Abstract
Background
Hospital admissions due to asthma are a reliable source of information on the morbidity of the disease which, after the increase observed in the last quarter of the last century, shows a declining trend in the last few years. The aim of this study was to look at hospital admission trends due to asthma in our community and analyze some of its associated factors.
Methods
Retrospective analysis of all hospital admissions involving adults aged 15 years and older with asthma as the primary or secondary diagnosis (if the first diagnosis was respiratory failure or respiratory infection) in Public Health Service hospitals in the Galician region of Spain between the years 1995-2009 (total 24,766 admissions).
Results
The majority of patients admitted were female (71%), over 60 years of age (64%), and admission occurred predominantly in the winter months. The hospitalization rate due to asthma tripled over the period studied, this being mainly accounted for by women aged over 60 years. Mean hospital stay was 9.2 days, longer in older patients or those admitted over the weekend.
Conclusions
A significant increase in hospital admissions due to asthma over the last few years has been observed in our community, mainly involving older women. The mean stay seems long, increasing with patients' age and admission over the weekend.
Keywords: Asthma, hospital admission, hospitalization, trends
Introduction
Asthma affects 300 million people in the world, with a prevalence greater than 10% in developed countries and 180,000 deaths per year attributable to the disease [1]. Hospital admissions due to asthma are one of the best sources of information on trends and prognosis in the morbidity of the disease [2,3], but there is no data available in many countries [2].
During the last quarter of the last century an increasing trend in asthma-related hospital admissions has been observed, although in the last few years this trend seems to be changing [4,5]; however, there are significant differences between countries as well as between sexes and age groups [2,5]. Hospital admissions due to asthma are affected by various interacting factors. Firstly, there can be changes in the diagnosis and coding systems, although when this is the cause, it is usually obvious as a drastic change is seen in trends. Secondly, changes in health care can have an influence: these can be in terms of access to the health system or treatment availability, or the education of the population. Lastly, changes in hospital admissions due to asthma may be caused by changes in the prevalence or severity of the disease [2,6,7].
The purpose of this study was to describe, in the adult population of our community, hospital admission trends due to asthma. Another aim was to characterize the epidemiology of this condition, analyzing differences due to age and sex, as well as the duration of the hospital stay, and identify some of the determining factors of these.
Material and methods
We retrospectively analyzed all the admissions due to asthma occurring in Public Health Service hospitals in our region (Galician Health Service, Spain), between the years 1995 and 2009. From the information collected from the Clinical Records Department, all patients with asthma as the primary or secondary diagnosis (if the first diagnosis was respiratory failure or respiratory infection) were included. The age and sex, date of admission and length of hospital stay of each patient was analyzed. To evaluate the effect of admissions over the weekend, the days of the week were grouped into two categories, one with admissions occurring between Monday and Thursday, the other with admissions from Friday to Sunday.
In our Autonomous Community, according to the 2002 population census, there were 2,420,303 inhabitants (47.6% males) aged 15 years or over [8]. Around 98% of these had public health system cover, leaving a small percentage excluded, with private health insurance.
The Review Board on Human Studies at our institution approved the protocol.
Statistical analysis
The data were tested for normal distribution using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. Student's t test was used for the comparison of the two category continuous variables when these had a normal distribution, and the Mann Whitney U test when they had a non-parametric distribution. For the comparison of continuous variables of more than two categories we used ANOVA for the normal distribution variables and the Kruskal Wallis test when the distribution was non-Gaussian. Comparison of the categorical variables was performed using the chi-squared test. The adjusted odds ratios of the increase in mean hospital stay were calculated as a function of sex, age, and admission during the week or weekend. All statistical analyses were performed using the SPSS 15 statistics program.
Results
During the 15-year period under analysis, there were 24,766 admissions (70.9% female) to our hospitals with asthma as the primary or secondary diagnosis (Table 1). About two thirds of the patients were over 60 years old (Table 2). The mean age of the females was 64 years, significantly higher than the 54 years for males (data not shown). The hospitalization rates per 100,000 inhabitants increased progressively throughout the period studied, from 38.2/100,000 in 1995 to 81.8/100,000 in 2009 (Table 1). The most significant increase was seen in women over 60 years, although an increasing trend was observed in all the age and sex groups (Figure 1). There was a clear predominance in admissions during the winter months, with an admission maximum in January, followed by December. Admissions were least during the months of July and August (Figure 2).
Table 1.
