Abstract
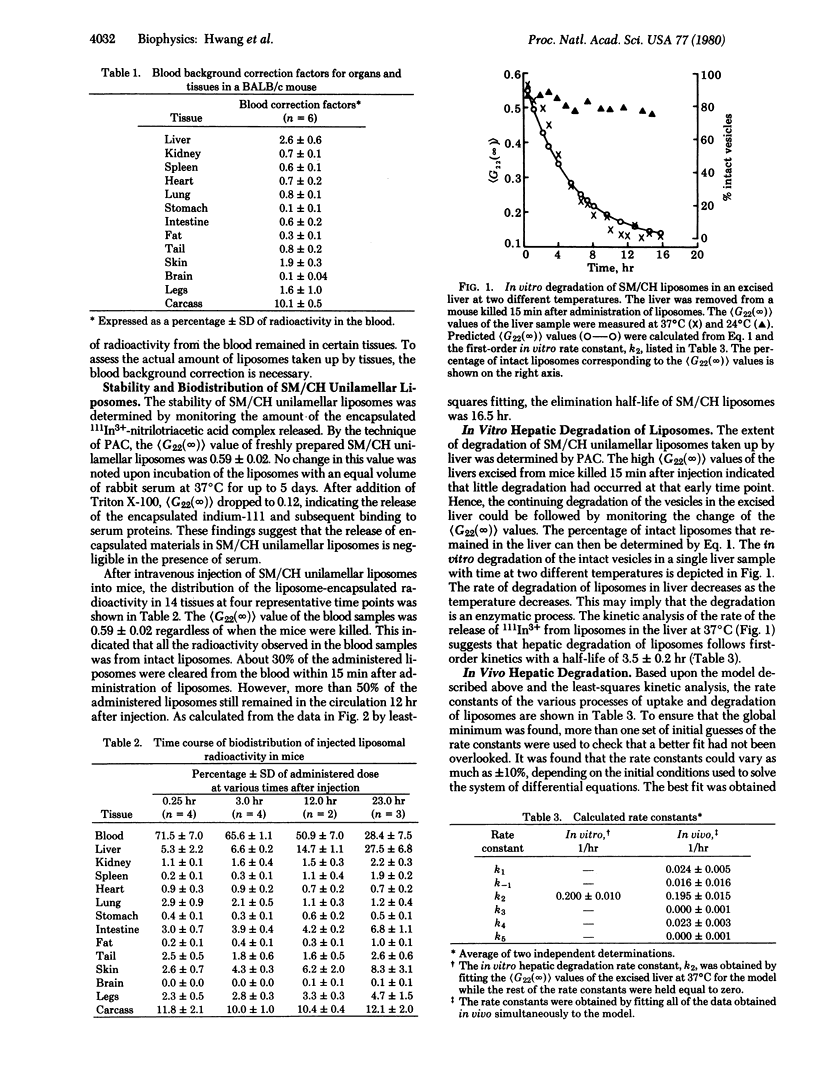
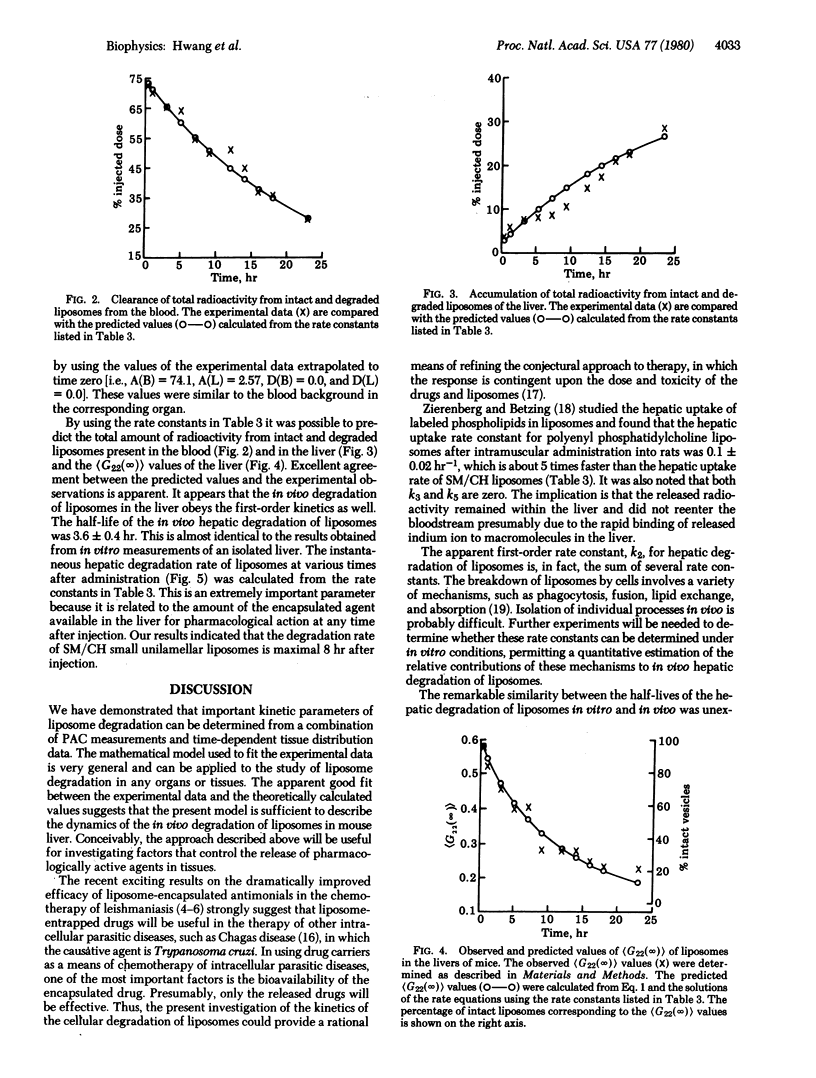
The kinetics of hepatic uptake and degradation of sphingomyelin/cholesterol (2:1, M/M) small unilamellar liposomes were investigated in a BALB/c mouse. The tissue distribution of liposomes was determined by scintillation spectrometry. The percentage of intact liposomes in tissues was estimated by the technique of gamma-ray perturbed angular correlation. A kinetic model was developed to analyze the above data. A remarkable agreement was noted between the experimental data and the corresponding theoretical values. Our results indicate that the sphingomyelin/cholesterol unilamellar liposomes had an unusually long half-life of 16.5 hr in the circulation after intravenous administration to mice. The hepatic degradation of the liposomes in vitro at 37 degrees C followed first-order kinetics, with a half-life of 3.5 +/- 0.2 (SEM) hr. Furthermore, the rate of the in vivo degradation of liposomes in the liver was found to be quite similar to that in vitro, with a half-life of 3.6 +/- 0.4 hr. The rate of release of the liposome-encapsulated agent, indium-111, in the liver was not constant, and reached a maximum at about 8 hr after the administration of liposomes. The approach developed in the present study is general and can be applied to the investigation of factors that may control the release of pharmacologically active agents in any tissue.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alving C. R., Steck E. A., Chapman W. L., Jr, Waits V. B., Hendricks L. D., Swartz G. M., Jr, Hanson W. L. Therapy of leishmaniasis: superior efficacies of liposome-encapsulated drugs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2959–2963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barenholz Y., Gibbes D., Litman B. J., Goll J., Thompson T. E., Carlson R. D. A simple method for the preparation of homogeneous phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry. 1977 Jun 14;16(12):2806–2810. doi: 10.1021/bi00631a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black C. D., Watson G. J., Ward R. J. The use of Pentostam liposomes in the chemotherapy of experimental leishmaniasis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1977;71(6):550–552. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(77)90155-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE DUVE C., BEAUFAY H. Tissue fractionation studies. 10. Influence of ischaemia on the state of some bound enzymes in rat liver. Biochem J. 1959 Dec;73:610–616. doi: 10.1042/bj0730610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmukh D. S., Bear W. D., Wisniewski H. M., Brockerhoff H. Long-living liposomes as potential drug carriers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 May 15;82(1):328–334. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90613-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregoriadis G., Buckland R. A. Enzyme-containing liposomes alleviate a model for storage disease. Nature. 1973 Jul 20;244(5412):170–172. doi: 10.1038/244170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregoriadis G. The carrier potential of liposomes in biology and medicine (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1976 Sep 23;295(13):704–710. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197609232951305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregoriadis G. The carrier potential of liposomes in biology and medicine (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1976 Sep 30;295(14):765–770. