activator for the adenylate cyclase of Bordetella pertussis. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):5602–5605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett E. L., Urban M. A., Manclark C. R., Wolff J. Extracytoplasmic adenylate cyclase of Bordetella pertussis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1926–1930. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett E. L., Wolff J., Manclark C. R. Regulation of Bordetella pertussis extracytoplasmic adenylate cyclase. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1978;9:621–628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett E., Wolff J. Soluble adenylate cyclase from the culture medium of Bordetella pertussis: purification and characterization. J Bacteriol. 1976 Aug;127(2):890–898. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.2.890-898.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B. Conformational transition accompanying the binding of Ca2+ to the protein activator of 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate phosphodiesterase. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 8;16(5):1017–1024. doi: 10.1021/bi00624a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B., Crouch T. H., Richman P. G. Calmodulin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:489–515. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.002421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch T. J., Tallant E. A., Cheung W. Y. Rat brain adenylate cyclase. Further studies on its stimulation by a Ca2+-binding protein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Jul;182(1):124–133. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90290-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Vaughan M. Choleragen activation of solubilized adenylate cyclase: requirement for GTP and protein activator for demonstration of enzymatic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4396–4400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P. M. Membrane stabilization by drugs: tranquilizers, steroids, and anesthetics. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1966;9:145–221. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7742(08)60138-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valverde I., Vandermeers A., Anjaneyulu R., Malaisse W. J. Calmodulin activation of adenylate cyclase in pancreatic islets. Science. 1979 Oct 12;206(4415):225–227. doi: 10.1126/science.225798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh M., Stevens F. C. Chemical modification studies on the Ca2+-dependent protein modulator of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Biochemistry. 1977 Jun 14;16(12):2742–2749. doi: 10.1021/bi00631a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. H., Waisman D. M. Calmodulin and its role in the second-messenger system. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1979;15:47–107. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152815-7.50006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westcott K. R., La Porte D. C., Storm D. R. Resolution of adenylate cyclase sensitive and insensitive to Ca2+ and calcium-dependent regulatory protein (CDR) by CDR-sepharose affinity chromatography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):204–208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff D. J., Brostrom C. O. Properties and functions of the calcium-dependent regulator protein. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;11:27–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff J., Jones A. B. Inhibition of hormone-sensitive adenyl cyclase by phenothiazines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Feb;65(2):454–459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.2.454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