Number of asthma-related hospital admissions in the galician region of spain 1995-2009, by year
| Total admissions | Total rate | Male admissions (%) | Male rate | Female admissions (%) | Female rate | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1995 | 925 | 38.22 | 317 (34.3) | 27.47 | 608 (65.7) | 48.01 | 0.0001 |
| 1996 | 1103 | 45.57 | 392 (35.5) | 33.97 | 711 (64.5) | 56.14 | 0.0001 |
| 1997 | 1269 | 52.43 | 413 (32.5) | 35.79 | 856 (67.5) | 67.59 | 0.0001 |
| 1998 | 1241 | 51.27 | 393 (31.7) | 34.06 | 848 (68.3) | 66.96 | 0.0001 |
| 1999 | 1703 | 70.36 | 528 (31.0) | 45.76 | 1175 (69) | 92.77 | 0.0001 |
| 2000 | 1803 | 74.49 | 573 (31.8) | 49.66 | 1230 (68.2) | 97.12 | 0.0001 |
| 2001 | 1352 | 55.86 | 440 (32.5) | 38.14 | 912 (67.5) | 72.01 | 0.0001 |
| 2002 | 1646 | 68.01 | 457 (27.8) | 39.61 | 1189 (72.2) | 93.88 | 0.0001 |
| 2003 | 1850 | 76.44 | 541(29.2) | 46.89 | 1309 (70.8) | 103.35 | 0.0001 |
| 2004 | 1646 | 68.01 | 437 (26.5) | 37.88 | 1209 (73.5) | 95.46 | 0.0001 |
| 2005 | 1801 | 74.41 | 452 (25.1) | 39.18 | 1349 (74.9) | 106.51 | 0.0001 |
| 2006 | 1720 | 71.07 | 466 (27.1) | 40.39 | 1254 (72.9) | 99.01 | 0.0001 |
| 2007 | 1803 | 74.49 | 458 (25.4) | 39.70 | 1345 (74.6) | 106.20 | 0.0001 |
| 2008 | 1830 | 75.61 | 444 (24.3) | 38.48 | 1386 (75.7) | 109.43 | 0.0001 |
| 2009 | 1979 | 81.77 | 522 (26.4) | 45.24 | 1457 (73.6) | 115.04 | 0.0001 |
| Total | 24766 | 1023.26 | 7212 (29.1) | 625.07 | 17554 (70.9) | 1386.01 | 0.0001 |
p: comparison male vs female.
Rate: rate per 100,000 population.
Table 2.
Number of asthma-related hospital admissions in the galician region of spain 1995-2009, by age group
| Admissions age 15-39 years n (%) | Rate | Admissions 40-59 years n (%) | Rate | Admissions ≥ 60 years n (%) | Rate | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1995 | 207 (22.4) | 20.84 | 214 (23.1) | 30.08 | 504 (54.5) | 70.43 | 0.0001 |
| 1996 | 263 (23.8) | 26.48 | 257 (23.3) | 36.12 | 583 (52.9) | 81.47 | 0.0001 |
| 1997 | 327 (25.8) | 32.92 | 262 (20.6) | 36.82 | 680 (53.6) | 95.03 | 0.0001 |
| 1998 | 300 (24.2) | 30.21 | 237 (19.1) | 33.31 | 704 (56.7) | 98.38 | 0.0001 |
| 1999 | 341 (20.0) | 34.33 | 369 (21.7) | 51.86 | 993 (58.3) | 138.77 | 0.0001 |
| 2000 | 361 (20.0) | 36.35 | 351 (19.5) | 49.33 | 1091 (60.5) | 152.47 | 0.0001 |
| 2001 | 289 (21.4) | 29.10 | 246 (18.2) | 34.57 | 817 (60.4) | 114.17 | 0.0001 |
| 2002 | 274 (16.6) | 27.59 | 297 (18.0) | 41.74 | 1075 (65.3) | 150.23 | 0.0001 |
| 2003 | 380 (20.5) | 38.26 | 317 (17.1) | 44.55 | 1153 (62.3) | 161.13 | 0.0001 |
| 2004 | 263 (16.0) | 26.48 | 288 (17.5) | 40.47 | 1095 (66.5) | 153.02 | 0.0001 |
| 2005 | 248 (13.8) | 24.97 | 301 (16.7) | 42.30 | 1252 (69.5) | 174.97 | 0.0001 |
| 2006 | 235 (13.7) | 23.66 | 272 (15.8) | 38.23 | 1213 (70.5) | 169.51 | 0.0001 |
| 2007 | 236 (13.1) | 23.76 | 251 (13.9) | 35.27 | 1316 (73.0) | 183.91 | 0.0001 |
| 2008 | 244 (13.3) | 24.57 | 263 (14.4) | 36.96 | 1323 (72.3) | 184.89 | 0.0001 |
| 2009 | 321 (16.2) | 32.32 | 309 (15.6) | 43.43 | 1349 (68.2) | 188.52 | 0.0001 |
| Total | 4289 (18.1) | 431.85 | 4234 (17.9) | 595.04 | 15148 (64.0) | 2116.91 | 0.0001 |
p: comparison between age groups.
n (%): number of admissions (percentage for each year).