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197609302951406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries G. K., McConnell H. M. Immune lysis of liposomes and erythrocyte ghosts loaded with spin label. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1691–1694. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang K. J. Modes of interaction of (In3+)-8-hydroxyquinoline with membrane bilayer. J Nucl Med. 1978 Oct;19(10):1162–1170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juliano R. L., Stamp D. The effect of particle size and charge on the clearance rates of liposomes and liposome encapsulated drugs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Apr 7;63(3):651–658. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80433-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KREBS H. A. Body size and tissue respiration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1950 Jan;4(1-3):249–269. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(50)90032-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimelberg H. K. Differential distribution of liposome-entrapped [3H]methotrexate and labelled lipids after intravenous injection in a primate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 2;448(4):531–550. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90108-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsky S. C. Antibody-complement interaction with lipid model membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 14;265(1):1–23. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(72)90017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauk M. R., Gamble R. C. Stability of lipid vesicles in tissues of the mouse: a gamma-ray perturbed angular correlation study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):765–769. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougall I. R., Dunnick J. K., McNamee M. G., Kriss J. P. Distribution and fate of synthetic lipid vesicles in the mouse: a combined radionuclide and spin label study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3487–3491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- New R. R., Chance M. L., Thomas S. C., Peters W. Antileishmanial activity of antimonials entrapped in liposomes. Nature. 1978 Mar 2;272(5648):55–56. doi: 10.1038/272055a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano R. E., Weinstein J. N. Interactions of liposomes with mammalian cells. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1978;7:435–468. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.07.060178.002251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyrrell D. A., Heath T. D., Colley C. M., Ryman B. E. New aspects of liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 14;457(3-4):259–302. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(76)90002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch M. J., Thakur M. L., Coleman R. E., Patel M., Siegel B. A., Ter-Pogossian M. Gallium-68 labeled red cells and platelets: new agents for positron tomography. J Nucl Med. 1977 Jun;18(6):558–562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zierenberg O., Betzing H. Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of i.m. injected polyenylphosphatidylcholine liposomes. Arzneimittelforschung. 1979;29(3):494–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



