Abstract
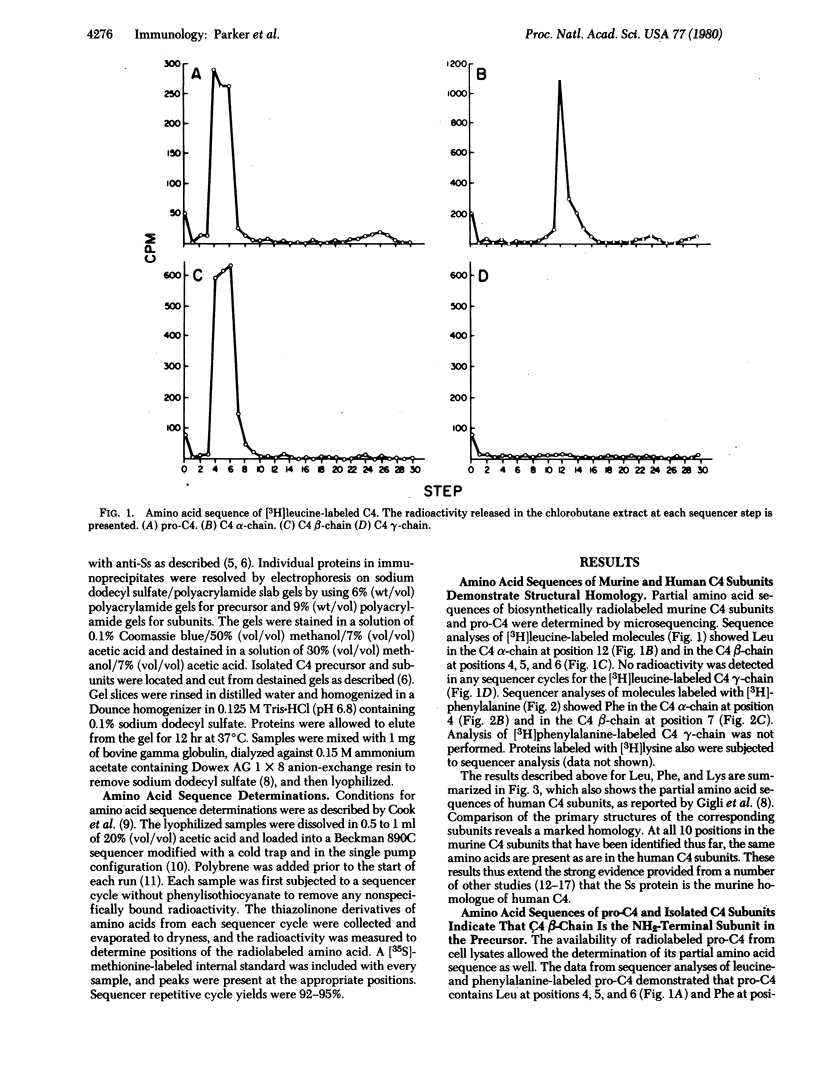
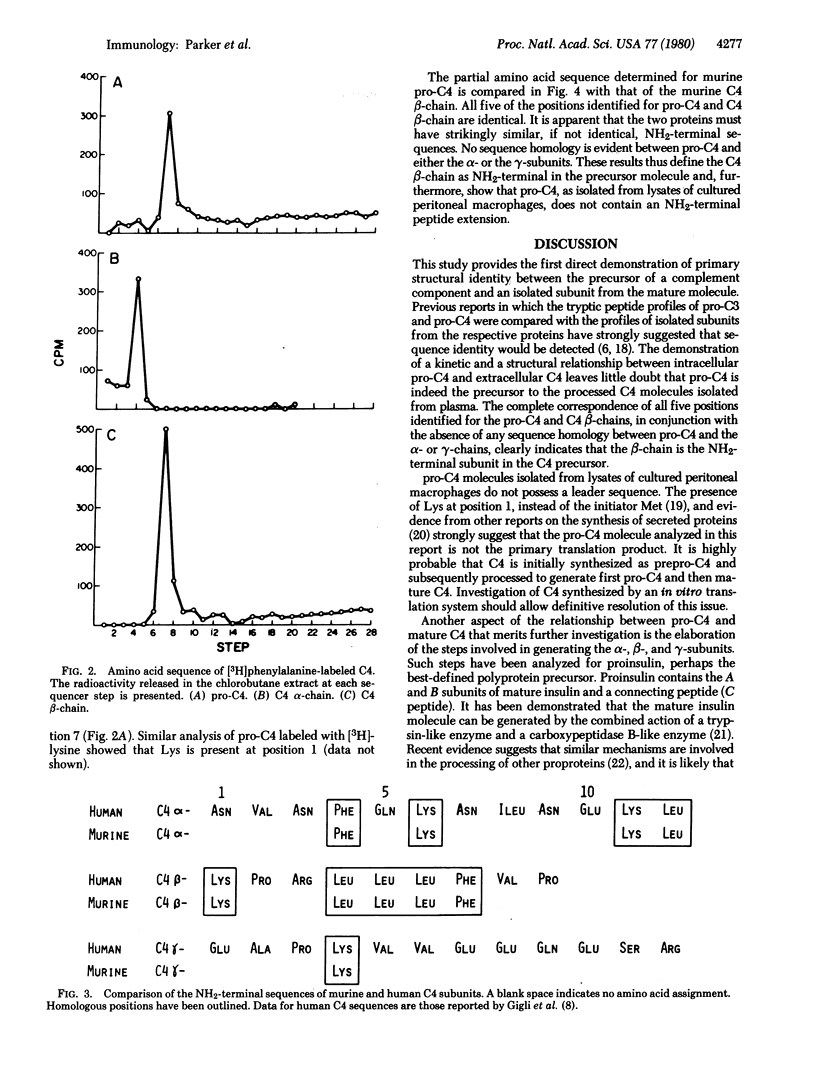
Radiolabeled murine C4 and C4 precursor (pro-C4) from cultured peritoneal macrophages were purified by immunoprecipitation and preparative gel electrophoresis. The partial NH2-terminal amino acid sequences of the isolated subunits demonstrated that murine C4 alpha, beta-, and gamma-chains all show sequence homology with the corresponding subunits of human C4; of the 10 residues identified in murine C4, all are identical to those in human C4. These data extend to the primary structural level the homology between the murine serum substance (Ss) protein and human C4. Comparisons of the amino acid sequences of murine pro-C4 and the constituent polypeptide chains of secreted C4 indicate that pro-C4 and the C4 beta-chain have an identical amino acid sequence. Both molecules have lysine at position 1, leucine at positions 4, 5, and 6, and phenylalanine at position 7. No sequence homology was found between pro-C4 and either the alpha- or gamma-subunits. These results define the beta-chain as the NH2-terminal subunit in the C4 precursor molecules.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson J. P., McGinnis K., Shreffler D. Development and characterization of a hemolytic assay for mouse C4. J Immunol Methods. 1980;33(4):351–368. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. C., Capra J. D. Studies on murine Ss protein: demonstration that S region encodes structural gene for fourth component of complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4641–4645. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. C., Capra J. D. Studies on the murine Ss protein: demonstration that the Ss protein is functionally the fourth component of complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. C., Passmore H. C., Capra J. D. Structural studies on the murine fourth component of complement (C4). IV. Demonstration that C4 and Slp are encoded by separate loci. J Immunol. 1980 Apr;124(4):1745–1749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook R. G., Vitetta E. S., Uhr J. W., Klein J., Wilde C. E., 3rd, Capra J. D. Structural studies on protein products of murine chromosome 17. III. Partial amino acid sequence of an H-2Kq molecule. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):1015–1019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curman B., Ostberg L., Sandberg L., Malmheden-Eriksson I., Stålenheim G., Rask L., Peterson P. A. H-2 linked Ss protein is C4 component of complement. Nature. 1975 Nov 20;258(5532):243–245. doi: 10.1038/258243a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B. D., Tai P. C. The mechanism of protein secretion across membranes. Nature. 1980 Jan 31;283(5746):433–438. doi: 10.1038/283433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira A., Nussenzweig V., Gigli I. Structural and functional differences between the H-2 controlled Ss and Slp proteins. J Exp Med. 1978 Nov 1;148(5):1186–1197. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.5.1186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigli I. A single chain precursor of C4 in human serum. Nature. 1978 Apr 27;272(5656):836–837. doi: 10.1038/272836a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigli I., von Zabern I., Porter R. R. The isolation and structure of C4, the fourth component of human complement. Biochem J. 1977 Sep 1;165(3):439–446. doi: 10.1042/bj1650439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habener J. F., Kronenberg H. M. Parathyroid hormone biosynthesis: structure and function of biosynthetic precursors. Fed Proc. 1978 Oct;37(12):2561–2566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R. E., Colten H. R. Cell-free synthesis of the fourth component of guinea pig complement (C4): identification of a precursor of serum C4 (pro-C4). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1707–1710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J., Grennan D., Martin A., Demant P. Identification of Ss protein as murine C4. Nature. 1975 Nov 20;258(5532):242–243. doi: 10.1038/258242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas-Lenard J. Protein biosynthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1971;40:409–448. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.40.070171.002205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meo T., Krasteff T., Shreffler D. C. Immunochemical characterization of murine H-2 controlled Ss (serum substance) protein through identification of its human homologue as the fourth component of complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4536–4540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker K. L., Roos M. H., Shreffler D. C. Structural characterization of the murine fourth component of complement and sex-limited protein and their precursors: evidence for two loci in the S region of the H-2 complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5853–5857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter R. R., Reid K. B. Activation of the complement system by antibody-antigen complexes: the classical pathway. Adv Protein Chem. 1979;33:1–71. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60458-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos M. H., Atkinson J. P., Shreffler D. C. Molecular characterization of the Ss and Slp (C4) proteins of the mouse H-2 complex: subunit composition, chain size polymorphism, and an intracellular (PRO-Ss) precursor. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):1106–1115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senger D. R., Hynes R. O. C3 component of complement secreted by established cell lines. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):375–384. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shreffler D. C. The S region of the mouse major histocompatibility complex (H-2): genetic variation and functional role in complement system. Transplant Rev. 1976;32:140–167. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1976.tb00232.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