Rate: rate per 100,000 population.
Figure 1.
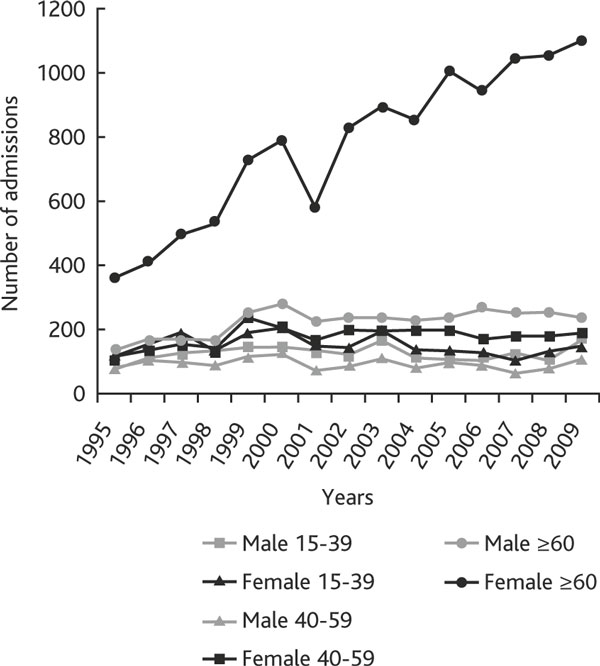
Trends in asthma hospital admissions from 1995 to 2009, by age and sex group.
Figure 2.
Asthma hospital admissions by month. Mean: monthly mean of admission.
The mean hospital stay was 9.2 days, with a median of 7 days (Table 3). Increased age and weekends were associated with longer stays (Table 3).
Table 3.
Table 3a. Asthma-related hosiptal stay in the galician region of spain, univariate analysis.
| Mean Hospital Stay* (SD) | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Male | 8.6 (8.8) | 0.0001 |
| Female | 9.4 (8.7) | ||
| Age (years) | 15-39 | 5.7 (5.5) | 0.0001 |
| 40-59 | 8.4 (10.5) | ||
| ≥ 60 | 10.4 (8.6) | ||
| Weekday | Monday-Thursday | 9.1 (8.9) | NS |
| Friday-Sunday | 9.3 (8.4) | ||
| Total | 9.2 (8.7) | ||
| Table 3b. Adjusted odds ratio of hospital stay over the mean, by sex, age group and weekday of admission | |||
| Odds Ratio | CI 95% | ||
| Sex | Male | 1 | |
| Female | 1.05 | 0.99-1.12 | |
| Age | 15-39 | 1 | |
| 40-59 | 2.93 | 2.62-3.29 | |
| ≥ 60 | 5.59 | 5.07-6.17 | |
| Weekday | Monday-Thursday | 1 | |
| Friday-Sunday | 1.33 | 1.25-1.40 | |
Comparison by sex, age group and weekday of admission
*Hospital stay in days.
Definition of abbreviations: SD, standard deviation; NS, not significant.
Definition of abbreviation: Cl, Confidence interval.
Discussion
Hospital admissions due to asthma can be a reliable indicator of how the morbidity of this disease is evolving, although many countries still do not have such data available [2]. In our region of Spain, there has been a significant increase in hospital admissions due to asthma over the last 15 years, mainly accounted for by women over 60 years of age. This is the opposite of what is seen in most developed countries, where there is a decreasing trend [3]. Another exception among developed countries is Holland, where hospital admissions due to acute exacerbation of asthma continue to rise, despite the high sales of inhaled corticosteroids [2].
The admission rates (from 18.1/100,000 inhabitants in the population aged 15-39 years, to 64.0/100,000 in the population aged over 60 years) are particularly high compared with other populations in the western world [5,9,10].
The reasons for the increase in hospitalizations could be related to several factors. One could be an increase in the prevalence or severity of the disease, which seems very likely, based on data available for the Spanish population, both in children and young adults, which show an increase over the last few years [11,12]. Another possible cause could be the increase in exacerbations of asthma due to poor control of the disease. In this sense, the level of control of asthma in the Spanish population still appears to be insufficient, as only 36.1% of the Spanish asthmatic population are said to be adequately controlled, although we do not know the situation during the initial period of our study [13]. A third factor could be changes in medical practice in making the decision to admit to hospital. We have no data available on this aspect, but the widespread use of asthma management guidelines should, on the contrary, produce a decrease in asthma-related admissions [14]. Lastly, the increase in hospitalizations could be due to there being a wider classification of patients with asthma due to an increase in knowledge of the disease, as has been pointed out in various studies [12].
