Abstract
Recombinant plasmids containing either the entire polyoma viral genome or one or the other of the two HindIII fragments of polyoma virus DNA were constructed and cloned in Escherichia coli X1776, and their DNAs were individually tested for the capacity to transform an established line of rat cells. The recombinant plasmids containing the entire polyoma genome and those containing the HindIII-1 fragment of polyoma DNA (45-1.4 map units) efficiently transform rat cells, whereas the plasmids containing the HindIII-2 fragment (1.4-45.0 map units) do not. The properties of many independent transformed cell lines established by infection with the cloned HindIII-1 fragment were determined. In contrast to the parent cell line, rat cells transformed with the cloned HindIII-1 fragment grow to high saturation densities, form colonies with high efficiency in dilute agar suspension, produce high levels of plasminogen activator, and display a disorganized arrangement of actin cables. By all criteria examined, these cells transformed by fragments are indistinguishable from cells transformed by whole polyoma viral DNA. Cellular DNA prepared from many HindIII-1 fragment-transformed cell lines was analyzed for the presence and arrangement of polyoma viral sequences by Southern blot-hybridization. In all cases examined, only those viral sequences contained within the HindIII-1 fragment of polyoma DNA were detected. These data establish a strong correlation between polyoma DNA sequences mapping within a restricted portion of the early region and the induction and maintenance of the transformed phenotype.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bacheler L. T. Virus-secific transcription in 3T3 cells transformed by the ts-a mutant of polyoma virus. J Virol. 1977 Apr;22(1):54–64. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.1.54-64.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beard P., Acheson N. H., Maxwell I. H. Strand-specific transcription of polyoma virus DNA-early in productive infection and in transformed cells. J Virol. 1975 Jan;17(1):20–26. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.1.20-26.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin T. L. Host range mutants of polyoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):394–399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botchan M., Topp W., Sambrook J. The arrangement of simian virus 40 sequences in the DNA of transformed cells. Cell. 1976 Oct;9(2):269–287. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90118-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouck N., Beales N., Shenk T., Berg P., di Mayorca G. New region of the simian virus 40 genome required for efficient viral transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2473–2477. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Mayorca G., Callender J., Marin G., Giordano R. Temperature-sensitive mutants of polyoma virus. Virology. 1969 May;38(1):126–133. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90134-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckhart W. Complementation and transformation by temperature-sensitive mutants of polyoma virus. Virology. 1969 May;38(1):120–125. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90133-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIED M. ISOLATION OF TEMPERATURE-SENSITIVE MUTANTS OF POLYOMA VIRUS. Virology. 1965 Apr;25:669–671. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90098-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman V. H., Shin S. I. Cellular tumorigenicity in nude mice: correlation with cell growth in semi-solid medium. Cell. 1974 Dec;3(4):355–359. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90050-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman A. E., Gilden R. V., Vernon M. L., Wolford R. G., Hugunin P. E., Huebner R. J. 5-Bromo-2'-deoxyuridine potentiation of transformation of rat-embryo cells induced in vitro by 3-methylcholanthrene: induction of rat leukemia virus gs antigen in transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2415–2419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedmann T., Esty A., LaPorte P., Deininger P. The nucleotide sequence and genome organization of the polyoma early region: extensive nucleotide and amino acid homology with SV40. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):715–724. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grady L. J., North A. B., Campbell W. P. Polyoma genome transcription in transformed mouse cells growing in culture and as tumors in syngeneic mice. Int J Cancer. 1977 Feb 15;19(2):236–239. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910190213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson M. A., Hunter T., Eckhart W. Characterization of T antigens in polyoma-infected and transformed cells. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):65–77. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90083-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel M. A., Chan H. W., Hourihan S. L., Rowe W. P., Martin M. A. Biological activity of polyoma viral DNA in mice and hamsters. J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):990–996. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.990-996.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel M. A., Chowdhury K., Ramseur J., Chandrasekaran K., Vanderryn D. F., Martin M. A. Tumorigenicity of polyoma virus in hamsters. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):591–596. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel M. A., Simmons D. T., Hourihan S. L., Rowe W. P., Martin M. A. Interrupting the early region of polyoma virus DNA enhances tumorigenicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3713–3716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Spurr N., Dulbecco R. Characterization of polyoma virus T antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1259–1263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamen R., Favaloro J., Parker J., Treisman R., Lania L., Fried M., Mellor A. Comparison of polyoma virus transcription in productively infected mouse cells and transformed rodent cell lines. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):63–75. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamen R., Lindstrom D. M., Shure H., Old R. W. Virus-specific RNA in cells productively infected or transformed by polyoma virus. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):187–198. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACPHERSON I., MONTAGNIER L. AGAR SUSPENSION CULTURE FOR THE SELECTIVE ASSAY OF CELLS TRANSFORMED BY POLYOMA VIRUS. Virology. 1964 Jun;23:291–294. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90301-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonell M. W., Simon M. N., Studier F. W. Analysis of restriction fragments of T7 DNA and determination of molecular weights by electrophoresis in neutral and alkaline gels. J Mol Biol. 1977 Feb 15;110(1):119–146. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80102-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. K., Fried M. Construction of the genetic map of the polyoma genome. J Virol. 1976 Jun;18(3):824–832. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.3.824-832.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack R., Osborn M., Weber K. Patterns of organization of actin and myosin in normal and transformed cultured cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):994–998. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
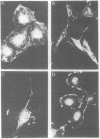
- Pollack R., Risser R., Conlon S., Rifkin D. Plasminogen activator production accompanies loss of anchorage regulation in transformation of primary rat embryo cells by simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4792–4796. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifkin D. B., Pollack R. Production of plasminogen activator by established cell lines of mouse origin. J Cell Biol. 1977 Apr;73(1):47–55. doi: 10.1083/jcb.73.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risser R., Rifkin D., Pollack R. The stable classes of transformed cells induced by SV40 infection of established 3T3 cells and primary rat embryonic cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):317–324. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffhausen B. S., Silver J. E., Benjamin T. L. Tumor antigen(s) in cell productively infected by wild-type polyoma virus and mutant NG-18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):79–83. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seif R., Cuzin F. Temperature-sensitive growth regulation in one type of transformed rat cells induced by the tsa mutant of polyoma virus. J Virol. 1977 Dec;24(3):721–728. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.3.721-728.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleigh M. J., Topp W. C., Hanich R., Sambrook J. F. Mutants of SV40 with an altered small t protein are reduced in their ability to transform cells. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90303-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smart J. E., Ito Y. Three species of polyoma virus tumor antigens share common peptides probably near the amino termini of the proteins. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1427–1437. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90066-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeda E., Arrand J. R., Smolar N., Griffin B. E. Sequence from early region of polyoma virus DNA containing viral replication origin and encoding small, middle and (part of) large T antigens. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):357–370. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90162-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staneloni R. J., Fluck M. M., Benjamin T. L. Host range selection of transformation-defective hr-t mutants of polyoma virus. Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):598–609. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90485-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R. Biochemical transfer of single-copy eucaryotic genes using total cellular DNA as donor. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):725–731. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90254-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]