Abstract
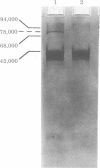
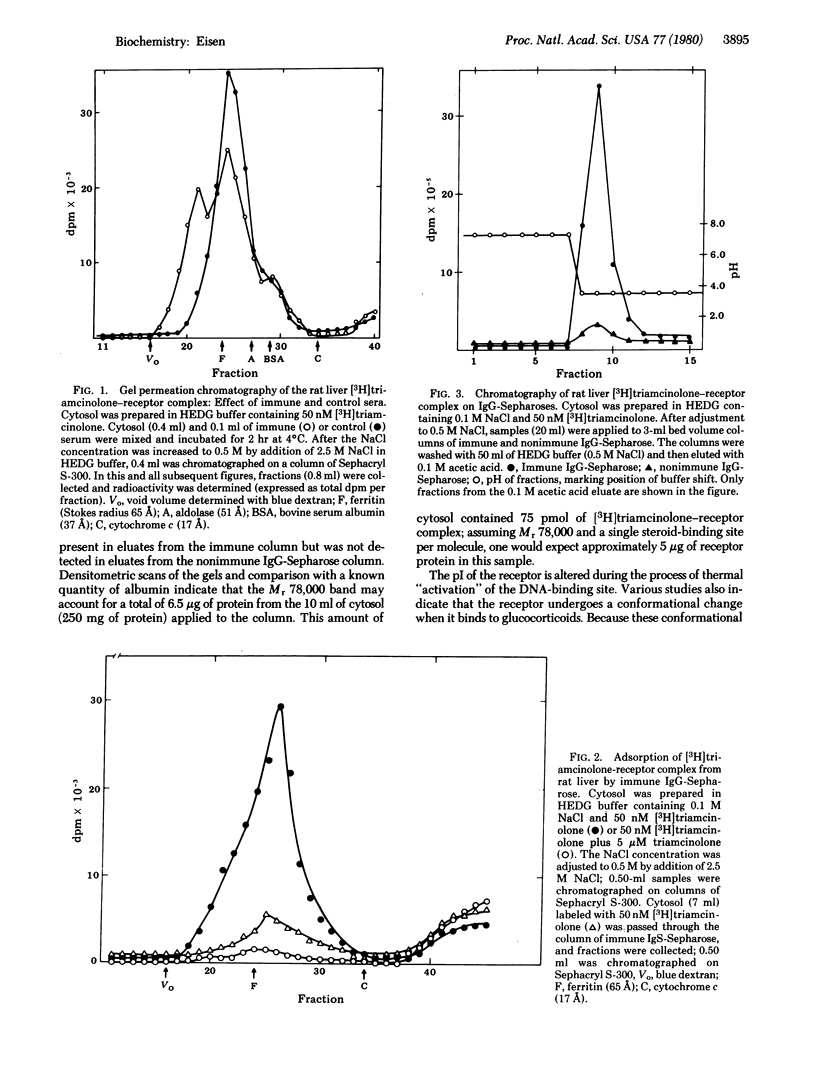
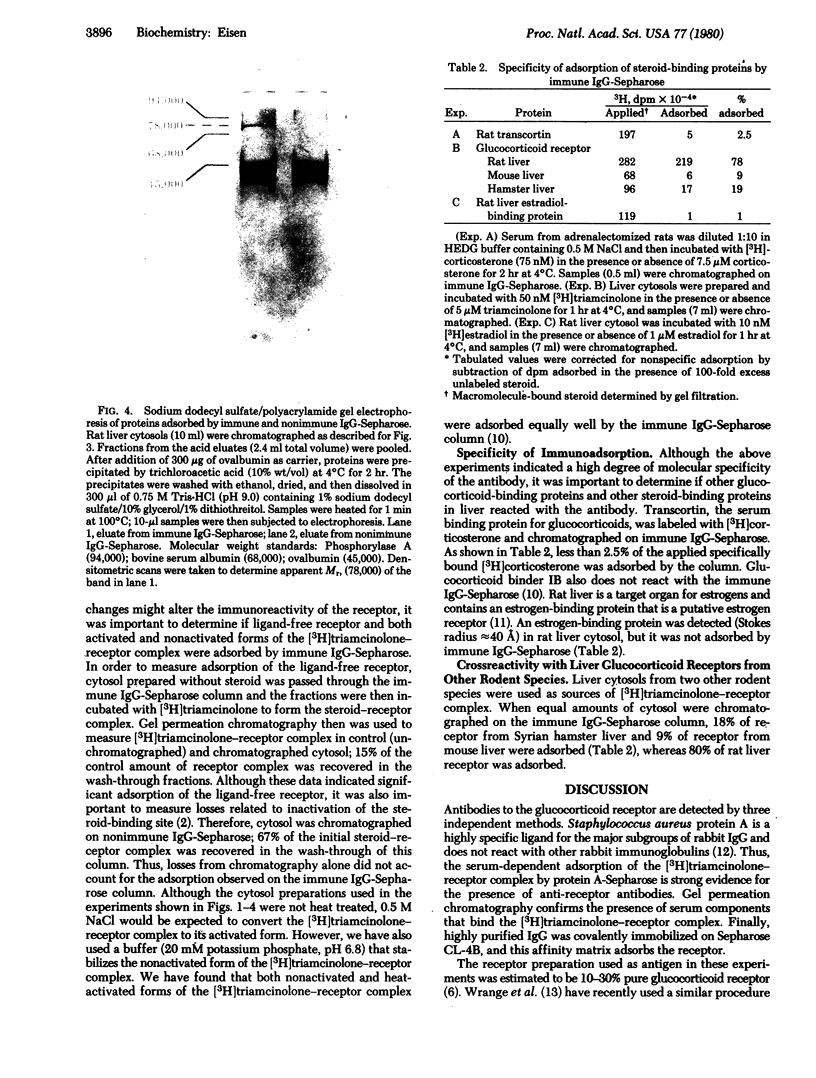
A rabbit immunized with a highly purified preparation of rat liver [3H]triamcinolone-receptor complex developed antibodies to the receptor. Although precipitating reactions were not detected, complexes formed between IgG and the receptor could be detected by Staphylococcus aureus protein A-Sepharose and gel permeation chromatography. IgG was purified and covalently immobilized on Sepharose CL-4B; this affinity matrix adsorbed the ligand-free receptor and both activated and nonactivated forms of the [3H]triamcinolone-receptor complex. Rat liver cytosol proteins adsorbed by control and immune immunoglobulin-Sepharoses were eluted with 0.1 M acetic acid and analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. A protein with molecular weight 78,000 was the major species eluted from immune immunglobulin-Sepharose, and it was not present in eluates from control columns. Rat transcortin, glucocorticoid binder IB, and an estrogen-binding protein from rat liver were not adsorbed by immune IgG-Sepharose. Mouse and hamster liver glucocorticoid receptors showed only limited adsorption. Thus, the antiserum does not crossreact with other major glucocorticoid-binding proteins and demonstrates species specificity.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aten R. F., Weinberger M. J., Eisenfeld A. J. Estrogen receptor in rat liver: translocation to the nucleus in vivo. Endocrinology. 1978 Feb;102(2):433–442. doi: 10.1210/endo-102-2-433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell P. A., Munck A. Steroid-binding properties and stabilization of cytoplasmic glucocorticoid receptors from rat thymus cells. Biochem J. 1973 Sep;136(1):97–107. doi: 10.1042/bj1360097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgeois S., Newby R. F., Huet M. Glucorticoid resistance in murine lymphoma and thymoma lines. Cancer Res. 1978 Nov;38(11 Pt 2):4279–4284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlstedt-Duke J., Gustaffson J. A., Wrange O. Formation and characteristics of hepatic dexamethasone-receptor complexes of different molecular weight. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Apr 27;497(2):507–524. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90208-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen H. J., Glinsmann W. H. Maximizing the purification of the activated glucocorticoid receptor by DNA-cellulose chromatography. Biochem J. 1978 Apr 1;171(1):177–183. doi: 10.1042/bj1710177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox T. O. Selective complexing of the "nuclear" 5S estradiol receptor by a serum component, 5S-CA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2664–2668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding J. W. Conjugation of antibodies with fluorochromes: modifications to the standard methods. J Immunol Methods. 