The admission peaks in the winter period are in agreement with other observations in the literature, associated mainly with viral infections, which are the most common cause of acute exacerbation of asthma [3,15,16].
The mean hospital stay in our population is not a very positive finding, being much higher than that observed by other authors [5,9,17,18]. Older age and weekend admissions are independent predictors of longer hospital stays. Being female is associated with longer hospital stays (than for males), but this significance is lost in the multivariate analysis, probably due to the higher mean age of the women admitted.
The increased morbidity (testified both by the number of admissions and the longer hospital stays) of asthma in women is in line with what is seen in other countries. Several factors may lead to a higher rate of female admissions: a higher prevalence of asthma in women than in males [19,20]; a greater expression of symptoms of the disease in females [21]; the fact that women are normally more exposed than men to cleaning products and other irritants [22,23]; higher female life expectancy, making their admission due to asthma more likely [18], despite adjustment for age and severity [24].
The increase in hospital stay with age has been described in other populations [9,25]. Increased morbidity [15,26] or the claim that these patients have a poorer response to treatment are also mentioned as causes [17].
The negative influence of weekend admissions has been associated with longer stays in other illnesses [27,28], and even with a higher mortality [29,30]. Possible causes could be the fact that fewer people work in hospitals on weekends than on weekdays, and those who do work on weekends often have less seniority and experience than those who work on weekdays [29]. The patients may also have different characteristics that might complicate their progression, such as a higher frequency of drugs taken abusively [30].
A limitation of this study is that the diagnosis and severity of asthma were not checked individually. In any case, the data used in this study are based on the diagnosis reached by the treating specialist. This should not affect the admission trends or hospital stays, since the same methodology was used for all subjects throughout the study period.
In conclusion, the main findings of our study are: 1) the progressive increase in the number of hospital admissions due to asthma throughout the period studied, mainly accounted for by women over 60 years; 2) that hospital stays in our population - particularly for older patients or those admitted at the weekend - are longer than in other populations.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors has any conflict of interest to declare in relation to the subject matter of this manuscript.
References
- Braman SS. The global burden of asthma. Chest. 2006;130(1 Suppl):4S–12S. doi: 10.1378/chest.130.1_suppl.4S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R, Anderson HR, Strachan DP, Maier W, Watson L. International trends in admissions and drug sales for asthma. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2006;10:138–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears MR. Epidemiology of asthma exacerbations. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008;122:662–668. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2008.08.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson HR, Gupta R, Strachan DP, Limb ES. 50 years of asthma: UK trends from 1955 to 2004. Thorax. 2007;62:85–90. doi: 10.1136/thx.2006.066407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singleton RJ, Holman RC, Cobb N, Curns AT, Paisano EL. Asthma hospitalizations among American Indian and Alaska Native people and for the general US population. Chest. 2006;130:1554–1562. doi: 10.1378/chest.130.5.1554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson DH, Tucker G, Frith P, Appleton S, Ruffin RE, Adams RJ. Trends in hospital admissions and mortality from asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Australia, 1993-2003. Med J Aust. 2007;186:408–411. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.2007.tb00974.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison DS, McLoone P. Changing patterns of hospital admission for asthma, 1981-97. Thorax. 2001;56:687–690. doi: 10.1136/thorax.56.9.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- http://www.ine.es
- Pascal L, Fuhrman C, Durif L, Nicolau J, Charpin D, Dujols P, Delmas MC. Trends in hospital admissions for asthma in France, 1998-2002. Rev Mal Respir. 2007;24:581–590. doi: 10.1016/S0761-8425(07)91125-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haahtela T, Tuomisto LE, Pietinalho A, Klaukka T, Erhola M, Kaila M, Nieminen MM, Kontula E, Laitinen LA. A 10 year asthma programme in Finland: major change for the better. Thorax. 2006;61:663–670. doi: 10.1136/thx.2005.055699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Marcos L, Quirós AB, Hernández GG, Guillén-Grima F, Díaz CG, Ureña IC, Pena AA, Monge RB, Suárez-Varela MM, Varela AL, Cabanillas PG, Garrido JB. Stabilization of asthma prevalence among adolescents and increase among schoolchildren (ISAAC phases I and III) in Spain. Allergy. 2004;59:1301–1307. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2004.00562.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urrutia I, Aguirre U, Sunyer J, Plana E, Muniozguren N, Martínez-Moratalla J, Payo F, Maldonado JA, Anto JM. Estudio de Salud Respiratoria de la Comunidad Europea. Changes in the prevalence of asthma in the Spanish cohort of the European Community Respiratory Health Survey (ECRHS-II) Arch Bronconeumol. 2007;43:425–430. doi: 10.1016/s1579-2129(07)60098-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González Barcala FJ, de la Fuente-Cid R, Alvarez-Gil R, Tafalla M, Nuevo J, Caamaño-Isorna F. Factors associated with asthma control in primary care patients: the CHAS study. Arch Bronconeumol. 2010;46:358–363. doi: 10.1016/j.arbres.2010.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe BH, Chahal AM, Spooner CH, Blitz S, Senthilselvan A, Wilson D, Holroyd BR, Bullard M. Increasing the use of anti-inflammatory agents for acute asthma in the emergency department: experience with an asthma care map. Can Respir J. 2008;15:20–26. doi: 10.1155/2008/431390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson L, Turk F, James P, Holgate ST. Factors associated with mortality after an asthma admission: a national United Kingdom database analysis. Respir Med. 2007;101:1659–1664. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2007.03.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes A, Johnston SL. Etiology of asthma exacerbations. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008;122:685–688. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2008.08.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji A, Clark S, Afilalo M, Blanda MP, Cydulka RK, Camargo CA Jr. Prospective multicenter study of acute asthma in younger versus older adults presenting to the emergency department. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2006;54:48–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2005.00563.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y, Stewart P, Johansen H, McRae L, Taylor G. Sex difference in hospitalization due to asthma in relation to age. J Clin Epidemiol. 2003;56:180–187. doi: 10.1016/S0895-4356(02)00593-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butland BK, Strachan DP, Rudnicka AR. C-reactive protein, obesity, atopy and asthma symptoms in middle-aged adults. Eur Respir J. 2008;32:77–84. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00077207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunyer J, Antó JM, Kogevinas M, Barceló MA, Soriano JB, Tobías A, Muniozguren N, Martínez-Moratalla J, Payo F, Maldonado JA. Risk factors for asthma in young adults. Spanish Group of the European Community Respiratory Health Survey. Eur Respir J. 1997;10:2490–2494. doi: 10.1183/09031936.97.10112490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz M, Clark S, Camargo CA Jr. Sex differences in the presentation and course of asthma hospitalizations. Chest. 2006;129:50–55. doi: 10.1378/chest.129.1.50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendonça EM, Algranti E, de Freitas JB, Rosa EA, dos Santos Freire JA, de Paula Santos Ud U, Pinto J, Bussacos MA. Occupational asthma in the city of São Paulo, 1995-2000, with special reference to gender analysis. Am J Ind Med. 2003;43:611–617. doi: 10.1002/ajim.10210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimich-Ward H, Camp PG, Kennedy SM. Gender differences in respiratory symptoms-does occupation matter? Environ Res. 2006;101:175–183. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2005.02.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baibergenova A, Thabane L, Akhtar-Danesh N, Levine M, Gafni A, Leeb K. Sex differences in hospital admissions from emergency departments in asthmatic adults: a population-based study. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2006;96:666–672. doi: 10.1016/S1081-1206(10)61063-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skobeloff EM, Spivey WH, St Clair SS, Schoffstall JM. The influence of age and sex on asthma admissions. JAMA. 1992;268:3437–3440. doi: 10.1001/jama.1992.03490240045034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas SD, Whitman S. Asthma hospitalizations and mortality in Chicago: an epidemiologic overview. Chest. 1999;116(4 Suppl 1):135S–141S. doi: 10.1378/chest.116.suppl_2.135s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ananthakrishnan AN, McGinley EL, Saeian K. Outcomes of weekend admissions for upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage: a nationwide analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;7:296–302e1. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2008.08.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow KM, Szeto CC. Impact of enforcing the Labour Ordinance, with 1-in-7-day off for hospital doctors, on weekend hospital discharge rate. J Public Health (Oxf) 2005;27:189–191. doi: 10.1093/pubmed/fdi022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saposnik G, Baibergenova A, Bayer N, Hachinski V. Weekends: a dangerous time for having a stroke? Stroke. 2007;38:1211–1215. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000259622.78616.ea. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell CM, Redelmeier DA. Mortality among patients admitted to hospitals on weekends as compared with weekdays. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:663–668. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsa003376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