1976;13(3-4):215–226. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govindan M. V., Sekeris C. E. Purification of two dexamethasone-binding proteins from rat-liver cytosol. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Aug 15;89(1):95–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb20900.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene G. L., Closs L. E., Fleming H., DeSombre E. R., Jensen E. V. Antibodies to estrogen receptor: immunochemical similarity of estrophilin from various mammalian species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3681–3685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene G. L., Fitch F. W., Jensen E. V. Monoclonal antibodies to estrophilin: probes for the study of estrogen receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):157–161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii D. N., Pratt W. B., Aronow L. Steady-state level of the specific glucocorticoid binding component in mouse fibroblasts. Biochemistry. 1972 Oct 10;11(21):3896–3904. doi: 10.1021/bi00771a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litwack G., Cake M. H., Filler R., Taylor K. Physical measurements of the liver glucocorticoid receptor. Biochem J. 1978 Feb 1;169(2):445–448. doi: 10.1042/bj1690445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen C. J., Sando J. J., Pratt W. B. Evidence that dephosphorylation inactivates glucocorticoid receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1398–1402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker D. F., Begent R. H., Hogg N. M. Characterization of immune complexes in serum by adsorption on staphylococcal protein A: model studies and application to sera of rats bearing a gross virus-induced lymphoma. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):1644–1651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrange O., Carlstedt-Duke J., Gustafsson J. A. Purification of the glucocorticoid receptor from rat liver cytosol. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9284–9290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrange O., Gustafsson J. A. Separation of the hormone- and DNA-binding sites of the hepatic glucocorticoid receptor by means of proteolysis. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 10;253(3):856–865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R., Gehring U., Stampfer M. R., Sibley C. H. Genetic approaches to steroid hormone action. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1976;32:3–32. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571132-6.50008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]